철 티타늄 분말 은 철과 티타늄으로 구성된 엔지니어링 소재로, 뛰어난 특성의 독특한 조합을 제공합니다. 이 심층 가이드에서는 야금 및 구성부터 주요 특성, 가공 방법 및 주요 산업 전반의 일반적인 응용 분야에 이르기까지 철 티타늄 분말의 모든 주요 측면을 다룹니다.
철 티타늄 분말 개요
철 티타늄 분말(FeTi 또는 철-티타늄 합금이라고도 함)은 주로 철(Fe)과 티타늄(Ti) 금속으로 구성됩니다. 특수 분무 공정을 통해 분말 형태로 생산됩니다.
철 티타늄을 우수한 기능성 소재로 만드는 주요 속성은 다음과 같습니다:
- 매우 부드러운 자기 특성
- 고채도 유도
- 우수한 온도 안정성
- 낮은 강제성
- 높은 저항률
- 낮은 와전류 손실
- 뛰어난 산화 및 내식성
고유한 특성으로 높은 인덕턴스, 낮은 손실, 안정성 및 강도가 중요한 전자기, 전자 및 전력 애플리케이션에 사용할 수 있습니다.
철 티타늄 분말의 구성
| 재료 | 무게 % 범위 |
|---|---|
| 철(Fe) | 40% – 60% |
| 티타늄(Ti) | 잔액 |
다양한 철 대 티타늄 비율과 촘촘한 파우더 크기 분포로 제공되므로 애플리케이션 요구 사항에 맞게 정밀하게 조정할 수 있습니다.
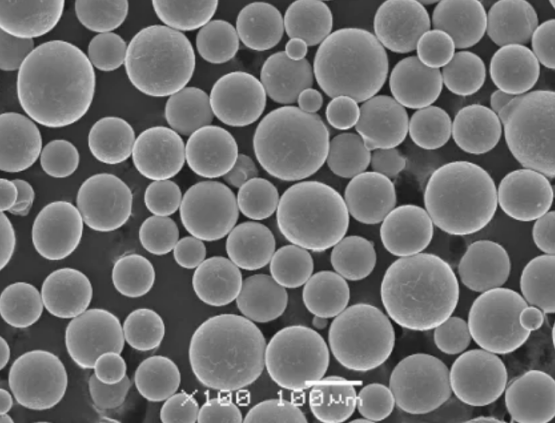

속성 철 티타늄 분말
주요 속성을 이해하면 다양한 작동 조건에 맞는 소재를 선택하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
물리적 및 기계적 특성
| 속성 | 일반 값 |
|---|---|
| 밀도 | 4.3 – 5.0 g/cm3 |
| 영의 계수 | 120-160 GPa |
| 포션 비율 | ~0.32 |
| 인장 강도 | 250-450 MPa |
| 압축 강도 | 500-650 MPa |
열 및 전기적 특성
| 속성 | 일반 값 |
|---|---|
| 전기 저항 | 70-90 μΩ.cm |
| 열 전도성 | 15-25 W/m.K |
| 퀴리 온도 | 350°C |
| 채도 유도 | 1.7-2.2 T |
내화학성 속성
에 대한 저항력이 뛰어납니다:
- 산화 및 부식
- 산과 알칼리
- 유기 용제
- 습도 및 습기
- 높은 온도
이러한 다목적성은 열악한 애플리케이션 환경에서도 사용할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
철 티타늄 분말의 가공 방법
철 티타늄 분말은 물 분무 방식을 사용하여 제조됩니다. 이 과정에는 다음이 포함됩니다:
- 진공 상태에서 철과 티타늄을 유도 용해합니다.
- 용융 합금 스트림을 고압 워터 제트에 붓기
- 미세한 구형 분말로 빠른 응고
- 엄격한 크기 분포로 선별
- 최적의 자기 특성을 위한 어닐링
용융 스트림 유량, 수압, 온도, 분무 노즐 설계와 같은 생산 파라미터를 정밀하게 제어하여 분말 특성을 맞춤화할 수 있습니다.
