매혹적인 적층 제조(AM) 기계의 세계에 오신 것을 환영합니다! 이 놀라운 기기는 우리가 제품을 만들고, 디자인하고, 제조하는 방식을 혁신하고 있습니다. 디지털 모델에서 직접 금속, 플라스틱, 세라믹과 같은 재료를 사용하여 물체를 한 층씩 쌓아 올린다고 상상해 보세요. 공상 과학 소설처럼 들리나요? 지금 바로 현실에서 일어나고 있습니다!
이 문서에서는 다음과 같은 복잡한 사항을 자세히 살펴봅니다. AM 기계를 통해 마술의 응용 분야와 장점, 그리고 마술의 원동력이 되는 금속 분말에 대해 알아보세요. 사용되는 금속 분말의 종류, 구성, 특성 등을 살펴볼 것입니다. 이제 안전벨트를 매고 3D 프린팅 기계의 세계로 흥미진진한 여행을 떠날 준비를 하세요.
AM 장비 개요
일반적으로 3D 프린팅으로 알려진 적층 제조는 재료를 한 층씩 추가하여 물체를 만드는 방식입니다. 재료를 깎아내는(절단, 드릴링 등) 기존 제조 방식과 달리 적층 제조는 정밀도와 효율성이 핵심입니다. 이 기계는 항공우주, 자동차, 의료, 소비재 등 다양한 산업에서 사용됩니다.
AM 머신이란 무엇인가요?
3D 프린터는 디지털 디자인을 사용하여 물리적 물체를 레이어별로 제작하는 첨단 기기입니다. 금속, 폴리머, 세라믹 등 다양한 재료로 작업할 수 있습니다. 이 기계는 기존 제조 방식으로는 불가능한 복잡한 형상을 만들 수 있습니다.
AM 머신은 어떻게 작동하나요?
적층 가공 기계는 간단하면서도 정교한 프로세스를 따릅니다:
- 디자인: 컴퓨터 지원 설계(CAD) 소프트웨어를 사용하여 3D 모델을 생성합니다.
- 슬라이싱: 모델이 얇은 층으로 슬라이스됩니다.
- 인쇄: 기계는 디지털 청사진에 따라 머티리얼을 레이어별로 추가합니다.
- 후처리: 인쇄된 개체는 연마 또는 열처리와 같은 필요한 처리로 완성됩니다.
AM 장비의 이점
- 복잡한 지오메트리: 기존 방식으로는 구현할 수 없는 복잡한 디자인을 만들 수 있습니다.
- 재료 효율성: 감산 제조에 비해 낭비가 최소화됩니다.
- 사용자 지정: 개인화된 제품을 위한 디자인을 쉽게 수정할 수 있습니다.
- 속도: 신속한 프로토타이핑 및 생산.

적층 가공기의 종류
각각 고유한 기능과 애플리케이션을 갖춘 다양한 유형의 적층 제조기에 대해 자세히 알아보겠습니다.
1. 광조형(SLA)
SLA는 레이저를 사용하여 액체 수지를 고체 물체로 경화합니다. 매끄러운 표면을 가진 디테일한 프로토타입을 제작하는 데 이상적입니다.
2. 선택적 레이저 소결(SLS)
SLS는 레이저를 사용하여 분말 재료를 융합합니다. 다양한 재료로 내구성이 뛰어나고 기능적인 부품을 제작하는 데 적합합니다.
3. 용융 증착 모델링(FDM)
FDM은 열가소성 필라멘트를 녹여 압출하여 물체를 제작합니다. 취미 및 산업용 애플리케이션에 널리 사용됩니다.
4. 직접 금속 레이저 소결(DMLS)
DMLS는 레이저를 사용하여 금속 분말을 소결하여 강하고 복잡한 금속 부품을 만듭니다. 항공우주 및 의료 산업에서 널리 사용됩니다.
5. 전자 빔 용융(EBM)
EBM은 전자빔을 사용하여 금속 분말을 녹입니다. 고강도, 고온 애플리케이션에 적합합니다.
