목차
헤더를 추가하여 목차 생성을 시작하세요.
우리 모두는 구형을 준비하는 일반적인 기술이 거의 없다는 것을 알고 있습니다. 금속 분말가스 자동화(GA), 플라즈마 회전 전극 공정(준비), 플라즈마 원자화(PA), 플라즈마 스페로이드화(PS)입니다.
4가지 최고의 구형 금속 분말 준비 기술:
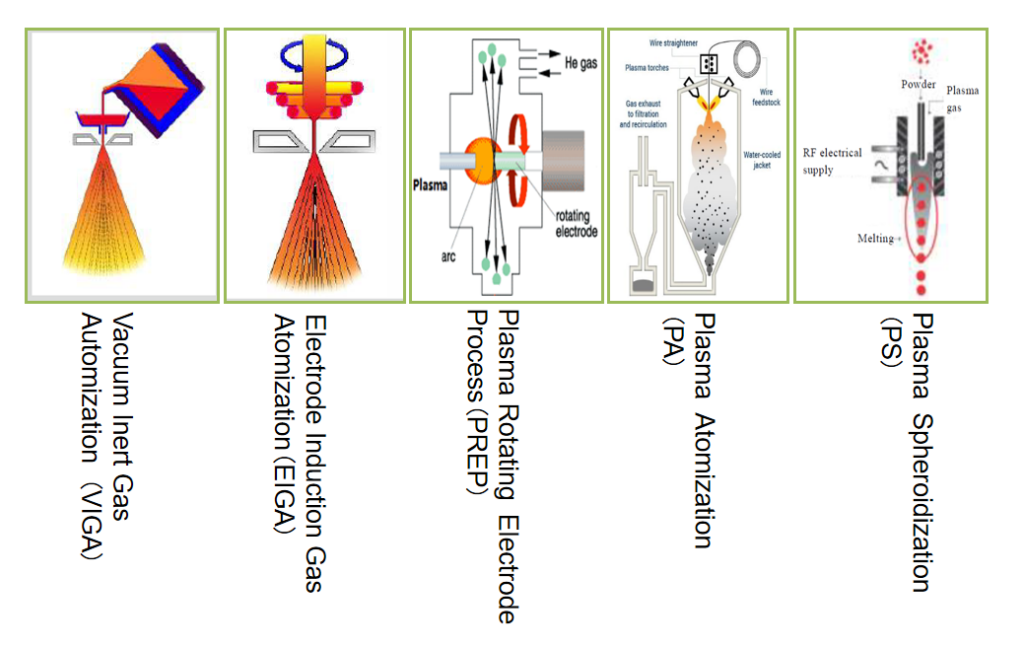
가스 자동화(GA)
에어로졸화된 분말 생산은 고속 기류를 사용하여 액체 금속 스트림을 작은 방울로 분해한 다음 빠르게 응축하여 모양을 갖춘 분말을 생산하는 것입니다.
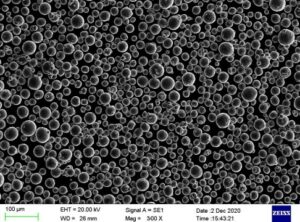
에어로졸화는 미세한 구형 금속 및 합금 분말을 제조하는 가장 중요한 방법이 되었으며, 통계에 따르면 분무에 의한 금속 분말 생산은 전 세계 전체 분말 생산량의 80%에 달합니다. 텅스텐 및 몰리브덴과 같은 내화성 금속과 반응성이 매우 높은 금속을 제외한 거의 모든 일반적인 금속 및 합금 시스템을 포함하여 분무로 산업적으로 생산할 수 있는 금속 분말에는 여러 가지 유형이 있습니다.
