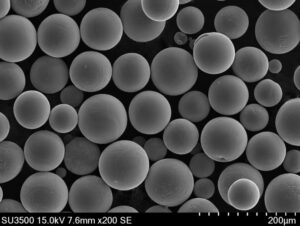
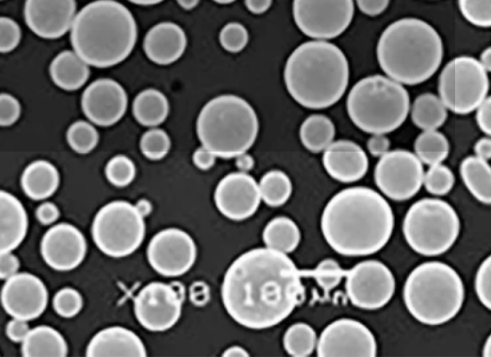
Tungsten metal tozu çeşitli endüstriyel uygulamalarda hammadde olarak kullanılan ince partiküllü bir tungsten formudur. Yüksek yoğunluk, mukavemet, korozyon direnci ve yüksek erime noktası gibi benzersiz özellikleri onu önemli bir mühendislik malzemesi haline getirmektedir.
Bileşim ve Üretim
| Parametre | Detaylar |
|---|---|
| Elemental Bileşim | Saf tungsten (W) veya diğer metallerle alaşım |
| Üretim Süreci | Tungsten çubuklardan öğütülmüş veya tungsten oksitlerden indirgenmiş |
| Parçacık Boyutları | Tipik olarak 1 mikron ila 150 mikron arasında değişir |
| Saflık Dereceleri | 99'dan ,995'e kadar saf tungsten |
Tungsten tozu, istenen şekli ve saflığı elde etmek için hidrojen indirgeme, öğütme veya termal plazma sferoidizasyonu gibi çeşitli işlemlerle üretilir.
Özellikler ve Karakteristikler
| Mülkiyet | Değer |
|---|---|
| Yoğunluk | 19.3 g/cm3, çeliğin neredeyse iki katı |
| Erime Noktası | 3422 °C, tüm metaller arasında en yüksek |
| Güç | Özellikle sinterlendiğinde çok yüksek sertlik ve mukavemet |
| İletkenlik | Düşük elektrik direnci, yüksek termal iletkenlik |
| Kararlılık | Mükemmel kimyasal stabilite ve korozyon direnci |

Bu benzersiz özellikler tungsten metal tozu çeşitli özel uygulamalar için.
Tungsten metal tozu uygulamaları ve kullanım alanları
| Uygulama | Kullanım |
|---|---|
| semente karbür aletler | kesici takımlar için kobalt matris içinde bağlanmış |
| Karşı ağırlıklar | Ağırlıklar ve balast için ideal yüksek yoğunluk |
| Radyasyon Koruması | X-ışını/gama kaynaklarına karşı etkili kalkan |
| Termiyonik Yayıcılar | Yüksek erime noktası nedeniyle filamentler |
| 3D Baskı Tozları | Yüksek mukavemetli tungsten parçaların basımı için |
Tungsten tozu savunma, tıp, havacılık ve diğer endüstrilerdeki görev açısından kritik ihtiyaçları destekler.
Teknik Özellikler ve Standart Sınıflar
Tungsten tozu, partikül boyutu dağılımını, saflık seviyelerini, üretim yöntemini vb. tanımlayan çeşitli uluslararası standartlar altında mevcuttur. Bazı yaygın özellikler şunlardır:
- ASTM B772 – Saf tungsten tozu türleri
- ISO 5453 – Kimyasal analiz ve boyut sınıflandırması
- ICDD 00-001-1202 – Kristal yapı referansı
Tedarikçiler ve Fiyatlandırma
| Tedarikçi | Kg başına fiyat |
|---|---|
| Midwest Tungsten | $70 – $500 |
| Buffalo Tungsten | $100 – $600 |
| Tungsten Ağır Toz | $150 – $800 |
| Küresel Tungsten Tozları | $250 – $1500 |
Fiyatlandırma büyük ölçüde saflık derecesine, partikül şekli/büyüklüğü tutarlılığına, sipariş edilen miktara ve katma değerli işleme bağlıdır.