일반적인 크기 분포
철 티타늄 분말은 매우 미세한 입자 크기부터 거친 입자 크기까지 제공됩니다:
| 메시 크기 | 마이크로미터 |
|---|---|
| -635 | 20μm |
| -325 | 40 μm |
| -100 | 150 μm |
| -50 | 300 μm |
표준 및 사용자 지정 입자 크기 모두 요구 사항을 충족할 수 있습니다.
철 티타늄 분말 응용 분야
철 티타늄의 특수한 재료 특성을 활용하는 주요 애플리케이션은 다음과 같습니다:
전자기 애플리케이션
- 솔레노이드 코어
- 선형 모터 전기자
- 액추에이터
- 마그네틱 베어링
- 인덕터 및 초크
전자 애플리케이션
- 소음 억제 시트
- EMI/RFI 차폐
- 안테나 코어
- 플라이백 변압기
- 전원 공급 장치 전환
전기 모터 애플리케이션
- 모터 라미네이션
- 회전 기계
- 발전기 로터 슬리브
- 매우 효율적인 모터
- 트랙션 모터
새로운 애플리케이션 공간
- 무선 충전
- 전기 자동차
- 재생 에너지
- 스마트 그리드 인프라
- 방위 및 항공 우주
신규 및 성숙 산업 모두 가장 까다로운 부품 및 하위 시스템에 철 티타늄 분말을 구현하는 새로운 방법을 계속 찾고 있습니다.
사양 및 등급
파우더 특성을 이해하면 적절한 소재를 선택할 수 있습니다.
일반적인 사양
| 속성 | 세부 정보 |
|---|---|
| 구성 | 40-60% Fe, 균형 Ti |
| 파티클 모양 | 구형 |
| 겉보기 밀도 | 2.5-3.5g/cm3 |
| 탭 밀도 | 3.5-4.5 g/cm3 |
| 하우스너 비율 | 1.25 |
| 유량 | 15-25초/50g |
| 입자 경도 | 250-450 HV |
철 티타늄 분말 등급
| 등급 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| FT-1X | ~Fe-50Ti : 일반 목적 |
| FT-2X | ~Fe-40Ti: 고유도 |
| FT-3X | ~Fe-60Ti: 안정성 향상 |
| FT-4X | 클라이언트 지정 |
등급을 통해 의도된 운영 환경에 맞게 자기 성능, 온도 등급 및 비용의 균형을 맞출 수 있습니다.
공급업체 및 가격
엔지니어링된 첨단 소재인 티타늄 분말은 전문 공급업체와의 연결이 고성능 철 티타늄 분말을 조달하는 데 중요합니다.
선도적인 철 티타늄 분말 제조업체 및 공급업체
| 회사 | 위치 |
|---|---|
| 마그네퀀치 | 싱가포르 |
| AMF | 미국 |
| 히타치 금속 | 일본 |
| TDK | 일본 |
| Vacuumschmelze GmBH(VAC) | 독일 |
가격 범위
| 파우더 등급 | kg당 가격 |
|---|---|
| FT-1X | $55 – $120 |
| FT-2X | $95 – $180 |
| FT-3X | $135 – $250 |
| FT-4X | 사례별로 인용 |
가격은 주문량, 입자 크기 분포, 구성 목표, 순도 수준에 따라 달라집니다.
장점과 단점 철 티타늄 분말
대안에 대한 주요 장단점을 이해하면 선택에 도움이 됩니다.
| 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|
| 매우 높은 채도 유도 | 실리콘강보다 낮은 인장 강도 |
| 온도 안정 특성 | 부서지기 쉬운 머티리얼 동작 |
| 부식 및 산화 방지 | 수소 취성에 취약함 |
| 다양한 투과성 사용 가능 | 보호 대기 처리 필요 |
| 비정질 및 나노 결정보다 저렴한 비용 | 페라이트보다 비싸다 |
대부분의 전자기 및 전기 기계 응용 분야에서 뛰어난 효율로 매우 부드러운 자기 거동이 기계적 한계를 능가하기 때문에 다양한 경쟁 옵션보다 선택되는 소재입니다.
