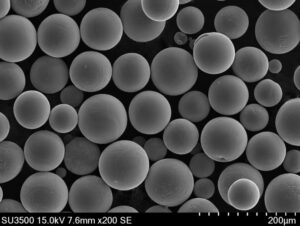
개요 니켈 몰리브덴 분말
니켈 몰리브덴 분말은 니켈과 몰리브덴으로 구성된 금속 합금 분말입니다. 고강도, 내식성, 내마모성, 고온 견딜 수 있는 능력 등 고유한 특성이 조합되어 있습니다.
니켈 몰리브덴 분말에 대한 몇 가지 주요 세부 정보입니다:
- 구성 – 일반적으로 중량 기준으로 니켈 60-70%, 몰리브덴 30-40%를 함유합니다. 특정 비율은 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다.
- 생산 방법 &8211; 일반적으로 니켈과 몰리브덴을 사전 합금하고 분무하여 미세한 균질 분말을 만드는 방식으로 제조합니다.
- 입자 크기 – 용도에 따라 10-150 미크론 범위입니다. 더 미세한 분말일수록 더 균일한 특성을 제공합니다.
- 모양 &8211; 구형 분말 입자는 더 높은 포장 밀도와 부드러운 흐름을 가능하게 합니다. 불규칙한 모양도 가능합니다.
- 일반적인 상품명 &8211; 니켈 몰리 분말, NiMo 분말, 60NiMo, 65NiMo
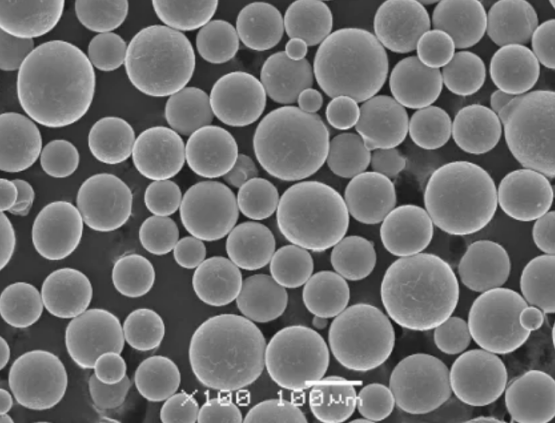

니켈 몰리브덴 분말 유형
| 유형 | 구성 | 특성 |
|---|---|---|
| 니켈 몰리브덴 전합금 분말 | 60-70% Ni, 30-40% Mo | 균일한 구성, 일관된 특성, 우수한 성능 |
| 맞춤형 니켈 몰리브덴 비율 | 50/50 Ni/Mo ~ 90/10 Ni/Mo | 특정 애플리케이션 요구 사항에 맞게 맞춤화 |
| 나노 결정 니켈 몰리브덴 분말 | 60-70% Ni, 30-40% Mo, 100nm 입자 크기 | 매우 높은 강도, 균일한 미세 구조 |
니켈 몰리브덴 분말 특성
| 속성 | 특징 |
|---|---|
| 구성 | 60-70% Ni, 30-40% Mo |
| 밀도 | 8.0-9.5g/cc |
| 녹는점 | 1315~1400°C(2400~2550°F) |
| 힘 | 높음, 700-1300 MPa |
| 연성 | 보통, 5-15% 신장 |
| 경도 | 250-450 HV |
| 내산화성 | 최대 1000°C의 공기 중에서 사용 가능 |
