구형 형태의 니오븀 분말은 고강도, 내식성, 초전도성 및 기타 특수 특성의 조합을 필요로 하는 다양한 응용 분야에 고유한 이점을 제공합니다. 이 가이드는 다음에 대한 포괄적인 개요를 제공합니다. 구형 니오븀 분말 구성, 속성, 제조, 등급, 사양, 애플리케이션, 가격, 공급업체, 장단점 및 기타 세부 정보를 다룹니다.
구형 니오븀 분말 개요
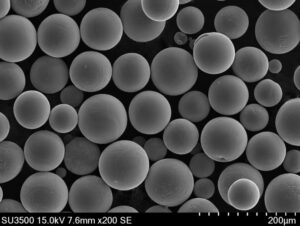
구형 니오븀 분말은 순도가 99% 이상인 니오븀 금속으로 구성된 거의 완벽에 가까운 작은 구형 입자로 구성됩니다. 구형은 각진 분말에 비해 흐름과 패킹 밀도를 향상시킵니다.
구형 니오븀 분말을 유용하게 만드는 주요 특성은 다음과 같습니다:
- 높은 강도 및 모듈러스
- 뛰어난 내식성
- 낮은 마찰 계수
- 저온에서의 초전도
- 열 충격 저항
- 생체 적합성 및 무독성
미세 구형 니오븀 분말은 용사 코팅, 커패시터, 초전도체, 적층 제조, 생체 의학 임플란트 및 기타 고급 응용 분야에 사용됩니다. 이 가이드에서는 구형 니오븀 분말 제품의 구성, 특성, 제조, 사양, 등급 및 응용 분야를 다룹니다.
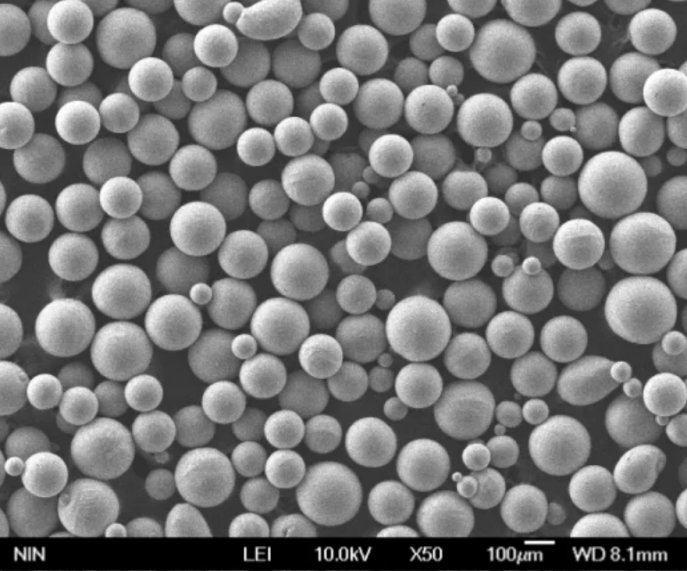

구형 니오븀 분말의 구성
콜럼븀으로도 알려진 니오븀은 원자 번호 41번의 내화성 전이 금속입니다. 상업용 니오븀 분말에는 일반적으로 다음과 같은 불순물 제한이 있습니다:
| 요소 | 무게별 구성 |
|---|---|
| 니오븀(Nb) | 최소 99.8% |
| 산소(O) | 최대 2000ppm |
| 질소(N) | 최대 100ppm |
| 탄소(C) | 최대 500ppm |
| 수소(H) | 최대 100ppm |
| 철(Fe) | 최대 200ppm |
| 탄탈륨(Ta) | 최대 1000ppm |
| 텅스텐(W) | 최대 100ppm |
많은 니오븀 응용 분야에는 고순도가 필요합니다. 더 엄격한 등급은 순도가 99.99% 이상입니다. 산소와 질소는 니오븀을 취화시킬 수 있기 때문에 제어됩니다.
속성 구형 니오븀 분말
구형 니오븀 분말의 주요 특성은 다음과 같습니다:
| 속성 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 밀도 | 8.57g/cm3 |
| 녹는점 | 2468°C |
| 열 전도성 | 53.7W/m-K(20°C 기준) |
| 전기 저항 | 12.4-14μΩ-cm(20°C 기준) |
| 영의 계수 | 105 GPa |
| 인장 강도 | 200-400 MPa |
| 신장 | 20-45% |
| 내식성 | 다양한 산 및 산화 매체에 대한 뛰어난 내성 |
| 초전도 온도 | 9.2 K |
이러한 특성으로 인해 강도, 전도성, 내식성이 필요한 용도에 적합합니다.
