Visão geral de Pó de Metal de Qualidade
Os pós de metal são materiais sólidos finamente divididos que desempenham um papel crucial em várias aplicações industriais. Da fabricação aditiva (impressão 3D) à metalurgia do pó, esses pós são os blocos de construção para criar materiais avançados com propriedades específicas. Neste guia, mergulharemos no mundo dos pós de metal de qualidade, explorando sua composição, propriedades, usos e muito mais.
Abordaremos tudo, desde o básico até os detalhes mais avançados, ajudando você a entender por que a qualidade é importante em pós de metal e como escolher o tipo certo para suas necessidades específicas.
O que é Pó de Metal de Qualidade?
Pó de metal de qualidade é um termo que engloba vários pós à base de metal que foram refinados, processados e fabricados para atender a padrões específicos para aplicações industriais e comerciais. Esses pós são caracterizados por sua pureza, tamanho de partícula e uniformidade, que garantem um desempenho consistente em suas aplicações de uso final.
A Importância da Qualidade em Pó de Metal
Por que a qualidade é tão crucial quando se trata de pós de metal? Imagine tentar assar um bolo com farinha de baixa qualidade. O resultado seria inconsistente, na melhor das hipóteses, e intragável, na pior. Da mesma forma, o uso de pó de metal inferior em processos de fabricação pode levar a defeitos, desempenho reduzido e até falhas catastróficas em aplicações críticas.
Pós de metal de alta qualidade garantem que os produtos finais exibam a resistência, durabilidade e outras propriedades-chave desejadas. Eles também contribuem para processos de fabricação eficientes, proporcionando uniformidade e consistência, reduzindo a necessidade de retrabalho ou ajustes.
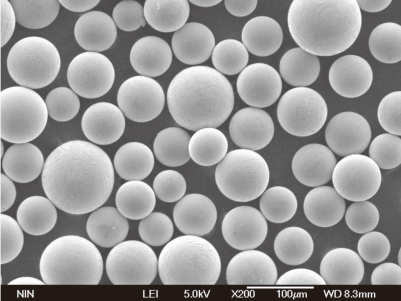
Tipos de Pós de Metal de Qualidade
Quando se trata de pós de metal de qualidade, não existe uma solução única para todos. Diferentes aplicações exigem diferentes tipos de pós de metal, cada um com sua composição, propriedades e vantagens exclusivas. Vamos explorar alguns dos pós de metal mais comumente usados na indústria.
| Pó metálico | Composição | Propriedades | Formulários |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pó de alumínio | Alumínio Puro (Al) | Leve, resistente à corrosão, excelente condutividade térmica | Aeroespacial, automotivo, pirotecnia |
| PÓ DE COBRE | Cobre Puro (Cu) | Alta condutividade elétrica, excelente condutividade térmica | Componentes elétricos, sistemas de gerenciamento térmico |
| Pó de ferro | Ferro Puro (Fe) | Propriedades magnéticas, boa resistência, econômico | Metalurgia do pó, materiais magnéticos, peças automotivas |
| Pó de aço inoxidável | Ferro, cromo, níquel | Resistência à corrosão, alta resistência, durabilidade | Dispositivos médicos, componentes aeroespaciais, peças automotivas |
| Pó de titânio | Titânio Puro (Ti) | Relação resistência-peso elevada, biocompatibilidade, resistência à corrosão | Aeroespacial, implantes médicos, componentes automotivos |
| Níquel em pó | Níquel Puro (Ni) | Resistência a altas temperaturas, resistência à corrosão, propriedades magnéticas | Superligas, baterias, eletrônicos |
| Pó de Cobalto-Cromo | Cobalto (Co), Cromo (Cr) | Alta resistência ao desgaste, biocompatibilidade, resistência à corrosão | Implantes médicos, restaurações dentárias, componentes aeroespaciais |
| Pó de tungstênio | Tungstênio Puro (W) | Alta densidade, alto ponto de fusão, excelente dureza | Ferramentas de corte, blindagem contra radiação, componentes aeroespaciais |
| Magnésio em pó | Magnésio Puro (Mg) | Leve, boa resistência, alta reatividade | Pirotecnia, aeroespacial, automotivo |
| Zinco em pó | Zinco Puro (Zn) | Boa resistência à corrosão, baixo ponto de fusão, propriedades de ânodo de sacrifício | Galvanização, baterias, tintas e revestimentos |
Pó de alumínio
O pó de alumínio é um dos pós de metal mais amplamente utilizados devido à sua natureza leve e excelente resistência à corrosão. É frequentemente empregado nas indústrias aeroespacial e automotiva, onde a redução de peso é crucial para melhorar a eficiência de combustível e o desempenho. Além disso, o pó de alumínio é usado em pirotecnia para produzir faíscas brancas brilhantes.
