Laser Wire Directed Energy Deposition (L-DED) of Ti-6Al-4V
Ti-6Al-4V is one of the most widely used titanium alloys in laser wire directed energy deposition (L-DED) due to its excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and strong industrial adaptability.
It shows significant potential for aerospace applications. Compared with other methods, the L-DED process offers higher material utilization, broader manufacturing capability, and greater process stability, making it particularly suitable for large-scale and high-volume production.
Overview of Deposited Parts:

Microstructure of Deposited Parts:
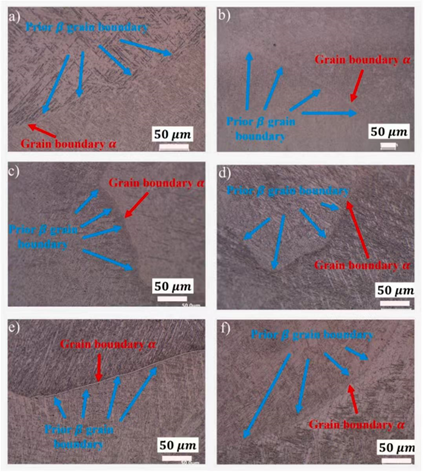
Different wire diameter: a & b. 0.8mm, c & d . 1.1mm, e & f . 1.6mm
Results showed that increasing wire diameter produced coarser grains and in return reduced strength. Fracture analysis further revealed that deposits made with larger wire diameters contained more defects, contributing to the loss of tensile performance.
Columnar β grains were the predominant microstructural feature in all deposits. In addition, equiaxed grains were observed along the edges, where altered solidification conditions arose from heat accumulation.
SEM Photo of Fracture:
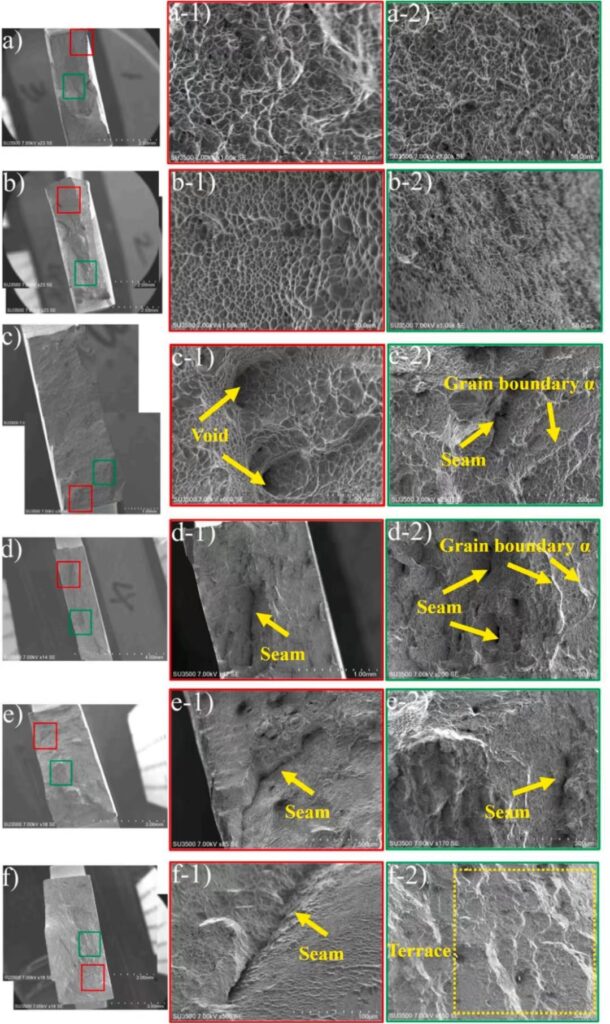
Different wire diameter: a & b. 0.8mm, c & d . 1.1mm, e & f . 1.6mm