タングステン粉の紹介
タングステン粉希少で強靭な金属タングステン由来のタングステン粉は、その卓越した特性と多彩な用途により、現代産業において重要な位置を占めている。本稿では、タングステンパウダーの世界を掘り下げ、そのユニークな特性、産業用途、環境への影響、価格要因、そして将来の展望を探る。
タングステン粉末の特性と用途
タングステンを理解する
タングステンは、卓越した高い融点と密度を持ち、周期表で最も重い元素のひとつに数えられています。その粉末はこれらの特性を受け継ぎ、様々な分野で求められる素材となっている。
パウダー製造法
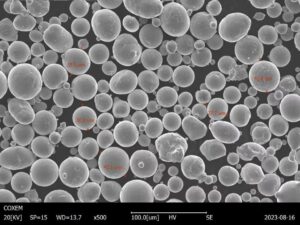
タングステン粉末は、酸化タングステンの水素還元やタングステンの直接浸炭のような方法で製造されます。これらのプロセスは、制御された粒径とさまざまなアプリケーションに適した特性を持つ粉末が得られます。
製造業への応用
製造業ではタングステン粉末が広く利用されています。航空宇宙分野から電子機器に至るまで、その高い引張強度と過酷な条件への耐性は、機械的ストレスに耐える部品の製造に理想的な候補となります。

タングステン粉末の利点
高い密度と強度
タングステンの密度は、その卓越した強度対重量比に寄与しており、航空宇宙工学のようなスペースが制約される用途では不可欠です。
熱伝導率と電気伝導率
タングステンの熱伝導性と電気伝導性は、エレクトロニクス産業において不可欠な要素となっています。効率的に熱を放散し、マイクロ回路や半導体の電気を伝導します。
耐摩耗性と耐腐食性
タングステン粉末は、耐摩耗性と耐腐食性で知られています。この特性は、過酷な環境で使用される工具や機器の耐久性のあるコーティングや材料の製造に利用されています。
タングステン粉末の産業用途
航空宇宙・防衛
タングステンの強度は、高温に耐える能力と相まって、航空機や宇宙船の部品として非常に貴重であり、過酷な条件下での安全性と信頼性を保証している。
電子・電気産業
タングステンの導電性と耐熱性は、白熱電球のフィラメントからマイクロチップやセンサーに至るまで、エレクトロニクス産業で幅広く利用されている。
医療機器とヘルスケア
タングステン粉末は、高密度であるため、医療用画像診断や放射線遮蔽において重要な役割を果たしており、正確な診断とより安全な治療を提供している。
積層造形におけるタングステン粉末
タングステン粉末による3Dプリンティング
アディティブ・マニュファクチャリングはタングステン粉末を採用し、特に航空宇宙や自動車などの産業において、複雑で耐久性のある金属部品の製造を可能にしている。
進歩と課題
タングステン粉末を使った3Dプリンティングが新たな可能性を開く一方で、粉末の取り扱いや後処理方法などの課題には、継続的な技術革新が必要だ。
環境への影響と持続可能性
リサイクルとリユース
資源の枯渇を減らすため、タングステン粉のリサイクルと再利用に向けた取り組みが進められている。循環型経済のアプローチは、廃棄物を最小限に抑え、材料の使用を最適化することを目的としています。
環境に優しいアプリケーション
タングステンの特性は、エネルギー効率の高い照明や再生可能エネルギーシステムなどのグリーンテクノロジーに貢献し、持続可能性における役割をさらに高めている。

タングステン粉の価格に影響を与える要因
需要と供給のダイナミクス
タングステンの価格は世界的な需要に左右される。地政学的問題、技術の進歩、産業の成長などの要因が需給均衡に影響を与える。
市場動向と世界経済
タングステン価格は、経済情勢や市場動向の変化により変動しやすく、タングステンの用途に依存する産業に影響を与える。
取り扱いおよび安全上の注意
健康と安全に関する注意事項
タングステン粉末は吸入の危険性があり、作業員の健康を守るため、取り扱い、保管、輸送において厳格な安全対策が必要である。
安全な保管と輸送
カプセル封入や保護コーティングを含む適切な保管と輸送の慣行は、タングステン粉末への暴露や事故のリスクを軽減する。
タングステン粉末の将来展望
研究と技術革新
現在進行中の研究は、タングステン粉末の特性を向上させ、ナノテクノロジーや先端材料といった新たな領域への応用を拡大することを目指している。
新たなアプリケーション
産業が発展するにつれ、タングステン粉末は宇宙開発から医療まで、最先端の分野で応用されるようになるだろう。

結論
タングステン粉は、その卓越した特性と汎用性により、様々な産業のバックボーンとしての役割を担っています。航空宇宙からエレクトロニクスに至るまで、現代のテクノロジーとイノベーションを形成するタングステン粉の役割は計り知れません。研究が進み、用途が多様化するにつれて、タングステン粉末の将来は有望視されており、更なる飛躍と変化し続ける世界への貢献が期待されています。
よくある質問
1.タングステン粉が工業用途で特別なのはなぜですか? タングステン粉末は、高密度、高強度、耐摩耗性、耐腐食性などの優れた特性を持っています。これらの特性により、耐久性と信頼性の高い材料を必要とする産業で好んで使用されています。その用途は航空宇宙部品から電子機器製造まで多岐にわたり、そのユニークな特性は様々な製品の長寿命化と効率化に貢献しています。
2.タングステン粉の環境に優しい使い道はありますか? もちろんタングステンの特性は、環境に優しい技術での使用を可能にします。例えば、タングステンはLED電球のようなエネルギー効率の高い照明に欠かせない成分です。さらに、タングステンは密度が高いため、医療機器の放射線遮蔽材として重宝され、X線検査などの際に患者の安全を確保しています。
3.3Dプリンティング産業はタングステン粉末からどのような恩恵を受けているのか? 3Dプリンティング業界は、タングステン粉末の能力を利用して、複雑で耐久性のある金属部品を製造しています。タングステンの高い融点と密度は、航空宇宙、自動車、その他要求の厳しい分野の部品のプリントに適しています。この技術により、従来の製造方法では困難であった複雑なデザインの製造が可能になる。
