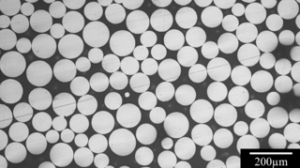
Visão geral de Pó de liga de fase dupla
Os pós de liga de fase dupla são materiais especializados usados em vários setores por sua combinação exclusiva de propriedades, como alta resistência, ductilidade e resistência ao desgaste e à fadiga. Esses pós consistem em duas fases distintas, geralmente uma combinação de fases macias e duras, que trabalham juntas para aprimorar o desempenho geral do material.
Neste artigo, vamos nos aprofundar nas especificidades dos pós de liga de fase dupla, incluindo sua composição, características, aplicações e os diferentes modelos disponíveis no mercado. Também exploraremos as vantagens e desvantagens desses pós em comparação com outros materiais e forneceremos informações sobre fornecedores, preços e padrões.

Composição do pó de liga de fase dupla
Os pós de liga de fase dupla são compostos de uma mistura de duas fases metálicas distintas, geralmente uma fase macia e uma fase dura. A fase macia geralmente proporciona ductilidade e tenacidade, enquanto a fase dura contribui para a força e a resistência ao desgaste. A composição desses pós pode variar significativamente, dependendo da aplicação pretendida.
| Modelo de pó metálico | Composição | Fase suave | Fase difícil | Outros elementos |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP1001 | Fe-Cr-Mn | Ferrite | Martensita | Mo, Ni |
| DP1002 | Fe-Mo-Ni | Ferrite | Bainita | Cr, C |
| DP1003 | Fe-Mn-Si | Austenita | Martensita | Cr, Ni |
| DP1004 | Ti-Al-V | Alfa-Titânio | Beta-Titânio | O, N |
| DP1005 | Ni-Cr-Mo | Austenita | Ferrite | Ti, Al |
| DP1006 | Fe-C-Mo | Martensita | Ferrite | Ni, Mn |
| DP1007 | Co-Cr-Mo | Austenita | Carbetos | Ni, W |
| DP1008 | Fe-Ni-Cr | Ferrite | Bainita | Mo, Mn |
| DP1009 | Ni-Fe-Cr | Austenita | Ferrite | Al, Ti |
| DP1010 | Fe-Mn-C | Austenita | Martensita | Cr, Mo |
Principais conclusões:
- A composição dos pós de liga de fase dupla varia de acordo com a aplicação e as propriedades desejadas.
- A presença de fases macias e duras é fundamental para alcançar o equilíbrio exclusivo de ductilidade e resistência do material.
Características do pó de liga de fase dupla
As características dos pós de liga de fase dupla são determinadas em grande parte por sua composição e pela proporção das fases macia e dura. Esses pós apresentam uma combinação exclusiva de propriedades mecânicas que os tornam adequados para aplicações exigentes.
Propriedades mecânicas
| Propriedade | Faixa típica | Importância |
|---|---|---|
| Resistência à tração | 500 - 1500 MPa | Aplicações de alta resistência |
| Ductilidade | 10% - 30% alongamento | Formabilidade e resistência |
| Dureza | 200 - 600 HV | Resistência ao desgaste |
| Resistência à fadiga | Alta | Durabilidade a longo prazo |
| Resistência à corrosão | Moderado a alto | Resistência química |
| Densidade | 7,0 - 8,5 g/cm³ | Influencia o peso e a massa |
Propriedades térmicas
| Propriedade | Faixa típica | Importância |
|---|---|---|
| Ponto de fusão | 1300°C - 1600°C | Aplicações de alta temperatura |
| Condutividade térmica | 15 - 25 W/m-K | Dissipação de calor |
| Expansão térmica | 10 - 15 µm/m-K | Estabilidade dimensional |
Principais conclusões:
- Os pós de liga de fase dupla oferecem um equilíbrio entre alta resistência e ductilidade, o que os torna ideais para aplicações em que ambas as propriedades são essenciais.
- Os pós também apresentam boa resistência ao desgaste e à corrosão, melhorando seu desempenho em ambientes adversos.
Aplicativos de Pó de liga de fase dupla
Os pós de liga de fase dupla são usados em uma ampla gama de setores devido às suas propriedades versáteis. Do setor automotivo ao aeroespacial, esses pós desempenham um papel crucial na fabricação de componentes de alto desempenho.
