소개
첨단 소재의 세계에서, 탄탈륨 분말 은 독특한 특성과 다양한 응용 분야로 인해 특별한 위치를 차지하고 있습니다. 이 글에서는 탄탈륨 분말의 특성, 생산 방법, 응용 분야 및 지속 가능성 측면을 살펴보면서 탄탈륨 분말의 매혹적인 세계를 탐구합니다. 현대 산업에서 탄탈륨 파우더의 중요성을 알아보는 이 여정에 함께하세요.
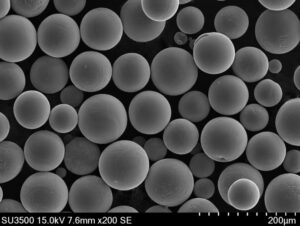
탄탈륨 파우더란 무엇인가요?
탄탈륨 분말은 자연에서 발견되는 희귀하고 밀도가 높은 전이 금속인 탄탈륨에서 추출한 미세하고 회색빛을 띠는 금속 분말입니다. 뛰어난 특성으로 인해 다양한 합금 및 화합물의 핵심 성분으로 자주 사용됩니다. 탄탈륨은 높은 융점, 우수한 내식성, 생체 적합성으로 잘 알려져 있어 여러 산업 분야에서 귀중한 소재입니다.

탄탈륨 분말 속성 및 특성
높은 융점
탄탈륨 분말의 가장 주목할 만한 특징 중 하나는 녹는점이 매우 높다는 점입니다. 녹는점이 섭씨 약 3,020도(화씨 5,468도)인 탄탈륨은 극한의 온도에서도 견딜 수 있어 제트 엔진이나 원자로와 같은 고온 환경의 응용 분야에 적합합니다.
내식성
탄탈륨은 내식성이 뛰어나 부식성이 강한 환경과 관련된 애플리케이션에 매우 적합합니다. 탄탈은 염산과 황산을 비롯한 다양한 산의 공격을 견디기 때문에 화학 처리 장비 및 기타 부식성 환경에서 매우 유용합니다.
연성
탄탈륨은 견고한 특성에도 불구하고 연성이 매우 뛰어납니다. 다양한 모양과 크기로 쉽게 성형할 수 있어 제조업체가 다양한 용도에 맞는 복잡한 부품을 만들 수 있습니다.
생체 적합성
탄탈륨은 생체 적합성이 뛰어나 의료용 임플란트 및 기기에 적합합니다. 탄탈륨은 인체에 사용될 때 부작용을 최소화하여 임플란트 거부 반응의 위험을 줄이고 환자 치료 결과를 개선합니다.
탄탈륨 분말의 응용 분야
전자 제품 및 커패시터
탄탈륨 분말은 전자 산업에서 에너지 저장 및 신호 필터링에 널리 사용되는 탄탈륨 커패시터 제조에 필수적인 부품입니다. 이 커패시터는 스마트폰, 컴퓨터 및 다양한 전자 기기에 적용되어 소형 크기와 성능 향상에 기여합니다.
항공우주 산업
항공우주 산업은 높은 강도, 열 안정성, 피로에 대한 저항성 때문에 탄탈륨 분말에 의존하고 있습니다. 탄탈륨 합금은 제트 엔진 부품, 항공기 프레임 및 기타 핵심 부품에 사용되어 높은 고도와 극한의 온도에서 안전하고 안정적인 작동을 보장합니다.
의료용 임플란트
탄탈륨의 생체 적합성은 고관절 교체 및 치과 임플란트와 같은 의료용 임플란트에 이상적인 소재입니다. 인체의 뼈 조직과 통합되는 능력은 빠른 치유를 촉진하고 합병증의 위험을 줄여줍니다.
적층 제조
적층 제조 또는 3D 프린팅이 부상하면서 탄탈륨 분말은 복잡하고 맞춤 설계된 부품 생산에 활용되고 있습니다. 적층 제조 기술을 사용하면 복잡한 형상을 만들 수 있으므로 탄탈륨은 다양한 산업 분야에서 매력적인 옵션이 될 수 있습니다.

탄탈륨 분말 생산 및 가공
채굴 및 추출
탄탈륨은 주로 탄탈라이트 광석에서 얻는데, 탄탈라이트 광석은 지질학적 매장지에서 니오븀과 함께 발견되는 경우가 많습니다. 채굴 및 추출 과정에는 탐사, 굴착, 광석 가공 등 다양한 단계가 포함됩니다.
정제 프로세스
탄탈라이트 광석을 얻으면 다른 광물 및 불순물로부터 탄탈륨을 분리하는 정제 과정을 거칩니다. 이 정제 공정은 다양한 용도에 적합한 고순도 탄탈륨을 얻는 데 매우 중요합니다.
분말 생산 방법
탄탈륨 분말은 나트륨 환원 공정, 마그네슘 환원 공정, 전기분해 공정 등 여러 가지 방법을 통해 생산됩니다. 각 방법에는 장점이 있으며 다양한 용도에 적합한 특정 특성을 가진 탄탈륨 분말을 생산합니다.
