球状形態のニオブ粉末は、高強度、耐食性、超伝導性、その他特殊な特性の組み合わせを必要とする様々な用途に独自の利点を提供します。このガイドでは 球状ニオブ粉末 組成, 特性, 製造, グレード, 仕様, 用途, 価格, サプライヤー, 長所/短所, その他の詳細を網羅。
球状ニオブ粉末の概要
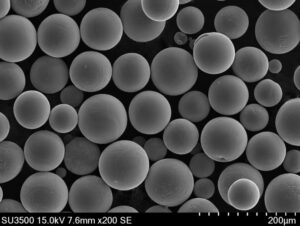
球状ニオブ粉末は、ニオブ金属から構成されるほぼ完全な球状の小粒子からなり、典型的な純度は99%以上です。球状であるため、角状粉末に比べて流動性と充填密度が向上します。
球状ニオブ粉末を有用なものにしている主な特性には、以下のようなものがある:
- 高い強度と弾性率
- 優れた耐食性
- 低摩擦係数
- 低温での超伝導
- 耐熱衝撃性
- 生体適合性と無毒性
微細な球状ニオブ粉末は、溶射皮膜、キャパシタ、超伝導体、積層造形、生物医学インプラント、その他の先端用途に使用されている。本ガイドは、球状ニオブ粉末製品の組成、特性、製造、仕様、グレード、用途について解説しています。
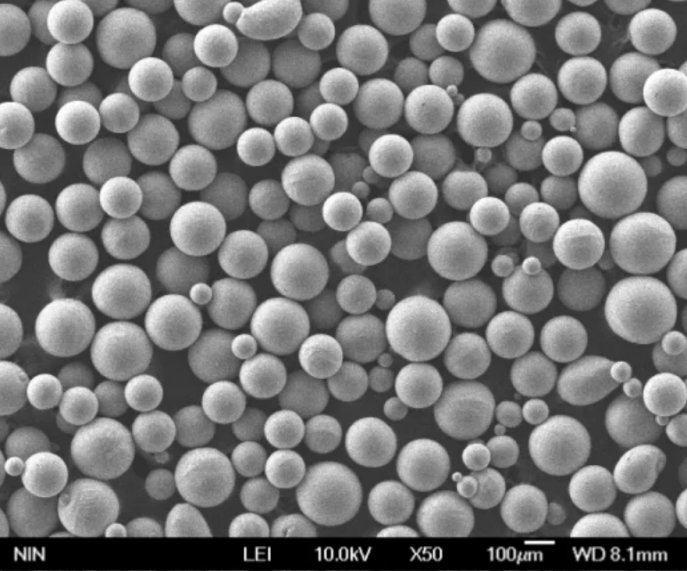

球状ニオブ粉末の組成
コロンビウムとしても知られるニオブは、原子番号41の耐火性遷移金属である。市販のニオブ粉末の不純物限界は、通常以下の通りである:
| エレメント | 重量構成 |
|---|---|
| ニオブ | 99.最低8 |
| 酸素 (O) | 2000ppm以下 |
| 窒素(N) | 100ppm以下 |
| カーボン(C) | 500ppm以下 |
| 水素 (H) | 100ppm以下 |
| 鉄(Fe) | 最大200ppm |
| タンタル (Ta) | 1000ppm以下 |
| タングステン(W) | 100ppm以下 |
多くのニオブの用途では高純度が要求される。より厳密なグレードは純度99.99%以上である。酸素と窒素はニオブを脆化させるので管理されている。
特性 球状ニオブ粉
球状ニオブ粉末の主な特性は以下の通り:
| プロパティ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 密度 | 8.57 g/cm3 |
| 融点 | 2468°C |
| 熱伝導率 | 53.7 W/m-K (20℃の場合) |
| 電気抵抗率 | 12.4~14μΩ・cm(20℃にて) |
| ヤング率 | 105 GPa |
| 引張強度 | 200-400 MPa |
| 伸び | 20-45% |
| 耐食性 | 多くの酸や酸化性媒体に対する優れた耐性 |
| 超伝導温度 | 9.2 K |
この特性は、強度、導電性、耐食性を必要とする用途に適している。
球状ニオブ粉末の製造工程
球状ニオブ粉末は、ガスアトマイズという高度な粉末冶金プロセスを用いて製造される:
| ステージ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| メルティング | 高純度ニオブは真空または不活性ガス中で誘導溶解される。 |
| 霧化 | メルトストリームは不活性ガスで微粒化され、微細な液滴となる。 |
| 固化 | 液滴は冷えると急速に固化し、球状の粉末粒子になる。 |
| コレクション | 球状の粉末はノズルの下のチャンバーに集められる。 |
| スクリーニング | 粒子を目的のサイズ範囲にふるい分ける |
微粒化パラメータは、要求される粒度分布、流動特性、見かけ密度、純度を達成するように制御される。不活性ガスが酸化を防ぎます。
球状ニオブ粉末のサイズと粒度分布
