مرحبًا بك في عالم آلات التصنيع الإضافي (AM) الرائع! تُحدث هذه الأجهزة المذهلة ثورة في كيفية إنشاء وتصميم وتصنيع المنتجات. تخيل أن تكون قادرًا على بناء الأجسام طبقة تلو الأخرى، باستخدام مواد مثل المعادن والبلاستيك والسيراميك، مباشرةً من النماذج الرقمية. هل يبدو ذلك خيالاً علمياً؟ حسناً، إنه يحدث الآن!
في هذه المقالة، سنتناول في هذه المقالة الخوض في تعقيدات ماكينات AMمع التركيز على تطبيقاتها ومزاياها، وبالطبع المساحيق المعدنية التي تغذي سحرها. سنستكشف أنواع المساحيق المعدنية المستخدمة وتكوينها وخصائصها وغير ذلك الكثير. لذا، اربط حزام الأمان واستعد لرحلة جذابة في عالم ماكينات التصنيع باستخدام الصمامات المعدنية.
نظرة عامة على ماكينات AM
ينطوي التصنيع الإضافي، المعروف باسم الطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد، على إنشاء كائنات عن طريق إضافة طبقة مواد طبقة تلو الأخرى. وعلى عكس طرق التصنيع التقليدية التي غالبًا ما تنطوي على طرح المواد (القطع والحفر وما إلى ذلك)، فإن التصنيع الإضافي يتمحور حول الدقة والكفاءة. تُستخدم هذه الآلات في العديد من الصناعات، بما في ذلك صناعة الطيران والسيارات والرعاية الصحية والسلع الاستهلاكية.
ما هي ماكينات AM؟
ماكينات AM هي أجهزة متقدمة تستخدم تصميمات رقمية لبناء أجسام مادية طبقة تلو الأخرى. وهي تعمل مع مجموعة متنوعة من المواد، بما في ذلك المعادن والبوليمرات والسيراميك. يمكن لهذه الماكينات إنشاء أشكال هندسية معقدة يستحيل تحقيقها بطرق التصنيع التقليدية.
كيف تعمل ماكينات AM؟
تتبع ماكينات AM عملية مباشرة ومتطورة في نفس الوقت:
- التصميم: يتم إنشاء نموذج ثلاثي الأبعاد باستخدام برنامج التصميم بمساعدة الحاسوب (CAD).
- التقطيع: يتم تقسيم النموذج إلى طبقات رقيقة.
- الطباعة: تضيف الماكينة المواد طبقة بعد طبقة، باتباع المخطط الرقمي.
- المعالجة اللاحقة: يتم الانتهاء من الجسم المطبوع بالمعالجات اللازمة، مثل التلميع أو المعالجة الحرارية.
فوائد ماكينات AM
- الأشكال هندسية معقدة: ابتكر تصميمات معقدة لا تستطيع الطرق التقليدية تحقيقها.
- كفاءة المواد: الحد الأدنى من النفايات مقارنة بالتصنيع الطرحي.
- التخصيص: تعديل التصميمات بسهولة للحصول على منتجات مخصصة.
- السرعة: النماذج الأولية السريعة والإنتاج السريع.

أنواع ماكينات AM
دعونا نتعمق في الأنواع المختلفة من ماكينات صمامات الصنعة المغناطيسية التي يتميز كل منها بقدرات وتطبيقات فريدة.
1. الطباعة الحجرية المجسمة (SLA)
تستخدم تقنية SLA الليزر لمعالجة الراتنج السائل إلى أجسام صلبة. وهو مثالي لإنشاء نماذج أولية مفصلة ذات أسطح ملساء.
2. التلبيد الانتقائي بالليزر (SLS)
تستخدم SLS الليزر لدمج المواد المسحوقة. وهي رائعة لإنتاج أجزاء متينة وعملية من مجموعة متنوعة من المواد.
3. النمذجة بالترسيب المنصهر (FDM)
تقوم FDM بصهر وبثق خيوط البلاستيك الحراري لبناء الأجسام. وهو خيار شائع للهواة والتطبيقات الصناعية.