탄탈륨 공급 및 수요
탄탈륨의 공급과 수요 역학은 탄탈륨의 가용성과 가격에 중요한 역할을 합니다. 희귀 금속인 탄탈륨은 다양한 산업에서 증가하는 수요를 충족하는 데 어려움을 겪고 있습니다. 이러한 역학 관계를 이해하는 것은 제조업체와 소비자 모두에게 중요합니다.
환경 및 윤리적 고려 사항
탄탈륨의 추출과 가공은 중요한 환경 및 윤리적 문제를 제기합니다. 채굴이 지역 생태계에 미치는 영향부터 분쟁 광물 문제까지, 탄탈륨 산업에서는 책임 있는 소싱과 지속 가능한 관행이 필수적입니다.
탄탈륨 파우더 사용의 장점과 과제
장점
탄탈륨 분말의 고유한 특성은 고온 저항성, 내식성, 생체 적합성 등 여러 가지 이점을 제공합니다. 이러한 장점 덕분에 탄탈륨은 중요한 애플리케이션에서 자리를 잡으며 기술 발전에 기여하고 있습니다.
도전 과제
탄탈륨은 놀라운 특성에도 불구하고 희소성, 높은 생산 비용, 분쟁 광물과 관련된 윤리적 문제 등 여러 도전 과제에 직면해 있습니다. 이러한 문제를 해결하는 것은 지속 가능한 공급망과 책임감 있는 소비를 보장하는 데 매우 중요합니다.

탄탈륨 재활용 및 지속 가능성
탄탈륨의 가용성이 제한되어 있기 때문에 재활용은 수요를 충족하는 동시에 환경에 미치는 영향을 줄이는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 탄탈륨 재활용 프로세스는 귀중한 소재의 회수를 보장하여 탄탈륨 산업의 지속 가능성을 촉진합니다.
향후 트렌드 및 전망
탄탈륨 산업은 기술의 발전과 다양한 분야의 수요 증가에 힘입어 지속적으로 진화하고 있습니다. 잠재적인 응용 분야와 새로운 트렌드를 살펴보면 탄탈륨 분말의 미래 전망에 대한 통찰력을 얻을 수 있습니다.
결론
탄탈륨 분말은 뛰어난 특성과 다양한 응용 분야로 인해 다양한 산업 분야에서 각광받는 소재입니다. 높은 융점, 내식성, 생체 적합성 덕분에 전자, 항공우주, 의료, 적층 제조 분야의 발전을 가능하게 했습니다. 미래를 내다볼 때 책임 있는 소싱, 재활용, 지속 가능성은 안정적인 탄탈륨 공급망을 보장하는 데 중요한 역할을 할 것입니다.
자주 묻는 질문
- 탄탈륨 파우더는 어떤 용도로 사용되나요?
- 탄탈륨 파우더는 어떻게 생산되나요?
- 전자제품에 탄탈륨 파우더를 사용하면 어떤 이점이 있나요?
- 탄탈륨 파우더는 환경 친화적인가요?
- 탄탈륨은 항공우주 산업에 어떻게 기여하나요?
Frequently Asked Questions (Supplemental)
1) What particle size and shape are optimal for additive manufacturing with Tantalum Powder?
- For LPBF/SLM, a spherical 15–45 μm PSD with low satellite content provides reliable flow and packing. Binder jetting often favors 10–30 μm with controlled agglomeration to balance spreadability and depowdering.
2) How is capacitor‑grade Tantalum Powder different from AM‑grade powder?
- Capacitor powders prioritize very high specific surface area and controlled pore size distribution for high CV (μF·V/g), along with ultra‑low metallic impurities and tight O/N/H. AM‑grade prioritizes sphericity, PSD, and moderate O levels for densification and ductility post‑HIP.
3) What standards or certifications indicate responsibly sourced tantalum?
- Look for RMAP (Responsible Minerals Assurance Process) conformant smelters and supplier due diligence aligned with OECD Guidance. EU Conflict Minerals Regulation and U.S. Dodd‑Frank 1502 disclosures further support ethical sourcing.
4) Can recycled tantalum maintain mechanical and electrical performance?
- Yes. Closed‑loop hydrometallurgical recycling and rigorous refining enable 20–50% recycled content in many grades without measurable performance loss, provided O/N/H, PSD, and trace impurities meet the same specifications as virgin powder.
5) What post‑processing is typical for LPBF tantalum medical implants?
- Stress relief at 900–1100°C in vacuum/inert, HIP at 1100–1400°C and ≥100 MPa to close porosity, followed by surface texturing or anodization to enhance osseointegration. Biocompatibility verification follows ISO 10993.
2025 Industry Trends and Data
- Ethical supply mainstreaming: Wider adoption of RMAP/RMI programs; OEMs increasingly mandate digital chain‑of‑custody from mine to powder lot.