球状ニオブ粉末は、標準メッシュサイズで分類された様々なサイズ分布で入手可能です:
| メッシュサイズ | 粒子径(μm) |
|---|---|
| -325 | 44%未満 |
| -230 | 44-63 |
| -170 | 63-90 |
| -140 | 90-125 |
| -100 | 125-149 |
| -325+500 | 15-44 |
| -230+270 | 63-74 |
一般的な粒度分布では、変動係数が30%未満に保たれ、安定した粒子径が得られます。10μm以下の小粒径は、特殊な噴霧化技術により製造可能です。
球状ニオブ粉末の等級
球状ニオブ粉末は、様々な純度レベルと仕様で入手可能である:
| グレード | 純度(%) | 酸素 (ppm) | 炭素(ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| グレードA | 99.8 | 1200 | 400 |
| グレードB | 99.9 | 800 | 300 |
| グレードC | 99.95 | 500 | 200 |
| Dグレード | 99.99 | 100 | 50 |
グレードDのような高グレードは、純度が高く、特殊用途に必要な格子間不純物レベルが低い。
球状ニオブ粉末の用途
球状ニオブ粉末を使用する主な用途には次のようなものがある:
| 産業 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| エレクトロニクス | 積層セラミックコンデンサ、超電導フィルム |
| コーティング | 溶射皮膜、表面強化 |
| ケミカル | 水素貯蔵、触媒、バッテリー |
| 製造業 | 金属射出成形、積層造形 |
| メディカル | インプラント、放射線不透過性マーカー |
| 航空宇宙 | ロケットノズル、燃焼室 |
最適化された粒子形状は、充填密度を向上させ、焼結、溶射、印刷、複合材料製造における性能を向上させる。
球状ニオブ粉末のグローバルサプライヤー
球状ニオブ粉末の主な世界的サプライヤーには次のようなものがある:
| 会社概要 | 所在地 |
|---|---|
| H.C.スタルク | ドイツ、アメリカ |
| CBMM | ブラジル |
| ジエン ニッケル | 中国 |
| 日本ニューメタルズ株式会社 | 日本 |
| ミクロン金属 | 米国 |
| テグテック | 韓国 |
評判の高いメーカーは、用途要件に適合する高水準の球状ニオブ粉末を製造しています。溶射などの付加サービスを提供するメーカーもあります。
価格 球状ニオブ粉
球状ニオブ粉末のコストは、純度、粒度、分布、数量、製造業者によって幅がある:
- 純度99.8%品位 –50-80ドル/ポンド、99.9%品位 –60-100ドル/ポンド、99.99%品位 –150-300ドル/ポンド
- 粒子径:44μm以下は値上げ
- 数量:25-50ポンド以上のご注文でバルクディスカウント
- メーカー:トップメーカーの高級グレードにプレミアム
お客様の仕様と数量に基づいた正確な価格については、実績のあるニオブのサプライヤーにお問い合わせください。

球状ニオブ粉末の長所と短所
メリット
- 高い強度と硬度
- 優れた耐食性
- 低摩擦係数
- 高い耐熱衝撃性
- 超伝導特性
- 医療用の生体適合性
- 球状の形状がパッキングとフローを改善
デメリット
- 他の金属に比べて高価
- 脆く、冷間時の延性が低い。
- 反応性のため不活性処理が必要
- 限られた世界的供給と生産
- 酸化物は性能に悪影響を与える
- 固形での加工が難しい
よくある質問
Q: 球状のニオブ粉末と不規則なニオブ粉末の違いは何ですか?