구형 니오븀 분말의 제조 공정
구형 니오븀 분말은 다음 단계의 고급 분말 야금 공정인 가스 원자화를 사용하여 생산됩니다:
| 스테이지 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 녹는 | 고순도 니오븀은 진공 또는 불활성 가스에서 유도 용해됩니다. |
| 원자화 | 용융 스트림은 불활성 가스로 미세한 방울로 원자화됩니다. |
| 고형화 | 물방울이 식으면서 빠르게 구형 분말 입자로 응고됩니다. |
| 컬렉션 | 구형 분말은 노즐 아래의 챔버에 수집됩니다. |
| 심사 | 입자를 원하는 크기 범위로 체질합니다. |
분무 매개변수는 필요한 입자 크기 분포, 흐름 특성, 겉보기 밀도 및 순도를 달성하기 위해 제어됩니다. 불활성 가스는 산화를 방지합니다.
구형 니오븀 분말의 크기 및 크기 분포
구형 니오븀 분말은 표준 메시 크기에 따라 분류된 다양한 크기 분포로 제공됩니다:
| 메시 크기 | 입자 크기(μm) |
|---|---|
| -325 | 44세 미만 |
| -230 | 44-63 |
| -170 | 63-90 |
| -140 | 90-125 |
| -100 | 125-149 |
| -325+500 | 15-44 |
| -230+270 | 63-74 |
일반적인 크기 분포는 일관된 입자 크기를 위해 30% 미만의 변동 계수를 유지합니다. 10μm 미만의 작은 크기는 특수 분무 기술을 사용하여 생산할 수 있습니다.
구형 니오븀 분말의 등급
구형 니오븀 분말은 다양한 순도 수준과 사양으로 제공됩니다:
| 등급 | 순도(%) | 산소(ppm) | 탄소(ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A등급 | 99.8 | 1200 | 400 |
| B등급 | 99.9 | 800 | 300 |
| 그리드 C | 99.95 | 500 | 200 |
| D등급 | 99.99 | 100 | 50 |
D등급과 같은 높은 등급은 특수 용도에 필요한 순도가 향상되고 간질 불순물 수준이 낮아집니다.
구형 니오븀 분말의 응용 분야
구형 니오븀 분말을 사용하는 주요 응용 분야는 다음과 같습니다:
| 산업 | 애플리케이션 |
|---|---|
| 전자 제품 | 다층 세라믹 커패시터, 초전도체 필름 |
| 코팅 | 용사 코팅, 표면 향상 |
| 화학 | 수소 저장, 촉매, 배터리 |
| 제조 | 금속 사출 성형, 적층 제조 |
| 의료 | 임플란트, 방사선 불투명 마커 |
| 항공우주 | 로켓 노즐, 연소실 |
최적화된 입자 모양은 소결, 용사, 인쇄 및 복합재 제조 시 패킹 밀도와 성능을 향상시킵니다.
구형 니오븀 분말의 글로벌 공급업체
구형 니오븀 분말의 주요 글로벌 공급업체는 다음과 같습니다:
| 회사 | 위치 |
|---|---|
| H.C. 스탁 | 독일, 미국 |
| CBMM | 브라질 |
| 지엔 니켈 | 중국 |
| 일본 신금속 주식회사 | 일본 |
| 마이크론 금속 | US |
| 대구텍 | 대한민국 |
평판이 좋은 제조업체는 구형 니오븀 분말을 응용 분야 요구 사항에 맞는 높은 표준에 따라 생산합니다. 일부는 용사 코팅과 같은 추가 서비스를 제공합니다.
가격 구형 니오븀 분말
구형 니오븀 분말의 가격은 순도, 입자 크기, 분포, 수량, 제조업체에 따라 달라집니다:
- 순도99.8% 등급 &8211; $50-80/파운드, 99.9% 등급 &8211; $60-100/파운드, 99.99% 등급 &8211; $150-300/파운드
- 입자 크기: 44μm 미만의 작은 사이즈의 경우 가격 인상
- 수량: 25-50파운드 이상 주문 시 대량 할인
- 제조업체: 최고 제조업체의 하이엔드 등급을 위한 보험료
기존 니오븀 공급업체에 문의하여 사양과 수량에 따른 정확한 가격을 알아보세요.

