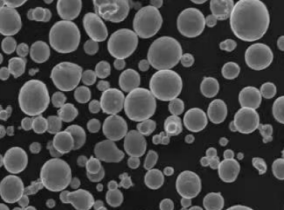
Les machines VIGA (Vacuum Inert Gas Atomization) sont devenues essentielles à la production de poudres métalliques de haute qualité. Ces machines sont largement utilisées dans diverses industries, notamment l'aérospatiale, le secteur médical et l'automobile, grâce à leur capacité à produire des poudres métalliques fines et uniformes. Dans ce guide détaillé, nous explorerons tous les aspects de la production de poudres métalliques Machines VIGAles machines VIGA sont des outils de production de pointe, de leur présentation aux modèles de poudres métalliques spécifiques, à leurs applications, et bien plus encore. Préparez-vous à un examen approfondi du monde des machines VIGA !
Aperçu des machines VIGA
L'atomisation sous vide de gaz inerte (VIGA) est une méthode utilisée pour produire des poudres métalliques en atomisant du métal en fusion dans un environnement contrôlé. Le processus consiste à faire fondre le métal sous vide, puis à le pulvériser à l'aide d'un gaz inerte tel que l'argon ou l'azote. Il en résulte des poudres métalliques de haute pureté dotées d'excellentes propriétés, ce qui les rend adaptées à divers processus de fabrication avancés.
Principales caractéristiques de VIGA Machines
- Processus: Fusion et atomisation dans un environnement sous vide/gaz inerte
- Sortie: Poudres métalliques sphériques de haute pureté
- Applications: Fabrication additive, métallurgie, métallurgie des poudres, technologies de revêtement

Types de poudres métalliques produites par les machines VIGA
La polyvalence des machines VIGA leur permet de produire une large gamme de poudres métalliques. Vous trouverez ci-dessous une liste de modèles de poudres métalliques spécifiques produites à l'aide de la technologie VIGA, ainsi que des descriptions détaillées.
1. Poudre d'acier inoxydable (316L)
Description: La poudre d'acier inoxydable 316L est connue pour son excellente résistance à la corrosion et ses propriétés mécaniques. Il est largement utilisé dans les industries médicales et aérospatiales.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Fer, chrome, nickel, molybdène
- Propriétés: Haute résistance à la corrosion, bonne résistance mécanique
2. Poudre d'alliage de titane (Ti-6Al-4V)
Description: Ti-6Al-4V est la poudre d'alliage de titane la plus couramment utilisée, connue pour son rapport résistance/poids élevé et son excellente biocompatibilité.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Titane, aluminium, vanadium
- Propriétés: Haute résistance, légèreté, biocompatibilité
3. Poudre d'Inconel (Inconel 718)
Description: La poudre d'Inconel 718 est un alliage de nickel et de chrome qui présente une excellente résistance à la corrosion et aux températures élevées, idéale pour les applications aérospatiales.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Nickel, chrome, fer, niobium
- Propriétés: Stabilité à haute température, résistance à la corrosion
4. Poudre d'alliage d'aluminium (AlSi10Mg)
Description: La poudre AlSi10Mg est un alliage aluminium-silicium-magnésium qui présente une bonne conductivité thermique et des propriétés de légèreté, ce qui le rend adapté aux applications automobiles et aérospatiales.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Aluminium, silicium, magnésium
- Propriétés: Léger, bonne conductivité thermique
5. Poudre d'alliage cobalt-chrome (CoCrMo)
Description: La poudre d'alliage CoCrMo est connue pour son excellente résistance à l'usure et sa biocompatibilité, largement utilisée dans les implants médicaux.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Cobalt, chrome, molybdène
- Propriétés: Haute résistance à l'usure, biocompatibilité
6. Poudre d'alliage de cuivre (CuCrZr)
Description: La poudre CuCrZr est un alliage de cuivre-chrome-zirconium présentant une excellente conductivité électrique et thermique, adaptée aux applications électriques et thermiques.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Cuivre, chrome, zirconium
- Propriétés: Haute conductivité, bonne résistance mécanique
7. Poudre d'acier maraging (18Ni300)
Description: La poudre d'acier maraging 18Ni300 est connue pour sa haute résistance et sa ténacité. Elle est couramment utilisée dans les industries de l'outillage et de l'aérospatiale.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Fer, nickel, cobalt, molybdène
- Propriétés: Haute résistance, ténacité
8. Poudre d'acier à outils (H13)
Description: La poudre d'acier à outils H13 est réputée pour sa grande dureté et sa résistance à la chaleur, ce qui la rend adaptée à la fabrication d'outils et de moules.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Fer, chrome, molybdène, vanadium
- Propriétés: Dureté élevée, résistance à la chaleur
9. Poudre d'alliage de nickel (NiCr8020)
Description: La poudre NiCr8020 est un alliage nickel-chrome présentant une excellente résistance à l'oxydation et une stabilité à haute température, utilisé dans les éléments chauffants et les fours industriels.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Nickel, chrome
- Propriétés: Résistance à l'oxydation, stabilité à haute température
10. Poudre de carbure de tungstène (WC-Co)
Description: La poudre de carbure de tungstène est connue pour son extrême dureté et sa résistance à l'usure. Elle est largement utilisée dans les outils de coupe et les revêtements résistants à l'usure.
