Flüssigmetall-Strahlen (LMJ) revolutioniert die Welt der Fertigung. Wenn Sie noch nichts davon gehört haben, keine Sorge, Sie sind nicht allein. Es ist wie ein verstecktes Juwel in der Welt der 3D-Drucktechnologien. In diesem Artikel tauchen wir tief in die Feinheiten von LMJ ein und erforschen die Komplexität, die Anwendungen und die Metallpulver, die dies alles möglich machen. Wir machen es unterhaltsam, fesselnd und, was am wichtigsten ist, leicht verständlich.
Überblick über das Flüssigmetallstrahlen (LMJ)
Stellen Sie sich vor, Sie könnten Metallteile mit der gleichen Leichtigkeit und Präzision drucken, mit der Tintenstrahldrucker Dokumente produzieren. Das ist das Versprechen des Liquid Metal Jetting. Beim Liquid Metal Jetting (LMJ) werden geschmolzene Metalltröpfchen präzise auf ein Substrat aufgebracht, wodurch komplexe 3D-Strukturen Schicht für Schicht aufgebaut werden. Diese Methode gewinnt aufgrund ihres Potenzials für hohe Auflösung und Materialeffizienz zunehmend an Bedeutung.
Wichtige Details
| Aspekt | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| Technologie | Additive Fertigung |
| Material | Geschmolzene Metallpulver |
| Prozess | Tröpfchenabscheidung |
| Anwendungen | Luft- und Raumfahrt, Medizin, Automobil, Elektronik |
| Vorteile | Hohe Präzision, Materialeffizienz, komplexe Geometrien |
| Beschränkungen | Ausrüstungskosten, Materialbeschränkungen, erforderliches technisches Fachwissen |

Arten und Merkmale von Flüssigmetall-Strahlen (LMJ) Metall-Pulver
Um das Beste aus LMJ herauszuholen, ist die Wahl des Metallpulvers entscheidend. Wir wollen uns mit einigen spezifischen Metallpulvern befassen und ihre einzigartigen Eigenschaften verstehen.
Häufige Metallpulver in LMJ verwendet
| Metall-Pulver | Zusammensetzung | Eigenschaften | Merkmale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titan (Ti) | Reines Titan | Hohe Festigkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Leicht, biokompatibel |
| rostfreier Stahl | Eisen, Chrom, Nickel | Langlebig, korrosionsbeständig | Hohe Festigkeit, hitzebeständig |
| Aluminium (Al) | Reines Aluminium | Leichtes Gewicht, gute Wärmeleitfähigkeit | Hohe Zerspanbarkeit, nicht magnetisch |
| Nickellegierung | Nickel, Chrom, Eisen | Hohe Temperaturbeständigkeit | Hohe Festigkeit, korrosionsbeständig |
| Kupfer (Cu) | Reines Kupfer | Ausgezeichnete elektrische Leitfähigkeit | Duktil, hohe Wärmeleitfähigkeit |
| Kobalt-Chrom | Kobalt, Chrom | Verschleißfest, hohe Festigkeit | Biokompatibel, hohe Härte |
| Gold (Au) | Reines Gold | Hohe elektrische Leitfähigkeit, duktil | Korrosionsbeständig, biokompatibel |
| Silber (Ag) | Reines Silber | Beste elektrische Leitfähigkeit | Duktil, antibakterielle Eigenschaften |
| Inconel | Nickel-Chrom-Legierung | Oxidationsbeständigkeit, hohe Festigkeit | Hohe Temperaturbeständigkeit |
| Tungsten (W) | Pure tungsten | Höchster Schmelzpunkt | Hohe Dichte, strahlenabschirmende Eigenschaften |
Anwendungen von LMJ Metallpulvern
| Metall-Pulver | Anwendungen |
|---|---|
| Titan (Ti) | Teile für die Luft- und Raumfahrt, medizinische Implantate |
| rostfreier Stahl | Automobilkomponenten, Werkzeugbau |
| Aluminium (Al) | Leichte Strukturkomponenten |
| Nickellegierung | Gasturbinen, Chemische Verarbeitung |
| Kupfer (Cu) | Elektrische Steckverbinder, Wärmetauscher |
| Kobalt-Chrom | Zahnimplantate, Orthopädische Implantate |
| Gold (Au) | Elektronik, Medizinische Geräte |
| Silber (Ag) | Antibakterielle Beschichtungen, Elektronik |
| Inconel | Luft- und Raumfahrt, Energieerzeugung |
| Tungsten (W) | Luft- und Raumfahrt, Verteidigung |
Merkmale und Eigenschaften
- Titan (Ti): Es ist bekannt für sein gutes Verhältnis von Festigkeit zu Gewicht und seine hervorragende Korrosionsbeständigkeit, wodurch es sich ideal für Anwendungen in der Luft- und Raumfahrt sowie in der Medizin eignet.