Setores e aplicações
| Setor | Formulários | Benefícios do uso de pós de liga de fase dupla |
|---|---|---|
| Automotivo | Componentes do motor, engrenagens de transmissão, peças do chassi | Maior força e resistência à fadiga |
| Aeroespacial | Componentes estruturais, lâminas de turbina | Alta relação resistência/peso, estabilidade térmica |
| Maquinário industrial | Ferramentas de corte, peças de desgaste, rolamentos | Resistência ao desgaste, durabilidade |
| Médico | Implantes, instrumentos cirúrgicos | Biocompatibilidade, resistência à corrosão |
| Petróleo e gás | Brocas, tubulações, válvulas | Resistência à corrosão, tenacidade |
| Eletrônicos | Conectores, dissipadores de calor, carcaças | Condutividade térmica, durabilidade |
| Marinha | Hélices, eixos, caixas subaquáticas | Resistência à corrosão, força |
| Construção | Reforços, fixadores, elementos estruturais | Alta resistência e tenacidade |
| Defesa | Revestimento de armadura, componentes de armas | Resistência balística, durabilidade |
| Energia | Componentes da turbina, trocadores de calor | Alta temperatura e resistência ao desgaste |
Principais conclusões:
- Os pós de liga de fase dupla são indispensáveis nos setores em que são necessárias resistência e ductilidade.
- Sua versatilidade permite que sejam usados em uma ampla gama de aplicações, desde itens do cotidiano até equipamentos especializados.
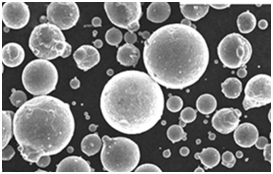


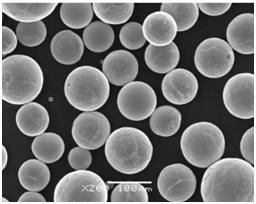


Especificações, tamanhos, classes e padrões
Ao selecionar pós de liga de fase dupla para aplicações específicas, é fundamental considerar suas especificações, incluindo tamanhos, graus e conformidade com os padrões do setor. Isso garante que o pó escolhido atenda aos critérios de desempenho exigidos.
Especificações e tamanhos
| Modelo | Faixa de tamanho de partícula | Grau | Padrão |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP1001 | 20 - 50 µm | Grau A | ASTM B243 |
| DP1002 | 15 - 45 µm | Grau B | ISO 3923-1 |
| DP1003 | 10 - 40 µm | Grau C | AMS 4998 |
| DP1004 | 25 - 55 µm | Grau A | MIL-P-46111 |
| DP1005 | 20 - 50 µm | Grau B | DIN EN 10204 |
| DP1006 | 15 - 45 µm | Grau C | ISO 4499-2 |
| DP1007 | 10 - 40 µm | Grau A | ASTM F2885 |
| DP1008 | 25 - 55 µm | Grau B | JIS Z 2506 |
| DP1009 | 20 - 50 µm | Grau C | ISO 4499-1 |
| DP1010 | 15 - 45 µm | Grau A | ASTM B214 |
Padrões e conformidade
| Padrão | Descrição | Importância |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM B243 | Terminologia padrão da metalurgia do pó | Garante a uniformidade das definições |
| ISO 3923-1 | Determinação da densidade aparente de pós | Ajuda no controle de qualidade |
| AMS 4998 | Padrões de pó de liga de titânio | Crítico para o setor aeroespacial |
| MIL-P-46111 | Especificação militar para metais em pó | Conformidade para aplicativos de defesa |
| DIN EN 10204 | Certificação de produtos metálicos | Garante a rastreabilidade do material |
| ISO 4499-2 | Padrões de microestrutura de pós metálicos | Essencial para a consistência |
| ASTM F2885 | Padrões para pó de manufatura aditiva (AM) | Importante para os processos de AM |
| JIS Z 2506 | Padrões industriais japoneses para metais em pó | Fundamental para o comércio internacional |
| ASTM B214 | Métodos de teste para análise de peneira de pós metálicos | Garante a distribuição adequada do tamanho das partículas |
Principais conclusões:
- A adesão aos padrões do setor garante que os pós de liga de fase dupla atendam aos critérios de qualidade e desempenho necessários.
- Diferentes graus e tamanhos de partículas permitem a personalização com base nas necessidades específicas da aplicação.