Caractéristiques:
- Composition: Carbure de tungstène, cobalt
- Propriétés: Dureté extrême, résistance à l'usure
Composition et caractéristiques des poudres métalliques VIGA
Vous trouverez ci-dessous un tableau résumant la composition et les caractéristiques des poudres métalliques produites par Machines VIGA.
| Poudre métallique | Composition | Propriétés |
|---|---|---|
| Acier inoxydable 316L | Fer, chrome, nickel, molybdène | Résistance élevée à la corrosion, résistance mécanique |
| ti-6al-4v | Titane, aluminium, vanadium | Haute résistance, légèreté, biocompatibilité |
| Inconel 718 | Nickel, chrome, fer, niobium | Stabilité à haute température, résistance à la corrosion |
| AlSi10Mg | Aluminium, silicium, magnésium | Léger, bonne conductivité thermique |
| CoCrMo | Cobalt, chrome, molybdène | Résistance élevée à l'usure, biocompatibilité |
| CuCrZr | Cuivre, chrome, zirconium | Haute conductivité, bonne résistance mécanique |
| 18ni300 | Fer, nickel, cobalt, molybdène | Haute résistance, ténacité |
| H13 | Fer, chrome, molybdène, vanadium | Dureté élevée, résistance à la chaleur |
| NiCr8020 | Nickel, chrome | Résistance à l'oxydation, stabilité à haute température |
| WC-Co | Carbure de tungstène, cobalt | Dureté extrême, résistance à l'usure |
Applications des poudres métalliques VIGA
Les poudres métalliques produites par les machines VIGA ont un large éventail d'applications dans diverses industries. Le tableau suivant présente quelques-unes de ces applications.
| L'industrie | Applications | Poudres métalliques utilisées |
|---|---|---|
| Aérospatiale | Composants du moteur, pièces structurelles | Ti-6Al-4V, Inconel 718, AlSi10Mg |
| Médical | Implants, prothèses | Acier inoxydable 316L, CoCrMo, Ti-6Al-4V |
| Automobile | Pièces légères, gestion thermique | AlSi10Mg, CuCrZr |
| Outillage | Moules, outils de coupe | H13, WC-Co, 18Ni300 |
| Électricité | Composants conducteurs, gestion thermique | CuCrZr, NiCr8020 |
| Industrie | Éléments chauffants, revêtements résistants à l'usure | NiCr8020, WC-Co |


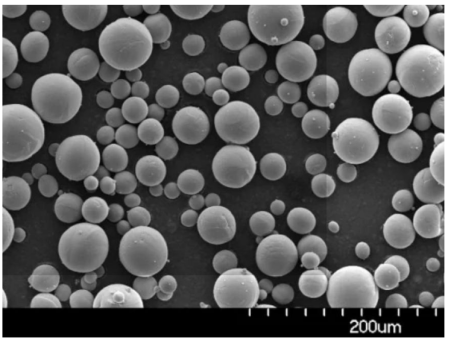


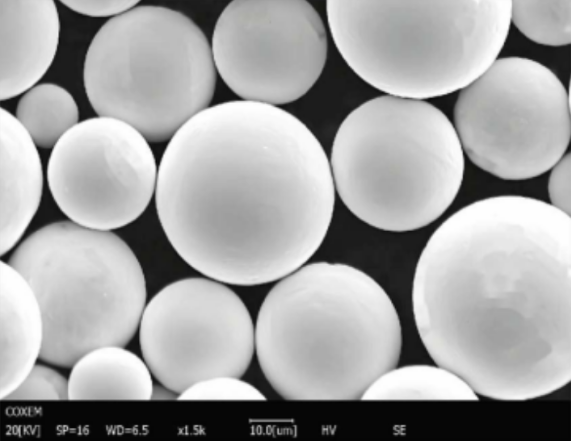
Spécifications, tailles, qualités et normes
Le tableau suivant présente les spécifications, les tailles, les qualités et les normes de certaines poudres métalliques couramment produites par les machines VIGA.