PÓ DE COBRE
O pó de cobre é valorizado por sua alta condutividade elétrica e térmica, tornando-o ideal para componentes elétricos e sistemas de gerenciamento térmico. Seja na produção de tintas condutoras ou como componente em materiais de fricção, o pó de cobre é essencial para muitas aplicações de alta tecnologia.
Pó de ferro
O pó de ferro, conhecido por suas propriedades magnéticas e boa resistência, é uma opção econômica para várias aplicações industriais. É amplamente utilizado na metalurgia do pó para criar formas complexas que seriam difíceis ou caras de produzir usando métodos tradicionais. Além disso, o pó de ferro é usado na indústria automotiva para fazer peças como engrenagens e rolamentos.
Pó de aço inoxidável
O pó de aço inoxidável é uma mistura de ferro, cromo e níquel, oferecendo excelente resistência à corrosão e alta resistência. Isso o torna perfeito para dispositivos médicos, componentes aeroespaciais e peças automotivas que precisam suportar ambientes agressivos.
Pó de titânio
O pó de titânio é conhecido por sua alta relação resistência-peso, tornando-o um material preferido em aplicações aeroespaciais e médicas. Sua biocompatibilidade também o torna adequado para implantes médicos, enquanto sua resistência à corrosão garante a longevidade em ambientes exigentes.
Níquel em pó
O pó de níquel é valorizado por sua resistência a altas temperaturas e resistência à corrosão, tornando-o um componente-chave em superligas usadas na indústria aeroespacial. Também é usado em baterias e eletrônicos, onde suas propriedades magnéticas são vantajosas.
Pó de Cobalto-Cromo
O pó de cobalto-cromo combina a resistência ao desgaste do cobalto com a resistência à corrosão do cromo, tornando-o ideal para implantes médicos e restaurações dentárias. Sua biocompatibilidade garante que ele funcione bem dentro do corpo humano, enquanto sua durabilidade o torna uma escolha confiável para componentes aeroespaciais.
Pó de tungstênio
O pó de tungstênio é conhecido por sua alta densidade, alto ponto de fusão e excelente dureza. Essas propriedades o tornam adequado para ferramentas de corte, blindagem contra radiação e componentes aeroespaciais que precisam suportar condições extremas.
Magnésio em pó
O pó de magnésio é a escolha ideal para aplicações onde a redução de peso é crítica. É leve, mas forte, tornando-o ideal para as indústrias aeroespacial e automotiva. Além disso, o pó de magnésio é altamente reativo, tornando-o um ingrediente-chave na pirotecnia.
Zinco em pó
O pó de zinco é amplamente utilizado por sua resistência à corrosão e propriedades de ânodo de sacrifício, tornando-o essencial nos processos de galvanização para proteger o aço da ferrugem. Também é usado em baterias, tintas e revestimentos por suas propriedades protetoras e condutoras.