| 내식성 | 우수한 내산성 |
| 전기 저항 | ~138μΩ.cm |
| 열 전도성 | 10-12.5 W/m.K |
| 열팽창 계수 | 12-14 x 10ˉ6/°C |
니켈 몰리브덴 분말 응용 분야
| 산업 | 애플리케이션 | 혜택 |
|---|---|---|
| 항공우주 | 터빈 블레이드, 엔진 부품 | 온도에서 높은 강도, 내산화성 |
| 석유 및 가스 | 다운홀 공구, 밸브, 펌프 | 강도, 내마모성 및 내식성 |
| 자동차 | 기어, 드라이브 샤프트 | 피로 및 내마모성 |
| 3D 프린팅 | 인쇄된 금속 부품 | 고성능 소재 |
| 전자 제품 | 전도성 두꺼운 필름 | 전기적 특성, 안정성 |
니켈 몰리브덴 분말 사양
| 매개변수 | 범위 |
|---|---|
| 니켈 함량 | 60-70 wt% |
| 몰리브덴 콘텐츠 | 30-40 wt% |
| 입자 크기 | 10-150 μm |
| 겉보기 밀도 | 2.5-4.5g/cc |
| 탭 밀도 | 4-6g/cc |
| 유량 | 25-35 s/50g |
| 산소 함량 | 0.5 wt% |
| 탄소 함량 | 0.1 wt% |
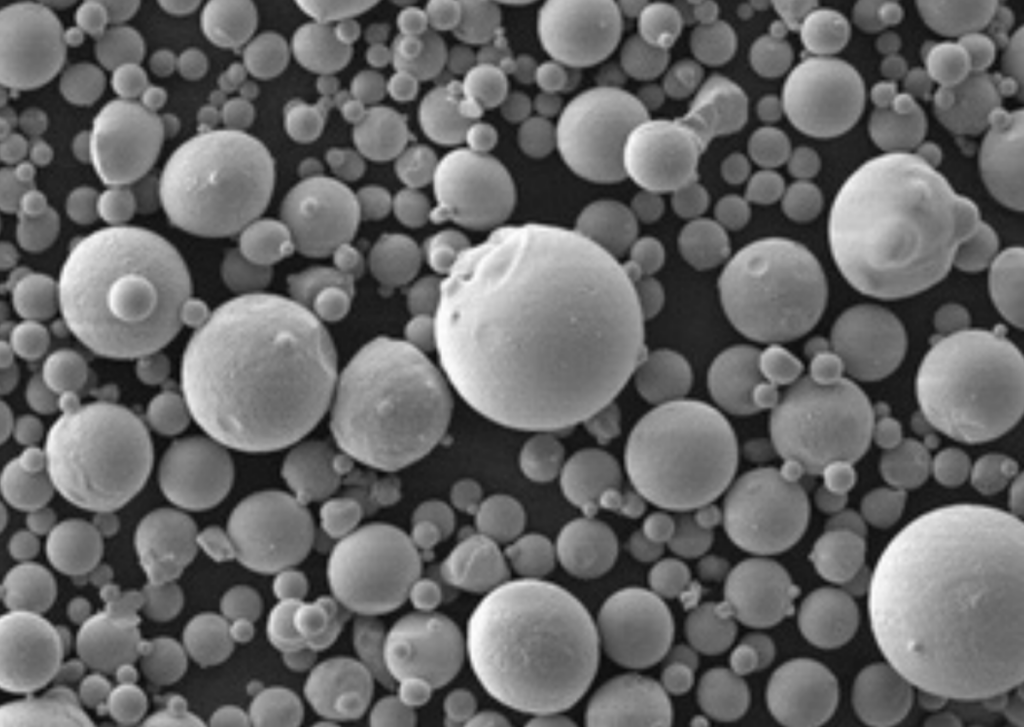
니켈 몰리브덴 분말의 장점과 한계를 비교하세요:
| 장점 | 제한 사항 |
|---|---|
| 높은 온도에서 높은 강도 | 니켈 파우더보다 비싸다 |
| 뛰어난 내식성 | 니켈보다 낮은 연성 |
| 높은 경도 및 내마모성 | 티타늄 합금보다 무겁습니다. |
| 최대 1000°C의 내산화성 | 순수 니켈만큼 전도성이 높지 않음 |
| 맞춤형 합금 비율 | 내화성 금속 분말은 녹는점이 높습니다. |
구매처 니켈 몰리브덴 분말
| 공급업체 | 설명 | 가격 책정 |
|---|---|---|
| 미국 요소 | 순수 프리알로이 분말, 맞춤형 입자 크기 | 50-200/파운드 |
| 스탠포드 머티리얼즈 | 조립식 및 혼합 NiMo 분말 | 75-250/kg |
| 미국 금속 및 합금 | 다양한 NiMo 비율 선택 | 100-350/kg |
| 금속 분말 회사 | 구형 및 불규칙한 NiMo 분말 | 60-180/kg |
자주 묻는 질문
니켈 몰리브덴 분말은 어떤 용도로 사용되나요?