4. التلبيد المباشر بالليزر المعدني (DMLS)
تستخدم تقنية DMLS الليزر لتلبيد المسحوق المعدني لتكوين أجزاء معدنية قوية ومعقدة. ويستخدم على نطاق واسع في صناعات الطيران والصناعات الطبية.
5. الذوبان بالحزمة الإلكترونية (EBM)
تستخدم EBM شعاع إلكتروني لصهر مسحوق المعادن. وهي مثالية للتطبيقات عالية القوة والحرارة العالية.
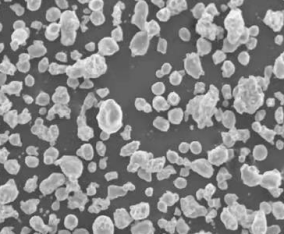
المساحيق المعدنية لماكينات الصقل الميكانيكي
المساحيق المعدنية هي جوهر العديد من عمليات تصنيع الإضافات المعدنية، خاصة في الصناعات التي تتطلب قوة ودقة عالية. فيما يلي بعض مساحيق المعادن الرئيسية المستخدمة في عمليات التصنيع الإضافي:
1. سبائك التيتانيوم (Ti-6Al-4V)
الوصف: سبائك التيتانيوم معروفة بقوتها العالية ووزنها المنخفض ومقاومتها الممتازة للتآكل.
التطبيقات: الفضاء، والغرسات الطبية، والسيارات.
الخصائص: نسبة قوة إلى وزن عالية، وتوافق حيوي، ومقاومة ممتازة للإجهاد.
2. الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ (316L)
الوصف: سبيكة متعددة الاستخدامات معروفة بمقاومتها للتآكل وقوتها.
التطبيقات: الأجهزة الطبية، وتجهيز الأغذية، والصناعات الكيميائية.
الخصائص: قوة عالية، ومقاومة للتآكل، وليونة جيدة.
3. إينكونيل (IN625)
الوصف: سبيكة فائقة من النيكل والكروم ذات قوة ممتازة في درجات الحرارة العالية ومقاومة ممتازة للتآكل.
التطبيقات: الفضاء، وتوليد الطاقة، والصناعات البحرية.
الخصائص: مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية والأكسدة، وقوة عالية.
4. سبائك الألومنيوم (AlSi10Mg)
الوصف: سبائك الألومنيوم خفيفة الوزن وقوية، وهي مثالية للأجزاء التي تتطلب خصائص حرارية جيدة.
التطبيقات: السيارات، والفضاء، والإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية.
الخصائص: نسبة قوة إلى وزن عالية، وموصلية حرارية جيدة، ومقاومة للتآكل.
5. فولاذ الأدوات (H13)
الوصف: معروف بصلابته ومقاومته للتآكل والتآكل.
التطبيقات: الأدوات والقوالب والقوالب والقوالب.
الخصائص: الصلابة العالية، ومقاومة التآكل، والثبات الحراري.
6. الكوبالت-كروم الكوبالت (CoCr)
الوصف: سبيكة فائقة معروفة بمقاومتها للتآكل وتوافقها الحيوي.
التطبيقات: الغرسات الطبية، والأطراف الصناعية للأسنان، والفضاء الجوي.
الخصائص: مقاومة عالية للتآكل، وتوافق حيوي ممتاز، وقوة عالية.
7. سبائك النحاس (CuCr1Zr)
الوصف: يتم تقييم سبائك النحاس لتوصيلها الحراري والكهربائي.
التطبيقات: المكونات الكهربائية، والمبادلات الحرارية، ومكونات محرك الصاروخ.
الخصائص: موصلية حرارية وكهربائية عالية، وقوة جيدة.
8. فولاذ ماراجنغ (1.2709)
الوصف: فولاذ عالي الصلابة مع صلابة ممتازة وثبات في الأبعاد.
التطبيقات: صناعة الطيران، والأدوات، والهندسة عالية الأداء.
الخصائص: قوة عالية، وصلابة جيدة، وقابلية لحام ممتازة.
9. سبائك النيكل (Hastelloy X)
الوصف: معروف بمقاومته للأكسدة وقوته في درجات الحرارة العالية.