Composição de Pó de Metal de Qualidade
A composição dos pós de metal é um fator crítico que determina suas propriedades e adequação para diferentes aplicações. Os pós de metal podem ser metais puros, ligas ou uma combinação de diferentes materiais para obter características específicas.
| Pó metálico | Elementos primários | Elementos adicionais |
|---|---|---|
| Pó de alumínio | Alumínio (Al) | Silício (Si), Ferro (Fe), Titânio (Ti) |
| PÓ DE COBRE | Cobre (Cu) | Fósforo (P), Níquel (Ni), Zinco (Zn) |
| Pó de ferro | Ferro (Fe) | Carbono (C), Manganês (Mn), Enxofre (S) |
| Pó de aço inoxidável | Ferro (Fe), Cromo (Cr), Níquel (Ni) | Molibdênio (Mo), Carbono (C), Manganês (Mn) |
| Pó de titânio | Titânio (Ti) | Alumínio (Al), Vanádio (V) |
| Níquel em pó | Níquel (Ni) | Cromo (Cr), Ferro (Fe), Molibdênio (Mo) |
| Pó de Cobalto-Cromo | Cobalto (Co), Cromo (Cr) | Molibdênio (Mo), Tungstênio (W), Níquel (Ni) |
| Pó de tungstênio | Tungstênio (W) | Carbono (C), Níquel (Ni), Ferro (Fe) |
| Magnésio em pó | Magnésio (Mg) | Alumínio (Al), Zinco (Zn), Manganês (Mn) |
| Zinco em pó | Zinco (Zn) | Alumínio (Al), Cobre (Cu), Ferro (Fe) |
A composição de cada pó de metal é cuidadosamente controlada para atender a padrões e critérios de desempenho específicos. Por exemplo, a adição de elementos como silício e ferro em pó de alumínio pode aumentar sua resistência e dureza, enquanto a presença de cromo e níquel em pó de aço inoxidável proporciona resistência à corrosão.
Propriedades do Pó de Metal de Qualidade
As propriedades dos pós de metal são determinadas por sua composição, tamanho e forma das partículas. Essas propriedades influenciam como os pós se comportam durante o processamento e como eles se comportam em suas aplicações finais.
Propriedades físicas
| Propriedade | Pó de alumínio | PÓ DE COBRE | Pó de ferro | Pó de aço inoxidável | Pó de titânio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Densidade (g/cm³) | 2.7 | 8.9 | 7.8 | 7.9 | 4.5 |
| Ponto de fusão (°C) | 660 | 1,085 | 1,538 | 1,400-1,530 | 1,668 |
| Condutividade térmica (W/m-K) | 237 | 401 | 80 | 15-30 | 22 |
| Condutividade Elétrica (S/m) | 37 x 10^6 | 58 x 10^6 | 10 x 10^6 | 1-10 x 10^6 | 2 x 10^6 |
| Tamanho da partícula (µm) | 10-50 | 5-100 | 5-50 | 10-100 | 10-50 |
Propriedades mecânicas
| Propriedade | Pó de alumínio | PÓ DE COBRE | Pó de ferro | Pó de aço inoxidável | Pó de titânio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dureza (HV) | 45-100 | 60-140 | 60-90 | 150-250 | 250-350 |
| Resistência à tração (MPa) | 70-150 | 200-350 | 150-250 | 600-1,200 | 800-1,200 |
| Alongamento (%) | 3-12 | 20-45 | 2-10 | 25-50 | 15-25 |
Propriedades quimicas
| Propriedade | Pó de alumínio | PÓ DE COBRE | Pó de ferro | Pó de aço inoxidável | Pó de titânio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistência à corrosão | Alta | Moderado | Baixa | Excelente | Alta |
| Resistência à oxidação | Moderado | Baixa | Alta | Excelente | Excelente |





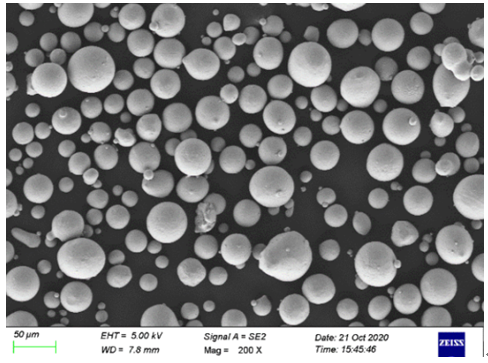
Aplicações de Pós de Metal de Qualidade
Os pós de metal são usados em uma ampla gama de aplicações, cada uma explorando suas propriedades exclusivas. Aqui está uma olhada em algumas aplicações comuns e nos pós de metal que melhor se encaixam nessas necessidades:
| Aplicativo | Pó metálico | Detalhes |
|---|---|---|
| Manufatura aditiva (impressão 3D) | Alumínio, Titânio, Aço Inoxidável | Esses pós são usados para criar geometrias complexas e peças com alta resistência e precisão. |
