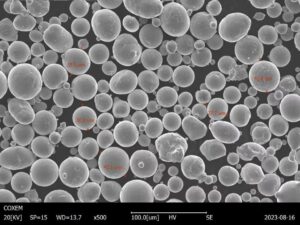
Hochfestes Stahlpulver ist ein Werkstoff, der in verschiedenen Branchen - von der Automobilindustrie bis zur Luft- und Raumfahrt - eine entscheidende Rolle spielt. Seine einzigartigen Eigenschaften in Verbindung mit technologischen Fortschritten haben es Ingenieuren und Herstellern ermöglicht, Bauteile zu entwickeln, die nicht nur stärker, sondern auch leichter und haltbarer sind. In diesem umfassenden Leitfaden erfahren Sie, was hochfestes Stahlpulver ist, wie es zusammengesetzt ist, welche Eigenschaften es hat, welche Anwendungen es gibt und vieles mehr. Egal, ob Sie ein erfahrener Fachmann oder einfach nur neugierig sind, bleiben Sie dran - dies wird eine informative Reise werden.
Überblick über hochfestes Stahlpulver
Hochfestes Stahlpulver ist eine Form von Metallpulver, die speziell für außergewöhnliche mechanische Eigenschaften wie hohe Zugfestigkeit, Härte, Verschleiß- und Ermüdungsbeständigkeit entwickelt wurde. Dieses Pulver wird in der Regel in fortschrittlichen Fertigungstechniken wie der additiven Fertigung (3D-Druck), der Pulvermetallurgie und dem Metall-Spritzguss verwendet, wo seine feine Körnung die Herstellung präziser und komplexer Formen ermöglicht.
Hochfeste Stahlpulver werden durch verschiedene Verfahren hergestellt, darunter die Zerstäubung, bei der geschmolzener Stahl in winzige Tröpfchen zerlegt wird, die sich in Pulverform verfestigen. Die spezifische Zusammensetzung des Pulvers kann auf die Anforderungen der verschiedenen Anwendungen zugeschnitten werden, die von hochfesten Automobilteilen bis hin zu leichten Komponenten für die Luft- und Raumfahrt reichen.

Arten von hochfesten Stahlpulvern, Zusammensetzung, Eigenschaften und Merkmale
| Modell | Zusammensetzung | Eigenschaften | Merkmale |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSLA-100 | Eisen, Kohlenstoff, Mangan, Nickel, Chrom | Hohe Zugfestigkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Hervorragend geeignet für Schiffsanwendungen, schweißbar |
| CPM 3V | Eisen, Kohlenstoff, Vanadium | Außergewöhnliche Zähigkeit, Verschleißfestigkeit | Ideal für Schneidwerkzeuge und Verschleißteile |
| Martensitaushärtung 300 | Eisen, Nickel, Kobalt, Molybdän | Hohe Streckgrenze, gute Schweißbarkeit | Geeignet für Luft- und Raumfahrt, Hochleistungsgetriebe |
| 17-4 PH | Eisen, Chrom, Nickel, Kupfer | Hohe Festigkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Einsatz in der Luft- und Raumfahrt, in der chemischen Verarbeitung |
| Aermet 100 | Eisen, Nickel, Kobalt, Chrom | Ultrahohe Festigkeit, Bruchzähigkeit | Verwendet in Fahrwerken, Luft- und Raumfahrtstrukturen |
| H13 Werkzeugstahl | Eisen, Kohlenstoff, Chrom, Vanadium | Hohe Zähigkeit, Beständigkeit gegen thermische Ermüdung | Üblich bei Druckguss- und Extrusionswerkzeugen |
| S136H | Eisen, Kohlenstoff, Chrom | Hohe Härte, Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Verwendung in Kunststoffformen, ausgezeichnete Polierbarkeit |
| M300 Martensitaushärtender Stahl | Eisen, Nickel, Kobalt, Molybdän | Hohe Festigkeit, gute Duktilität | Geeignet für hochbeanspruchte Anwendungen |
| D2 Werkzeugstahl | Eisen, Kohlenstoff, Chrom, Vanadium | Hohe Härte, Verschleißfestigkeit | Ideal für Stanz- und Umformwerkzeuge |
| PMD-100 | Eisen, Kohlenstoff, Molybdän, Nickel | Ausgewogene Zähigkeit und Verschleißfestigkeit | Vielseitig einsetzbar im Automobil- und Industriebereich |
Zusammensetzung der Hochfestes Stahlpulver
Die Zusammensetzung von hochfestem Stahlpulver wird sorgfältig entwickelt, um bestimmte mechanische Eigenschaften zu erzielen. Zu den in diesen Pulvern häufig verwendeten Elementen gehören Eisen, Kohlenstoff, Chrom, Nickel, Vanadium, Kobalt und Molybdän. Jedes Element trägt zur Gesamtleistung des Pulvers bei:
- Eisen (Fe): Der Hauptbestandteil von Stahl, der die Grundstruktur bildet.