니켈 몰리브덴 분말은 최대 1000°C의 고온에서 강도가 높습니다. 부식과 산화에 강합니다. 주요 용도는 터빈 블레이드와 같은 항공우주 부품, 자동차 기어 및 샤프트, 석유 및 가스 다운홀 공구, 산업 전반의 3D 프린팅 금속 부품 등입니다.
니켈 몰리브덴 분말은 전도성이 있나요?
예, 니켈 몰리브덴 분말은 니켈 함량이 약 138μΩ.cm로 높아 전기 전도성이 우수합니다. 따라서 전도성 두꺼운 필름 애플리케이션에 유용합니다.
니켈 몰리브덴의 구성은 무엇인가요?
일반적인 구성은 중량 기준으로 니켈 60-70%, 몰리브덴 30-40%입니다. 정확한 비율은 애플리케이션 요구 사항에 따라 맞춤 설정할 수 있습니다.
니켈 몰리브덴과 인코넬의 차이점은 무엇인가요?
인코넬은 니켈-크롬 기반 초합금 계열입니다. 니켈 몰리브덴 합금은 크롬 대신 몰리브덴을 사용하여 높은 강도, 경도 및 내식성을 달성합니다.
니켈 몰리브덴보다 더 강한 합금은 무엇인가요?
텅스텐이나 레늄과 같은 내화성 금속 합금은 니켈 몰리브덴보다 녹는점이 높습니다. 텅스텐 카바이드 코발트 분말은 극한의 경도와 내마모성을 제공합니다. 그러나 니켈 몰리브덴은 고온 강도, 연성 및 산화 저항성의 최상의 조합을 제공합니다.
Additional FAQs About Nickel Molybdenum Powder
1) What PSD and morphology are recommended for additive manufacturing?
- For LPBF, use spherical Nickel Molybdenum Powder with PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.92, satellites <5%. For DED, 45–150 µm with tight sieving and low hollow fraction verified by CT.
2) How does Ni:Mo ratio affect properties?
- Higher Mo (35–40 wt%) increases solid-solution strengthening and acid corrosion resistance (reduces pitting/crevice attack) but can reduce ductility and raise flow stress during processing. Higher Ni improves ductility and thermal conductivity.
3) What environments benefit most from Ni–Mo alloys?
- Reducing, chloride- and acid-rich media (HCl, H2SO4) and sour service (H2S/CO2) where Mo improves resistance to localized corrosion and stress corrosion cracking relative to Ni-only or Ni–Cr systems.
4) Which atomization gas is preferred and why?
- Argon is generally preferred to minimize nitrogen pickup and unwanted nitrides; nitrogen can be acceptable for some Ni–Mo grades if N is controlled and does not embrittle the alloy. Target O ≤0.05 wt% and N per spec.
5) What post-processing improves performance of AM parts made with Ni–Mo powder?
- HIP to close porosity, followed by solution treatment/ageing per grade; precision machining plus corrosion passivation/electropolishing for flow-critical or corrosive-service components.
2025 Industry Trends for Nickel Molybdenum Powder
- Energy sector pull-through: Upstream and chemical processing investments drive demand for Ni–Mo powders for corrosion-critical valves, pumps, and downhole tools.
