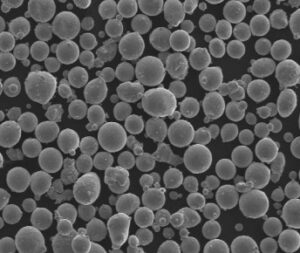
Niedrig legiertes Stahlpulver ist ein vielseitiges und unverzichtbares Material in verschiedenen Industriezweigen, von der Automobilindustrie bis zur Luft- und Raumfahrt. Diese Pulver werden mit spezifischen chemischen Zusammensetzungen und Eigenschaften entwickelt, um die hohen Anforderungen der modernen Technik zu erfüllen. Ganz gleich, ob Sie als Ingenieur die Leistung Ihres Produkts optimieren wollen, als Hersteller auf der Suche nach dem richtigen Material sind oder einfach nur neugierig auf das Thema sind, dieser Leitfaden führt Sie tief in die Welt der niedrig legierten Stahlpulver ein.
Überblick über Niedrig legierte Stähle Pulver
Pulver aus niedrig legierten Stählen wird durch verschiedene Verfahren hergestellt, darunter Zerstäubung, Reduktion und Elektrolyse, wodurch ein feines, gleichmäßiges Pulver entsteht, das in einer Vielzahl von Anwendungen eingesetzt wird. Im Gegensatz zu hochlegierten Stählen enthalten niedriglegierte Stähle einen geringeren Anteil an Legierungselementen, in der Regel weniger als 8%. Dies ermöglicht ein ausgewogenes Verhältnis zwischen Festigkeit, Härte und Schweißbarkeit und macht sie ideal für Anwendungen, die bestimmte mechanische Eigenschaften erfordern.
Was macht das Pulver aus niedrig legierten Stählen so besonders?
Niedrig legierte Stahlpulver werden auf bestimmte Eigenschaften zugeschnitten, wie z. B. erhöhte Festigkeit, Zähigkeit und Verschleißbeständigkeit. Die präzise Zusammensetzung dieser Pulver ermöglicht es den Herstellern, Bauteile herzustellen, die sowohl langlebig als auch leicht sind, ohne dass die Leistung darunter leidet.

Arten von niedrig legierten Stählen - Pulver
Die Vielfalt der niedrig legierten Pulverstähle ist immens. Im Folgenden werden wir einige der am häufigsten verwendeten Modelle untersuchen und ihre Zusammensetzung, Eigenschaften und Anwendungen aufschlüsseln.
| Modell | Zusammensetzung | Wichtige Eigenschaften | Anwendungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 4130 | Chrom, Molybdän | Hohe Festigkeit, Zähigkeit, gute Schweißbarkeit | Flugzeugteile, Automobil, Öl und Gas |
| AISI 4340 | Nickel, Chrom, Molybdän | Ausgezeichnete Ermüdungsfestigkeit, hohe Zähigkeit | Zahnräder, Kurbelwellen, hochbelastete Maschinen |
| AISI 6150 | Chrom, Vanadium | Gute Schlagfestigkeit, Verschleißfestigkeit | Federn, Schäfte, Messer |
| AISI 8620 | Nickel, Chrom, Molybdän | Einsatzhärtung, gute Zähigkeit | Zahnräder, Kurbelwellen, Buchsen |
| AISI 5140 | Chrom | Hohe Zugfestigkeit, Zähigkeit | Bolzen, Muttern, Achsen |
| AISI 5120 | Chrom | Hohe Verschleißfestigkeit, Härte | Zahnräder, Nocken, Hydraulikteile |
| AISI 50B44 | Bor | Verbesserte Härtbarkeit, Festigkeit | Strukturelle Komponenten, Verbindungselemente |
| AISI 5145 | Chrom | Hohe Härtbarkeit, gute Zähigkeit | Automobilindustrie, Maschinenbau |
| AISI 5160 | Chrom | Ausgezeichnete Ermüdungsfestigkeit, Zähigkeit | Blattfedern, Torsionsstäbe |
| AISI 52100 | Chrom | Hohe Verschleißfestigkeit, Festigkeit | Lager, Werkzeuge, stark beanspruchte Teile |
Zusammensetzung der Niedrig legierte Stähle Pulver
Die Zusammensetzung des Pulvers aus niedrig legierten Stählen ist ein entscheidender Faktor für die Eigenschaften des Materials. Der Zusatz von Elementen wie Chrom, Molybdän, Nickel, Vanadium und Bor trägt zu den mechanischen Eigenschaften des Materials wie Härte, Zähigkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit bei.