Vantagens do pó de liga de fase dupla
Os pós de liga de fase dupla oferecem várias vantagens que os tornam uma opção atraente para fabricantes e engenheiros. Esses benefícios decorrem das propriedades exclusivas conferidas pela combinação de fases macias e duras.
Vantagens sobre as ligas monofásicas
| Vantagens | Explicação | Comparação |
|---|---|---|
| Força aprimorada | As ligas de fase dupla apresentam maior resistência à tração do que as ligas de fase única devido à presença de uma fase dura que reforça o material. | Em comparação com as ligas monofásicas, as ligas bifásicas podem suportar melhor o estresse mecânico. |
| Ductilidade aprimorada | A fase macia nas ligas de fase dupla proporciona ductilidade, tornando o material mais moldável sem comprometer a resistência. | As ligas monofásicas geralmente trocam a resistência pela ductilidade, mas as ligas bifásicas alcançam ambas. |
| Melhor resistência ao desgaste | A fase dura dessas ligas oferece resistência superior ao desgaste, aumentando a vida útil dos componentes. | As ligas de fase dupla superam as ligas de fase única em aplicações que exigem alta resistência ao desgaste. |
| Maior resistência à fadiga | A combinação de fases permite que as ligas bifásicas resistam melhor à fadiga, o que é fundamental para peças sujeitas a cargas cíclicas. | As ligas monofásicas podem falhar sob estresse repetido, enquanto as ligas bifásicas são excelentes. |
| Aplicações versáteis | As propriedades exclusivas das ligas bifásicas as tornam adequadas para uma ampla gama de aplicações, do setor automotivo ao aeroespacial. | As ligas monofásicas geralmente são limitadas em seu escopo de aplicação. |
Principais conclusões:
- As ligas de fase dupla atingem um equilíbrio entre resistência e ductilidade, o que geralmente é um desafio na ciência dos materiais.
- Suas propriedades aprimoradas as tornam mais versáteis e duráveis em comparação com as ligas monofásicas.
Limitações do pó de liga de fase dupla
Embora os pós de liga de fase dupla ofereçam muitos benefícios, eles também apresentam certas limitações. É essencial entender essas desvantagens para tomar decisões informadas ao selecionar materiais.
Desafios e limitações
| Limitação | Explicação | Impacto nos aplicativos |
|---|---|---|
| Custo | Os pós de liga de fase dupla costumam ser mais caros de produzir devido à complexidade de sua composição e dos processos de fabricação. | O custo mais alto pode limitar seu uso a aplicativos de alto desempenho, em que os benefícios justificam a despesa. |
| Dificuldades de processamento | A presença de várias fases pode complicar as técnicas de processamento, como sinterização e manufatura aditiva. | Podem ser necessários equipamentos e processos especializados, o que aumenta o tempo e o custo da produção. |
| Disponibilidade limitada | Nem todos os pós de liga de fase dupla estão prontamente disponíveis, especialmente aqueles com composições especializadas. | Isso pode levar a prazos de entrega mais longos e possíveis desafios na cadeia de suprimentos. |
| Potencial para desequilíbrio de fase | O processamento ou o controle de composição inadequados podem levar a um desequilíbrio entre as fases mole e dura, resultando em propriedades abaixo do ideal. | O desempenho do material pode ser comprometido, afetando a confiabilidade do produto final. |
| Sensibilidade ao ambiente | Algumas ligas de fase dupla podem ser sensíveis a condições ambientais específicas, como altas temperaturas ou ambientes corrosivos. | Isso pode limitar seu uso em determinadas aplicações, especialmente em condições adversas ou variáveis. |
Principais conclusões:
- As complexidades e os custos associados aos pós de liga de fase dupla podem ser uma barreira para sua adoção generalizada.
- O processamento adequado e as considerações ambientais são cruciais para a realização de todo o potencial desses materiais.
Fornecedores e preços de Pó de liga de fase dupla
A escolha do fornecedor certo e a compreensão da estrutura de preços são fundamentais para a aquisição de pós de liga de fase dupla. Aqui, exploramos alguns dos principais fornecedores e apresentamos uma visão geral das tendências de preços.
