Übersicht
Reines Kupfer (Cu)-Pulver ist ein Metallpulver, das wegen seiner hervorragenden Leitfähigkeit, Formbarkeit und Vielseitigkeit in industriellen Anwendungen sehr geschätzt wird. Aufgrund seiner hohen Reinheit, Reines Cu-Pulver ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil in Bereichen wie Elektronik, Metallurgie, additive Fertigung und chemische Prozesse. Mit einer typischen Zusammensetzung von mehr als 99,5% reinem Kupfer bietet diese Pulverform von Kupfer Ingenieuren, Herstellern und Forschern ein wertvolles Material mit einzigartigen Eigenschaften.
Was macht reines Cu-Pulver so wertvoll? Seine Kombination von Eigenschaften: hohe elektrische und thermische Leitfähigkeit, Duktilität und die Fähigkeit, mit anderen Materialien gemischt oder in eine Vielzahl von Formen gegossen zu werden. Ganz gleich, ob Sie komplizierte elektronische Komponenten oder robuste Konstruktionsteile herstellen möchten, Reines Kupferpulver ist eine flexible und leistungsstarke Option.

Zusammensetzung von reinem Cu-Pulver
Reines Cu-Pulver besteht hauptsächlich aus Kupfer (Cu) in fein gemahlener Form. Je nach Anwendung kann es jedoch kleine Abweichungen in Bezug auf Reinheitsgrad, Partikelgröße und Form geben, so dass die Hersteller das Pulver auf spezifische Anforderungen zuschneiden können. Hier ist eine Aufschlüsselung:
| Komponente | Typische Zusammensetzung (%) |
|---|---|
| Kupfer (Cu) | ≥ 99.5 |
| Sauerstoff (O) | < 0.3 |
| Eisen (Fe) | < 0.05 |
| Andere Verunreinigungen | < 0.15 |
Dieser Reinheitsgrad gewährleistet eine optimale Leistung, insbesondere bei elektronischen und leitenden Anwendungen, bei denen die elektrischen Eigenschaften von Kupfer entscheidend sind. Die meisten Reinkupferpulver werden mit Hilfe von Zerstäubungstechniken verarbeitet, die eine präzise Kontrolle der Partikelgröße und -form ermöglichen und somit Eigenschaften wie Fließfähigkeit und Kompressibilität beeinflussen.
Merkmale von Reines Cu-Pulver
Um die Fähigkeiten von reinem Cu-Pulver voll ausschöpfen zu können, müssen wir seine wichtigsten Eigenschaften untersuchen. Jede Eigenschaft spielt eine wichtige Rolle und beeinflusst das Verhalten des Pulvers in verschiedenen Anwendungen.
| Charakteristisch | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| Elektrische Leitfähigkeit | Die Leitfähigkeit von Kupfer ist die zweithöchste nach der von Silber, wodurch reines Cu-Pulver in der Elektronik und im Wärmemanagement sehr effektiv ist. |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit | Mit seiner ausgezeichneten Wärmeleitfähigkeit leitet reines Cu-Pulver die Wärme effizient ab, was in der Elektronik und in Wärmetauschern von entscheidender Bedeutung ist. |
| Duktilität | Dank seiner Duktilität lässt sich reines Cu-Pulver formen und umformen, ohne zu brechen - ideal für die additive Fertigung und Metallurgie. |
| Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Während Kupfer an der Oberfläche eine Oxidschicht bildet, ist Pure Cu Powder resistent gegen tiefere Korrosion und schützt die Kernfunktionen in verschiedenen Umgebungen. |
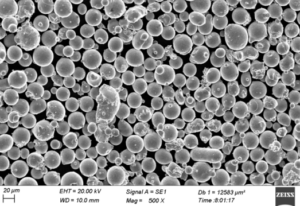
| Morphologie der Partikel | Die Morphologie, in der Regel kugelförmig oder unregelmäßig, beeinflusst die Fließfähigkeit, die Dichte und die Art und Weise, wie sich das Pulver in Formen oder Additivierungsverfahren mischt oder verpackt. |