- Chrom (Cr): Verbessert die Härte, Korrosionsbeständigkeit und Verschleißfestigkeit.
- Molybdän (Mo): Erhöht die Festigkeit bei hohen Temperaturen und verbessert die Zähigkeit.
- Nickel (Ni): Erhöht die Zähigkeit und verbessert die Stoßfestigkeit.
- Vanadium (V): Verbessert die Festigkeit, Verschleißfestigkeit und Zähigkeit.
- Bor (B): Verbessert die Härtbarkeit und ermöglicht eine tiefere Aushärtung des Materials.
Detaillierte Tabelle der Zusammensetzung
| Element | Funktion | Auswirkungen auf die Eigenschaften |
|---|---|---|
| Chrom | Härtemittel | Erhöht die Härte, Verschleißfestigkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit |
| Molybdän | Verfestigungsmittel | Verbessert die Hochtemperaturfestigkeit und Zähigkeit |
| Nickel | Härtebildner | Verbessert Zähigkeit, Schlagfestigkeit |
| Vanadium | Verstärkung von Kraft und Zähigkeit | Verbessert Verschleißfestigkeit, Festigkeit |
| Bor | Mittel zur Erhärtung | Erhöht die Härtbarkeit, Härtetiefe |
Eigenschaften von niedrig legierten Stählen in Pulverform
Das Verständnis der Eigenschaften von niedrig legierten Stahlpulvern ist der Schlüssel zur Auswahl des richtigen Materials für Ihre Anwendung. Nachfolgend sind die wichtigsten Eigenschaften aufgeführt, die diese Pulver auszeichnen.
- Hohe Festigkeit: Niedrig legierte Stähle bieten eine hohe Festigkeit und eignen sich daher für anspruchsvolle strukturelle Anwendungen.
- Gute Zähigkeit: Die Ausgewogenheit der Legierungselemente sorgt dafür, dass das Material auch bei hoher Beanspruchung zäh bleibt.
- Abnutzungswiderstand: Diese Pulver sind so konzipiert, dass sie verschleißfest sind und die Lebensdauer der Bauteile verlängern.
- Schweißeignung: Im Gegensatz zu einigen hochlegierten Stählen lassen sich niedriglegierte Stähle relativ leicht schweißen und sind daher ideal für komplexe Konstruktionen.
- Kostengünstig: Niedrig legierte Stahlpulver bieten eine kostengünstige Lösung, ohne Kompromisse bei der Leistung einzugehen.
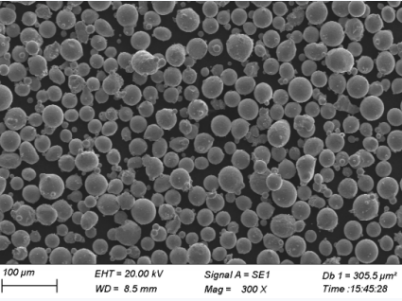
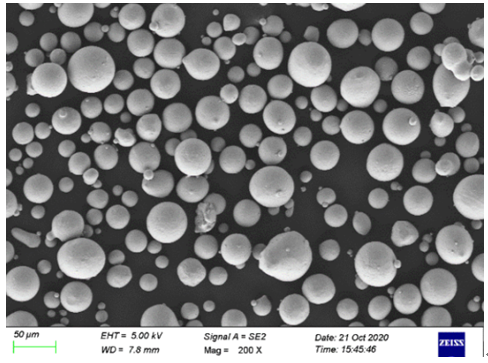



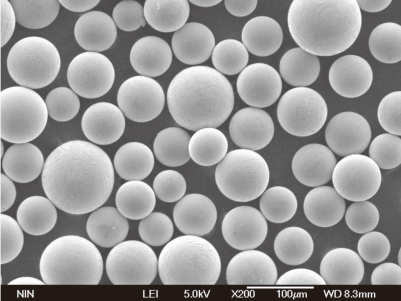
Vergleichstabelle der Merkmale
| Charakteristisch | Beschreibung | Vorteile | Beschränkungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stärke | Hohe Zugfestigkeit | Geeignet für Schwerlastanwendungen | Kann eine Wärmebehandlung erfordern |
| Zähigkeit | Fähigkeit, Stößen standzuhalten | Ideal für Strukturbauteile | Nimmt mit höherem Kohlenstoffgehalt ab |
| Verschleißfestigkeit | Widerstandsfähigkeit gegen Abrieb | Verlängert die Lebensdauer der Komponenten | Kann eine Legierung mit härteren Elementen erfordern |
| Schweißeignung | Einfaches Schweißen | Vereinfacht die Herstellung | Erfordert Wärmebehandlung vor/nach dem Schweißen |
| Kosten-Wirksamkeit | Erschwingliche Materialkosten | Reduziert die Gesamtproduktionskosten | Kann zusätzliche Bearbeitung erfordern |
Vorteile von niedriglegierten Stählen in Pulverform
Pulver aus niedrig legierten Stählen bietet eine Reihe von Vorteilen, die es zu einer attraktiven Wahl für verschiedene Branchen machen:
- Vielseitigkeit: Geeignet für eine breite Palette von Anwendungen, von der Automobilindustrie bis zur Luft- und Raumfahrt.