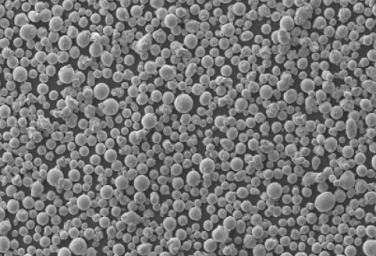
자주 묻는 질문
Q: 철 티타늄 파우더는 3D 프린팅과 호환되나요?
A: 예, 철 티타늄 분말은 바인더 분사 및 기타 금속 적층 제조 공정에 사용하여 기존 제조의 제한 없이 복잡한 연자성 부품을 제작할 수 있습니다.
Q: 철 티타늄과 바나듐 철 티타늄의 차이점은 무엇인가요?
A: 소량의 바나듐(V)을 첨가하면 퀴리점을 높여 온도 안정성이 더욱 향상됩니다. 그러나 포화 자화도는 약간 떨어집니다. 운영 환경에 대한 장단점을 평가하세요.
Q: 철 티타늄을 와이어로 뽑을 수 있나요?
A: 까다롭기는 하지만 적절한 윤활제를 사용한 특수 와이어 드로잉 공정을 통해 틈새 애플리케이션을 위한 초박형 철 티타늄 와이어를 만들 수 있습니다. 패스당 면적 감소를 줄이고 정기적으로 어닐링합니다.
Q: 철 티타늄은 극저온의 영향을 받나요?
A: 아니요, 철 티타늄은 극저온의 극저온에서도 부서지거나 변형되지 않고 일관된 자기 거동과 기계적 무결성을 유지하므로 특수 저온 애플리케이션에 적합합니다.
결론
매우 부드러운 자기 특성, 높은 유도성, 온도 안정성, 우수한 내식성을 갖춘 철 티타늄 분말은 경쟁 소재와 비교할 수 없는 독보적인 기능을 제공합니다. 이를 통해 차세대 전기 기계 및 전력 전자 시스템은 획기적인 차원의 효율성, 전력 밀도 및 신뢰성에 도달할 수 있습니다. 이 기술 가이드는 철 티타늄이 귀사의 전자기 또는 전자 설계 요구 사항에 적합한 솔루션인지 평가할 때 출발점이 될 수 있습니다. 정확한 응용 분야 요구 사항에 맞는 분말 특성에 대한 자세한 정보와 도움을 받으려면 엔지니어링 소재 전문가에게 문의하시기 바랍니다.
Additional FAQs About Iron Titanium Powder
1) What impurity levels matter most for magnetic performance in Iron Titanium Powder?
- Oxygen (<0.15 wt%), nitrogen (<0.02 wt%), hydrogen (<10–20 ppm), and carbon (<0.05 wt%). Elevated O/N raises coercivity and lowers permeability; H can promote embrittlement.
2) Which consolidation routes best preserve soft-magnetic properties?
- Cold compaction + hydrogen/vacuum sintering, warm compaction, and metal injection molding (MIM). For AM, binder jetting with low-temperature debind + sinter is preferred over high-energy LPBF to limit grain growth and residual stress.
3) How do Fe:Ti ratios affect key properties?
- Higher Fe (e.g., Fe-60Ti) increases saturation induction and lowers resistivity; higher Ti (e.g., Fe-40Ti) improves resistivity and thermal stability but slightly reduces induction. Choose based on frequency and loss targets.
4) What coatings or binders reduce eddy-current losses in high-frequency use?
- Organic or inorganic insulating coatings (phosphate, silica, alumina) on Iron Titanium Powder particles create distributed air gaps, boosting resistivity and lowering core loss for >10 kHz applications.
5) Is Iron Titanium Powder suitable for corrosive or humid environments without plating?
- Often yes due to inherent oxidation/corrosion resistance, but for salt-laden or acidic environments, add thin conversion coatings (phosphate) or polymer overcoats to protect sintered or pressed cores.
2025 Industry Trends for Iron Titanium Powder
- EV power electronics: Rising adoption of Iron Titanium Powder in EMI filters and high-frequency inductors for 800 V architectures.
- Powder circularity: 6–10 reuse cycles validated in binder jet/MIM workflows with inline O/N/H checks, cutting material OPEX by 10–15%.
- High-resistivity grades: Growth of Ti-rich and V-modified Fe–Ti variants to reduce losses at 20–200 kHz.