التطبيقات: الفضاء، والمعالجة الكيميائية، والتوربينات الغازية الصناعية.
الخصائص: مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية، ومقاومة الأكسدة، ومقاومة التآكل.
10. كربيد التنغستن (WC-Co)
الوصف: صلبة للغاية ومقاومة للاهتراء وتستخدم في البيئات الصعبة.
التطبيقات: أدوات القطع، والأجزاء المقاومة للتآكل، ومعدات التعدين.
الخصائص: صلابة عالية، ومقاومة ممتازة للتآكل، وموصلية حرارية عالية.
تكوين المساحيق المعدنية وخصائصها
إليك نظرة مفصلة على تركيبة هذه المساحيق المعدنية وخصائصها:
| المسحوق المعدني | التركيب | الخصائص |
|---|---|---|
| سبائك التيتانيوم | Ti، Al، V | نسبة عالية من القوة إلى الوزن، والتوافق الحيوي |
| الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ | الحديد، الكروم، النيكل، المونيوم | مقاومة التآكل، ليونة جيدة |
| إنكونيل | النيكل، الكروم، المونيوم، النحاس الأصفر | مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية، ومقاومة الأكسدة |
| سبائك الألومنيوم | Al، Si، Mg | خفة الوزن، والتوصيل الحراري، ومقاومة التآكل |
| فولاذ الأدوات | الحديد، C، Cr، Mo | الصلابة، ومقاومة التآكل، والثبات الحراري |
| الكوبالت-الكروم | كولورادو، كروم، مو | مقاومة التآكل، والتوافق الحيوي |
| سبائك النحاس | النحاس، الكروم، الزر | الموصلية الحرارية والكهربائية، والقوة |
| الفولاذ المصهور | الحديد، النيكل، الكوكس، المونيوم | قوة وصلابة وقابلية لحام عالية |
| سبائك النيكل | النيكل، الكروم، المونيوم، الحديد | مقاومة الأكسدة، قوة مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية |
| كربيد التنجستن | مرحاض، شركة | الصلابة، ومقاومة التآكل، والتوصيل الحراري |






تطبيقات مساحيق المعادن في الصقل الذكي
يتيح تعدد استخدامات مساحيق المعادن في التصنيع الإضافي لمجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات في مختلف الصناعات:
| الصناعة | التطبيقات |
|---|---|
| الفضاء | مكونات المحرك، والأجزاء الهيكلية، والمبادلات الحرارية |
| الطبية | الغرسات والأطراف الصناعية والأدوات الجراحية |
| السيارات | الأجزاء خفيفة الوزن، ومكونات المحرك، والأجزاء المخصصة |
| الإلكترونيات | المشتتات الحرارية والموصلات والعلب |
| الأدوات | القوالب والقوالب وأدوات القطع |
| الطاقة | شفرات التوربينات، والمبادلات الحرارية، وأجزاء توليد الطاقة |
| السلع الاستهلاكية | المجوهرات والنظارات والمنتجات المصممة حسب الطلب |
المواصفات والأحجام والدرجات والمعايير
عند اختيار مساحيق المعادن لصنع الصمامات المعدنية، من المهم مراعاة مواصفاتها وأحجامها ودرجاتها ومعاييرها:
| المسحوق المعدني | المواصفات | المقاسات | درجات | المعايير |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| سبائك التيتانيوم | أستم ب 348، أم أس 4999 | 15-45 ميكرومتر، 45-106 ميكرومتر | Ti-6Al-4V ELI | معيار الفلك القياسي F2924، ISO 5832-3 |
| الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ | أستم A276، أستم f138 | 10-50 ميكرومتر، 20-63 ميكرومتر | 316L، 17-4 PH | معيار النجم F138، ISO 5832-1 |
| إنكونيل | AMS 5666، NS N06625 | 15-45 ميكرومتر، 20-60 ميكرومتر | IN625, IN718 | أستم ب 443، أم أس 5662 |