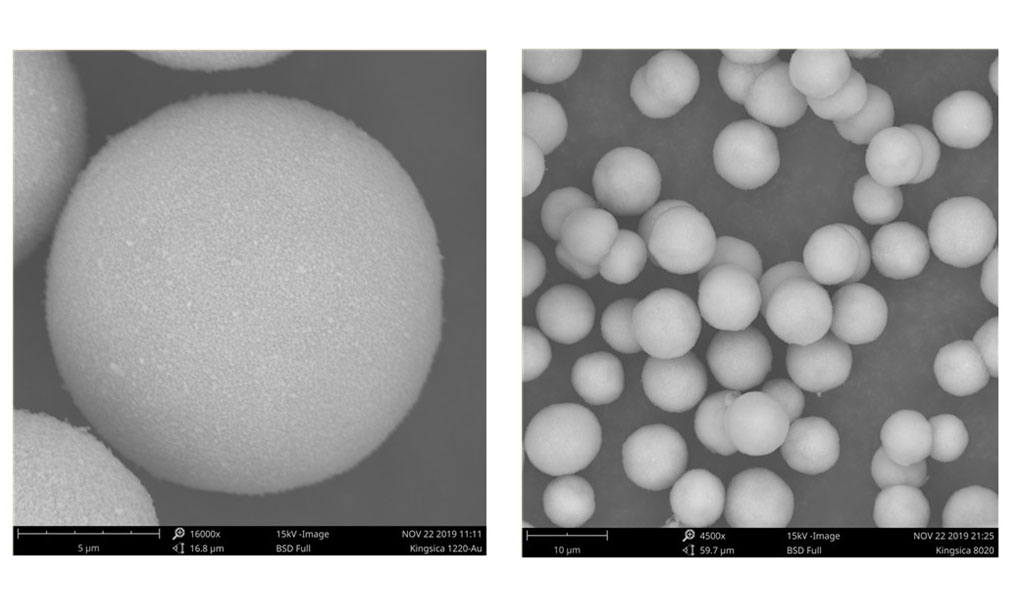
이 방법은 입자 크기(150μm)가 미세하고 구형성이 우수하며 순도가 높고 산소 함량이 낮으며 성형 속도가 빠르고 환경 오염이 적은 금속 분말을 생산하며 분말 야금, 금속 사출 성형 및 금속 첨가제 제조용 금속 분말을 제조하는 주류 방법입니다.
플라즈마 원자화(PA)
플라즈마 원자화(PA)는 특수 공급 메커니즘을 통해 금속 원료(일반적으로 와이어)를 일정한 속도로 공급하는 공정입니다. 원료는 퍼니스 상단에 대칭으로 장착된 여러 개의 플라즈마 토치에서 생성된 집중 플라즈마 제트에 의해 초미립자 또는 에어로졸로 빠르게 분산되고 증착 과정에서 냉각을 위해 불활성 가스와 열 교환되어 구형에 가까운 분말이 만들어집니다.
플라즈마 분무 기술을 사용하면 입자 크기가 작고 순도가 높으며 유동성이 좋은 티타늄 합금 분말을 얻을 수 있습니다. 기존의 분말 제조 기술과 달리 플라즈마 원자화는 일반적으로 사용되는 물 또는 기체 매체 스트림을 사용하여 액체 스트림을 분쇄하는 것이 아니라 고온 플라즈마를 사용하므로 급속 냉각으로 인한 용융 방울의 구형성 저하 문제를 방지할 수 있습니다. 또한 이 방법은 기존의 세라믹 도가니를 사용할 필요가 없으며 녹일 수 있는 모든 금속 재료, 특히 도가니의 오염을 유발하는 티타늄을 포함하는 반응성이 높은 금속 재료의 분말화에 적합합니다.
플라즈마 회전 전극 공정(PREP)
플라즈마 회전 전극 원자화 방법은 고순도 고밀도 구형 분말 재료를 제조하는 가장 이상적인 방법 중 하나입니다. 플라즈마 빔은 열원, 금속 또는 합금은 자체 소비 전극, 전극 끝은 동축 플라즈마에 의해 액체 필름으로 녹고 구형 분말은 자체 고속 원심력과 표면 장력의 작용으로 얻어지는 메커니즘은 다음과 같이 간단히 설명할 수 있습니다.