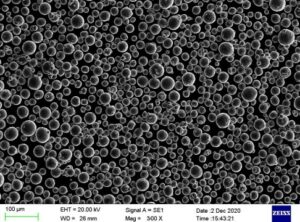
AM 장비용 금속 분말
금속 분말은 특히 고강도와 정밀도가 요구되는 산업에서 많은 적층 제조 공정의 핵심입니다. 다음은 적층 가공에 사용되는 주요 금속 분말입니다:
1. 티타늄 합금(Ti-6Al-4V)
설명: 티타늄 합금은 강도가 높고 무게가 가벼우며 내식성이 뛰어난 것으로 알려져 있습니다.
애플리케이션: 항공우주, 의료용 임플란트, 자동차.
속성: 높은 중량 대비 강도, 생체 적합성, 우수한 피로 저항성.
2. 스테인리스 스틸(316L)
설명: 내식성과 강도로 잘 알려진 다용도 합금.
애플리케이션: 의료 기기, 식품 가공, 화학 산업.
속성: 고강도, 내식성, 우수한 연성.
3. 인코넬(IN625)
설명: 고온 강도와 내식성이 뛰어난 니켈-크롬 초합금.
애플리케이션: 항공우주, 발전, 해양 산업.
속성: 고온 및 내산화성, 고강도.
4. 알루미늄 합금(AlSi10Mg)
설명: 가볍고 튼튼한 알루미늄 합금은 우수한 열 특성이 필요한 부품에 이상적입니다.
애플리케이션: 자동차, 항공우주, 소비자 가전.
속성: 높은 중량 대비 강도, 우수한 열전도율, 내식성.
5. 공구강(H13)
설명: 경도와 내마모성 및 내마모성으로 유명합니다.
애플리케이션: 툴링, 금형 및 금형.
속성: 높은 경도, 내마모성, 열 안정성.
6. 코발트-크롬(CoCr)
설명: 내마모성과 생체 적합성으로 잘 알려진 초합금.
애플리케이션: 의료용 임플란트, 치과 보철, 항공우주.
속성: 높은 내마모성, 우수한 생체 적합성, 고강도.
7. 구리 합금(CuCr1Zr)
설명: 구리 합금은 열 및 전기 전도성으로 인해 가치가 높습니다.
애플리케이션: 전기 부품, 열교환기, 로켓 엔진 부품.
속성: 높은 열 및 전기 전도성, 우수한 강도.
8. 마레이징 스틸(1.2709)
설명: 인성과 치수 안정성이 뛰어난 고강도 강철입니다.
애플리케이션: 항공우주, 툴링, 고성능 엔지니어링.
속성: 고강도, 우수한 인성, 우수한 용접성.
9. 니켈 합금(하스텔로이 X)
설명: 산화에 대한 내성과 고온 강도로 유명합니다.
애플리케이션: 항공우주, 화학 처리, 산업용 가스 터빈.
속성: 고온 강도, 내산화성, 내식성.
10. 텅스텐 카바이드(WC-Co)
설명: 매우 단단하고 내마모성이 뛰어나 까다로운 환경에서도 사용할 수 있습니다.
애플리케이션: 절삭 공구, 내마모성 부품, 채굴 장비.
속성: 높은 경도, 우수한 내마모성, 높은 열전도율.