| سبائك الألومنيوم | أستم ب 209، أم أس 4225 | 20-63 ميكرومتر، 10-50 ميكرومتر | AlSi10Mg، AlSi12 | أستم ب 918، أيزو 3522 |
| فولاذ الأدوات | ASTM A681، AISI H13 | 15-45 ميكرومتر، 20-60 ميكرومتر | H13، D2 | أستم إيه 681، داين 1.2344 |
| الكوبالت-الكروم | أستم f75، أيزو 5832-12 | 15-45 ميكرومتر، 10-50 ميكرومتر | CoCrMo، CoCrW | أستم f75، أيزو 5832-12 |
| سبائك النحاس | أستم B152، ج18150، ج18150 | 10-50 ميكرومتر، 15-45 ميكرومتر | النحاس CuCr1Zr، C18150 | أستم ب 187، أم أس 4980 |
| الفولاذ المصهور | AMS 6514، AISI 18Ni(300) | 10-45 ميكرومتر، 20-60 ميكرومتر | 1.2709، 18 نيوتن (300) | AMS 6520، DIN 1.6358 |
| سبائك النيكل | أستم B435، رقم N06002 من منظمة الأمم المتحدة للتوحيد القياسي | 10-45 ميكرومتر، 20-60 ميكرومتر | هاستيلوي X، N06002 | أستم ب435، أم أس 5754 |
| كربيد التنجستن | ISO 9001, ASTM B777، ISO 9001 | 5-20 ميكرومتر، 10-45 ميكرومتر | WC-Co، مرتبط بالكوبالت | ISO 9001, ASTM B777، ISO 9001 |
تفاصيل الموردين والأسعار
فيما يلي نظرة على بعض الموردين الرئيسيين لمساحيق المعادن وتفاصيل أسعارها:
| المورد | المساحيق المعدنية | نطاق السعر (لكل كيلوغرام) |
|---|---|---|
| هوغاناس إيه بي | الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ، فولاذ الأدوات | $50 – $200 |
| تكنولوجيا النجار | سبائك التيتانيوم، إنكونيل | $300 – $600 |
| ساندفيك | فولاذ مقاوم للصدأ، فولاذ مصهور | $100 – $400 |
| تقنية LPW | الكوبالت-كروم، إنكونيل | $250 – $700 |
| مضافات GKN | سبائك الألومنيوم، سبائك التيتانيوم | $150 – $500 |
| مضافات AP&C (GE المضافة) | سبائك التيتانيوم، سبائك الألومنيوم، سبائك الألومنيوم | $200 – $800 |
| إتش سي ستارك | كربيد التنجستن، كربيد الكوبالت والكروم | $100 – $300 |
| أركام إيه بي | سبائك التيتانيوم، الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ | $200 – $600 |
| إراستيل | فولاذ الأدوات، الفولاذ المخروطي | $150 – $400 |
| أوبير ودوفال | سبائك النيكل، فولاذ الأدوات | $200 – $500 |
مزايا وقيود ماكينات AM
مثل أي تقنية، فإن ماكينات AM لها نقاط قوتها وضعفها:
مزايا
| الميزة | الشرح |
|---|---|
| حرية التصميم | ابتكر أشكالاً هندسية معقدة وتصميمات معقدة. |
| كفاءة المواد | الحد الأدنى من النفايات حيث يتم إضافة المواد طبقة تلو الأخرى. |
| التخصيص | يمكنك تعديل التصميمات بسهولة للحصول على منتجات مخصصة. |
| النماذج الأولية السريعة | تحول سريع من التصميم إلى المنتج النهائي. |
| الإنتاج عند الطلب | إنتاج القطع حسب الحاجة، مما يقلل من تكاليف المخزون. |
محددات
| التقييد | الشرح |
|---|---|
| القيود المادية | ليست كل المواد مناسبة لعمليات التصنيع الإضافي. |
| تشطيب السطح | قد يتطلب معالجة لاحقة لتحقيق جودة السطح المطلوبة. |
| قيود الحجم | حجم البناء المحدود مقارنةً بطرق التصنيع التقليدية. |
| التكلفة | استثمار أولي مرتفع للمعدات والمواد. |
| السرعة | أبطأ من بعض طرق التصنيع التقليدية للإنتاج على نطاق واسع. |
تكوين وخصائص ماكينات AM
إن فهم تركيبة وخصائص ماكينات AM أمر بالغ الأهمية لاختيار الماكينة المناسبة لاحتياجاتك.