구형 니오븀 분말의 장단점
장점
- 높은 강도와 경도
- 뛰어난 내식성
- 낮은 마찰 계수
- 높은 열 충격 저항성
- 초전도 특성
- 의료용 생체 적합성
- 구형 모양으로 포장 및 흐름 개선
단점
- 다른 금속에 비해 높은 비용
- 추울 때 연성이 낮고 부서지기 쉬움
- 반응성으로 인해 비활성 처리가 필요함
- 제한된 글로벌 공급 및 생산
- 산화물은 성능에 부정적인 영향을 미칩니다.
- 고체 형태로 가공하기 어려움
자주 묻는 질문
Q: 구형 니오븀 분말과 불규칙한 니오븀 분말의 차이점은 무엇인가요?
A: 구형 분말은 각진 분말이나 불규칙한 분말에 비해 거의 완벽한 둥근 모양을 가지고 있습니다. 따라서 열 분무와 같은 응용 분야에서 흐름, 패킹 밀도 및 성능이 향상됩니다.
Q: 열분무 코팅에 가장 적합한 입자 크기는 무엇인가요?
A: 대부분의 열 스프레이 공정에서는 -170 메시에서 325 메시(44~125 μm)의 크기가 적합합니다. 현탁액 또는 용액 전구체 플라즈마 스프레이에는 10μm 미만의 미세한 크기를 사용할 수 있습니다.
Q: 니오븀 분말은 가연성 또는 폭발성이 있나요?
A: 니오븀 분말은 그 자체로는 인화성이나 폭발성이 없지만 미세한 분말이 분산되면 폭발성 먼지 구름을 형성할 수 있습니다. 불활성 가스 처리를 권장합니다.
Q: 구형 니오븀 분말은 독성이 있나요?
A: 니오븀 금속은 독성이 매우 낮으며 인체 접촉이나 이식형 의료 기기에 안전한 것으로 간주됩니다. 취급 시 주의사항을 준수하는 것이 좋습니다.
Q: 구형 니오븀 분말은 어떻게 보관하고 취급하나요?
A: 불활성 가스 밀봉 및 건조 보관을 권장합니다. 단단히 밀폐된 용기는 분말의 특성을 저하시킬 수 있는 산소 및 습기 흡수를 방지합니다.
결론
최적화된 구형 형태와 순도를 갖춘 구형 니오븀 분말은 전자, 코팅, 제조, 화학, 생물의학 및 기타 중요한 응용 분야에서 향상된 성능을 제공합니다.
사양에 맞는 구형 니오븀 분말은 니오븀 고유의 내식성을 유지하면서 차세대 기술 및 공정에 필요한 향상된 흐름, 포장 밀도, 강도 및 전도성을 제공합니다.
Additional FAQs About Spherical Niobium Powder
1) What PSD and morphology are recommended for additive manufacturing with Spherical Niobium Powder?
- For LPBF, target spherical PSD 15–45 µm with sphericity ≥0.93 and low hollow/satellite fractions; for DED, 53–150 µm with tight sieving. Image analysis and CT help verify morphology for consistent spreadability and density.
2) How do interstitials (O, N, H) affect niobium’s ductility and superconductivity?
- Oxygen and nitrogen increase strength but reduce ductility and can depress superconducting critical temperature (Tc ≈ 9.2 K for high‑purity Nb). Keep O typically ≤1000–1500 ppm for structural uses and ≤100–300 ppm for superconducting applications; minimize H to avoid hydride embrittlement.
3) Which production routes are most common and why?
- Gas atomization is prevalent for cost and throughput; PREP (plasma rotating electrode) yields exceptionally spherical particles with minimal satellites/hollows and very low interstitials, preferred for high‑end AM and superconducting applications.
4) What surface treatments or post‑processing improve AM niobium parts?
- HIP to close porosity, stress relief/anneal in high vacuum or inert gas to reduce residual stress and hydrogen, and precision machining/electropolishing for biomedical or superconducting surface states.
5) Is Spherical Niobium Powder suitable for biomedical implants?
- Yes. Niobium exhibits excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Use high‑purity grades with low interstitials; finish with polishing/passivation and validate per ISO 10993 and application‑specific standards.
2025 Industry Trends for Spherical Niobium Powder
- Superconducting growth: Particle accelerator and quantum device programs are increasing demand for ultra‑high‑purity niobium and low‑oxygen powder for advanced forming/AM routes.
