金属合金粉末 は、強度、耐食性、延性、導電性などの特性を向上させるために、2種類以上の金属元素を組み合わせて作られた微細な金属粉末を指します。このガイドでは、金属合金粉末の種類、製造方法、用途、仕様、選択上の注意点、よくある質問など、金属合金粉末の概要について説明します。
合金粉末の概要
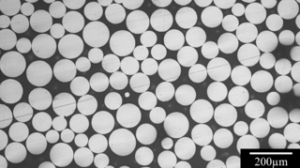
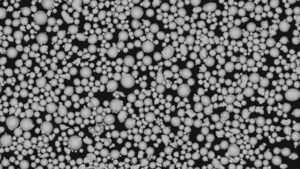
金属合金粉末は、2種類以上の金属からなる粒子状物質で、微粒化または化学的還元により、工業用途に最適な微細な球状粉末に製造される。
金属合金粉末を使用する主な利点は以下の通りである:
- 金属の組み合わせによる特性の調整
- 鋳造合金よりも均一な構造
- 多様な製造技術に対応する汎用性
- 複雑な部品形状を製造する能力
- 優れた再現性と品質管理
- 大量生産における費用対効果
粉末状の一般的な金属合金には、ステンレス鋼、工具鋼、超合金、低合金鋼、ニッケル合金、コバルト合金などがあります。鉄および非鉄合金の両方が粉末として製造されます。
金属合金粉末は、金属射出成形、積層造形、粉末冶金などの製造技術や表面コーティングを可能にする。
金属合金粉末の種類
様々な金属合金は、要求される特性や用途に応じて粉末状に変換される:
| 合金タイプ | 構成 | プロパティ |
|---|---|---|
| ステンレス鋼 | Fe、Cr、Ni | 耐食性 |
| 工具鋼 | Fe、Cr、C | 耐摩耗性 |
| 低合金鋼 | Fe、Mn、C | 強さ |
| 超合金 | Ni、Cr、Co | 耐熱性 |
| コバルト合金 | Co、Cr、W、Ni | 耐摩耗性 |
| 銅合金 | 銅、亜鉛 | 電気伝導度 |
| ニッケル合金 | Ni、Cr | 耐食性 |
粉末の特性を組み合わせることで、硬度、強度、延性、導電性、磁性、耐食性、耐摩耗性、耐高温性などの性能を最適化することができる。
金属合金粉末製造
金属合金粉末は商業的に生産されている:
- 霧化 – 溶融した合金を水またはガスジェット中に流し、液滴を形成する。
- 電解 水系電解プロセスにより、金属イオンを粉末に還元する。
- カルボニル – 金属は一酸化炭素と反応して揮発性の粉末を形成する。
- 機械的合金化 溶接と破砕を繰り返すことで、ナノ構造の粉末ができる。
アトマイズは、製造工程に理想的な一貫した球状合金粉末の迅速な大量生産を可能にする最も一般的な方法である。
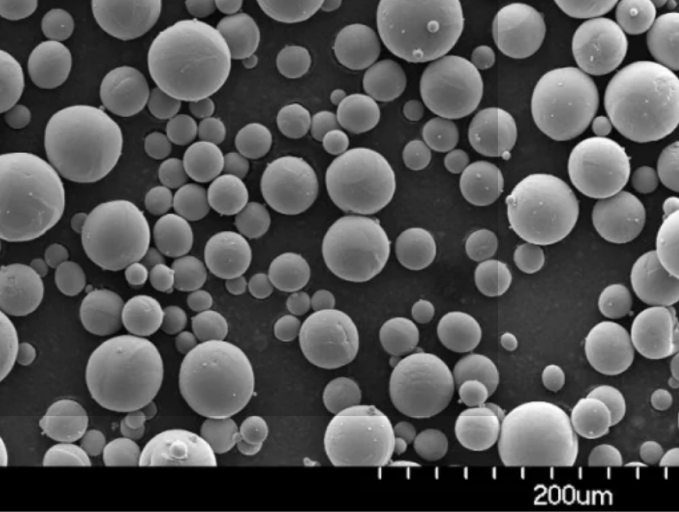

応用例 メタル合金パウダー
調整された特性と複雑な形状を形成する能力により、金属合金粉末は産業界における多様な用途を可能にする:
付加製造
- 超合金を使用した航空宇宙部品
- コバルトクロムとチタンを使用した医療用インプラント
- 工具鋼による自動車試作
金属射出成形
- ギアやノズルのような小さな複雑な金属部品
- 大量生産が可能
表面コーティング
- 工具鋼の耐摩耗コーティング
- ステンレススチールの耐食コーティング
粉末冶金
- 高性能自動車部品
- 永久磁石
- ブレーキやクラッチなどの摩擦材
焼結部品
- 気孔率を制御した構造部品
- フィルター、ブッシング、ベアリング
ロー付けペースト
- 類似金属と異種金属の接合
化学工業
- 金属触媒
エレクトロニクス
- 導電性フィルムと熱管理
メタル合金パウダー仕様
金属合金粉末は、組成、粒度分布、形態、流動性、その他の仕様によって特徴付けられる:
メタル合金粉末の特性
| 仕様 | 代表値 |
|---|---|
| 合金組成 | 鋼、Ni、Co、Cu合金 |
| 粒子サイズ | 5 – 150ミクロン |
| 粒子形状 | 球形、不規則 |
| サイズ分布 | D10、D50、D90 |
| 流動性 | 安息角、流量 |
| 見かけ密度 | 2 – 8 g/cm3 |
| タップ密度 | 固形密度の80%まで |
| 酸化物含有量 | 2%未満 |
| 含水率 | 0.2%未満 |
| 純度 | 98%以上 |
粉末の特性は、製造工程の適合性、品質、機械的特性、性能を決定する。
メタル合金パウダー サイズの種類
重要な仕様は粒度分布です。粉体はさまざまなサイズ範囲に分類されます:
金属合金粉末のサイズ分類
| タイプ | 粒子径範囲 |
|---|---|
| 粗粉 | 75~150 μm |
| ミディアム・パウダー | 25~75 μm |
| ファインパウダー | 15~45 μm |
| エクストラ・ファイン・パウダー | 5~25 μm |
| ナノパウダー | 100nm以下 |
- 粒子が大きいと流動性と浸透性が向上する
- 粒子が小さいため、分解能と密度が高い
- ほとんどのパウダーは、製造工程では45μm以下である。
- ナノパウダーはユニークな特性を提供する
粒度と形状は製造中に管理され、スクリーニングによって分類されます。特注の粒子分布も可能です。
金属合金粉末の選択要因
適切な金属合金粉末を選択する際の主な考慮事項は以下の通りである:
- 申し込み 必要な材料特性と能力
- 製造工程 装置および方法との適合性
- コスト 原材料コストと生産効率
- リードタイム – 在庫または特注生産による入手可能性
- 品質 – 一貫した組成、形態、粒度分布
- テクニカルサポート 粉体メーカーのノウハウ
- 健康と安全 引火性、反応性、毒性因子
- 環境への影響 リサイクル性、排出ガス、廃棄物処理
設計の初期段階で、知識豊富な粉末メーカーと協力し、用途に最適な合金と粉末特性を選択する。
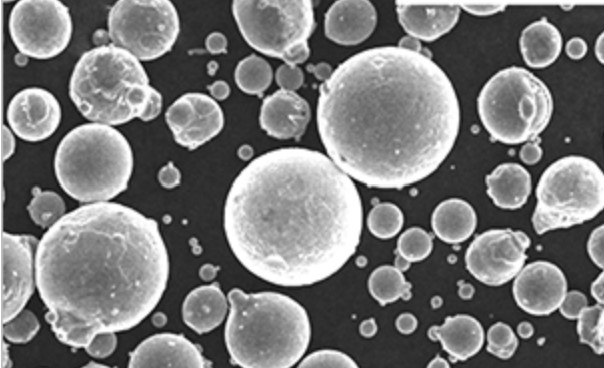
金属粉末サプライヤーの評価と選択
すべての金属粉末メーカーが、同じ範囲の合金、品質、ロットサイズ、能力を提供しているわけではありません。サプライヤーを選択する際の主な要因は以下の通りです:
金属粉末サプライヤーの選び方
| ファクター | 基準 |
|---|---|
| 能力 | 合金の範囲、サイズ分布、生産量、サンプリング、テスト |
| 品質 | 粉末の形態、一貫性、純度、認証基準 |
| 技術的専門知識 | 合金の知識、製造工程の経験、R&A;D能力 |
| カスタマーサービス | 対応力、注文処理の信頼性、コミュニケーション |
| 設備 | 品質管理・検査機器、安全衛生システム |
| 物流 | 納期、在庫、リードタイム |
| ビジネス・スタンディング | 業界の評判、財務、成長 |
| 価格 | パウダー価格、最低価格、送料 |
| 用語 | 支払い方法、保証 |
サプライヤーの候補を訪問し、その業務を直接監査することは、能力とプロフェッショナリズムを保証する最良の方法である。
コスト分析 金属合金粉末
金属合金粉末の価格設定は以下の通り:
- 構成 – より高価な合金は、より高い粉末コストを意味する
- 純度 – 化学規制強化で価格上昇
- 粒子径 – より微細な粉末は製造コストが高い
- 製造方法 –アトマイズは、特殊な方法よりも低コストである。