- Langlebigkeit: Verbesserte Verschleiß- und Korrosionsbeständigkeit sorgen für eine lang anhaltende Leistung.
- Anpassungen: Durch die Möglichkeit, die Zusammensetzung individuell anzupassen, können bestimmte mechanische Eigenschaften erzielt werden.
- Kosteneffizienz: Bietet ein ausgewogenes Verhältnis zwischen Leistung und Kosten und ist damit eine wirtschaftliche Wahl für Hersteller.
Anwendungen von niedriglegierten Stählen in Pulverform
Niedriglegierte Stahlpulver werden aufgrund ihrer einzigartigen Eigenschaften in zahlreichen Branchen eingesetzt. Im Folgenden wird ein detaillierter Blick auf einige der häufigsten Anwendungen geworfen.
| Industrie | Anmeldung | Warum niedrig legierter Stahl? |
|---|---|---|
| Automobilindustrie | Zahnräder, Wellen, Kurbelwellen | Hohe Festigkeit, Ermüdungsbeständigkeit |
| Luft- und Raumfahrt | Strukturelle Komponenten, Fahrwerk | Zähigkeit, geringes Gewicht |
| Öl & Gas | Bohrer, Pipelines | Abriebfestigkeit, Zähigkeit |
| Verteidigung | Panzerplatten, Waffen | Hohe Festigkeit, Haltbarkeit |
| Bauwesen | Strukturelle Balken, Befestigungselemente | Schweißbarkeit, Festigkeit |
Spezifische Verwendungszwecke in der Industrie
| Industrie | Spezifische Verwendung | Modell Beispiel |
|---|---|---|
| Automobilindustrie | Kurbelwellen | AISI 4340 |
| Luft- und Raumfahrt | Fahrwerk | AISI 4130 |
| Öl & Gas | Bohrer | AISI 8620 |
| Verteidigung | Panzerplatten | AISI 5140 |
| Bauwesen | Strukturelle Balken | AISI 6150 |
Spezifikationen, Größen, Güteklassen und Normen
Bei der Auswahl von niedrig legierten Stahlpulvern ist es wichtig, die Spezifikationen, Größen, Güten und Normen zu berücksichtigen, die für Ihren speziellen Anwendungsfall gelten. Nachstehend finden Sie eine Tabelle, die diese Aspekte zusammenfasst.
| Klasse | Spezifikation | Größenbereich (µm) | Normen |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 4130 | ASTM A829 | 10-100 | ASTM, ISO |
| AISI 4340 | AMS 6415 | 15-150 | AMS, ASTM |
| AISI 6150 | ASTM A231 | 20-200 | ASTM, ISO |
| AISI 8620 | AMS 6274 | 10-120 | AMS, SAE |
| AISI 5140 | ASTM A322 | 15-180 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 5120 | ASTM A29 | 10-100 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 50B44 | ASTM A331 | 20-160 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 5145 | ASTM A108 | 10-120 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 5160 | ASTM A689 | 15-150 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 52100 | AMS 6440 | 10-110 | AMS, SAE |
Lieferanten und Preisgestaltung von Niedrig legierte Stähle Pulver
Preis- und Lieferanteninformationen sind für Hersteller, die niedrig legierte Stahlpulver beziehen möchten, von entscheidender Bedeutung. Nachstehend finden Sie eine Übersicht über einige der führenden Anbieter und deren Richtpreise.