أنواع ماكينات AM وخصائصها
| النوع | المواد | صفات |
|---|---|---|
| جيش تحرير السودان | راتنج البوليمر الضوئي | دقة عالية، سطح أملس وعالي الدقة، مثالي للنماذج الأولية |
| SLS | نايلون، بولي أميد، معدن | أجزاء قوية ومتينة ومناسبة للنماذج الأولية الوظيفية |
| FDM | خيوط لدن بالحرارة | ميسورة التكلفة، وجيدة للنماذج الأولية السريعة والهواة |
| DMLS | مسحوق معدني (Ti، Al، SS) | الأجزاء المعدنية المعقدة عالية القوة والمعقدة، المستخدمة في مجال الطيران والفضاء والطب |
| EBM | مسحوق معدني (Ti، CoCr) | الأجزاء عالية الحرارة وعالية القوة المستخدمة في الصناعات الحساسة |
خصائص ماكينات AM
| الممتلكات | الوصف |
|---|---|
| حجم البناء | الحد الأقصى لحجم الكائن الذي يمكن طباعته. |
| دقة الطبقة | سماكة كل طبقة، مما يؤثر على تشطيب السطح وتفاصيله. |
| توافق المواد | مجموعة المواد التي يمكن للماكينة استخدامها. |
| سرعة الطباعة | السرعة التي يمكن للماكينة الطباعة بها، مما يؤثر على وقت الإنتاج. |
| الدقة | دقة الأجزاء المطبوعة، وهي ضرورية للتطبيقات عالية الدقة. |
تطبيقات وحالات استخدام ماكينات صُنع المعادن الآلية
تُعد ماكينات صُنع الإضافات المعدنية أدوات متعددة الاستخدامات تُستخدم في مختلف الصناعات. دعونا نستكشف بعض التطبيقات الشائعة:
الفضاء
تُستخدم ماكينات صُنع الإضافات الإضافية لإنشاء مكونات خفيفة الوزن وعالية القوة، مثل أجزاء المحرك والمكونات الهيكلية. تقلل القدرة على إنتاج أشكال هندسية معقدة من وزن المكونات الفضائية وتزيد من كفاءتها.
الطبية
في المجال الطبي، تُنتج ماكينات AM آلات تصنيع آلات AM غرسات وأطراف صناعية وأدوات جراحية مخصصة. تضمن الدقة وقدرات التخصيص أن الأجهزة الطبية تناسب المرضى بشكل مثالي، مما يحسن النتائج والراحة.
السيارات
تستخدم صناعة السيارات ماكينات AM لتصنيع قطع خفيفة الوزن ومكونات مخصصة ونماذج أولية. وتسمح هذه التقنية بإنتاج النماذج الأولية السريعة واختبار التصميمات الجديدة، مما يسرّع عملية التطوير.
السلع الاستهلاكية
تتيح ماكينات AM إنتاج سلع استهلاكية مصممة حسب الطلب، من المجوهرات إلى النظارات. إن القدرة على تخصيص المنتجات تجذب المستهلكين الذين يبحثون عن سلع فريدة ومصممة حسب الطلب.
الإلكترونيات
في مجال الإلكترونيات، تقوم ماكينات التصنيع باستخدام صمامات الألومنيوم المغناطيسية بتصنيع العلب والمشتتات الحرارية والموصلات. تضمن الدقة والقدرات المادية لآلات التصنيع باستخدام الإضافات المعدنية أن تفي المكونات الإلكترونية بالمواصفات المطلوبة للأداء والمتانة.
الأدوات
تُستخدم ماكينات التصنيع باستخدام الإضافات المعدنية لإنشاء القوالب والقوالب وأدوات القطع ذات الأشكال الهندسية المعقدة والدقة العالية. ويقلل هذا التطبيق من المهل الزمنية والتكاليف المرتبطة بطرق تصنيع الأدوات التقليدية.