- Kohlenstoff (C): Erhöht die Härte und Festigkeit durch die Bildung von Karbiden.
- Chrom (Cr): Verbessert die Korrosionsbeständigkeit und Härte.
- Nickel (Ni): Verbessert die Zähigkeit und Schlagfestigkeit.
- Vanadium (V): Erhöht die Verschleißfestigkeit und Festigkeit bei hohen Temperaturen.
- Kobalt (Co): Verbessert die Hochtemperaturstabilität und die magnetischen Eigenschaften.
- Molybdän (Mo): Verbessert die Festigkeit und Härtbarkeit, insbesondere bei erhöhten Temperaturen.
Diese Elemente werden in unterschiedlichen Anteilen kombiniert, um Stahlpulver herzustellen, die den Anforderungen bestimmter Anwendungen entsprechen. Ein hoher Kohlenstoffgehalt erhöht beispielsweise die Härte, während die Zugabe von Chrom die Korrosionsbeständigkeit erheblich verbessern kann, so dass sich das Stahlpulver für den Einsatz in rauen Umgebungen eignet.
Merkmale von hochfestem Stahlpulver
Hochfeste Stahlpulver zeichnen sich durch eine Reihe einzigartiger Eigenschaften aus, zu denen auch die folgenden gehören:
- Hohe Zugfestigkeit: Diese Pulver sind so konzipiert, dass sie erheblichen Dehnungs- oder Zugkräften standhalten, ohne zu brechen.
- Korrosionsbeständigkeit: Viele hochfeste Stahlpulver sind resistent gegen Rost und andere Formen der Korrosion, was sie ideal für den Einsatz in maritimen oder chemischen Umgebungen macht.
- Abnutzungswiderstand: Hochfeste Stahlpulver werden häufig in Anwendungen eingesetzt, bei denen das Material wiederholt mechanischem Verschleiß ausgesetzt ist.
- Ermüdungswiderstand: Die Fähigkeit, zyklischen Belastungen standzuhalten, ohne zu versagen, ist entscheidend für Bauteile, die immer wiederkehrenden Belastungen ausgesetzt sind.
- Härte: Diese Pulver können so behandelt werden, dass sie einen sehr hohen Härtegrad erreichen, wodurch sie sich für Schneidwerkzeuge und Formen eignen.
- Duktilität: Trotz ihrer Festigkeit weisen viele dieser Pulver eine gute Duktilität auf, so dass sie ohne Rissbildung geformt und verformt werden können.
Diese Eigenschaften machen hochfeste Stahlpulver unentbehrlich für Industrien, in denen Langlebigkeit, Präzision und Zuverlässigkeit an erster Stelle stehen.




Anwendungen von hochfestem Stahlpulver
Die Vielseitigkeit von hochfesten Stahlpulvern ermöglicht ihren Einsatz in verschiedenen Branchen, die alle von ihren einzigartigen Eigenschaften profitieren. Hier erfahren Sie, wie diese Pulver in verschiedenen Sektoren eingesetzt werden:
Automobilindustrie:
- Hochfeste Strukturkomponenten: Wird für die Herstellung von leichten und dennoch stabilen Fahrgestell- und Karosserieteilen verwendet.
- Motorteile: Sorgt für Verschleißfestigkeit bei kritischen Komponenten wie Nockenwellen und Zahnrädern.