- AM qualification momentum: More vendors publish LPBF/DED material cards and heat-treatment windows for Ni–Mo compositions, including HIP’d property data.
- Cleaner powders: Expanded EIGA/PA capacity lowers O/N/H levels and tightens satellite/hollow control, improving fatigue and corrosion outcomes.
- Cost stabilization: Mo price volatility moderated in 2025; long-term contracts reduce powder price swings for Ni–Mo prealloys.
- Sustainability: Increased revert usage with O/N/H monitoring and documented powder-reuse cycles without compromising corrosion performance.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Nickel Molybdenum Powder)
| Metric (2025) | Typical Value/Range | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM-grade Ni–Mo powder price | $70–$160/kg | -2–6% | Supplier quotes; moderated Mo pricing |
| Recommended PSD (LPBF / DED) | 15–45 µm / 45–150 µm | Stable | OEM parameter guides |
| Sphericity (SEM/image analysis) | ≥0.92–0.97 | Slightly up | Supplier CoAs |
| Oxygen content (AM-grade) | ≤0.03–0.05 wt% | Down | EIGA/PA adoption |
| Typical LPBF density after HIP | 99.7–99.95% | +0.1–0.2 pp | OEM/academic datasets |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 6–8 cycles | Stable | O/N/H tracking + sieving |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards (52900 series; 52907 powders; 52908 machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench and powder metrology: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM International Handbooks (Nickel Alloys; Corrosion; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Ni–Mo Impellers for Acid Transfer Pumps (2025)
Background: A chemical processor needed corrosion‑resistant impellers with internal channels for HCl service.
Solution: Argon gas‑atomized Ni–Mo powder (65Ni–35Mo), PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.95; 280°C plate heating; island scan with contour-first; HIP + solution treat; electropolish of flow paths.
Results: Density 99.9% post‑HIP; CT showed zero through‑wall porosity; corrosion rate in 10% HCl at 60°C reduced by 35% vs. cast Ni alloy baseline; pump efficiency +4.2%.
Case Study 2: DED Repair of Ni–Mo Valve Seats in Sour Gas (2024)
Background: Oil & gas operator sought on‑site repair with high sour‑service resistance.
Solution: DED using 45–125 µm Ni–Mo powder with controlled O ≤0.04 wt%; preheat and interpass temperature control; post‑weld HIP surrogate (high‑pressure heat treat) + finish machining.
Results: Hardness 320–360 HV; no sulfide stress cracking in NACE TM0177 testing; service life projected +25% vs. prior weld overlay.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Tresa Pollock, Distinguished Professor of Materials, UC Santa Barbara
Key viewpoint: “Powder cleanliness and morphology—especially low hollow and satellite fractions—are decisive for fatigue and corrosion reliability in Ni–Mo AM components.” - Dr. John R. Scully, Charles Henderson Professor of Materials Science, University of Virginia
Key viewpoint: “Molybdenum’s role in stabilizing passive films under reducing acids makes Ni–Mo alloys uniquely suited to aggressive chloride environments.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “Inline O/N/H trending and CT quantification of defects are now standard for qualifying Ni–Mo powder lots for aerospace and chemical service.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and corrosion guidance
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders) and 52908 (Machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NACE/AMPP standards for sour service corrosion testing: https://www.ampp.org
- Handbooks and data
- ASM Handbooks (Nickel and High‑Temperature Alloys; Corrosion; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
- Metrology and QC
- Interstitials: LECO O/N/H analyzers
- PSD/shape: Malvern Mastersizer, SEM image analysis
- CT for hollow/satellite fraction: industrial CT solutions
- Electrochemical test methods for corrosion rate and pitting potential
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced 2025 trends with data table and sources; provided two recent Ni–Mo case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; listed practical tools/resources for Nickel Molybdenum Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM or AMPP publish updated powder/corrosion standards, major OEMs release validated Ni–Mo AM property cards, or new datasets on powder cleanliness–corrosion correlations become available