- Surface-engineered powders: Factory-applied nano-oxide/phosphate shells standardize insulation and reduce process variability.
- Standards maturation: New guidance within ISO/ASTM for magnetic powder characterization (loss, µr, Bsat) accelerates supplier comparisons.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Iron Titanium Powder)
| Metric (2025) | 값/범위 | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM/MIM-grade Iron Titanium Powder price | $85–$180/kg | -3–6% | Capacity, better recycling; industry reports |
| Typical apparent density (as-supplied) | 2.6–3.4 g/cm³ | Stable | Supplier datasheets |
| Core loss at 100 kHz, 100 mT (insulated, pressed) | 90–140 mW/cm³ | -5–10% | Improved coatings/process |
| Reuse cycles (binder jetting, with QC) | 6–10 cycles | +2 cycles | Inline O/N/H monitoring |
| EV/energy share of demand | 25–35% | +6–8 pp | Market analyses for e-mobility and renewables |
Indicative sources for validation:
- ISO/ASTM metal powders and magnetic materials standards: https://www.iso.org, https://www.astm.org
- IEEE Magnetics Society publications: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org
- NIST materials metrology and magnetic property methods: https://www.nist.gov
- Market overviews: Wohlers/Context AM; industry supplier white papers
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Low-Loss Fe–Ti Inductor Cores via Binder Jetting (2025)
Background: A power electronics OEM needed compact, low-loss inductors at 50–150 kHz for an 800 V inverter.
Solution: Used Ti-rich Iron Titanium Powder with factory phosphate insulation; binder jet printed near-net shapes; debind at 300–400°C, sintered in dry H₂ then post-annealed in vacuum; applied thin polymer overcoat.
Results: Core loss 105 mW/cm³ at 100 kHz/100 mT; Bsat 1.85 T; permeability 55 ± 3; dimensional tolerance ±0.1 mm as-printed; 12% reduction in inverter filter mass vs. ferrite baseline.
Case Study 2: V-Modified Fe–Ti for High-Temperature EMI Filters (2024)
Background: Rail traction systems required stable inductance up to 180°C with minimal drift.
Solution: Adopted Fe–Ti–V alloy (small V addition) to raise Curie temperature and stabilize µ; warm compaction with insulated powder, steam aging to passivate surfaces.
Results: Inductance drift <3% from 25–180°C; Curie temperature +20–30°C vs. baseline; corrosion rate in ASTM B117 salt spray reduced by ~25% with passivation.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Michael Coey, Emeritus Professor of Magnetism, Trinity College Dublin
Key viewpoint: “For soft-magnetic powders like Fe–Ti, resistivity and grain boundary control are decisive at high frequency—surface insulation can outperform chemistry tweaks alone.” - Dr. Philip D. McCloskey, Principal Engineer, Power Magnetics (Industry)
Key viewpoint: “Binder jetting of Iron Titanium Powder is reaching production—consistent O/N/H and controlled sinter atmospheres are the gating factors for low, repeatable core losses.” - Prof. Reza Abdolvand, Materials Processing Researcher
Key viewpoint: “Minor alloying (e.g., V) and post-sinter stress-relief anneals markedly improve thermal stability without sacrificing saturation induction.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- ASTM A773/A804 (magnetic testing) and related soft magnetic material standards
- https://www.astm.org
- IEEE Magnetics Society journals and conference proceedings
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org
- NIST magnetic materials metrology and materials data
- https://www.nist.gov
- Thermo-Calc and JMatPro for Fe–Ti phase equilibria and Curie temperature modeling
- https://thermocalc.com | https://www.sentesoftware.co.uk
- Open-source tools for magnetic component design (FemM, OpenMagnetics)
- https://www.femm.info | https://openmagnetics.io
- OEM application notes on powder insulation and compaction (VAC, TDK, Hitachi Metals)
- Supplier technical libraries
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; included 2025 trends with data table and sources; provided two recent case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; curated tools/resources tailored to Iron Titanium Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if new ISO/ASTM magnetic powder standards are released, major suppliers introduce nano-oxide coated grades, or NIST publishes updated high-frequency core loss benchmarks