| Dichte | Reines Cu-Pulver hat eine Dichte von ca. 8,96 g/cm³, was sich auf die Vermischung oder Verdichtung auswirken kann, insbesondere bei Anwendungen mit hoher Dichte. |
| Schmelzpunkt | Kupfer schmilzt bei 1.084 °C und ist damit hochtemperaturstabil, was für Sinter- und Metallspritzgussverfahren unerlässlich ist. |
Partikelform und -größe in reinem Cu-Pulver
Form und Größe der Partikel in reinem Cu-Pulver können variieren und sich auf Eigenschaften wie Fließgeschwindigkeit, Kompressibilität und sogar das Sinterverhalten auswirken. Hier sind die häufigsten Formen und ihre Auswirkungen:
| Partikelform | Beschreibung | Anwendungen |
|---|---|---|
| Sphärisch | Sorgt für gleichmäßigen Fluss und Packungsdichte, ideal für 3D-Druck und Beschichtungen. | Wird häufig in der Pulvermetallurgie und der additiven Fertigung für eine gleichmäßige Schichtabscheidung verwendet. |
| Unregelmäßig | Bietet eine größere Oberfläche, die die Bindung in Verbundwerkstoffen oder Mischungen verbessert. | Bevorzugt für Anwendungen, bei denen eine starke Verbindung oder mechanische Verriegelung mit anderen Materialien erforderlich ist. |
| Flocke | Dünne, flache Partikel, die den Oberflächenkontakt maximieren. | Wird häufig in leitfähigen Beschichtungen und Farben verwendet, wo Deckkraft und Leitfähigkeit entscheidend sind. |
Anwendungen von reinem Cu-Pulver
Reines Cu-Pulver kommt in einer Vielzahl von Branchen zum Einsatz, die sich alle seine spezifischen Eigenschaften zunutze machen. Hier ist ein Blick auf seine wichtigsten Anwendungen:
| Industrie | Anmeldung | Warum reines Cu-Pulver? |
|---|---|---|
| Elektronik | Leitfähige Druckfarben, gedruckte Schaltungen und EMI-Abschirmung | Die Leitfähigkeit von Kupfer ist ideal für elektronische Präzisionsbauteile. |
| Metallurgie | Pulvermetallurgie, Sintern und Löten | Die Pulverform ermöglicht das Formen und Verdichten in komplexen Formen mit ausgezeichneter mechanischer Festigkeit. |
| Additive Fertigung | 3D-Druck von Funktionsteilen und Prototypen | Die Fließfähigkeit und Formbarkeit von reinem Cu-Pulver eignet sich für die Herstellung komplizierter Designs und die strukturelle Integrität. |
| Automobilindustrie | Wärmesenken, Reibmaterialien und Brennstoffzellen | Reines Cu-Pulver leitet Wärme effektiv ab und ist daher eine ausgezeichnete Wahl für das Wärmemanagement und Energielösungen in der Automobilindustrie. |
| Chemische Industrie | Katalysatoren und leitfähige Beschichtungen | Die Reaktivität von Kupfer mit bestimmten Verbindungen und seine hervorragende Leitfähigkeit verbessern die chemischen Reaktionen und die Haltbarkeit der Produkte. |
| Medizinische Geräte | Antimikrobielle Oberflächen und Implantate | Kupfer hat natürliche antimikrobielle Eigenschaften, die für medizinische Geräte zur Verringerung des Infektionsrisikos wichtig sind. |

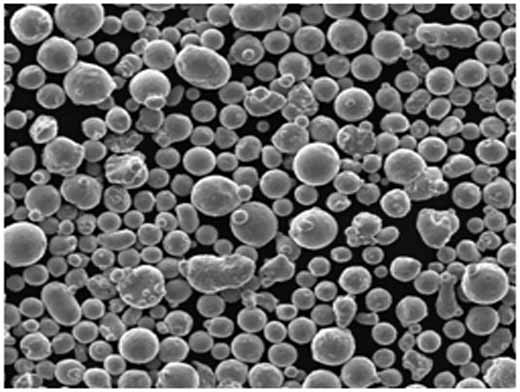



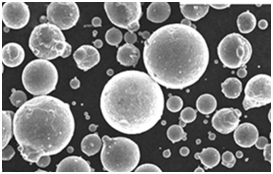
Spezifikationen, Größen, Qualitäten und Normen für reines Kupferpulver
Die Kenntnis der Spezifikationen, Größen, Qualitäten und Standards von reinem Cu-Pulver kann Ihnen bei der Auswahl des richtigen Materials für ein bestimmtes Projekt helfen. Reinheit, Partikelgröße und Form beeinflussen die Leistung bei jeder Anwendung erheblich.