Principais fornecedores
| Nome do fornecedor | Localização | Especialidade | Reputação |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tecnologia Carpenter | EUA | Ligas de grau aeroespacial | Alta qualidade, confiável |
| Höganäs AB | Suécia | Pós metálicos para vários setores | Líder do setor |
| Tecnologia de Materiais Sandvik | Suécia | Ligas e pós especiais | Inovador, confiável |
| Metalurgia do pó da GKN | Alemanha | Pós metálicos avançados | Estabelecido, com boa reputação |
| Metais em pó ATI | EUA | Pós de liga personalizados | Soluções personalizadas e de alto nível |
| Eramet | França | Pós de níquel e ligas | Fornecedor global |
| Indústrias Elétricas Sumitomo | Japão | Pós de alto desempenho | Precisão, qualidade |
| HC Starck | Alemanha | Pós metálicos refratários | Nicho, especializado |
| Pós metálicos da Rio Tinto | Canadá | Pós de metais ferrosos | Consistente, confiável |
| Tekna | Canadá | Pós esféricos para AM | Tecnologia avançada |
Visão geral dos preços
| Modelo em pó | Preço (USD/kg) | Fornecedor | Observações |
|---|---|---|---|
| DP1001 | $75 – $90 | Tecnologia Carpenter | Aplicações aeroespaciais |
| DP1002 | $65 – $80 | Höganäs AB | Uso industrial geral |
| DP1003 | $85 – $100 | Tecnologia de Materiais Sandvik | Aplicativos de alto desempenho |
| DP1004 | $90 – $110 | Metalurgia do pó da GKN | Uso automotivo especializado |
| DP1005 | $70 – $85 | Metais em pó ATI | Soluções personalizadas |
| DP1006 | $60 – $75 | Eramet | Econômico e de uso geral |
| DP1007 | $95 – $115 | Indústrias Elétricas Sumitomo | Fabricação de precisão |
| DP1008 | $80 – $95 | HC Starck | Aplicativos de nicho |
| DP1009 | $75 – $90 | Pós metálicos da Rio Tinto | Qualidade consistente |
| DP1010 | $100 – $120 | Tekna | Processos avançados de fabricação |
Principais conclusões:
- O preço dos pós de liga de fase dupla varia muito, dependendo da aplicação e do fornecedor.
- Os pós de alto desempenho geralmente têm um preço mais alto, refletindo suas propriedades especializadas e a complexidade de sua produção.
Comparação de modelos de pó de liga de fase dupla
A comparação de diferentes modelos de pó de liga de fase dupla pode ajudar a selecionar o material mais adequado para uma aplicação específica. A seguir, comparamos as principais propriedades e aplicações dos dez modelos discutidos anteriormente.
Comparação de modelos
| Modelo | Força | Ductilidade | Resistência ao desgaste | Aplicativo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP1001 | Alta | Moderado | Alta | Aeroespacial, automotivo |
| DP1002 | Moderado | Alta | Moderado | Máquinas industriais |
| DP1003 | Alta | Moderado | Muito alta | Ferramentas de corte, peças de desgaste |
| DP1004 | Muito alta | Baixa | Alta | Componentes estruturais |
| DP1005 | Alta | Alta | Moderado | Implantes médicos |
| DP1006 | Moderado | Moderado | Alta | Fabricação geral |
| DP1007 | Muito alta | Baixa | Muito alta | Defesa, aeroespacial |
| DP1008 | Alta | Moderado | Alta | Marítimo, petróleo e gás |
| DP1009 | Moderado | Alta | Moderado | Eletrônicos, dissipadores de calor |
| DP1010 | Muito alta | Moderado | Muito alta | Fabricação avançada |
Principais conclusões:
- A escolha do pó de liga de fase dupla deve se basear nos requisitos específicos da aplicação, como a necessidade de força, ductilidade ou resistência ao desgaste.
- Diferentes modelos oferecem diferentes equilíbrios dessas propriedades, o que torna essencial combinar o material com o uso pretendido.
Prós e contras do uso de pó de liga de fase dupla
Compreender os prós e os contras dos pós de liga de fase dupla ajuda a tomar decisões informadas sobre seu uso em várias aplicações. Aqui, descrevemos as principais vantagens e limitações.