- Rostfreier Stahl: Ein vielseitiges Metall mit hoher Festigkeit und Korrosionsbeständigkeit, das in der Automobilindustrie und in industriellen Anwendungen weit verbreitet ist.
- Aluminium (Al): Aluminium ist leicht und wärmeleitend und eignet sich daher perfekt für Anwendungen, bei denen Gewichtseinsparungen und Wärmeableitung erforderlich sind.
- Nickel-Legierung: Diese Legierungen bieten eine ausgezeichnete Hochtemperaturfestigkeit und Oxidationsbeständigkeit und sind daher für raue Umgebungen geeignet.
- Kupfer (Cu): Mit seiner hervorragenden elektrischen und thermischen Leitfähigkeit ist Kupfer für elektrische Anwendungen unverzichtbar.
- Kobalt-Chrom: Diese Legierung ist extrem verschleißfest und stabil und eignet sich aufgrund ihrer Biokompatibilität für medizinische Implantate.
- Gold (Au): Gold ist hoch leitfähig und biokompatibel und wird in der Elektronik und in medizinischen Geräten verwendet.
- Silber (Ag): Als bester elektrischer Leiter und mit seinen antibakteriellen Eigenschaften wird Silber in der Spezialelektronik und in der Medizin eingesetzt.
- Inconel: Bekannt für seine hohe Festigkeit und Oxidationsbeständigkeit bei hohen Temperaturen, wird es in der Luft- und Raumfahrt und bei der Energieerzeugung eingesetzt.
- Wolfram (W): Wolfram hat den höchsten Schmelzpunkt aller Metalle und wird für Anwendungen verwendet, die eine hohe Dichte und Temperaturbeständigkeit erfordern.



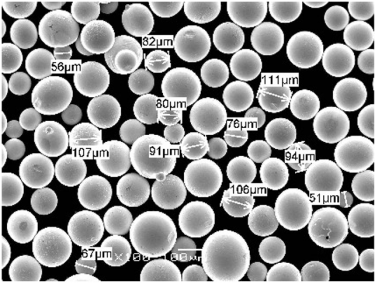
Spezifikationen, Größen, Güteklassen, Normen
| Metall-Pulver | Spezifikationen | Größen | Klassen | Normen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titan (Ti) | ASTM B348, AMS 4928 | -325 Maschen | Klasse 1-5 | ASTM, ISO, AMS |
| rostfreier Stahl | ASTM A276, AISI 316L | -325 Maschen | 316L, 304, 17-4PH | ASTM, ISO, AISI |
| Aluminium (Al) | ASTM B209, AMS 4037 | -325 Maschen | 6061, 7075 | ASTM, ISO, AMS |
| Nickellegierung | ASTM B637, AMS 5662 | -325 Maschen | Inconel 718, 625 | ASTM, ISO, AMS |
| Kupfer (Cu) | ASTM B216, ASTM B152 | -325 Maschen | C11000, C10100 | ASTM, ISO, UNS |
| Kobalt-Chrom | ASTM F1537, ISO 5832-12 | -325 Maschen | CoCrMo | ASTM, ISO |
| Gold (Au) | ASTM B562 | -325 Maschen | 99.99% rein | ASTM |
| Silber (Ag) | ASTM B700 | -325 Maschen | 99.99% rein | ASTM |
| Inconel | ASTM B637, AMS 5662 | -325 Maschen | 718, 625 | ASTM, ISO, AMS |
| Tungsten (W) | ASTM B777 | -325 Maschen | 99.95% Rein | ASTM, ISO |
Anwendungen von Flüssigmetall-Strahlen (LMJ)
LMJ hat dank seiner Fähigkeit, komplexe Geometrien mit hoher Präzision herzustellen, ein breites Anwendungsspektrum in verschiedenen Branchen.