| Spezifikation | Einzelheiten |
|---|---|
| Reinheit | ≥ 99,5% (oft bis zu 99,9% für High-End-Anwendungen) |
| Partikelgröße | Bereiche von Nanoskala (<100 nm) bis Mikrometer (bis zu 100 μm) |
| Dichte | 8,96 g/cm³ |
| Schmelzpunkt | 1,084°C |
| Leitfähigkeit | Ungefähr 5,96 x 10^7 S/m |
| Standard-Grade | ASTM B212, ASTM B848, ISO 4287 |
| Morphologie | Erhältlich in kugelförmigen, flockigen und unregelmäßigen Formen |
Jede dieser Qualitäten und Spezifikationen entspricht internationalen Normen wie ASTM und ISO und stellt sicher, dass das Pulver hohe Anforderungen erfüllt. Hier finden Sie eine Übersicht über die gängigen Größen und Qualitäten:
Gängige Größen und Qualitäten
| Klasse | Reinheit (%) | Typischer Partikelgrößenbereich (μm) | Am besten für Anwendungen |
|---|---|---|---|
| CP1 | 99.5 | 10-45 | Leitfähige Druckfarben, gedruckte Schaltungen |
| CP2 | 99.8 | 20-60 | Pulvermetallurgie, Sintern |
| CP3 | 99.9 | 1-15 | Katalysatoren, Spezialbeschichtungen |
| Nano-Cu | 99.9 | <0.1 | Fortgeschrittene Elektronik, Nanotechnologie |
| Flocke Cu | 99.5 | 15-45 | Leitfähige Lacke, EMI-Abschirmung |
| Sphärisches Cu | 99.7 | 20-100 | Additive Fertigung, 3D-Druck |
Vorteile und Grenzen von reinem Cu-Pulver
Die Wahl von reinem Cu-Pulver gegenüber anderen Metallpulvern wie Silber, Aluminium oder sogar Nickel bringt einzigartige Vorteile mit sich, aber es gibt auch einige Einschränkungen zu beachten. Hier ist eine vergleichende Analyse:
| Aspekt | Vorteile von reinem Cu-Pulver | Grenzen von reinem Cu-Pulver |
|---|---|---|
| Leitfähigkeit | Hervorragende elektrische und thermische Leitfähigkeit (ähnlich wie Silber) | Niedriger als Silber, aber viel höher als Aluminium oder Nickel |
| Kosten | Günstiger als Silber bei vergleichbarer Leitfähigkeit | Teurer als Aluminium, insbesondere bei hochreinen Sorten |
| Verformbarkeit | Hochgradig dehnbar, daher geeignet zum Gießen und Formen | Verformbarkeit kann zu Verformung unter Belastung führen |
| Korrosionsbeständigkeit | Gute Korrosionsbeständigkeit in nicht-sauren Umgebungen | Anfällig für Oxidation, die die Leitfähigkeit der Oberfläche beeinträchtigt |
| Verfügbarkeit | In verschiedenen Qualitäten, Partikelgrößen und Formen erhältlich | Einige spezielle Größen und Formen können teurer sein |
| Reaktivität | Weniger reaktiv als andere Metalle in gemäßigten Umgebungen | Kann mit bestimmten Chemikalien reagieren, was seine Verwendung in einigen Anwendungen einschränkt |
Top-Modelle von reinem Cu-Pulver und ihre spezifischen Anwendungen
Sehen wir uns einige der derzeit erhältlichen Spitzenmodelle von Pure Cu Powder an, die jeweils für bestimmte industrielle Anwendungen entwickelt wurden. Jedes Modell bietet einzigartige Eigenschaften, die auf die Anforderungen bestimmter Prozesse zugeschnitten sind, vom hochpräzisen 3D-Druck bis hin zu leitfähigen Beschichtungen und Hochleistungselektronik.
