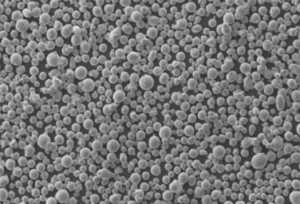
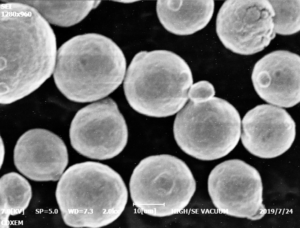
구리 합금 분말 은 산업 전반에 걸쳐 제조 및 표면 엔지니어링을 위한 다용도 소재입니다. 이 가이드는 다양한 구리 분말 유형, 구성, 주요 특성, 제조 방법, 코팅, 프레스, 사출 성형에서의 사용, 가격 및 공급업체 세부 정보에 대한 포괄적인 개요를 제공합니다.
구리 합금 분말이란 무엇인가요?
구리 합금 분말은 구리가 아연, 주석, 알루미늄, 니켈, 실리콘, 크롬 등의 다른 원소와 미세한 입자 수준에서 결합된 것으로 구성됩니다. 블렌딩은 열/전기 전도도, 내식성, 내마모성, 경도 등의 재료 강도의 균형을 맞추고 최종 사용 케이스 사양에 맞게 조정합니다.
구리 합금을 가치 있게 만드는 주요 특성:
- 높은 열 및 전기 전도성
- 내식성
- 충격 및 내마모성
- 사용자 정의 가능한 기계적 특성
- 납땜 가능성
- 분말 야금을 통한 제조 가능성
구리를 2차 금속으로 조정하면 자동차, 해양, 전자, 방위산업 등 다양한 산업에서 순수 구리와 황동 분말을 넘어선 옵션이 확장됩니다.
구리 합금 분말 구성
구리 합금의 잠재적 조합과 비율은 수천 가지가 존재합니다. 몇 가지 일반적인 합금과 그 원소 구성은 다음과 같습니다:
| 합금 유형 | 주요 구성 요소 |
|---|---|
| 황동 | 구리 + 아연 |
| 브론즈 | 구리 + 주석 + 아연 |
| 구리-니켈 | 구리 + 니켈 |
| 컵로니켈 | 구리 + 니켈 + 망간 |
| 노르딕 골드 | 구리 + 아연 + 알루미늄 + 주석 |
추적 요소 철, 납, 인, 흑연 또는 마그네슘과 같은 원소도 특정 합금에 존재할 수 있습니다. 순도 수준을 지정하면 오염 물질을 걸러낼 수 있습니다.
합금 등급 백분율을 정의합니다(예: CuZn30은 구리 70%, 아연 30%를 의미합니다). 다양한 비율을 통해 경도, 강도, 융점 및 전도도를 애플리케이션 요구 사항에 맞게 조정할 수 있습니다.
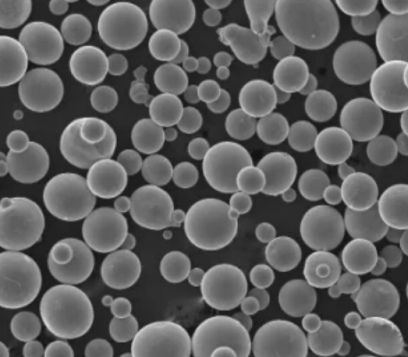
구리 분말 합금의 주요 특성
구리 합금 입자 가치 있는 특성을 보여줍니다:
| 속성 | 기여 |
|---|---|
| 전기 전도성 | 효율적인 열 방출로 과열 방지 |
| 열 전도성 | 빠른 열 전달로 작동 온도 유지 |
| 내식성 | 풍화 및 대기 노출을 견뎌냅니다. |
| 항균성 | 고유한 생체 정전기 표면 활성으로 미생물 감소 |
| 소음 감쇠 | 진동 및 소리 에너지 흡수 |
| 기계 가공성 | 철 합금보다 부드럽고 제작이 용이합니다. |
| 마찰 저항 | 슬라이딩 표면 사이의 윤활성 유지 |
| 스파크 저항 | 가연성 물질 주변의 발화 위험 완화 |
다양한 원소 비율을 통해 인장 강도, 융점, 도금성, 자성 등의 특성을 조정하여 염분이 많은 해양 환경부터 고전압 회로에 이르기까지 다양한 응용 분야의 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
구리 합금 분말 제조
구리 합금 분말의 상업적 생산 방법은 다음과 같습니다:
| 방법 | 세부 정보 | 입자 크기 |
|---|---|---|
| 원자화 | 용융 금속 흐름이 빠르게 냉각되는 작은 물방울로 회전합니다. | 5μm ~ 150μm |
| 카보닐 | 화학 반응으로 순수한 금속을 입자에 증착 | 1μm ~ 15μm |
| 롤러 밀 | 금속을 평평한 조각으로 압축 및 연마하기 | 메시 플레이크 100개(~150μm) |
| 전기 분해 | 음극에 용해되어 전해 증착된 양극 금속 | 광범위한 분포 |
이러한 기술을 통해 산업 용도에 맞게 크기 분포를 제어할 수 있는 미세한 구형, 벗겨지거나 불규칙한 입자를 생산합니다. 추가 어닐링, 분쇄, 분류, 체질을 통해 정밀한 입자 크기와 순도를 달성할 수 있습니다.