Luft- und Raumfahrtindustrie:
- Fahrwerk: Die extrem hohe Festigkeit und Zähigkeit von speziellen Pulvern wie Aermet 100 eignen sich hervorragend für Fahrwerkskomponenten.
- Strukturelle Komponenten: Wird in Flugzeugzellen verwendet, bei denen ein hohes Festigkeits-Gewichts-Verhältnis wichtig ist.
Werkzeugbau und Formenbau:
- Druckgussformen: Pulver wie H13 Tool Steel sind aufgrund ihrer Beständigkeit gegen thermische Ermüdung ideal.
- Spritzgießen: S136H-Stahlpulver wird bevorzugt für Kunststoffformen verwendet, die eine hohe Polierbarkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit erfordern.
Anwendungen in der Schifffahrt:
- Korrosionsbeständige Teile: HSLA-100 wird aufgrund seiner ausgezeichneten Schweißbarkeit und Beständigkeit gegen Seewasserkorrosion häufig für Schiffskonstruktionen verwendet.
- Offshore-Bohrausrüstung: Die Kombination aus Festigkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit macht diese Pulver ideal für raue Meeresumgebungen.
Industrielle Maschinen:
- Verschleißteile: CPM 3V-Stahlpulver bietet eine hervorragende Verschleißfestigkeit und ist daher für Schneidwerkzeuge und Industriemaschinen geeignet.
- Hochbelastbares Getriebe: Wird bei der Herstellung von Zahnrädern verwendet, die sowohl Festigkeit als auch Haltbarkeit erfordern.
Medizinische Geräte:
- Chirurgische Instrumente: Hohe Härte und Korrosionsbeständigkeit sind bei medizinischen Werkzeugen von entscheidender Bedeutung, weshalb hochfeste Stahlpulver bevorzugt eingesetzt werden.
- Orthopädische Implantate: Bestimmte Pulver sind aufgrund ihrer Biokompatibilität und Festigkeit ideal für tragende Implantate.
Anwendungen und Einsatzmöglichkeiten von Hochfestes Stahlpulver
| Industrie | Anmeldung | Modell/Typ | Warum es verwendet wird |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automobilindustrie | Strukturelle Komponenten | HSLA-100 | Hohe Festigkeit, geringes Gewicht |
| Motorenteile | CPM 3V | Verschleißfestigkeit | |
| Luft- und Raumfahrt | Fahrwerk | Aermet 100 | Ultrahohe Festigkeit, Zähigkeit |
| Strukturelle Komponenten | Martensitaushärtung 300 | Hohes Festigkeits-Gewichts-Verhältnis | |
| Werkzeugbau und Formenbau | Druckgussformen | H13 Werkzeugstahl | Widerstand gegen thermische Ermüdung |
| Spritzgießen | S136H | Hohe Polierbarkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit | |
| Marine | Korrosionsbeständige Teile | HSLA-100 | Schweißbarkeit, Seewasserbeständigkeit |
| Offshore-Bohrausrüstung | Aermet 100 | Festigkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit | |
| Industrielle Maschinen | Verschleißteile | CPM 3V | Hervorragende Verschleißfestigkeit |
| Hochbelastbare Zahnräder | D2 Werkzeugstahl | Stärke, Haltbarkeit | |
| Medizinische Geräte | Chirurgische Instrumente | 17-4 PH | Härte, Korrosionsbeständigkeit |
| Orthopädische Implantate | M300 Martensitaushärtender Stahl | Biokompatibilität, Festigkeit |
Spezifikationen, Größen, Güteklassen und Normen
Die Kenntnis der Spezifikationen, Größen, Güten und Normen von hochfesten Stahlpulvern ist für die Auswahl des richtigen Materials für Ihre Anwendung unerlässlich. Nachstehend finden Sie eine detaillierte Tabelle, die diese Aspekte zusammenfasst.