Artıları ve Eksileri
| Artıları | Eksiler |
|---|---|
| Olağanüstü sertlik ve yoğunluk | Alternatiflerine kıyasla pahalı |
| Yüksek sıcaklıklara dayanır | Ağır – ürünlerde kullanılırsa ağırlık ekler |
| Korozyona ve aşınmaya dayanıklı | Uygun şekilde işlenmezse kırılgan |
| Çevresel olarak kararlı | Belirli formlarda işlenmesi zor |
| Düzgün parçacık dağılımı | Koruyucu atmosferler gerektirebilir |
SSS
Tungsten metal tozu ne için kullanılır?
Özel özellikleri nedeniyle aletler, ağırlıklar, radyasyon kalkanı, elektronik, 3D baskı ve diğer yüksek performanslı alanlarda uygulamaları vardır.
Hangi saflık dereceleri mevcuttur?
Yaygın saflık seviyeleri ila ,995 arasında değişmektedir. Daha yüksek saflık çok daha yüksek fiyatlandırma gerektirir.
Tipik partikül boyutu nedir?
Partikül boyutu 1 mikron ila 150 mikron arasında değişebilir. İstenen boyut, uygulama yöntemine ve son kullanım gereksinimlerine bağlıdır.
Tungsten çevreye zararlı mıdır?
Hayır. Tungsten metal tozu genellikle toksik değildir ve çevre dostudur. Bazı işlemlerde dikkat gerektiren tehlikeli bileşikler kullanılabilir.
daha fazla 3D baskı süreci öğrenin
Additional FAQs: Tungsten Metal Powder
1) What particle morphology is best for different processes?
- Press-and-sinter: irregular/sponge for better green strength. Thermal spray and AM (LPBF): spherical for high flowability and packing. DED/wire-DED: coarser spherical or crushed granules.
2) How do oxygen and carbon impurities affect tungsten metal powder?
- Elevated O and C form WOx and carbides during sintering, increasing brittleness and porosity. For critical applications, target O ≤ 0.05 wt% and C ≤ 0.01 wt% unless intentionally alloyed.
3) Can tungsten metal powder be used in laser powder bed fusion?
- Yes, but it requires preheating and optimized parameters to mitigate cracking due to high stiffness and thermal gradients. Typical LPBF PSD: 15–45 µm spherical, with low O/N and tight PSD.
4) What are common tungsten composites and why use them?
- W-Ni-Fe/W-Ni-Cu heavy alloys for radiation shielding and kinetic energy components; W-Cu for thermal management and EDM electrodes; WC-Co for cutting tools. Composites balance density, ductility, and conductivity.
5) How should tungsten powder be stored and handled safely?
- Keep sealed and dry, under inert gas if possible; use local exhaust ventilation, antistatic grounding, and explosion-rated dust controls. Although tungsten is not highly reactive, fine powders can pose a dust explosion hazard.
2025 Industry Trends: Tungsten Metal Powder
- Semiconductor and medical growth: Demand up for W-Cu heat spreaders and high-density shielding components.
- Advanced manufacturing: More spherical, plasma-atomized W powders available for LPBF/DED; crack-mitigation strategies mature.
- Sustainability: Increased closed-loop recycling and take-back programs for W scrap/powders with certified impurity control.
- Standards tightening: Stricter impurity and PSD specs for AM-grade W and W-heavy alloys; wider adoption of in-line O/N/H analysis.
- Defense/aerospace: Continued shift from lead to tungsten-based shielding/ballast and kinetic components.