현장 합금 구성 금속 분말을 공식에 따라 혼합한 다음 압축, 3D 프린팅 또는 사출 성형을 통해 그물 모양의 구성 요소로 통합하는 과정을 거칩니다. 이를 통해 소규모로 특수 혼합이 필요한 경우 물류가 간소화됩니다.
구리 분말 합금의 응용 분야
구리 합금 분말의 주요 산업적 용도는 다음과 같습니다:
| 애플리케이션 | 세부 정보 |
|---|---|
| 표면 코팅 | 용사 코팅, PVD, 용접 와이어 |
| 부싱 및 베어링 | 무급유 윤활성, 내장성 |
| 브레이징 합금 | 금속, 세라믹용 접합제 |
| 사출 성형 부품 | 그물 모양의 작은 구성 요소 |
| 부품 프레스 및 소결 | 구조용 부싱, 가이드, 슬리브 |
| 3D 프린팅 필라멘트 | 프린터용 맞춤형 등급 |
| EMI 차폐 | 전자제품의 신호 선명도 |
| 다이아몬드 도구 | 바인더 매트릭스, 절단 보조 |
구리 합금의 독특한 열적, 전기적, 기계적 특성은 중장비의 마찰을 줄이는 것부터 첨단 전자제품의 방열판을 활성화하는 것까지 중요한 요구 사항을 충족합니다.
구리 합금 분말 사양
구리 분말 합금을 특징짓는 주요 매개변수:
| 속성 | 일반적인 값 |
|---|---|
| 입자 모양 | 구형, 불규칙, 벗겨짐 |
| 치수 | 1 미크론 ~ 150 미크론 |
| 크기 분포 | 10μm 미만, 53μm 등의 비율. |
| 겉보기 밀도 | 약 2-4g/cm3 |
| 탭 밀도 | 최대 약 70%의 재료 밀도 |
| 흐름 속도 | 휴식 각도 &t; 40° |
| 산화물 콘텐츠 | 3% 목표 |
| 오염 제한 | 구성별 1% |
크기 분포, 순도 수준, 입자 형상, 겉보기 밀도 및 유속을 지정하면 주어진 제조 공정 요구 사항에 맞게 생산 실행 전반에 걸쳐 성능 반복성을 보장할 수 있습니다.
구리 합금 분말 가격
구리 합금 입자의 가격 동인은 다음과 같습니다:
- 비금속 시장 가격
- 순도 등급
- 정확한 합금 비율
- 특수 구성
- 입자 크기 및 분포
- 주문량 및 로트 크기
| 유형 | 가격 범위 |
|---|---|
| 구리 분말 | 5 &8211; 파운드당 $15 |
| 황동 분말 | 파운드당 $6 &8211; $25 |
| 브론즈 파우더 | 파운드당 $6 &8211; $30 |
| 구리 니켈 분말 | 15 &8211; 파운드당 $50 |
가격은 생산 방식에 따라 달라지며, 예를 들어 원자화는 비용이 많이 들지만 적층 제조에 적합한 매우 구형의 정제된 분말을 얻을 수 있습니다. 가격의 뉘앙스를 더 자세히 설명하려면 여기에 필요한 시간 또는 콘텐츠와 같은 모든 매개변수를 정량화하세요.
구리 합금 분말의 상위 공급업체
| 공급업체 | Locaiton | 참고 |
|---|---|---|
| 금속 분말 제조 | UK | 다양한 청동, 황동, 구리 분말 |
| ACuPowder | US | 구리 니켈, 주석 합금 |
| 상하이 CNPC | 중국 | 황동, 청동, 크롬 구리 분말 |
| 호가나스 | 스웨덴 | 브레이징, 표면 엔지니어링 합금 |
이러한 주요 분말 금속 가공 공급업체는 표준 카탈로그 합금과 함께 글로벌 시장에서 주어진 생산 기술 및 부품 성능 요구 사항에 적합한 구성 및 미립자 사양을 맞춤화할 수 있는 기능을 제공합니다.