4.タングステン粉末を扱う際には、どのような安全上の注意が必要ですか? タングステンパウダーを取り扱う際には、安全性が最も重要です。タングステン粉末は粒子が細かいため空気中に浮遊しやすく、吸入の危険があります。作業者は、呼吸保護具や手袋などの適切な個人用保護具(PPE)を着用し、曝露を最小限に抑える必要があります。これらのリスクを効果的に軽減するには、適切な換気、管理された環境、安全ガイドラインの遵守が不可欠です。
5.市場動向はタングステン粉の価格にどのような影響を与えるのか? タングステン粉の価格は、様々な市場動向や経済的要因の影響を受けます。エレクトロニクス、航空宇宙、防衛などの産業が牽引するタングステンの世界的な需要は、供給不足と価格上昇につながる可能性があります。さらに、地政学的な問題、技術の進歩、世界経済のシフトは、タングステン粉末の価格ダイナミクスを形成する役割を果たします。これらの要因が変われば、この貴重な材料のコストも変わる可能性があります。
Additional FAQs on Tungsten Powders
1) What particle sizes are optimal for 3D printing with tungsten powders?
For LPBF/SLM, a D10–D90 of roughly 15–45 μm balances flowability and resolution. For binder jetting and sinter-HIP, slightly finer cuts (5–25 μm) improve packing density and sinter necking, though dust control becomes more critical.
2) How do tungsten heavy alloys (W-Ni-Fe/W-Ni-Cu) differ from pure tungsten powders in applications?
WHA powders sinter to high density at lower temperatures and offer improved toughness and machinability versus pure W. They are preferred for radiation shielding, balancing weights, and kinetic energy components, while pure W is favored for high-temperature and thermal management uses.
3) Can tungsten powders be used in electronics thermal management?
Yes. Tungsten and W-based composites are used for heat spreaders and vias due to high thermal conductivity and CTE compatibility with semiconductors. Binder-jetted or LPBF W/Cu graded structures are emerging for next-gen power electronics.
4) What are the main safety risks when processing tungsten powders with lasers or electron beams?
Key risks include fine-powder inhalation, metal dust combustibility of alloying additions or binders, and X-ray generation in high-energy EBM. Controls: local exhaust ventilation (LEV), HEPA filtration, inert atmospheres, ATEX-rated equipment where applicable, and radiation shielding per OEM guidance.
5) How do oxygen and carbon impurities affect sintering and properties of tungsten parts?
Excess O and C form WOx/CO/CO2 at high temperature, causing porosity, grain boundary embrittlement, and reduced thermal conductivity. Maintain low O (typically <0.1 wt% for AM feedstock) and use hydrogen debinding/sintering or vacuum cycles to purge contaminants.
2025 Industry Trends in Tungsten Powders
- Additive manufacturing adoption: Growth in LPBF and binder jetting of tungsten for x-ray collimators, RF components, and high-temp tooling; sinter-HIP routes improve density and toughness.
- Supply diversification: Expanded APT (ammonium paratungstate) and powder capacity outside China to de-risk supply; increased recycling of hardmetal scrap and W-bearing swarf.