A: 球状粉末は、角張った粉末や不規則な粉末に比べ、ほぼ完全な丸みを帯びた形状をしています。そのため、流動性、充填密度が向上し、溶射などの用途で性能を発揮します。
Q: 溶射皮膜に最適な粒子径は?
A: ほとんどの溶射プロセスでは、-170メッシュから-325メッシュ(44~125μm)のサイズが効果的です。10μm以下の微細サイズは、懸濁液または溶液前駆体プラズマ溶射に使用できます。
Q: ニオブ粉末は可燃性や爆発性がありますか?
A: ニオブ粉末は、それ自体では可燃性や爆発性はないが、微粉末は飛散すると爆発性の粉塵雲を形成する可能性がある。不活性ガス処理を推奨する。
Q: 球状ニオブ粉末に毒性はありますか?
A: 金属ニオブの毒性は非常に低く、人体への接触や埋め込み型医療機器には安全であると考えられている。取り扱い上の注意が必要である。
Q: 球状ニオブ粉末はどのように保管され、取り扱われるのですか?
A: 不活性ガス封入と乾燥保管を推奨する。密閉された容器は、粉体の特性を劣化させる酸素や水分の吸収を防ぎます。
結論
最適化された球状形態と純度を持つ球状ニオブ粉末は、エレクトロニクス、コーティング、製造、化学、生物医学、その他の重要な用途において、より優れた性能を発揮します。
球状ニオブ粉末は、ニオブ本来の耐食性を維持しながら、次世代技術やプロセスに必要な流動性、充填密度、強度、導電性を向上させます。
Additional FAQs About Spherical Niobium Powder
1) What PSD and morphology are recommended for additive manufacturing with Spherical Niobium Powder?
- For LPBF, target spherical PSD 15–45 µm with sphericity ≥0.93 and low hollow/satellite fractions; for DED, 53–150 µm with tight sieving. Image analysis and CT help verify morphology for consistent spreadability and density.
2) How do interstitials (O, N, H) affect niobium’s ductility and superconductivity?
- Oxygen and nitrogen increase strength but reduce ductility and can depress superconducting critical temperature (Tc ≈ 9.2 K for high‑purity Nb). Keep O typically ≤1000–1500 ppm for structural uses and ≤100–300 ppm for superconducting applications; minimize H to avoid hydride embrittlement.
3) Which production routes are most common and why?
- Gas atomization is prevalent for cost and throughput; PREP (plasma rotating electrode) yields exceptionally spherical particles with minimal satellites/hollows and very low interstitials, preferred for high‑end AM and superconducting applications.
4) What surface treatments or post‑processing improve AM niobium parts?
- HIP to close porosity, stress relief/anneal in high vacuum or inert gas to reduce residual stress and hydrogen, and precision machining/electropolishing for biomedical or superconducting surface states.
5) Is Spherical Niobium Powder suitable for biomedical implants?
- Yes. Niobium exhibits excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Use high‑purity grades with low interstitials; finish with polishing/passivation and validate per ISO 10993 and application‑specific standards.
2025 Industry Trends for Spherical Niobium Powder
- Superconducting growth: Particle accelerator and quantum device programs are increasing demand for ultra‑high‑purity niobium and low‑oxygen powder for advanced forming/AM routes.
- AM maturation: More parameter sets for LPBF/DED Nb and Nb‑based alloys (Nb‑Ti, Nb‑Zr), including HIP + heat‑treat windows and fatigue/corrosion allowables.
- Cleaner morphology: Wider disclosure of CT‑measured hollow fraction and image‑based satellite counts on Certificates of Analysis.