| Modell | Reinheit | Partikelgröße (μm) | Form | Ideale Anwendungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-Pulver CP1 | 99.5% | 10-45 | Unregelmäßig | Leitfähige Druckfarben, gedruckte Schaltungen und grundlegende elektronische Anwendungen |
| Cu-Pulver CP2 | 99.8% | 20-60 | Sphärisch | Aufgrund seiner Fließfähigkeit für die Pulvermetallurgie und Sinterung geeignet |
| Cu-Pulver CP3 | 99.9% | 1-15 | Feiner Flake | Hochwertige leitfähige Beschichtungen und spezialisierte elektronische Komponenten |
| Nano-Cu 99,9 | 99.9% | <0.1 | Nano | Moderne elektronische Geräte, Sensoren, Nanotechnologie und Katalyse |
| Cu-Sph 45 | 99.7% | 15-45 | Sphärisch | 3D-Druck, additive Fertigung und Herstellung von Präzisionsteilen |
| Cu-Flocke 99,5 | 99.5% | 15-45 | Flocke | Leitfähige Farben, EMI-Abschirmung und Beschichtungen, die eine große Fläche abdecken müssen |
| Cu-Pulver 80 | 99.8% | 45-80 | Sphärisch | Aufgrund seiner Dichte und Festigkeit ideal für Strukturteile in der additiven Fertigung |
| Hochreines Cu 100 | 99.99% | 10-30 | Sphärisch | Hochleistungselektronik, insbesondere in empfindlichen oder miniaturisierten Geräten |
| Cu-Pulver M10 | 99.7% | 10-50 | Gemischt | Verwendung in Automobilteilen, Brennstoffzellen und Reibmaterialien |
| Cu-Katalysator 99,8 | 99.8% | 1-5 | Feines Puder | Spezialisiert auf die chemische und pharmazeutische Industrie für katalytische Anwendungen |
Lieferanten und Preisinformationen für Reines Cu-Pulver
Preisgestaltung und Verfügbarkeit der Lieferanten sind von entscheidender Bedeutung, wenn Sie die Verwendung von reinem Cu-Pulver in großen Mengen planen. Nachstehend finden Sie eine Tabelle, in der gängige Lieferanten, ihre Produkte und ungefähre Preisspannen verglichen werden, die je nach Menge und spezifischen Anforderungen an die Qualität variieren können.
| Anbieter | Modell Verfügbarkeit | Preisgestaltung (ungefähr) | Kommentare |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amerikanische Elemente | CP1, CP2, Nano-Cu, kugelförmig | $50-200/kg | Bekannt für hochreines Pulver; kundenspezifische Schlichtung |
| Goodfellow Gesellschaft | Hochreines Cu, Nano-Cu | $150-400/kg | High-End-Modelle für medizinische und fortschrittliche Elektronik |
| Metall-Pulver Co. Ltd. | CP3, Schuppe Cu | $70-150/kg | Bietet große Mengen und flexible Größenoptionen |
| SkySpring Nanomaterialien | Nano-Cu, hochreines Cu | $250-500/kg | Spezialisiert auf Nanomaterialien; Premiumpreise |
| Auswahlmöglichkeiten | Sphärisches Cu | $80-220/kg | Große Auswahl für additive Fertigungsanwendungen |
| Nanografi Nano Technologie | Cu-Katalysator, Nano-Cu | $200-450/kg | Bekannt für Pulver in Forschungsqualität mit hohem Reinheitsgrad |

FAQ
| Frage | Antwort |
|---|---|
| Wofür wird Pure Cu Powder verwendet? | Reines Cu-Pulver wird vor allem in der Elektronik, Metallurgie, additiven Fertigung, für Automobilteile und als Katalysator in der chemischen Industrie verwendet. |
| Warum wird Kupferpulver in der Elektronik bevorzugt? | Kupferpulver bietet eine hervorragende elektrische und thermische Leitfähigkeit, die für leitfähige Druckfarben, gedruckte Schaltungen und EMI-Abschirmung in elektronischen Bauteilen unerlässlich ist. |