- 注文数量 – バルク発注 >1000キログラムはキログラムあたりの価格を下げる
- テスト – 追加のキャラクタライゼーションはコスト増
- パッケージング –密封袋のような特殊なオプションはコストアップになる
典型的な金属合金粉末のコスト範囲
| 合金タイプ | kgあたりのコスト |
|---|---|
| 鉄および低合金鋼 | $5 – $15 |
| ステンレス鋼 | $15 – $30 |
| 工具鋼 | $20 – $50 |
| 銅合金 | $50 – $100 |
| コバルト合金 | $50 – $200 |
| 超合金 | $100 – $500 |
候補となったサプライヤーに見積もりを依頼し、必要な合金、粒度、純度、検査、納品に関する価格を比較する。
取り扱いおよび保管に関する推奨事項
反応しやすい微細な金属粉を取り扱う場合は、特に注意が必要である:
- 接地された導電性の容器とスクープを使用する。
- 火花、炎、発火源を避けること
- ハウスキーピングでほこりを分散させる
- マスク、手袋、防護服などのPPEの使用
- 適切な換気と集塵を行う
- 密封した容器を涼しく乾燥した場所に保管する。
粉体メーカーの SDS 文書に記載されているすべての安全ガイドラインに従ってください。爆発性粉塵の危険性は適切に管理しなければならない。
メタル合金パウダー トレンドとイノベーション
金属合金粉末技術の最近の動向には次のようなものがある:
- 積層造形用のよりカスタマイズ可能な合金
- ナノパウダーの製造方法
- 粉体ハンドリングと品質管理の自動化
- 粉体製造用シミュレーション・ソフトウェア
- 3Dプリンティング用金属粉末の使用増加
- 複数の元素を含む新しい機能性合金
- 粉体リサイクルシステム
合金とプロセスの開発が続けば、高性能粉末冶金部品の可能性が広がる。

よくある質問
Q: 最も一般的に使用されている金属合金粉末は何ですか?
A: ステンレス鋼、工具鋼、ニッケル合金は、最も広く使用されている金属合金粉末のひとつです。
Q: 金属合金粉末はどのような産業で最も多く使用されていますか?
A: 航空宇宙、自動車、医療、工業/消費者向け製品では、金属合金粉が広く利用されています。
Q: どのような製造方法が最高品質の粉体を作るのですか?
A: 不活性ガスアトマイズは、AMやMIMプロセスに適した、最も球形で安定した合金粉末を製造します。
Q:金属粉の安全な取り扱い方法は?
A: 粉末を安全に取り扱うために、導電性容器、接地、接着、不活性ガスブランケット、換気、爆発防止システムを使用する。
Q: 金属合金粉末は高価ですか?
A: 一般的なスチールパウダーの5ドル/kgから、特殊超合金の500ドル/kg以上まで、幅広い価格帯があります。現在の価格はサプライヤーからの見積もりで決定されます。
Q: 製造用の粉体の一般的なサイズ範囲はどのくらいですか?
A: ほとんどの製造用途では、10ミクロンから45ミクロンの粉末が使用されています。100nm以下の微細なナノパウダーもニッチな用途で使用されています。
Q: 密封された金属粉の保存可能期間はどのくらいですか?
A: 密閉容器で乾燥した状態で保管すれば、金属粉末は合金の組成や保管条件にもよるが、1~5年間は安定である。
Q: 金属粉は環境に優しいのですか?
A: 金属粉末は非常に効率的に原料を使用することができます。粉塵を抑制し、廃棄物を適切に処理することで、環境への影響を最小限に抑えることができます。
Q: 金属粉末製造にはどのような規格が適用されますか?