LMJ Anwendungen und Einsatzmöglichkeiten
| Industrie | Anmeldung |
|---|---|
| Luft- und Raumfahrt | Motorkomponenten, Strukturteile |
| Medizinische | Implantate, Prothetik, Chirurgische Instrumente |
| Automobilindustrie | Motorenteile, kundenspezifische Komponenten |
| Elektronik | Kühlkörper, Schaltungskomponenten |
| Werkzeugbau | Formen, Matrizen, Schneidwerkzeuge |
| Schmuck | Kundenspezifische Entwürfe, Prototypen |
| Verteidigung | Waffenteile, Schutzausrüstung |
| Energie | Turbinenschaufeln, Wärmetauscher |
Vorteile von LMJ
Warum schlägt LMJ in der Fertigungsindustrie Wellen? Hier sind einige wichtige Vorteile:
- Hohe Präzision: LMJ kann komplizierte und präzise Geometrien herstellen, die mit herkömmlichen Fertigungsmethoden nur schwer zu erreichen sind.
- Materialeffizienz: Da LMJ nur die notwendige Menge an Material verwendet, wird der Abfall auf ein Minimum reduziert, was es zu einer kosteneffizienten und umweltfreundlichen Option macht.
- Komplexe Geometrien: Der schichtweise Aufbau ermöglicht die Schaffung komplexer Strukturen, die mit herkömmlichen Techniken nicht möglich sind.
- Vielseitigkeit: LMJ kann mit einer Vielzahl von Metallen verwendet werden und eignet sich daher für eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen in unterschiedlichen Branchen.
Beschränkungen von LMJ
Trotz seiner vielen Vorteile hat LMJ auch einige Einschränkungen:
- Kosten der Ausrüstung: Die Anfangsinvestitionen für LMJ-Ausrüstung können hoch sein, was für kleine Unternehmen ein Hindernis darstellen kann.
- Materielle Zwänge: Nicht alle Metalle sind für LMJ geeignet, und einige erfordern besondere Verarbeitungsbedingungen.
- Technisches Fachwissen: Die Bedienung und Wartung der LMJ-Ausrüstung erfordert spezielle Kenntnisse und Fähigkeiten.
Tabelle: Vor- und Nachteile von LMJ
| Aspekt | Profis | Nachteile |
|---|---|---|
| Präzision | Hoch | – |
| Materialeffizienz | Geringer Abfall | – |
| Komplexität | Kann komplexe Geometrien erstellen | – |
| Kosten | – | Hohe Anfangsinvestition |
| Material Vielseitigkeit | Arbeitet mit verschiedenen Metallen | Einige Metalle sind nicht geeignet |
| Technisches Geschick | – | Erfordert spezielles Fachwissen |
Lieferanten und Preise von LMJ-Metallpulvern
Die Wahl des richtigen Lieferanten ist für LMJ-Betriebe entscheidend. Hier finden Sie eine Liste einiger namhafter Lieferanten und deren Preisangaben.
Tabelle: LMJ-Metallpulver-Lieferanten und Preisgestaltung
| Anbieter | Metall-Pulver | Preis (pro kg) | Kontakt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hoganas AB | rostfreier Stahl | $80 | www.hoganas.com |
| Tischlertechnik | Titan, Nickellegierung | 150 $ (Ti), 200 $ (Ni) | www.cartech.com |
| LPW-Technologie | Aluminium, Inconel | $100 (Al), $250 (In) | www.lpwtechnology.com |
| GKN-Zusatzstoff | Kupfer, Kobalt-Chrom | 90 $ (Cu), 300 $ (CoCr) | www.gkn.com/en/our-divisions/gkn-additive |
| Arcam AB | Titan, rostfreier Stahl | $160 (Ti), $85 (SS) | www.arcam.com |
| Tekna | Wolfram, Aluminium | 400 $ (W), 110 $ (Al) | www.tekna.com |
| HC Starck | Gold, Silber | $50.000 (Au), $1.200 (Ag) | www.hcstarck.com |
Vergleich von Metallpulvern für LMJ
Die Wahl des richtigen Metallpulvers hängt von den spezifischen Anforderungen der jeweiligen Anwendung ab. Hier ein vergleichender Blick auf verschiedene Metallpulver, die in der LMJ verwendet werden.