플라즈마 회전 분무 분말 제조 특성: (1) 분말 입자 크기 분포가 좁고, 입자 크기를 더 제어할 수 있으며, 높은 구형성 가스 분무 방법으로 제조된 합금 분말 입자 크기는 주로 0-150μm의 범위에 집중되며, 플라즈마 회전 전극 분무 방법은 주로 20-200μm의 합금 분말 입자 크기에 집중된다.(2) 분말은 기본적으로 중공 분말, 위성 분말이 존재하지 않습니다 (3) 분말 세라믹 개재물이 적고 청결도가 높습니다 (4) 합금 용융 공정없이 분말 산소 증가가 적습니다. 액체 흐름을 끊는 고속 불활성 기류 없음; 100ppm 이상의 에어로졸 화 분말 산소 증가, 플라즈마 회전 분무 분말 산소 증가는 50ppm 이하로 제어 할 수 있습니다. 적층 제조에서 플라즈마 회전 분무 분말 제조 기술의 장점 1) 분말 고체, 인쇄 공정은 공극, 침입 및 침전 기공, 균열 및 기타 결함으로 인한 중공 볼에 존재하지 않습니다. 2) 분말 입자 크기, 좁은 입자 크기 분포, 인쇄 공정 덜 / 없음 구형화, 응집 현상, 높은 표면 마무리 및 인쇄의 일관성과 균일 성을 완전히 보장 할 수 있습니다.
플라즈마 스페로이드화(PS)
플라즈마 구상화 기술은 플라즈마의 고온 특성을 이용하여 플라즈마에 공급된 불규칙한 모양의 분말 입자를 빠르게 가열하고 녹여 표면 장력과 매우 높은 온도 구배의 결합 효과로 빠르게 응고시켜 구형 분말을 형성하는 기술입니다. 플라즈마는 고온(~104K), 큰 플라즈마 토치 부피, 높은 에너지 밀도, 전극 오염 없음, 빠른 열 전달 및 냉각 등의 장점을 가지고 있습니다. 특히 희귀 내화 금속, 산화물, 질화물, 탄화물 및 기타 구형 분말을 제조할 때 균일한 성분, 높은 구형도 및 우수한 유동성을 가진 고품질 구형 분말을 생산하는 좋은 방법입니다.
위는 여러 유형의 3D 프린팅 파우더 제조 장비의 원리와 특성에 대해 간략하게 소개한 것입니다. 요약하면, 원자화된 분말 제조 기술, 특히 VIGA와 EIGA는 현재 가장 많이 사용되는 분말 제조 기술이지만 다른 여러 기술에 비해 분말의 순도와 구형도에 제한이 있습니다.
PREP, PA, PS 기술을 비교했을 때, PA는 위성 파우더가 더 많고, PS는 원료에 의해 제한되며, PREP는 다른 두 기술에 비해 상대적으로 미세한 수율이 낮습니다.
Additional FAQs on Spherical Metallic Powder
1) Which method yields the highest sphericity and cleanliness for reactive alloys like Ti or Ni superalloys?
PREP generally delivers the highest sphericity and lowest inclusion/oxygen pickup because there is no crucible and minimal melt exposure; EIGA/PA are also strong for reactivity control.
2) How do I choose between Gas Atomization (GA) and Plasma Atomization (PA) for AM powders?
Choose GA for broad alloy coverage and cost efficiency, especially steels and Ni alloys; choose PA for finer PSD, higher sphericity, and lower oxygen in Ti/CoCr, where flowability and purity are critical.
3) When is Plasma Spheroidization (PS) preferable?
PS is ideal for converting irregular feedstocks (e.g., milled, hydride–dehydride Ti, refractory/ceramic powders) to high-sphericity particles, improving flowability without fully remelting large ingots.
4) What PSD ranges are typical for LPBF vs. L-DED from each method?
LPBF: D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm (PA, PREP, fine GA, PS-refined). L-DED: 45–150 μm (coarser GA/PREP cuts). Binder jetting often prefers 5–25 μm with tight tails.
5) How does satellite powder formation impact print quality and how can it be minimized?
Satellites reduce flowability and increase porosity risk. Mitigate via optimized atomization pressure/temperature, nozzle design, post-process classification/sieving, and PS reconditioning for GA/PA lots.
2025 Industry Trends in Spherical Metallic Powder
- Multi-laser AM drives tighter PSD control and lower oxygen specs for GA and PA powders.
- Blue/green laser compatibility pushes demand for high-reflectivity Cu/Al spherical metallic powder with enhanced sphericity and oxide control (e.g., EIGA + PS).