A: ISO 10149、ASTM B835、MPIF Standard 35などの国際規格は、様々な粉末の物理的特性と試験手順を規定しています。
Q: 金属合金粉末はリサイクルできますか?
A: はい、未使用の粉末はリサイクルして再加工することができます。一部の積層造形では、リサイクルパウダーを原料として使用しています。
金属合金粉末に関する主要な要点
- 金属合金粉末は複数の金属を組み合わせ、より優れた特性を実現する
- アトマイズは主要な工業生産方法である。
- 粒度分布は製造工程のニーズに適合していなければならない
- 金属粉が積層造形、MIM、コーティング、PM部品を可能にする
- 合金の選択は、機械的・物理的特性とともにコストを考慮する
- 流動性や見かけ密度などの粉体特性は重要である。
- アプリケーションとプロセスを理解する専門的なサプライヤーと協力する。
- 反応性粉体を扱う際には、安全な取り扱いに関する注意事項が重要である。
粉末冶金アプリケーションの継続的な成長により、金属合金粉末は、従来の金属加工だけでは不可能だった能力の幅を広げている。
Frequently Asked Questions (Supplemental)
1) What powder characteristics matter most for AM vs MIM?
- AM (LPBF/EBM/BJ): Highly spherical morphology, narrow PSD (typically D10/50/90 ≈ 15/30/45 μm for LPBF), low satellites, very low O/N/H, and consistent apparent/tap density. MIM: slightly finer PSD (D50 ≈ 10–18 μm), flow stability (Hausner ≤1.20), and controlled oxygen to aid sintering without embrittlement.
2) How does oxygen content impact Metal Alloy Powder performance?
- Elevated oxygen increases oxide films and viscosity (MIM) and causes lack‑of‑fusion or spatter (AM). Typical limits: 316L O ≤0.30 wt% (MIM) and ≤0.05–0.10 wt% (AM); Ni‑base superalloys often target O ≤0.03–0.05 wt% for AM. Verify via inert gas fusion (ASTM E1019).
3) Can recycled Metal Alloy Powder be blended without compromising quality?
- Yes, with powder passport controls: sieve to spec, remove spatter/inclusions, monitor PSD, flow, apparent/tap density, and interstitials. Many sites use 10–30% blend‑back ratios validated by tensile/fatigue and CT porosity checks.
4) What’s the best atomization route for highly reactive alloys?
- Inert gas atomization using vacuum induction melting (VIM) plus argon/nitrogen with O2/H2O scrubbing. Plasma atomization or PREP yield ultra‑spherical powders for Ti and superalloys but at higher cost.
5) How should Metal Alloy Powder be stored for long shelf life?
- Keep in sealed moisture‑barrier packaging with desiccant, purge headspace with dry inert gas, store at 15–25°C, RH <40%, and minimize handling cycles. Re‑test O/N/H and flow after any prolonged storage or reuse.
2025 Industry Trends and Data
- Digital traceability: Powder passports with chemistry (including O/N/H/C), PSD, inclusion ratings, reuse counts, and recycled content are standard in RFQs for aerospace/medical.
- ESG and cost: Argon recirculation, energy‑efficient atomization, and disclosed recycled content (metals and packaging) are increasingly demanded.
- Micro‑scale and large‑format divergence: Ultra‑fine PSDs for micro‑MIM and micro‑LPBF; coarser, high‑flow powders for DED/wire‑powder hybrid systems.
- Qualification acceleration: In‑situ monitoring (melt‑pool, acoustic) paired with standardized test artifacts shortens allowables development.
- Safer handling: Wider adoption of ISO 80079 and NFPA 484 guidance, conductive packaging, and dust‑exposure monitoring.