| Wie wird reines Cu-Pulver hergestellt? | In der Regel wird es durch Zerstäubung hergestellt, wobei geschmolzenes Kupfer in feine Tröpfchen zerteilt wird, die abkühlen und sich in Pulverform verfestigen, wobei Größe und Form kontrolliert werden. |
| Welche Partikelformen gibt es, und warum sind sie wichtig? | Zu den verfügbaren Formen gehören kugelförmig, flockig und unregelmäßig. Kugelförmige Partikel fließen besser und sind dicht gepackt, ideal für den 3D-Druck, während Flocken eine größere Oberfläche für Beschichtungen bieten. |
| Was sind die Vorteile von hochreinem Kupferpulver? | Hochreines Kupferpulver (99,9% oder höher) bietet eine bessere Leitfähigkeit und weniger Verunreinigungen, was für empfindliche Anwendungen wie moderne Elektronik und Katalysatoren unerlässlich ist. |
| Ist Kupferpulver sicher in der Handhabung? | Ja, mit den üblichen Vorsichtsmaßnahmen wie dem Tragen von Handschuhen und Masken. Kupferpulver ist ungiftig, aber das Einatmen feiner Partikel kann gesundheitsschädlich sein, weshalb eine Staubkontrolle empfohlen wird. |
| Kann Kupferpulver oxidieren, und wie wirkt sich das auf die Anwendungen aus? | Ja, Kupferpulver kann oxidieren, insbesondere bei hoher Luftfeuchtigkeit. Die Oxidation kann sich auf die Leitfähigkeit auswirken, daher werden Pulver oft in sauerstoffarmen Umgebungen gelagert oder mit Schutzbeschichtungen behandelt. |
| Welches sind die wichtigsten Normen für Kupferpulver? | Zu den Normen gehören ASTM B212, ASTM B848 und ISO 4287, in denen Qualität, Reinheit, Partikelgröße und andere Spezifikationen festgelegt sind, die sicherstellen, dass das Produkt den industriellen Anforderungen entspricht. |
| Wie wird die Partikelgröße gemessen, und warum ist sie wichtig? | Die Partikelgröße wird mittels Laserbeugung oder Mikroskopie gemessen. Die Größe beeinflusst die Fließfähigkeit, die Packungsdichte und die Oberfläche und wirkt sich auf die Leistung in bestimmten Anwendungen aus. |
| Wo kann ich reines Cu-Pulver kaufen, und was sollte ich beachten? | Viele Anbieter wie American Elements, Goodfellow und Valimet bieten reines Cu-Pulver an. Achten Sie beim Kauf auf Reinheit, Partikelgröße, Verwendungszweck und den Ruf des Lieferanten. |
| Wie schneidet Kupferpulver im Vergleich zu anderen Metallpulvern wie Silber oder Nickel ab? | Kupfer ist hoch leitfähig und preiswerter als Silber. Es ist leitfähiger als Nickel, hat aber eine geringere Korrosionsbeständigkeit und eignet sich daher für kostensensible, leitfähige Anwendungen. |
| Kann reines Cu-Pulver für den 3D-Druck verwendet werden? | Unbedingt! Sphärisches Rein-Cu-Pulver wird aufgrund seiner ausgezeichneten Fließfähigkeit und Dichte häufig im 3D-Metalldruck verwendet und ist ideal für die Herstellung starker, detaillierter Teile. |
| Ist Kupferpulver recycelbar? | Ja, Kupferpulver ist recycelbar und damit umweltfreundlich. Schrott oder unbenutztes Pulver kann oft raffiniert und in anderen Anwendungen wiederverwendet werden. |