Vantagens
| Vantagens | Explicação |
|---|---|
| Alta resistência | Oferece resistência superior à tração, ideal para ambientes de alta tensão. |
| Ductilidade | Oferece a flexibilidade necessária para formar e moldar componentes. |
| Resistência ao desgaste | Aumenta a vida útil das peças expostas a condições abrasivas. |
| Resistência à fadiga | Aumenta a durabilidade sob cargas cíclicas, reduzindo o risco de falhas. |
| Versatilidade | Adequado para uma ampla gama de setores e aplicações. |
Desvantagens
| Desvantagem | Explicação |
|---|---|
| Custo | Os custos de produção mais altos podem limitar seu uso em aplicações sensíveis ao custo. |
| Processamento complexo | Requer equipamentos e processos especializados, aumentando o tempo de produção. |
| Disponibilidade | A disponibilidade limitada de determinados modelos pode levar a problemas na cadeia de suprimentos. |
| Sensibilidade ambiental | Algumas ligas podem não ter um bom desempenho em ambientes extremos, o que limita seu uso. |
Principais conclusões:
- Embora os pós de liga de fase dupla ofereçam benefícios significativos, eles também apresentam desafios que precisam ser considerados, principalmente em termos de custo e complexidade de processamento.
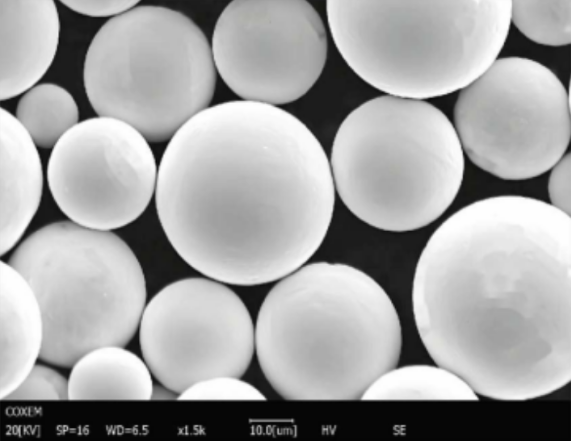
perguntas frequentes
| Pergunta | Resposta |
|---|---|
| O que é pó de liga de fase dupla? | O pó de liga de fase dupla é um material composto de duas fases metálicas distintas, geralmente uma combinação de fases macias e duras, que proporciona um equilíbrio exclusivo de resistência e ductilidade. |
| Quais são as principais aplicações dos pós de liga de fase dupla? | Eles são usados em setores como o automotivo, aeroespacial, de maquinário industrial, médico e de defesa, nos quais a alta resistência e a resistência ao desgaste são cruciais. |
| Como são feitos os pós de liga de fase dupla? | Esses pós são normalmente produzidos por meio de técnicas de metalurgia do pó, incluindo atomização e sinterização, que permitem o controle preciso da composição e das propriedades do material. |
| Por que as ligas de fase dupla são preferíveis às ligas de fase única? | As ligas de fase dupla oferecem um melhor equilíbrio de propriedades mecânicas, como resistência e ductilidade, em comparação com as ligas de fase única, o que as torna mais versáteis para aplicações exigentes. |
| Quais são as limitações do uso de pós de liga de fase dupla? | As principais limitações incluem custos mais altos, requisitos de processamento complexos e possível sensibilidade às condições ambientais. |
| Os pós de liga de fase dupla podem ser usados na manufatura aditiva? | Sim, os pós de liga de fase dupla são cada vez mais usados na manufatura aditiva devido à sua capacidade de produzir peças complexas e de alta resistência. |
| Quais padrões os pós de liga de fase dupla devem atender? | Eles devem estar em conformidade com os padrões do setor, como as especificações ASTM, ISO, AMS e MIL, dependendo da aplicação. |
| Como o tamanho das partículas afeta o desempenho dos pós de liga de fase dupla? | Tamanhos menores de partículas podem melhorar a sinterabilidade e as propriedades mecânicas do pó, enquanto as partículas maiores podem ser preferidas para determinados processos de fabricação. |
| Há alguma preocupação ambiental com os pós de liga de fase dupla? | Algumas ligas de fase dupla podem ser sensíveis a condições ambientais específicas, como altas temperaturas ou ambientes corrosivos, o que pode afetar seu desempenho. |
| Como posso escolher o pó de liga bifásica certo para a minha aplicação? | Considere fatores como as propriedades mecânicas necessárias, o ambiente de aplicação, os métodos de processamento e o custo ao selecionar um pó de liga de fase dupla. |