금속 분말의 구성 및 특성
다음은 이러한 금속 분말의 구성과 특성에 대해 자세히 살펴보는 내용입니다:
| 금속 분말 | 구성 | 속성 |
|---|---|---|
| 티타늄 합금 | Ti, Al, V | 높은 중량 대비 강도, 생체 적합성 |
| 스테인리스 스틸 | Fe, Cr, Ni, Mo | 내식성, 우수한 연성 |
| 인코넬 | Ni, Cr, Mo, Nb | 고온 강도, 내산화성 |
| 알루미늄 합금 | Al, Si, Mg | 경량, 열 전도성, 내식성 |
| 공구강 | Fe, C, Cr, Mo | 경도, 내마모성, 열 안정성 |
| 코발트-크롬 | Co, Cr, Mo | 내마모성, 생체 적합성 |
| 구리 합금 | Cu, Cr, Zr | 열 및 전기 전도성, 강도 |
| 마레이징 스틸 | Fe, Ni, Co, Mo | 고강도, 인성, 용접성 |
| 니켈 합금 | Ni, Cr, Mo, Fe | 내산화성, 고온 강도 |
| 텅스텐 카바이드 | WC, Co | 경도, 내마모성, 열 전도성 |






금속 분말의 적층 제조 응용 분야
금속 분말의 다용도성 덕분에 적층 제조는 다양한 산업 분야에서 폭넓게 응용할 수 있습니다:
| 산업 | 애플리케이션 |
|---|---|
| 항공우주 | 엔진 부품, 구조 부품, 열교환기 |
| 의료 | 임플란트, 보철물, 수술 기구 |
| 자동차 | 경량 부품, 엔진 부품, 맞춤형 부품 |
| 전자 제품 | 방열판, 커넥터, 하우징 |
| 툴링 | 금형, 금형, 절삭 공구 |
| 에너지 | 터빈 블레이드, 열교환기, 발전 부품 |
| 소비재 | 주얼리, 안경, 맞춤형 디자인 제품 |
사양, 크기, 등급 및 표준
적층 제조용 금속 분말을 선택할 때는 사양, 크기, 등급 및 표준을 고려하는 것이 중요합니다:
| 금속 분말 | 사양 | 크기 | 성적 | 표준 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 티타늄 합금 | ASTM B348, AMS 4999 | 15-45µm, 45-106µm | Ti-6Al-4V ELI | ASTM F2924, ISO 5832-3 |
| 스테인리스 스틸 | ASTM A276, ASTM F138 | 10-50µm, 20-63µm | 316L, 17-4 PH | ASTM F138, ISO 5832-1 |
| 인코넬 | AMS 5666, UNS N06625 | 15-45µm, 20-60µm | IN625, IN718 | ASTM B443, AMS 5662 |
| 알루미늄 합금 | ASTM B209, AMS 4225 | 20-63µm, 10-50µm | AlSi10Mg, AlSi12 | ASTM B918, ISO 3522 |
| 공구강 | ASTM A681, AISI H13 | 15-45µm, 20-60µm | H13, D2 | ASTM A681, DIN 1.2344 |
| 코발트-크롬 | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-12 | 15-45µm, 10-50µm | CoCrMo, CoCrW | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-12 |
| 구리 합금 | ASTM B152, C18150 | 10-50µm, 15-45µm | CuCr1Zr, C18150 | ASTM B187, AMS 4980 |
| 마레이징 스틸 | AMS 6514, AISI 18Ni(300) | 10-45µm, 20-60µm | 1.2709, 18Ni(300) | AMS 6520, DIN 1.6358 |
| 니켈 합금 | ASTM B435, UN N06002 | 10-45µm, 20-60µm | 하스텔로이 X, N06002 | ASTM B435, AMS 5754 |
| 텅스텐 카바이드 | ISO 9001, ASTM B777 | 5-20µm, 10-45µm | WC-Co, 코발트 결합 | ISO 9001, ASTM B777 |
공급업체 및 가격 세부 정보
다음은 금속 분말의 주요 공급업체와 가격 세부 정보를 살펴봅니다:
| 공급업체 | 금속 분말 | 가격 범위(kg당) |
|---|---|---|
| 호가나스 AB | 스테인리스 스틸, 공구강 | $50 – $200 |
| 카펜터 기술 | 티타늄 합금, 인코넬 | $300 – $600 |