구리 합금 분말 &8211; 장단점
구리 입자의 장점:
- 높은 전기 및 열 전도성
- 내식성으로 수명 유지
- 항균 특성으로 생물 오염 방지
- 강철 합금보다 부드럽고 쉽게 제작 가능
- 결합 표면과의 마찰 감소
- 원하는 속성에 대한 사용자 지정 비율
구리 파우더의 단점은 다음과 같습니다:
- 일반적으로 경쟁 합금보다 무겁습니다.
- 강철 또는 알루미늄보다 더 큰 재료 비용
- 작은 입자 크기로 인한 산화 위험
- 심미성을 위한 더 무거운 마감 요구 사항
- EPA 기준치 이상의 밀도에서 수생 생물에 영향을 미칩니다.
316L 스테인리스 또는 알루미늄과 같은 대체 소재에 대한 전체적인 수명 주기 비용을 이해하면 대상 애플리케이션 전반에 걸쳐 유용한 강점과 장기적인 사용 가치의 균형을 맞출 수 있습니다.

자주 묻는 질문
Q: 일반적인 구리 합금 분말에는 어떤 것이 있나요?
A: 황동, 청동, 구리-니켈, 노르딕 골드는 전기적, 내식성, 기계적 특성이 균형을 이루는 널리 생산되는 합금입니다.
Q: 구리 분말의 일반적인 입자 크기는 어느 정도인가요?
A: 입자는 MIM 프레스에 적합한 1미크론 분말부터 열분무에 사용할 수 있는 120메쉬 플레이크까지 다양한 범위의 입자를 포함합니다.
Q: 구리 합금 분말의 가격은 얼마인가요?
A: 가격은 기본 금속 가격, 순도, 생산 방식, 주문량에 따라 단순 구리의 경우 5~15달러/파운드에서 더 이색적인 조합의 경우 최대 50달러/파운드까지 다양합니다.
Q: 특수 구리 합금 분말은 어디에서 구입할 수 있나요?
A: Makin, Hoganas, ACuPowder와 같은 주요 분말 금속 가공 공급업체는 공통 카탈로그 등급 공급과 함께 맞춤형 미립자 생산을 지원합니다.
Q: 구리 분말을 취급할 때 어떤 안전 예방 조치가 필요한가요?
A: 요구 사항은 다른 비금속 분말과 유사하며, 먼지 흡입 위험을 제어하기 위한 환기 장치, 정전기 방지를 위한 접지 장비, 오염 방지를 위한 승인된 방진 마스크 및 장갑 등이 있습니다.
Additional FAQs on Copper Alloy Powder
1) Which copper alloy powder should I choose for high-conductivity thermal management?
Cu–Cr–Zr and Cu–Ni–Si alloys balance conductivity with strength. For maximum conductivity, high‑Cu bronzes or OFHC‑derived copper powders are preferred; for higher softening resistance, Cu–Cr–Zr is common.
2) Can copper alloy powder be used for additive manufacturing (AM)?
Yes. Gas/plasma‑atomized spherical powders with PSD D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm are used in laser PBF; green/blue lasers improve absorption for pure Cu. Binder jetting with fine Cu or bronze powders followed by H2 sinter/HIP is increasingly used for larger, lower‑cost parts.
3) How do zinc and tin contents impact performance in brass and bronze powders?
Higher Zn in brass increases strength but reduces corrosion resistance in chlorides; Sn in bronze improves wear and corrosion resistance but lowers conductivity. Tailor content to prioritize either conductivity or durability.
4) What are best practices to limit oxidation in copper alloy powder?
Specify low O2 content (often <0.3 wt% for AM‑grade bronzes; stricter for pure Cu), store in dry inert conditions, minimize exposure during handling, and consider reducing heat treatments (H2/vacuum) before sinter/print.
5) Do copper alloy powders provide antimicrobial performance?
Yes, many Cu‑rich surfaces inactivate bacteria and some viruses rapidly. Validate efficacy per ISO 22196 or EPA protocols; note that surface finish, alloying additions, and oxide state affect kill rates.
2025 Industry Trends for Copper Alloy Powder
- AM-ready copper feedstocks: Wider availability of spherical Cu and Cu‑alloy powders with low oxygen for LPBF; blue/green lasers standard on premium platforms.
- Power electronics cooling: Cu–alloy lattice heat exchangers and vapor chamber interfaces for SiC/GaN modules scale in production.
- EMI/EMC growth: Binder‑jetted Cu–Sn and Cu–Ni housings used for lightweight shielding with corrosion resistance.
- Sustainable sourcing: Higher recycled copper content with material passports and EPDs demanded by OEMs.