| Poudre métallique | Gamme de tailles (µm) | Grade | Normes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acier inoxydable 316L | 10-45 | AISI 316L | ASTM F138, ISO 5832-1 |
| ti-6al-4v | 15-45 | 5e année | ASTM F136, ISO 5832-3 |
| Inconel 718 | 15-53 | AMS 5662 | ASTM B637 |
| AlSi10Mg | 20-63 | AlSi10Mg | EN AC-43400, ISO 3522 |
| CoCrMo | 10-45 | ASTM F75 | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-4 |
| CuCrZr | 20-63 | CuCrZr | ASTM B505, DIN 17670 |
| 18ni300 | 10-53 | Acier maraging 300 | AMS 6521 |
| H13 | 15-45 | H13 | ASTM A681 |
| NiCr8020 | 20-63 | NiCr8020 | ASTM B163, DIN 17742 |
| WC-Co | 10-45 | WC-Co | ISO 3327 |
Fournisseurs et détails des prix
Voici un tableau présentant certains fournisseurs et les prix approximatifs de diverses poudres métalliques produites par les machines VIGA.
| Poudre métallique | Fournisseur | Prix (par kg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acier inoxydable 316L | Technologie des charpentiers | $50 – $70 | Remises en vrac disponibles |
| ti-6al-4v | AP&C | $200 – $250 | Qualité supérieure, qualité aérospatiale |
| Inconel 718 | Praxair Surface Technologies | $150 – $200 | Applications à haute température |
| AlSi10Mg | ECKART | $30 – $50 | Courant dans la fabrication additive |
| CoCrMo | Arcam AB | $300 – $350 | Qualité d'implant médical |
| CuCrZr | GKN Additive | $40 – $60 | Conductivité élevée |
| 18ni300 | Hoganas AB | $80 – $100 | Haute résistance, applications d'outillage |
| H13 | Technologie des charpentiers | $70 – $90 | Outillage résistant à la chaleur |
| NiCr8020 | Oerlikon Metco | $100 – $130 | Fours industriels |
| WC-Co | Kennametal | $250 – $300 | Dureté extrême, outils de coupe |
Comparaison des avantages et des inconvénients des poudres métalliques VIGA
Le tableau suivant compare les avantages et les inconvénients des différentes poudres métalliques produites par les machines VIGA.
| Poudre métallique | Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|---|
| Acier inoxydable 316L | Excellente résistance à la corrosion, résistance mécanique | Coût plus élevé que celui de l'acier ordinaire |
| ti-6al-4v | Rapport résistance/poids élevé, biocompatibilité | Coûteux, difficile à usiner |
| Inconel 718 | Résistance aux températures élevées, résistance à la corrosion | Coûteux, usinabilité limitée |
| AlSi10Mg | Léger, bonnes propriétés thermiques | Résistance moindre par rapport à d'autres alliages |
| CoCrMo | Résistance à l'usure, biocompatibilité | Cher, disponibilité limitée |
| CuCrZr | Excellente conductivité électrique et thermique | Résistance mécanique plus faible |
| 18ni300 | Haute résistance, ténacité | Coûteux, nécessite une manipulation particulière |
| H13 | Dureté élevée, résistance à la chaleur | Sujet à la fissuration |
| NiCr8020 | Résistance à l'oxydation, stabilité à haute température | Cher, disponibilité limitée |
| WC-Co | Dureté extrême, résistance à l'usure | Très cher, cassant |

FAQ
Qu'est-ce que le processus VIGA ?
Le procédé VIGA consiste à fondre le métal sous vide et à l'atomiser à l'aide d'un gaz inerte pour produire de fines poudres métalliques.
Quelles sont les industries qui utilisent les poudres métalliques VIGA ?
Les industries telles que l'aérospatiale, le médical, l'automobile, l'outillage et l'électricité utilisent les poudres métalliques VIGA.
Quels sont les avantages de l'utilisation des poudres métalliques VIGA ?
Les poudres métalliques VIGA offrent une grande pureté, une taille de particule uniforme et d'excellentes propriétés adaptées aux processus de fabrication avancés.
Comment les machines VIGA se comparent-elles aux autres méthodes d'atomisation ?
Les machines VIGA permettent un meilleur contrôle de la qualité et de la pureté de la poudre par rapport à d'autres méthodes telles que l'atomisation à l'eau ou au gaz.
Les poudres métalliques VIGA sont-elles chères ?
Le coût des poudres métalliques VIGA peut être plus élevé en raison de la technologie avancée et du rendement de haute qualité, mais les avantages l'emportent souvent sur les coûts.
Quelles sont les poudres métalliques les plus courantes produites par les machines VIGA ?
Les poudres courantes comprennent l'acier inoxydable 316L, le Ti-6Al-4V, l'Inconel 718, l'AlSi10Mg, le CoCrMo, le CuCrZr, le 18Ni300, le H13, le NiCr8020 et le WC-Co.
Conclusion
Machines VIGA représentent un sommet dans le domaine de la production de poudres métalliques, fournissant des matériaux de haute qualité à un large éventail d'industries. Leur capacité à produire des poudres avec un contrôle précis de la composition et de la taille des particules les rend indispensables dans la fabrication moderne. Qu'il s'agisse de composants aérospatiaux, d'implants médicaux ou d'outils industriels, la polyvalence et la fiabilité des poudres produites par VIGA garantissent qu'elles restent une ressource essentielle dans les applications de matériaux avancés.