| Anbieter | Standort | Modell verfügbar | Preis pro kg (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hoganas AB | Schweden | AISI 4340, AISI 8620 | $15 – $25 |
| GKN Hoeganaes | USA | AISI 4130, AISI 6150 | $12 – $22 |
| Sandvik Werkstofftechnik | Schweden | AISI 5140, AISI 52100 | $18 – $30 |
| Tischlertechnik | USA | AISI 5120, AISI 5160 | $20 – $28 |
| Rio Tinto Metall-Pulver | Kanada | AISI 5145, AISI 50B44 | $14 – $26 |
Vergleich von niedrig legierten Stählen Pulver
Die Wahl des richtigen niedrig legierten Stahlpulvers kann eine Herausforderung sein, insbesondere wenn man verschiedene Faktoren wie Kosten, Verfügbarkeit und spezifische Eigenschaften berücksichtigt. Im Folgenden finden Sie einen Vergleich, der Ihnen helfen soll, eine fundierte Entscheidung zu treffen.
| Parameter | AISI 4130 | AISI 4340 | AISI 8620 | AISI 5140 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stärke | Hoch | Sehr hoch | Mäßig | Hoch |
| Zähigkeit | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch | Mäßig |
| Verschleißfestigkeit | Mäßig | Hoch | Mäßig | Hoch |
| Schweißeignung | Gut | Messe | Ausgezeichnet | Gut |
| Kosten | Mäßig | Hoch | Niedrig | Mäßig |

Vorteile und Grenzen von niedrig legierten Stählen - Pulver
Um das richtige Material für Ihre Anwendung auszuwählen, ist es wichtig, die Vorteile und Grenzen von niedrig legierten Stahlpulvern zu kennen. Nachstehend finden Sie eine Tabelle, die diese Aspekte zusammenfasst.
| Vorteile | Beschränkungen |
|---|---|
| Hohe Festigkeit: Bietet eine robuste strukturelle Integrität. | Wärmebehandlung erforderlich: Kann zusätzliche Bearbeitung erfordern. |
| Gute Zähigkeit: Kann hohe Energie absorbieren, ohne zu zerbrechen. | Kosten: Einige Legierungen können teurer sein. |
| Abnutzungswiderstand: Verlängert die Lebensdauer der Komponenten. | Verfügbarkeit: Bestimmte Klassen können nur begrenzt verfügbar sein. |
| Schweißeignung: Leichtere Herstellung und Montage. | Komplexität: Erfordert eine sorgfältige Auswahl je nach Anwendung. |
| Anpassungen: Kann auf spezifische Bedürfnisse zugeschnitten werden. | Verarbeitung: Kann eine genaue Kontrolle während der Herstellung erfordern. |
FAQ
Wozu werden niedrig legierte Stahlpulver verwendet?
Niedrig legierte Stahlpulver werden in einer Vielzahl von Anwendungen eingesetzt, darunter Automobilkomponenten wie Getriebe und Kurbelwellen, Luft- und Raumfahrtstrukturen, Öl- und Gasanlagen, Verteidigungsmaterialien und Bauelemente.
Wie unterscheiden sich niedrig legierte Stähle von hoch legierten Stählen?
Niedriglegierte Stähle enthalten im Vergleich zu hochlegierten Stählen einen geringeren Anteil an Legierungselementen (in der Regel weniger als 8%), wodurch sie kostengünstiger und leichter zu schweißen sind, jedoch eine geringere Korrosionsbeständigkeit aufweisen.
Können niedrig legierte Stähle leicht geschweißt werden?
Ja, niedrig legierte Stähle sind im Allgemeinen gut schweißbar, insbesondere im Vergleich zu hoch legierten Stählen. Allerdings kann eine Wärmebehandlung vor und nach dem Schweißen erforderlich sein, um optimale Ergebnisse zu erzielen.
Welche Rolle spielt Chrom in niedrig legierten Stählen?
Chrom erhöht die Härte, die Verschleißfestigkeit und die Korrosionsbeständigkeit von niedrig legierten Stählen, was es zu einem entscheidenden Element in der Zusammensetzung vieler niedrig legierter Stahlpulver macht.
Wo kann ich Pulver aus niedrig legiertem Stahl kaufen?
Niedrig legierte Stahlpulver können von verschiedenen Anbietern wie Höganäs AB, GKN Hoeganaes, Sandvik Materials Technology, Carpenter Technology und Rio Tinto Metal Powders bezogen werden. Die Preise variieren je nach Sorte und Anbieter.