2025 Tungsten Powder Market Snapshot (Indicative)
| Metrik | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD (Aug) | Notlar |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global W powder demand (kt) | ~18.5 | ~19.3 | ~20.1 | Semiconductor + defense |
| Spherical W (15–45 µm) price (USD/kg) | 180–320 | 190–340 | 200–360 | PA/spheroidized, low O/N |
| Irregular W (-325 mesh) price (USD/kg) | 70–140 | 75–150 | 80–160 | Hydrogen-reduced |
| Typical O spec (AM-grade W) | ≤0.06 wt% | ≤0.05 wt% | ≤0.04 wt% | Tighter QC, in-line analyzers |
| AM adoption (W/W-alloys programs) | Gelişmekte olan | Early pilots | Pilot-to-production | LPBF + DED parameter maturity |
| W-Cu demand growth (YoY) | +6% | +8% | +9–11% | Power electronics, EDM |
Sources:
- USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (Tungsten): https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- ASTM/ISO powder standards: https://www.astm.org, https://www.iso.org
- Supplier technical notes (Global Tungsten & Powders, H.C. Starck Solutions, Plansee) and industry trackers
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Crack-Resistant LPBF of Tungsten for Collimators (2025)
Background: A medical device OEM needed dense, fine-featured W collimators with reduced post-machining.
Solution: Used plasma-atomized W powder (D50 ~28 µm, O=0.035 wt%) with build plate preheat >600°C, beam shaping, and contour-remelting; stress-relief + hot isostatic pressing (HIP).
Results: Relative density 99.5–99.8%, microcrack incidence reduced by 70% vs. baseline; dimensional accuracy ±60 µm on 2 mm walls; machining time cut 25%.
Case Study 2: W-Cu Heat Spreaders via PM Infiltration for SiC Power Modules (2024)
Background: An EV inverter supplier sought CTE-matched plates with high thermal conductivity.
Solution: Sintered porous W skeletons from -325 mesh W, followed by capillary Cu infiltration to 15–30 vol% Cu; final surface lapped.
Results: Thermal conductivity 200–230 W/m·K; CTE 7.5–8.5 ppm/K (25–200°C); warpage <8 µm over 50 mm; yield +10% compared to prior route.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Dirk N. Schwab, Head of R&D, Plansee High Performance Materials
- “For AM-grade tungsten metal powder, controlling interstitials and applying elevated preheat are decisive to suppress solidification cracking and achieve near-wrought density.”
- Prof. Susanne Wurster, Materials Processing, TU Munich
- “W–Cu and W–Ni–Fe heavy alloys continue to expand as lead replacements. Process route selection—PM infiltration vs. AM—should follow CTE and flatness tolerance needs.”
- Dr. Kevin J. Hemker, Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University
- “Grain boundary engineering and beam shaping are enabling finer W features with improved toughness, opening opportunities in radiation optics and micro heat exchangers.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- ASTM B777 (tungsten heavy alloys), B772 (tungsten powder), B214/B212 (sieve/flow), E1019 (O/N/H): https://www.astm.org
- ISO 4497 (particle size by sieving), ISO 13320 (laser diffraction), ISO 7637-equivalent PM methods: https://www.iso.org
- USGS Tungsten Statistics and Information: https://www.usgs.gov
- OSHA/NIOSH guidance for metal powder handling and combustible dust: https://www.osha.gov, https://www.cdc.gov/niosh
- MatWeb materials database for W and W-composites: https://www.matweb.com
- Senvol Database for AM machine–material compatibility: https://senvol.com
- Supplier technical libraries: Global Tungsten & Powders, H.C. Starck Solutions, Plansee, Midwest Tungsten
Last updated: 2025-08-25
Changelog: Added 5 FAQs; inserted 2025 market snapshot table; provided two recent case studies; included expert opinions; compiled practical tools/resources with standards and datasets
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if USGS data revises demand/pricing >10%, new ASTM/ISO standards for AM-grade tungsten publish, or major LPBF/DED breakthroughs reduce cracking further