| 샌드빅 | 스테인리스 스틸, 마레이징 스틸 | $100 – $400 |
| LPW 기술 | 코발트-크롬, 인코넬 | $250 – $700 |
| GKN 첨가제 | 알루미늄 합금, 티타늄 합금 | $150 – $500 |
| AP&C(GE 애디티브) | 티타늄 합금, 알루미늄 합금 | $200 – $800 |
| HC 스탁 | 텅스텐 카바이드, 코발트-크롬 | $100 – $300 |
| Arcam AB | 티타늄 합금, 스테인리스 스틸 | $200 – $600 |
| 에라스틸 | 공구강, 마레이징 강 | $150 – $400 |
| 오베르 & 듀발 | 니켈 합금, 공구강 | $200 – $500 |
의 장점과 한계 AM 머신
다른 기술과 마찬가지로 적층 가공기에도 장단점이 있습니다:
장점
| 이점 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 자유로운 디자인 | 복잡한 형상과 복잡한 디자인을 만듭니다. |
| 재료 효율성 | 자료가 레이어별로 추가되므로 낭비가 최소화됩니다. |
| 사용자 지정 | 개인화된 제품을 위한 디자인을 쉽게 수정할 수 있습니다. |
| 신속한 프로토타이핑 | 디자인부터 완제품까지 빠르게 처리할 수 있습니다. |
| 온디맨드 프로덕션 | 필요에 따라 부품을 생산하여 재고 비용을 절감하세요. |
제한 사항
| 제한 사항 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 재료 제한 | 모든 재료가 AM 공정에 적합한 것은 아닙니다. |
| 표면 마감 | 원하는 표면 품질을 얻기 위해 후처리가 필요할 수 있습니다. |
| 크기 제약 | 기존 제조 방식에 비해 제작량이 제한적입니다. |
| 비용 | 장비 및 재료에 대한 초기 투자 비용이 높습니다. |
| 속도 | 대규모 생산을 위한 일부 기존 제조 방식보다 느립니다. |
적층 제조 장비의 구성 및 특성
적층 제조 장비의 구성과 특성을 이해하는 것은 필요에 맞는 장비를 선택하는 데 매우 중요합니다.
적층 제조 장비의 종류와 특성
| 유형 | 재료 | 특성 |
|---|---|---|
| SLA | 광폴리머 수지 | 고정밀, 매끄러운 표면 마감, 프로토타입에 이상적 |
| SLS | 나일론, 폴리아미드, 금속 | 기능적 프로토타입에 적합한 견고하고 내구성 있는 부품 |
| FDM | 열가소성 필라멘트 | 경제적인 가격으로 신속한 프로토타이핑과 취미 활동에 적합합니다. |
| DMLS | 금속 분말(Ti, Al, SS) | 고강도, 복잡한 금속 부품, 항공 우주, 의료용 |
| EBM | 금속 분말(Ti, CoCr) | 핵심 산업에서 사용되는 고온, 고강도 부품 |
AM 장비의 속성
| 속성 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 볼륨 구축 | 인쇄할 수 있는 개체의 최대 크기입니다. |
| 레이어 해상도 | 각 레이어의 두께는 표면 마감과 디테일에 영향을 미칩니다. |
| 재료 호환성 | 기계가 사용할 수 있는 재료의 범위. |
| 인쇄 속도 | 기계가 인쇄할 수 있는 속도로, 생산 시간에 영향을 줍니다. |
| 정밀도 | 고정밀 애플리케이션에 필수적인 인쇄 부품의 정확도. |
적층 제조 장비의 응용 분야 및 사용 사례
적층 가공 기계는 다양한 산업 분야에서 사용되는 다용도 도구입니다. 몇 가지 일반적인 응용 분야를 살펴보겠습니다:
항공우주
적층 가공 기계는 엔진 부품이나 구조 부품과 같은 경량, 고강도 부품을 제작하는 데 사용됩니다. 복잡한 형상을 제작할 수 있기 때문에 항공우주 부품의 무게를 줄이고 효율성을 높일 수 있습니다.
의료
의료 분야에서 3D 프린팅 기계는 맞춤형 임플란트, 보철물, 수술 기구를 제작합니다. 정밀도와 맞춤화 기능을 통해 의료 기기가 환자에게 완벽하게 맞도록 하여 치료 결과와 편안함을 개선합니다.
자동차
자동차 업계에서는 경량 부품, 맞춤형 부품 및 프로토타입을 제작하기 위해 3D 프린팅 기계를 사용합니다. 이 기술을 통해 새로운 설계의 프로토타입을 신속하게 제작하고 테스트하여 개발 프로세스를 가속화할 수 있습니다.
소비재
적층 가공 기계를 사용하면 보석에서 안경에 이르기까지 맞춤형 디자인의 소비재를 생산할 수 있습니다. 제품을 개인화할 수 있다는 점은 독특하고 맞춤화된 제품을 찾는 소비자들에게 어필할 수 있습니다.