Tabelle: Vergleich von Metallpulvern
| Eigentum | Titan (Ti) | rostfreier Stahl | Aluminium (Al) | Nickellegierung | Kupfer (Cu) | Kobalt-Chrom | Gold (Au) | Silber (Ag) | Inconel | Tungsten (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stärke | Hoch | Hoch | Mittel | Sehr hoch | Mittel | Sehr hoch | Mittel | Niedrig | Sehr hoch | Sehr hoch |
| Dichte | Niedrig | Mittel | Niedrig | Hoch | Mittel | Hoch | Hoch | Mittel | Hoch | Sehr hoch |
| Leitfähigkeit | Mittel | Niedrig | Hoch | Niedrig | Sehr hoch | Niedrig | Sehr hoch | Sehr hoch | Niedrig | Niedrig |
| Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Hoch | Hoch | Mittel | Hoch | Mittel | Hoch | Sehr hoch | Hoch | Hoch | Hoch |
| Kosten | Hoch | Niedrig | Niedrig | Hoch | Mittel | Hoch | Sehr hoch | Hoch | Hoch | Mittel |

FAQ
| Frage | Antwort |
|---|---|
| Was ist Liquid Metal Jetting (LMJ)? | LMJ ist ein additives Fertigungsverfahren, bei dem geschmolzene Metalltröpfchen aufgebracht werden, um 3D-Strukturen Schicht für Schicht aufzubauen. |
| Welche Metalle können in LMJ verwendet werden? | Verwendet werden können Metalle wie Titan, Edelstahl, Aluminium, Nickellegierungen, Kupfer, Kobalt-Chrom, Gold, Silber, Inconel und Wolfram. |
| Was sind die Vorteile von LMJ? | Hohe Präzision, Materialeffizienz, Fähigkeit zur Herstellung komplexer Geometrien und Vielseitigkeit bei der Verwendung verschiedener Metalle. |
| Was sind die Grenzen von LMJ? | Hohe Ausrüstungskosten, Materialbeschränkungen und der Bedarf an speziellem technischem Fachwissen. |
| Wie schneidet LMJ im Vergleich zu anderen 3D-Drucktechnologien ab? | LMJ bietet eine höhere Präzision und Materialeffizienz, erfordert aber im Vergleich zu anderen Verfahren eine höhere Anfangsinvestition und mehr technisches Wissen. |
| Wo wird LMJ üblicherweise verwendet? | LMJ wird in Branchen wie Luft- und Raumfahrt, Medizintechnik, Automobilbau, Elektronik, Werkzeugbau, Schmuck, Verteidigung und Energie eingesetzt. |
| Welche Faktoren sollten bei der Auswahl eines Metallpulvers für LMJ berücksichtigt werden? | Zu den Faktoren gehören die erforderliche Festigkeit, Dichte, Leitfähigkeit, Korrosionsbeständigkeit und die Kosten des Metallpulvers. |
| Wer sind einige namhafte Lieferanten von LMJ-Metallpulvern? | Zu den namhaften Lieferanten gehören Höganäs AB, Carpenter Technology, LPW Technology, GKN Additive, Arcam AB, Tekna und HC Starck. |
| Wie hoch sind die Kosten für LMJ-Metallpulver? | Die Kosten sind je nach Metall sehr unterschiedlich und reichen von 80 Dollar pro Kilogramm für rostfreien Stahl bis zu 50.000 Dollar pro Kilogramm für Gold. |
| Kann LMJ für die Massenproduktion verwendet werden? | LMJ eignet sich zwar für die Herstellung von Hochpräzisionsteilen, ist aber aufgrund der hohen Ausrüstungskosten im Allgemeinen eher für die Kleinserienfertigung und das Prototyping geeignet. |