Tabelle: Spezifikationen, Größen, Güten und Normen von hochfesten Stahlpulvern
| Modell | Spezifikationen | Verfügbare Größen | Klassen | Normen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSLA-100 | Zugfestigkeit: 690 MPa | 5µm - 150µm | Note 80 | MIL-S-16216K, ASTM A710 |
| CPM 3V | Härte: 58-60 HRC | 10µm - 100µm | Note A | ASTM A681 |
| Martensitaushärtung 300 | Streckgrenze: 1930 MPa | 20µm - 120µm | Klasse 300 | AMS 6514 |
| 17-4 PH | Zugfestigkeit: 1170 MPa | 15µm - 125µm | H900, H1025 | AMS 5643, ASTM A564 |
| Aermet 100 | Zugfestigkeit: 2070 MPa | 10µm - 150µm | Note 100 | MIL-S-46119 |
| H13 Werkzeugstahl | Härte: 50-52 HRC | 10µm - 90µm | Note A | ASTM A681 |
| S136H | Härte: 48-52 HRC | 5µm - 100µm | Klasse S136 | DIN 1.2083, GB/T 1220 |
| M300 Martensitaushärtung | Zugfestigkeit: 2050 MPa | 20µm - 120µm | Klasse 300 | AMS 6514 |
| D2 Werkzeugstahl | Härte: 55-62 HRC | 15µm - 110µm | Note A | ASTM A681 |
| PMD-100 | Zugfestigkeit: 750 MPa | 20µm - 130µm | Note 100 | ASTM F75, AMS 5758 |
Lieferanten und Preisangaben
Die Preise für hochfestes Stahlpulver können je nach Zusammensetzung, Qualität und Lieferant erheblich variieren. Nachstehend finden Sie einen Vergleich einiger gängiger Anbieter und ihrer Preisspannen.
Tabelle: Lieferanten und Preisangaben für hochfestes Stahlpulver
| Anbieter | Modell | Preis pro kg (USD) | Mindestbestellmenge (kg) | Versandoptionen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fortschrittliche Metallpulver | HSLA-100 | $50 – $75 | 10 | Globaler Versand, expedited |
| SteelTech-Zubehör | CPM 3V | $80 – $110 | 5 | Innerstaatlich und international |
| Präzisionslegierungen Inc. | Martensitaushärtung 300 | $120 – $150 | 2 | Expressversand verfügbar |
| Metallpulver direkt | 17-4 PH | $60 – $90 | 20 | Mengenrabatte, weltweiter Versand |
| Luft- und Raumfahrtmaterialien Ltd. | Aermet 100 | $200 – $250 | 1 | Kundenspezifische Versandoptionen |
| Lösungen für Werkzeugstahl | H13 Werkzeugstahl | $70 – $100 | 15 | Nur im Inland |
| Global Powder Metals | S136H | $90 – $130 | 10 | Globaler Versand, expedited |
| Maraging Metals LLC | M300 Martensitaushärtung | $140 – $180 | 5 | Expressversand verfügbar |
| Industrielle Stahlpulver | D2 Werkzeugstahl | $85 – $120 | 8 | Mengenrabatte, international |
| PowderMet Inc. | PMD-100 | $55 – $80 | 25 | Weltweiter Versand, Mengenrabatte |
Vorteile und Grenzen von hochfesten Stahlpulvern
Hochfeste Stahlpulver bieten zahlreiche Vorteile, sind aber auch mit gewissen Einschränkungen verbunden. Hier ist eine Aufschlüsselung:
Tabelle: Vorteile und Grenzen von hochfesten Stahlpulvern
| Vorteile | Beschränkungen |
|---|---|
| Hohes Festigkeits-Gewichts-Verhältnis | Kann teurer sein als herkömmlicher Stahl |
| Ausgezeichnete Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Erfordert präzise Fertigungsprozesse |
| Hervorragende Verschleißbeständigkeit | Möglicherweise ist spezielle Ausrüstung für die Handhabung erforderlich |
| Vielseitigkeit bei verschiedenen Anwendungen | Begrenzte Verfügbarkeit einiger bestimmter Sorten |
| Gute Ermüdungsbeständigkeit | Die Zubereitung und Lagerung von Pulver kann eine Herausforderung sein |
| Einfaches Legieren und Anpassen | Potenzielle Porosität in gesinterten Teilen |
| Umweltvorteile in der Fertigung | Eingeschränkte Rezyklierbarkeit einiger hochlegierter Pulver |

FAQ
| Frage | Antwort |
|---|---|