전자 제품
전자 제품에서 적층 가공 기계는 하우징, 방열판, 커넥터를 제작합니다. 적층 가공의 정밀도와 소재 능력은 전자 부품이 성능과 내구성에 필요한 사양을 충족하도록 보장합니다.
툴링
적층 가공 기계는 복잡한 형상과 고정밀도를 갖춘 금형, 금형, 절삭 공구를 제작하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 애플리케이션은 기존 툴링 방법과 관련된 리드 타임과 비용을 줄여줍니다.
다음 용도의 금속 분말 비교 AM 머신
적층 제조용 금속 분말을 선택할 때는 각 분말의 특성과 특정 응용 분야에 대한 적합성을 비교하는 것이 중요합니다.
티타늄 합금 대 스테인리스 스틸
티타늄 합금 는 무게 대비 강도와 생체 적합성이 높아 항공우주 및 의료 분야에 이상적인 것으로 알려져 있습니다. 스테인리스 스틸반면에 내식성과 강도가 우수하여 다양한 산업 분야에 적합합니다.
인코넬 대 알루미늄 합금
인코넬 은 고온 강도와 내산화성으로 잘 알려진 니켈-크롬 초합금으로 항공우주 및 발전 분야에 이상적입니다. 알루미늄 합금 는 가볍고 열 특성이 우수하여 자동차 및 소비자 가전 애플리케이션에 적합합니다.
공구강 대 코발트-크롬
공구강 는 경도와 내마모성으로 높은 평가를 받고 있어 툴링 애플리케이션에 이상적입니다. 코발트-크롬 는 높은 내마모성과 생체 적합성을 제공하여 의료용 임플란트 및 치과 보철에 적합합니다.
구리 합금 대 마레이징 강철
구리 합금 는 열 및 전기 전도성이 우수하여 전기 부품 및 열교환기에 적합합니다. 마레이징 스틸 는 높은 강도와 인성을 제공하여 항공우주 및 고성능 엔지니어링 애플리케이션에 이상적입니다.

자주 묻는 질문
| 질문 | 답변 |
|---|---|
| 적층 제조란 무엇인가요? | 적층 제조(AM)는 재료를 한 층씩 추가하여 물체를 만드는 프로세스입니다. |
| AM 머신은 어떻게 작동하나요? | 3D 프린팅 기계는 디지털 설계를 사용하여 재료를 레이어별로 추가하여 물리적 개체를 만듭니다. |
| AM 장비에 어떤 재료를 사용할 수 있나요? | 적층 가공 기계는 금속, 폴리머, 세라믹 등 다양한 재료를 사용할 수 있습니다. |
| 적층 가공기의 장점은 무엇인가요? | 디자인 자유도, 재료 효율성, 사용자 지정, 신속한 프로토타이핑, 온디맨드 생산 등의 이점이 있습니다. |
| 적층 가공기의 한계는 무엇인가요? | 재료 제한, 표면 마감 품질, 크기 제약, 비용 및 속도 등의 제약이 있습니다. |
| 어떤 산업에서 AM 장비를 사용하나요? | 항공우주, 의료, 자동차, 전자, 소비재, 툴링 등의 산업이 여기에 포함됩니다. |
| AM에 적합한 금속 파우더를 선택하려면 어떻게 해야 하나요? | 애플리케이션 요구 사항, 재료 특성, 3D 프린팅 장비와의 호환성 등의 요소를 고려하세요. |
| 적층 가공에 사용되는 일반적인 금속 분말에는 어떤 것이 있나요? | 일반적인 금속 분말에는 티타늄 합금, 스테인리스강, 인코넬, 알루미늄 합금, 공구강, 코발트-크롬 등이 있습니다. |
| AM 기계로 기능성 부품을 생산할 수 있나요? | 예, 3D 프린팅 기계는 높은 정밀도와 내구성을 갖춘 기능성 부품을 생산할 수 있습니다. |
| 적층 가공 기계의 미래는 어떻게 될까요? | 재료, 공정 및 애플리케이션의 발전으로 성장을 주도하는 적층 제조 기계의 미래는 유망합니다. |