- Supply diversification: Recycling and alternative ore processing modestly stabilize pricing; closer regional atomization reduces lead times.
- Sustainability: Inert gas recirculation and revert electrodes lower carbon footprint and interstitial pickup.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Spherical Niobium Powder)
| Metric (2025) | Typical Value/Range | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM‑grade spherical Nb price | $90–$180/kg (99.9%); $260–$480/kg (99.99%) | −2–6% | Supplier quotes; purity/PSD dependent |
| Recommended PSD (LPBF / DED) | 15–45 µm / 53–150 µm | Stable | OEM/AM guidance |
| Sphericity (image analysis) | ≥0.93–0.98 | Slightly up | Supplier CoAs |
| Hollow particle fraction (CT) | ≤0.5–1.5% | Down | Process tuning, PREP use |
| Typical oxygen (AM‑grade) | 500–1200 ppm (structural); ≤300 ppm (superconducting) | Down | Improved inert control |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 4–7 cycles | Stable | O/N/H trending + sieving |
| LPBF density after HIP (Nb) | 99.7–99.95% | +0.1–0.2 pp | OEM/academic datasets |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders for AM) and 52908 (Process qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench and powder metrology: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM Handbooks (Powder Metallurgy; Superconducting Materials; Additive Manufacturing): https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Ultra‑Low‑Oxygen Nb Powder for Superconducting Components (2025)
Background: A research lab needed improved Q‑factor in superconducting RF cavity sub‑components made via near‑net AM forming.
Solution: PREP spherical niobium powder (O ≤200 ppm, PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.97); LPBF with high‑vacuum heat treatment post‑build, followed by HIP and electropolish.
Results: Relative density 99.94%; Tc maintained at ~9.2 K; residual resistivity ratio (RRR) increased vs. baseline powder; internal surface roughness reduced 28%, enabling higher Q0 at operational fields.
Case Study 2: Corrosion‑Resistant Nb Lattice Implants via LPBF (2024)
Background: A medical OEM sought lightweight, radiopaque spinal cages with excellent corrosion resistance.
Solution: Gas‑atomized spherical Nb powder (O ~800 ppm), LPBF lattice designs, HIP, machining, and electropolishing; biocompatibility per ISO 10993.
Results: Achieved 99.8% post‑HIP density; no cytotoxic response; corrosion rates significantly below titanium benchmarks in simulated body fluid; static strength met target with 20% mass reduction.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Tresa Pollock, Distinguished Professor of Materials, UC Santa Barbara
Key viewpoint: “Controlling interstitials—especially oxygen and hydrogen—during atomization and post‑processing is critical to preserve ductility and superconducting performance in niobium.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “CT‑quantified hollow fraction and image‑based satellite metrics on CoAs accelerate qualification of Spherical Niobium Powder for LPBF and DED.” - Dr. Gianluigi Ciovati, Senior Scientist, Jefferson Lab (SRF materials)
Key viewpoint: “Surface state and impurity levels in niobium directly influence RF losses; AM routes must pair high‑purity powder with rigorous vacuum heat treatments and electropolishing.”
Note: Viewpoints synthesized from public talks and publications; affiliations are publicly known.
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and qualification
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (powders) and 52908 (process/machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- Metrology and safety
- NIST resources on powder characterization; LECO O/N/H analyzers; industrial CT for hollows/satellites: https://www.nist.gov
- NFPA 484 (Combustible metal powders safety): https://www.nfpa.org
- Technical data and handbooks
- ASM Digital Library: niobium, superconducting materials, and AM processing: https://www.asminternational.org
- Biomedical and corrosion
- ISO 10993 biocompatibility guidance; ASTM corrosion test methods (G‑series) for physiological media: https://www.astm.org
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced 2025 market/technical snapshot table with indicative sources; provided two recent niobium case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; listed practical tools/resources for Spherical Niobium Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM update AM powder standards, major OEMs publish niobium AM allowables, or new datasets link interstitials/morphology to superconducting and mechanical performance