| Metalurgia do pó | Ferro, aço inoxidável, cobre | Usado para produzir peças com alta precisão e formas complexas que são econômicas de produzir. |
| Componentes aeroespaciais | Titânio, Alumínio, Cobalto-Cromo | Crítico para peças que exigem alta relação resistência-peso e resistência a condições extremas. |
| Peças automotivas | Ferro, Aço Inoxidável, Alumínio | Para fabricar peças duráveis e de alto desempenho, como componentes de motores e engrenagens de transmissão. |
| Implantes médicos | Titânio, Cobalto-Cromo | Materiais biocompatíveis usados para implantes e próteses. |
| Componentes eletrônicos | Cobre, Níquel | Essencial para componentes de alta condutividade, como conectores e placas de circuito. |
| Sistemas de Gerenciamento Térmico | Cobre, alumínio | Usado em dissipadores de calor e materiais de interface térmica para gerenciar a dissipação de calor. |
| Ferramentas de corte | Tungstênio, Cobalto-Cromo | Conhecidos por sua dureza e resistência ao desgaste, ideais para ferramentas de corte e brocas. |
| Pirotecnia | Magnésio, Alumínio | Para criar fogos de artifício e fogos de artifício com cores brilhantes e efeitos intensos. |
| Galvanização | Zinco | Fornece proteção contra corrosão para produtos de aço e ferro. |
Especificações, Tamanhos e Graus de Pós de Metal
As especificações, tamanhos e graus de pós de metal podem afetar significativamente seu desempenho em várias aplicações. Aqui está uma análise detalhada:
| Pó metálico | Tamanhos disponíveis | Notas | Especificações |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pó de alumínio | 10-500 µm | Padrão, Fino, Ultra-Fino | ASTM B211, ISO 3250 |
| PÓ DE COBRE | 5-200 µm | Padrão, Alta Pureza | ASTM B244, ISO 2740 |
| Pó de ferro | 5-100 µm | Padrão, Alta Pureza | ASTM A595, ISO 3290 |
| Pó de aço inoxidável | 10-150 µm | 316L, 304L, 17-4PH | ASTM A313, ISO 5832 |
| Pó de titânio | 10-100 µm | CP Ti, Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM B348, ISO 5832 |
| Níquel em pó | 10-200 µm | Padrão, Alta Pureza | ASTM B679, ISO 6207 |
| Pó de Cobalto-Cromo | 10-150 µm | Co-Cr-Mo, Co-Cr-WC | ASTM F75, ISO 5832 |
| Pó de tungstênio | 10-100 µm | Puro, Ligado | ASTM B777, ISO 1176 |
| Magnésio em pó | 10-200 µm | Padrão, Alta Pureza | ASTM B93, ISO 1625 |
| Zinco em pó | 10-150 µm | Padrão, Alta Pureza | ASTM B6, ISO 1407 |
Fornecedores e preços de pós metálicos
Encontrar fornecedores confiáveis e entender os preços é crucial para obter pós de metal de qualidade. Aqui está uma visão geral:
| Fornecedor | Pó metálico | Preços (por kg) | Informações de contato |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alcoa | Pó de alumínio | $10 – $50 | www.alcoa.com |
| Umicore | PÓ DE COBRE | $20 – $80 | www.umicore.com |
| Höganäs | Pó de ferro | $15 – $60 | www.hoganas.com |
| BASF | Pó de aço inoxidável | $25 – $100 | www.basf.com |
| ATI | Pó de titânio | $100 – $300 | www.atimetals.com |
| SGL Carbon | Níquel em pó | $50 – $150 | www.sglcarbon.com |
| Elementum | Pó de Cobalto-Cromo | $150 – $500 | www.elementum3d.com |
| Tungstênio e pós globais | Pó de tungstênio | $200 – $600 | www.globaltungsten.com |
| Elementos americanos | Magnésio em pó | $30 – $120 | www.americanelements.com |
| Óxido de Zinco | Zinco em pó | $20 – $70 | www.zincoxide.com |
Os preços podem variar com base na pureza, tamanho das partículas e volume do pedido. É essencial obter orçamentos diretamente dos fornecedores para garantir que você está obtendo o melhor negócio para suas necessidades específicas.