- Radiation shielding demand: Medical imaging and nuclear SMR projects drive W and WHA consumption, favoring near-net AM to reduce machining waste.
- Advanced thermal management: W/Cu and W/Mo graded structures for power electronics and aerospace heat sinks.
- ESG and traceability: Material passports and chain-of-custody reporting adopted by major OEMs; lifecycle data integrated with MES/QMS.
| 2025 Metric | Typical Range/Value | Relevance/Notes | ソース |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF tungsten relative density (pure W) | 96–99% after optimized scan + HIP | Achieved via preheat strategies and contour scans | Peer-reviewed AM studies, OEM apps notes |
| Binder-jetted W final density | 94–98% (sinter/HIP) | Suited for complex shielding geometries | Journal reports; vendor data |
| Thermal conductivity of W bulk | 160–180 W/m·K | Benchmark for heat spreaders | MatWeb, handbooks |
| Global tungsten recycling share | ~35–40% of supply | Driven by hardmetal scrap recovery | USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries |
| APT price trend YoY (indicative) | +2–6% | Tight supply, energy costs, demand from defense/medical | Market trackers; ITIA context |
| Typical pore size target for AM shielding lattices | 0.5–2.0 mm cells | Balances mass attenuation vs. weight | Device OEM guidance |
Authoritative sources and references:
- USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (Tungsten): https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- International Tungsten Industry Association (ITIA): https://www.itia.info
- ISO/ASTM AM standards: https://www.iso.org and https://www.astm.org
- NIST materials data: https://www.nist.gov
- FDA device database (radiation shielding, imaging): https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Binder-Jetted Tungsten Collimators for CT Imaging (2025)
Background: A medical OEM needed lighter, complex x-ray collimators with tight channel geometries and high attenuation.
Solution: Adopted binder jetting of pure tungsten powders (D50 ~18 μm), followed by debinding, vacuum sintering, and HIP. Implemented lattice-filled walls to tune attenuation.
Results: Achieved 97.5% density, 18% weight reduction versus machined WHA, improved beam shaping accuracy, and 22% cost reduction due to lower machining time. Early regulatory submission supported with ASTM-based material qualification.
Case Study 2: LPBF W/Cu Functionally Graded Heat Sink for Power Electronics (2024)
Background: An aerospace supplier sought improved thermal cycling reliability for high-power converters.
Solution: Printed a functionally graded tungsten-copper structure using dual-powder deposition and post-infiltration to reach target conductivity; stress-relief plus HIP applied.
Results: 30% lower peak junction temperature and 2× thermal-cycle life vs. monolithic Cu baseline. Non-destructive CT confirmed <1% lack-of-fusion defects in critical regions.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Andreas Gasse, Senior Scientist, International Tungsten Industry Association (ITIA)
Key viewpoint: “Recycling and closed-loop powder management will be the dominant levers to stabilize tungsten powder costs and reduce ESG risk across medical and defense supply chains.” - Prof. Suresh Babu, Governor’s Chair of Advanced Manufacturing, University of Tennessee & ORNL Joint Appointment
Key viewpoint: “For additively manufactured tungsten, process windows that mitigate cracking—preheat, beam shaping, and controlled cooling—are essential to approach wrought-like performance.” - Dr. Elena López, Head of Additive Manufacturing, AIMEN Technology Centre
Key viewpoint: “Binder jetting with sinter-HIP is now a credible route for complex tungsten shielding, provided oxygen is controlled and dimensional change is modeled during densification.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and data
- ITIA technical briefs on tungsten powders: https://www.itia.info
- USGS tungsten statistics and reports: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (powder feedstock), 52910 (design), ASTM B777 (WHA), ASTM B777M: https://www.astm.org
- AM design/simulation
- Ansys Additive Suite (distortion, porosity prediction): https://www.ansys.com
- nTopology for lattice shielding and graded structures: https://ntop.com
- Autodesk Netfabb for support and sintering compensation: https://www.autodesk.com
- Powder QC and processing
- LECO O/N/H analyzers for impurity control: https://www.leco.com
- HIP services and parameters (W/WHA): https://www.bodycote.com
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- Safety and compliance
- OSHA/NIOSH guidance on metal dusts and LEV: https://www.osha.gov and https://www.cdc.gov/niosh
- AMPP resources on corrosion and finishing: https://www.ampp.org
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 curated FAQs, 2025 trend table with metrics and sources, two recent tungsten AM case studies, expert viewpoints, and practical tools/resources.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if APT prices shift >10% QoQ, new ISO/ASTM standards for refractory metal AM are released, or major OEMs publish updated LPBF/binder jet parameters for tungsten.