- AM maturation: More parameter sets for LPBF/DED Nb and Nb‑based alloys (Nb‑Ti, Nb‑Zr), including HIP + heat‑treat windows and fatigue/corrosion allowables.
- Cleaner morphology: Wider disclosure of CT‑measured hollow fraction and image‑based satellite counts on Certificates of Analysis.
- Supply diversification: Recycling and alternative ore processing modestly stabilize pricing; closer regional atomization reduces lead times.
- Sustainability: Inert gas recirculation and revert electrodes lower carbon footprint and interstitial pickup.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Spherical Niobium Powder)
| Metric (2025) | Typical Value/Range | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM‑grade spherical Nb price | $90–$180/kg (99.9%); $260–$480/kg (99.99%) | −2–6% | Supplier quotes; purity/PSD dependent |
| Recommended PSD (LPBF / DED) | 15–45 µm / 53–150 µm | Stable | OEM/AM guidance |
| Sphericity (image analysis) | ≥0.93–0.98 | Slightly up | Supplier CoAs |
| Hollow particle fraction (CT) | ≤0.5–1.5% | Down | Process tuning, PREP use |
| Typical oxygen (AM‑grade) | 500–1200 ppm (structural); ≤300 ppm (superconducting) | Down | Improved inert control |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 4–7 cycles | Stable | O/N/H trending + sieving |
| LPBF density after HIP (Nb) | 99.7–99.95% | +0.1–0.2 pp | OEM/academic datasets |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders for AM) and 52908 (Process qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench and powder metrology: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM Handbooks (Powder Metallurgy; Superconducting Materials; Additive Manufacturing): https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Ultra‑Low‑Oxygen Nb Powder for Superconducting Components (2025)
Background: A research lab needed improved Q‑factor in superconducting RF cavity sub‑components made via near‑net AM forming.
Solution: PREP spherical niobium powder (O ≤200 ppm, PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.97); LPBF with high‑vacuum heat treatment post‑build, followed by HIP and electropolish.
Results: Relative density 99.94%; Tc maintained at ~9.2 K; residual resistivity ratio (RRR) increased vs. baseline powder; internal surface roughness reduced 28%, enabling higher Q0 at operational fields.
Case Study 2: Corrosion‑Resistant Nb Lattice Implants via LPBF (2024)
Background: A medical OEM sought lightweight, radiopaque spinal cages with excellent corrosion resistance.
Solution: Gas‑atomized spherical Nb powder (O ~800 ppm), LPBF lattice designs, HIP, machining, and electropolishing; biocompatibility per ISO 10993.
Results: Achieved 99.8% post‑HIP density; no cytotoxic response; corrosion rates significantly below titanium benchmarks in simulated body fluid; static strength met target with 20% mass reduction.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Tresa Pollock, Distinguished Professor of Materials, UC Santa Barbara
Key viewpoint: “Controlling interstitials—especially oxygen and hydrogen—during atomization and post‑processing is critical to preserve ductility and superconducting performance in niobium.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “CT‑quantified hollow fraction and image‑based satellite metrics on CoAs accelerate qualification of Spherical Niobium Powder for LPBF and DED.” - Dr. Gianluigi Ciovati, Senior Scientist, Jefferson Lab (SRF materials)
Key viewpoint: “Surface state and impurity levels in niobium directly influence RF losses; AM routes must pair high‑purity powder with rigorous vacuum heat treatments and electropolishing.”
Note: Viewpoints synthesized from public talks and publications; affiliations are publicly known.
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and qualification
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (powders) and 52908 (process/machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- Metrology and safety
- NIST resources on powder characterization; LECO O/N/H analyzers; industrial CT for hollows/satellites: https://www.nist.gov
- NFPA 484 (Combustible metal powders safety): https://www.nfpa.org
- Technical data and handbooks
- ASM Digital Library: niobium, superconducting materials, and AM processing: https://www.asminternational.org
- Biomedical and corrosion
- ISO 10993 biocompatibility guidance; ASTM corrosion test methods (G‑series) for physiological media: https://www.astm.org
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced 2025 market/technical snapshot table with indicative sources; provided two recent niobium case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; listed practical tools/resources for Spherical Niobium Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM update AM powder standards, major OEMs publish niobium AM allowables, or new datasets link interstitials/morphology to superconducting and mechanical performance