- Sustainability: Powder genealogy, higher recycle blend-back with inline O2/H2O monitoring, and EPDs requested by aerospace/medical OEMs.
- Hybrid routes: GA base powder reconditioned by PS to reduce satellites and narrow PSD; PREP used for premium lots where defect tolerance is minimal.
- Cost-down focus: Improved yield in PREP (adaptive electrode control) and PA (torch optimization) narrowing price gap with GA for Ti-6Al-4V.
| 2025 Metric (Spherical Metallic Powder) | Typical Range/Value | Relevance | 출처 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF PSD target (D10–D90) | 15–45 μm | Flowability and layer quality | ISO/ASTM 52907 |
| Tap density of premium Ti-6Al-4V PA/PREP powders | 2.5–2.9 g/cm³ | Packing, density | OEM datasheets |
| Oxygen spec (Ti AM-grade) | ≤0.13 wt% (ELI), ≤0.20 wt% (Grade 5) | Ductility, fatigue | ASTM F136/F3001 |
| Satellite content (post-PS reconditioning) | <3–5% by count | Flow/defect control | Supplier QC notes |
| Indicative lot yield in PREP (20–200 μm) | 55–70% after classification | Cost and availability | Vendor application notes |
| Market price band (Ti-6Al-4V powder) | ~$80–$200/kg (GA) vs. ~$120–$300/kg (PA/PREP) | Budgeting | Market trackers/suppliers |
Authoritative references and further reading:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Additive manufacturing feedstock): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F2924, F3001 (Ti alloys for AM): https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench datasets: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM Handbook: Powder Metallurgy and Additive Manufacturing: https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: PS Reconditioning of GA Inconel 718 to Reduce Satellites (2025)
Background: An aerospace supplier experienced recoater streaks and variable density from GA IN718 due to satellite-rich lots.
Solution: Applied plasma spheroidization to re-melt particle surfaces, followed by tight classification; implemented inline O2/H2O monitoring and argon recirculation.
Results: Satellite count reduced from ~12% to <3%; Hall flow improved by 18%; LPBF porosity fell from 0.45% to 0.12% without parameter change.
Case Study 2: PREP Titanium Alloy Powder for Thin‑Wall LPBF Lattice Structures (2024)
Background: A medical OEM required high ductility and fatigue life in Ti‑6Al‑4V ELI lattices.
Solution: Switched to PREP powder with narrow PSD (20–40 μm) and O ≤0.12 wt%; applied low‑energy contour scans and stress relief.
Results: 10–15% higher elongation, 25% improvement in HCF endurance at 10⁷ cycles; surface defect incidence reduced, enabling lower CT sampling.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. John Campbell, Casting and Atomization Specialist (Emeritus), University of Birmingham
Key viewpoint: “Control of melt cleanliness and turbulence during atomization is as decisive as gas velocity for minimizing satellites and inclusions.” - Dr. Martina Zimmermann, Head of Additive Materials, Fraunhofer IWM
Key viewpoint: “PS as a secondary step is proving cost‑effective to lift GA powder quality to PA/PREP performance for many aerospace parts.” - Dr. Brent Stucker, AM standards contributor and industry executive
Key viewpoint: “Powder passports tying PSD, O/N/H, and in‑process monitoring to acceptance are accelerating serial qualification of spherical metallic powder.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- University of Birmingham: https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- Fraunhofer IWM: https://www.iwm.fraunhofer.de
- ASTM AM CoE: https://amcoe.org
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and QC
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock), ASTM B214/B822 (PSD), ASTM B212/B329 (apparent/tap density)
- NFPA 484 (combustible metals safety): https://www.nfpa.org
- Characterization labs and equipment
- LECO O/N/H analyzers: https://www.leco.com
- Laser diffraction and SEM services at accredited labs
- Process and design tools
- Ansys Additive, Simufact Additive for parameter optimization and distortion control
- nTopology for lattice design tailored to powder PSD
- Market/data
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- NIST AM Bench datasets: https://www.nist.gov
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 trends with metrics table and sources, two recent case studies on PS and PREP routes, expert viewpoints with citations, and practical tools/resources relevant to spherical metallic powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM feedstock standards update, major OEMs publish new PSD/oxygen specs, or significant price/yield shifts occur in GA/PA/PREP/PS routes.