Comparando Pós de Metal de Qualidade
Ao escolher entre diferentes pós de metal, é importante ponderar os prós e contras de cada opção com base em suas propriedades, aplicações e custos.
| Pó metálico | Vantagens | Desvantagens |
|---|---|---|
| Pó de alumínio | Leve, excelente resistência à corrosão, econômico | Menor resistência em comparação com outros metais |
| PÓ DE COBRE | Alta condutividade elétrica e térmica, boa usinabilidade | Caro, pode manchar com o tempo |
| Pó de ferro | Econômico, boa resistência, propriedades magnéticas | Menos resistência à corrosão, pode ser frágil |
| Pó de aço inoxidável | Resistência à corrosão, alta resistência, durável | Mais caro, pode ser difícil de processar |
| Pó de titânio | Alta relação resistência-peso, resistente à corrosão, biocompatível | Muito caro, difícil de processar |
| Níquel em pó | Resistência a altas temperaturas, boa resistência à corrosão | Caro, pode ser difícil de trabalhar |
| Pó de Cobalto-Cromo | Excelente resistência ao desgaste e à corrosão, biocompatível | Muito caro, disponibilidade limitada |
| Pó de tungstênio | Extremamente duro, alto ponto de fusão, denso | Muito caro, frágil |
| Magnésio em pó | Leve, boa resistência, reativo | Altamente reativo, pode ser difícil de manusear |
| Zinco em pó | Boa proteção contra corrosão, econômico | Menos durável em comparação com outros metais |
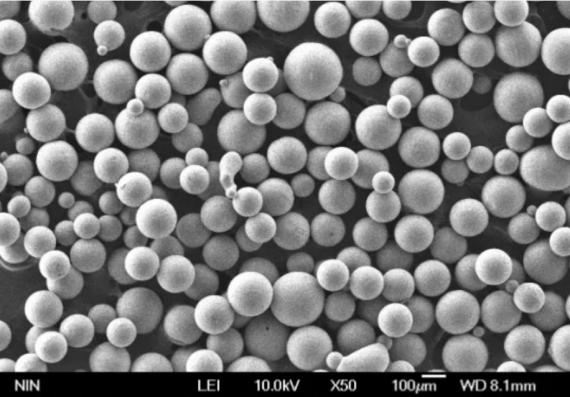
Perguntas frequentes
Aqui estão algumas perguntas e respostas comuns sobre pós de metal de qualidade:
| Pergunta | Resposta |
|---|---|
| Qual é o pó de metal mais comumente usado? | O pó de alumínio é amplamente utilizado devido à sua natureza leve e excelente resistência à corrosão. |
| Como escolho o pó metálico certo para minha aplicação? | Considere as propriedades necessárias para sua aplicação, como resistência, condutividade ou resistência à corrosão. |
| Existem preocupações ambientais com pós de metal? | Alguns pós de metal podem ser perigosos se não forem manuseados corretamente. Siga sempre as diretrizes e regulamentos de segurança. |
| Os pós metálicos podem ser reciclados? | Sim, muitos pós de metal podem ser reciclados, embora o processo dependa do tipo de metal e dos níveis de contaminação. |
| Que fatores afetam o preço dos pós de metal? | Os fatores incluem pureza, tamanho das partículas, quantidade pedida e demanda do mercado. |