- Process integration: Hybrid routes (AM preforms + forging/HIP) deliver conductivity with improved mechanical properties.
| 2025 Metric (Copper Alloy Powder/AM/PM) | Typical Range/Value | Why it matters | 출처 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF density (spherical Cu/Cu–alloy, post‑HIP) | 98.5–99.8% | Near‑wrought properties for heat exchangers | OEM app notes; peer‑reviewed AM studies |
| Conductivity (LPBF pure Cu, HIP, blue/green laser) | 70–90% IACS | Motor coils and cold plates | Materials datasheets; lab reports |
| Binder‑jetted Cu/Cu‑alloy final density (sinter/HIP) | 95–99% | Large, lower‑cost shielding and housings | Vendor case data |
| Typical LPBF PSD for Cu/Cu‑alloys | D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm | Recoating and melt stability | ISO/ASTM 52907 |
| Indicative price (AM‑grade spherical Cu‑alloys) | $12–$40/kg (brass/bronze); $20–$80/kg (Cu–Cr–Zr, Cu–Ni–Si) | Budgeting and sourcing | Supplier quotes/market trackers |
| Oxygen content (AM‑grade Cu) | ≤0.10 wt% O (target) | Limits porosity/oxidation | OEM specs; ASM references |
Authoritative references and further reading:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (AM feedstock), 52910 (DFAM): https://www.astm.org and https://www.iso.org
- ASM Handbook: Copper and Copper Alloys: https://www.asminternational.org
- NIST AM resources and data: https://www.nist.gov
- EPA antimicrobial copper information: https://www.epa.gov
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Cu–Cr–Zr Cold Plate with Conformal Micro‑Channels (2025)
Background: A power electronics OEM needed high‑conductivity cold plates compatible with SiC modules, with low warp and stable flatness.
Solution: Used spherical Cu–Cr–Zr powder (15–45 μm) on a blue‑laser LPBF system; platform preheat, optimized scan vectors; post‑HIP and aging to restore strength; nickel flash on sealing lands.
Results: 21% lower thermal resistance vs. machined Cu baseplate, flatness maintained within 30 μm after 1,000 thermal cycles (−40 to 150°C), leak‑tight at 10 bar; cost per part reduced 18% at series rate.
Case Study 2: Binder‑Jetted Bronze EMI Housings for Avionics (2024)
Background: An avionics supplier sought corrosion‑resistant, conductive housings with reduced machining.
Solution: Binder jetting fine bronze powder; debind, H2 sinter, selective HIP; chromate‑free passivation for salt‑fog durability.
Results: 96–98% density, shielding effectiveness improved by 8–12 dB (10 MHz–1 GHz) vs. aluminum baseline; 30% lead‑time reduction; passed 500 h ASTM B117 salt fog without red rust.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Alan Luo, Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, The Ohio State University
Key viewpoint: “Cu–Cr–Zr and Cu–Ni–Si offer the best compromise between conductivity and softening resistance for thermal hardware produced from copper alloy powder.” - Dr. Katharina Müller, Head of Surface Engineering, Fraunhofer IFAM
Key viewpoint: “Surface state—oxide chemistry and roughness—governs both corrosion and antimicrobial efficacy on Cu‑alloy parts; post‑treatments must be tuned to the alloy and use case.” - Dr. Brent Stucker, AM Standards Contributor and Industry Executive
Key viewpoint: “Wavelength‑optimized lasers and robust powder specifications have turned copper alloy powder into a production‑grade AM feedstock for heat exchangers and EMI components.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- The Ohio State University: https://www.osu.edu
- Fraunhofer IFAM: https://www.ifam.fraunhofer.de
- ASTM AM Center of Excellence: https://amcoe.org
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and qualification
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock testing), 52910 (DFAM)
- ASTM B214/B212 (sieve/flow), B923 (density), B846 (PM terminology)
- Design and simulation
- Ansys Icepak/Mechanical for electronics cooling and structural checks: https://www.ansys.com
- COMSOL Multiphysics (Heat Transfer, AC/DC): https://www.comsol.com
- nTopology for lattice cold plates and conformal channels: https://ntop.com
- Powder QC and processing
- LECO O/N/H analyzers: https://www.leco.com
- Senvol Database for AM machines/materials: https://senvol.com/database
- HIP and heat‑treat services: https://www.bodycote.com
- Antimicrobial and corrosion guidance
- EPA antimicrobial copper resources: https://www.epa.gov
- ASTM B117 (salt fog) and ISO 22196 (antibacterial activity) references
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 focused FAQs, 2025 trends with metric table and sources, two recent copper alloy powder case studies, expert viewpoints with credible affiliations, and a practical tools/resources list.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM feedstock standards change, major OEMs release new blue/green‑laser Cu AM datasets, or copper alloy powder pricing/availability shifts >10% QoQ.