- AM growth in healthcare: Porous tantalum lattices expand in orthopedic and dental implants due to superior osseointegration vs. Ti in select indications.
- Performance uptick in capacitors: Process refinements in sodium/magnesium reduction improve CV and reliability for high‑temp automotive electronics.
- Recycling scale: Higher yields from end‑of‑life capacitor recovery and AM scrap boost recycled content while stabilizing pricing.
- Inline QC: Broader deployment of real‑time O/N/H and PSD monitoring reduces lot variability for both capacitor and AM grades.
| KPI (Tantalum Powder, 2025) | 2023 Baseline | 2025 Typical/Target | Why it matters | Sources/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSD for LPBF (D10–D90) | 20–63 μm | 15–45 μm | Layer quality, density | ISO/ASTM 52907; OEM specs |
| Oxygen content (AM grade) | 0.15–0.30 wt% | 0.08–0.20 wt% | Ductility, porosity | Supplier datasheets |
| RMAP‑conformant tantalum coverage | ~60–70% | 75–85% | Ethical sourcing assurance | RMI/RMAP reports |
| Recycled content in commercial grades | 10–30% | 20–50% | Sustainability, cost | EPD/LCA disclosures |
| Relative density after HIP (AM parts) | 99.3–99.6% | ≥99.8% | Mechanical reliability | OEM/clinic reports |
| Capacitor CV (μF·V/g) improvement | Incremental | +5–10% vs. 2023 | Miniaturization/reliability | Vendor roadmaps |
References:
- Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI/RMAP): https://www.responsiblemineralsinitiative.org
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (powder characterization): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM B708 (tantalum capacitor powders), ASTM B365 (tantalum products): https://www.astm.org
- ASM Handbook, Powder Metallurgy; Medical Applications: https://dl.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Porous Tantalum Acetabular Cups with Enhanced Osseointegration (2025)
- Background: An orthopedic OEM needed improved bone ingrowth and fatigue life versus Ti‑6Al‑4V lattices.
- Solution: Used spherical AM‑grade Tantalum Powder (15–45 μm; O ≤0.15 wt%), designed 65–75% lattice porosity, applied HIP and micro‑texturing; validated per ISO 13314 and ISO 10993.
- Results: Push‑out strength +28% vs. Ti benchmark; fatigue endurance limit +18%; solid regions achieved 99.85% density (CT); no adverse ion release observed.
Case Study 2: High‑CV Capacitor Powder via Optimized Sodium Reduction (2024)
- Background: An automotive electronics supplier sought higher volumetric efficiency at elevated temperatures.
- Solution: Tuned sodium reduction to narrow pore size distribution and increase specific surface area; multi‑stage washing minimized Na/Mg residues; tightened O/N/H control.
- Results: CV +9% at constant leakage/ESR; AEC‑Q200 defect rate −22%; process yield +6% with stable PSD and improved lot‑to‑lot consistency.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Iver E. Anderson, Senior Metallurgist, Ames Laboratory (USDOE)
- Viewpoint: “Tight control of oxygen and residuals is pivotal for both ductile AM builds and high‑CV capacitor performance from Tantalum Powder.”
- Prof. Paulo J. Ferreira, Professor of Materials Science, The University of Texas at Austin
- Viewpoint: “Engineered lattice architectures in LPBF tantalum can simultaneously elevate osseointegration and fatigue resistance when coupled with HIP and surface functionalization.”
- Dr. Julie Silov, Director, Responsible Minerals Assurance, RMI
- Viewpoint: “RMAP conformity and digital traceability from ore to powder lot are quickly becoming default requirements for global OEMs.”
Affiliations:
- Ames Laboratory: https://www.ameslab.gov
- The University of Texas at Austin: https://www.utexas.edu
- Responsible Minerals Initiative: https://www.responsiblemineralsinitiative.org
Practical Tools/Resources
- Standards and testing: ASTM B708 (capacitor powders), ASTM F2989 (metallic powders for AM), ISO/ASTM 52907 (powder characterization), ISO 10993 (biocompatibility), ISO 13314 (porous metals compression)
- Sourcing and compliance: RMI/RMAP conformant smelter lists and OECD Guidance tools
- Metrology: LECO O/N/H analyzers (https://www.leco.com), BET surface area, ICP‑MS for trace impurities, laser diffraction PSD
- AM design/validation: nTopology (lattice design), Ansys Additive (scan/distortion simulation), CT scanning for density mapping
- Data/benchmarks: NIST AM Bench (https://www.nist.gov/ambench); MatWeb materials database (https://www.matweb.com)
Last updated: 2025-08-22
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced 2025 trend KPI table with sources; provided two recent case studies (AM implants and capacitor powder optimization); included expert viewpoints with affiliations; compiled standards, sourcing, and metrology resources for Tantalum Powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if RMAP guidance or ASTM/ISO standards change, OEMs update AM/feedstock oxygen or PSD limits, or new clinical/AM performance data is published.