| Wozu wird hochfestes Stahlpulver verwendet? | Es wird in Branchen wie der Automobilindustrie, der Luft- und Raumfahrt, dem Werkzeugbau, der Schifffahrt und der Medizintechnik für Teile verwendet, die hohe Festigkeit, Verschleißfestigkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit erfordern. |
| Wie wird hochfestes Stahlpulver hergestellt? | Es wird in der Regel durch Zerstäubung hergestellt, bei der geschmolzener Stahl in feine Tröpfchen zerteilt wird, die sich zu Pulver verfestigen. |
| Was sind die Vorteile der Verwendung von hochfestem Stahlpulver? | Zu den Vorteilen gehören hohe Zugfestigkeit, Verschleißfestigkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit und die Fähigkeit, komplexe Formen zu bilden. |
| Kann hochfestes Stahlpulver recycelt werden? | Während einige hochfeste Stahlpulver recycelt werden können, stellen solche mit komplexen Legierungszusammensetzungen eine Herausforderung dar. |
| Ist hochfestes Stahlpulver für den 3D-Druck geeignet? | Ja, es ist in der additiven Fertigung aufgrund seiner Fähigkeit, präzise und komplexe Komponenten herzustellen, weit verbreitet. |
| Welches sind die gebräuchlichen Sorten von hochfestem Stahlpulver? | Gängige Sorten sind unter anderem HSLA-100, CPM 3V, Maraging 300, 17-4 PH und Aermet 100. |
| Wie verhält sich hochfestes Stahlpulver im Vergleich zu herkömmlichem Stahl? | Hochfestes Stahlpulver bietet überlegene mechanische Eigenschaften und Flexibilität bei der Herstellung, ist aber unter Umständen teurer und erfordert fortschrittliche Verarbeitungstechniken. |
| Welche Branchen profitieren am meisten von hochfestem Stahlpulver? | Branchen wie die Luft- und Raumfahrt, die Automobilindustrie, die Schifffahrt, der Werkzeugbau und die Herstellung medizinischer Geräte profitieren erheblich vom Einsatz hochfester Stahlpulver. |
| Wie sollte hochfestes Stahlpulver gelagert werden? | Es sollte in einer trockenen, temperaturgeregelten Umgebung gelagert werden, um Oxidation und Feuchtigkeitsaufnahme zu vermeiden. |
| Welche Umweltauswirkungen hat die Herstellung von hochfestem Stahlpulver? | Der Produktionsprozess kann zwar energieintensiv sein, aber die Möglichkeit, leichtere und stärkere Bauteile herzustellen, kann in Anwendungen wie der Automobil- und Luftfahrtindustrie zu Energieeinsparungen führen. |
Schlussfolgerung
Hochfeste Stahlpulver sind eine bemerkenswerte Innovation auf dem Gebiet der Werkstofftechnik. Ihre einzigartigen Eigenschaften machen sie in einer Vielzahl von Branchen unverzichtbar, von der Automobilindustrie über die Luft- und Raumfahrt bis hin zu medizinischen Geräten und Industriewerkzeugen. Durch das Verständnis der verschiedenen Zusammensetzungen, Eigenschaften, Anwendungen und Einschränkungen können Fachleute fundierte Entscheidungen darüber treffen, welches hochfeste Stahlpulver für ihre spezifischen Anforderungen am besten geeignet ist.
Dieser Leitfaden soll eine gründliche Untersuchung von hochfesten Stahlpulvern bieten, die Nuancen ihrer Verwendung beleuchten und Ihnen helfen, die Komplexität der Auswahl des richtigen Materials für Ihr nächstes Projekt zu bewältigen. Ganz gleich, ob Sie Hersteller, Ingenieur oder Forscher sind, die hier gebotenen detaillierten Einblicke sollten Ihnen bei Ihren Bemühungen als wertvolle Ressource dienen.
Denken Sie daran, dass bei Materialien wie hochfestem Stahlpulver der Teufel im Detail steckt - nehmen Sie sich also Zeit, prüfen Sie Ihre Optionen und wählen Sie mit Bedacht.