مقارنة المساحيق المعدنية لـ ماكينات AM
عند اختيار مساحيق المعادن لتصنيع الإضافات الإضافية، من الضروري مقارنة خصائصها ومدى ملاءمتها لتطبيقات محددة.
سبائك التيتانيوم مقابل الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ
سبائك التيتانيوم تشتهر بنسبة قوتها العالية إلى وزنها وتوافقها الحيوي، مما يجعلها مثالية للتطبيقات الفضائية والطبية. الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأمن ناحية أخرى، يوفر مقاومة ممتازة للتآكل والقوة، مما يجعله مناسبًا لمجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات الصناعية.
الإينكونيل مقابل سبائك الألومنيوم
إنكونيل عبارة عن سبيكة فائقة من النيكل والكروم معروفة بقوتها في درجات الحرارة العالية ومقاومتها للأكسدة، وهي مثالية للفضاء وتوليد الطاقة. سبائك الألومنيوم خفيفة الوزن مع خصائص حرارية جيدة، مما يجعلها مناسبة لتطبيقات السيارات والإلكترونيات الاستهلاكية.
فولاذ الأدوات مقابل الكوبالت-الكروم
فولاذ الأدوات يتميز بالصلابة ومقاومة التآكل، مما يجعله مثاليًا لتطبيقات الأدوات. الكوبالت-الكروم مقاومة عالية للتآكل والتوافق الحيوي، ومناسبة للغرسات الطبية والأطراف الصناعية للأسنان.
خلائط النحاس مقابل الفولاذ المصفح
سبائك النحاس توفر توصيل حراري وكهربائي ممتاز، مما يجعلها مناسبة للمكونات الكهربائية والمبادلات الحرارية. الفولاذ المصهور توفر قوة وصلابة عالية، وهي مثالية للتطبيقات الهندسية عالية الأداء في مجال الطيران والفضاء.

التعليمات
| سؤال | الإجابة |
|---|---|
| ما هو التصنيع المضاف؟ | التصنيع الإضافي (AM) هو عملية إنشاء أجسام عن طريق إضافة طبقة مادة تلو الأخرى. |
| كيف تعمل ماكينات AM؟ | تستخدم ماكينات AM التصاميم الرقمية لإضافة المواد طبقة بعد طبقة، مما يؤدي إلى إنشاء جسم مادي. |
| ما هي المواد التي يمكن استخدامها في ماكينات AM؟ | يمكن أن تستخدم ماكينات AM مجموعة متنوعة من المواد، بما في ذلك المعادن والبوليمرات والسيراميك. |
| ما هي مزايا ماكينات AM؟ | تشمل المزايا حرية التصميم وكفاءة المواد والتخصيص والنماذج الأولية السريعة والإنتاج حسب الطلب. |
| ما هي حدود ماكينات AM؟ | تشمل القيود قيود المواد وجودة تشطيب السطح وقيود الحجم والتكلفة والسرعة. |
| ما هي الصناعات التي تستخدم ماكينات AM؟ | تشمل الصناعات الفضاء والطب والسيارات والإلكترونيات والسلع الاستهلاكية والأدوات. |
| كيف أختار المسحوق المعدني المناسب ل AM؟ | ضع في اعتبارك عوامل مثل متطلبات التطبيق، وخصائص المواد، والتوافق مع ماكينة التصنيع المُصغَّر. |
| ما هي بعض مساحيق المعادن الشائعة المستخدمة في AM؟ | تشمل المساحيق المعدنية الشائعة سبائك التيتانيوم والفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ والإينكونيل وسبائك الألومنيوم وفولاذ الأدوات والكروم الكوبالت. |
| هل يمكن لماكينات AM إنتاج أجزاء وظيفية؟ | نعم، يمكن لماكينات AM إنتاج أجزاء وظيفية بدقة ومتانة عالية. |
| ما هو مستقبل ماكينات AM؟ | إن مستقبل ماكينات الصغر حجمًا واعدًا، مع التطورات في المواد والعمليات والتطبيقات التي تقود النمو. |