| KPI (Metal Alloy Powder Quality & Use), 2025 | 2023 Baseline | 2025 Typical/Target | Why it matters | Sources/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF PSD (μm, D10/D50/D90) | 20/35/55 | 15/30/45 | Packing, melt stability | ISO/ASTM 52907; supplier QC |
| Oxygen limit 316L (AM) wt% | 0.07–0.12 | 0.04–0.08 | Density, corrosion | ASTM E1019 |
| Satellite count (≥5 μm per 100 particles) | 4–6 | 2–3 | Spreadability/defects | SEM image analysis |
| Binder‑jet + HIP final density (%) | 98–99 | 99.0–99.5 | 信頼性 | OEM/peer‑reviewed data |
| Qualified reuse cycles (LPBF) | 3–6 | 6–10 | Cost, consistency | Plant case studies |
| Disclosed recycled content (%) | 限定 | 15-35 | ESG, cost | EPD/LCA reports |
| Powder lot acceptance with passports | エマージング | 共通 | Faster qualification | RFQ requirements |
Authoritative resources:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (metal powder characterization), 52904 (PBF practice), 52910 (design for AM): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM B822/B214 (PSD), B212/B213 (apparent density/flow), B923 (true density), E1019 (O/N/H), F3122 (property reporting): https://www.astm.org
- ASM Handbook: Powder Metallurgy; Additive Manufacturing: https://dl.asminternational.org
- NIST AM Bench datasets and monitoring research: https://www.nist.gov/ambench
- NFPA 484 (combustible metals): https://www.nfpa.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Low‑Oxygen 316L Metal Alloy Powder for Corrosion‑Critical LPBF Parts (2025)
- Background: A medical device OEM needed improved pitting resistance for LPBF 316L fluidic manifolds.
- Solution: VIM + inert gas atomized powder (15/30/45 μm PSD; O = 0.045 wt%); optimized gas‑flow baffles; contour + chessboard hatch; stress‑relief + electropolish; passivation per ASTM A967.
- Results: As‑built density 99.92%; pitting potential +120 mV vs. 2023 baseline; CT porosity <0.05%; scrap −17%; validated 8 reuse cycles with blend‑back 20%.
Case Study 2: Binder‑Jetted Ni‑Cu Metal Alloy Powder Cores with Sinter‑HIP (2024)
- Background: A chemical processing customer sought corrosion‑resistant, thin‑fin heat‑exchange cores at lower cost.
- Solution: Fine spherical Ni‑Cu powder (D50 ≈ 20 μm); hydrogen‑rich sinter followed by HIP; SPC on linear shrinkage; helium leak testing; selective Ni‑P plating.
- Results: Final density 99.2–99.4%; leak rate <1×10⁻⁹ mbar·L/s; unit cost −14% at 2k units/year vs. brazed assembly; lead time −25%.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Randall M. German, Powder Metallurgy Scholar and Author
- Viewpoint: “Packing density—from PSD engineering and morphology—controls shrinkage predictability across MIM and sinter‑based AM more than marginal thermal tweaks.”
- Dr. Brandon Lane, Research Engineer, NIST
- Viewpoint: “Linking powder passports to in‑situ monitoring accelerates process qualification and provides early warning of off‑spec lots in powder bed fusion.”
- Dr. Martina Zimmermann, Head of Additive Materials, Fraunhofer IWM
- Viewpoint: “Disclosed recycled content with tight O/N/H control is now feasible for many Metal Alloy Powder families without sacrificing performance.”
Affiliation links:
- NIST: https://www.nist.gov
- Fraunhofer IWM: https://www.iwm.fraunhofer.de
- ASM International: https://www.asminternational.org
Practical Tools/Resources
- QC and standards: ISO/ASTM 52907; ASTM B212/B213/B214/B822; ASTM B923; ASTM E1019; ASTM F3122
- Metrology: LECO inert‑gas fusion for O/N/H (https://www.leco.com); laser diffraction PSD; SEM for morphology/satellites; helium pycnometry for true density; CT for porosity
- Design/simulation: Thermo‑Calc/DICTRA for alloy behavior; Ansys/Simufact Additive for scan/distortion; nTopology/Materialise Magics for build prep and lattices
- Databases: Senvol Database (https://senvol.com/database); MatWeb (https://www.matweb.com); MPIF resources (https://www.mpif.org)
- Safety: NFPA 484 guidance; ISO 80079 for explosive atmospheres; supplier SDS libraries and handling SOPs
Last updated: 2025-08-22
Changelog: Added 5 supplemental FAQs, a 2025 KPI table and trend insights, two recent case studies (LPBF 316L manifolds; BJ Ni‑Cu cores), expert viewpoints with affiliations, and a curated tools/resources list focused on Metal Alloy Powder selection and qualification.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, major suppliers change O/N/H or PSD specs, or new datasets on powder reuse and in‑situ monitoring correlations are published.