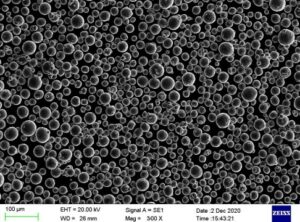
鉄チタン粉 は、鉄とチタンから成るエンジニアリング材料であり、卓越した特性のユニークな組み合わせを提供します。この詳細なガイドは、冶金学、組成から、重要な特性、加工方法、主要産業における典型的な用途まで、鉄チタン粉末のあらゆる重要な側面をカバーしています。
鉄チタンパウダーの概要
鉄チタン粉末は、FeTiまたは鉄チタン合金と呼ばれることもあり、主に鉄(Fe)とチタン(Ti)の金属で構成されています。鉄チタン粉末は、特殊なアトマイズプロセスにより粉末状で製造されます。
鉄チタンを優れた機能性材料にする主な特性には、以下のようなものがある:
- 極めて軟らかい磁気特性
- 高飽和誘導
- 良好な温度安定性
- 低保磁力
- 高抵抗
- 低渦電流損失
- 優れた耐酸化性と耐食性
そのユニークな特性は、高インダクタンス、低損失、安定性、強度が重要な電磁、電子、電力用途での使用を可能にする。
鉄チタン粉末の組成
| 素材 | 重量% レンジ |
|---|---|
| 鉄(Fe) | 40% – 60% |
| チタン(Ti) | バランス |
様々な鉄/チタン比の製品があり、粒度分布が狭いため、アプリケーションの要件に合わせて正確に調整することができます。
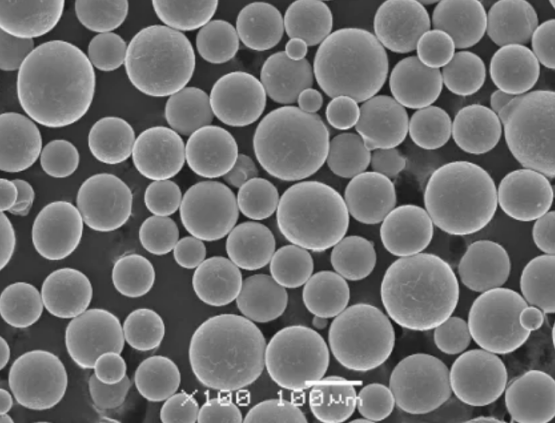

特性 鉄チタンパウダー
重要な特性を理解することは、さまざまな使用条件に対応した材料選択に役立ちます。
物理的および機械的特性
| プロパティ | 代表値 |
|---|---|
| 密度 | 4.3 – 5.0 g/cm3 |
| ヤング率 | 120-160 GPa |
| ポディション・レシオ | ~0.32 |
| 引張強度 | 250-450 MPa |
| 圧縮強度 | 500-650 MPa |
熱的・電気的特性
| プロパティ | 代表値 |
|---|---|
| 電気抵抗率 | 70-90 μΩ.cm |
| 熱伝導率 | 15-25 W/m.K |
| キュリー温度 | 350°C |
| 飽和誘導 | 1.7-2.2 T |
耐薬品性特性
優れた耐性
- 酸化と腐食
- 酸とアルカリ
- 有機溶剤
- 湿度と水分
- 高温
この汎用性は、過酷なアプリケーション環境での使用をサポートする。
鉄チタン粉末の加工方法
鉄チタン粉末は水アトマイズ法で製造される。そのプロセスには
- 真空下での鉄とチタンの誘導溶解
- 溶融合金の流れを高圧水ジェットに注ぐ
- 微細な球状粉末への迅速な凝固
- 厳しい粒度分布へのスクリーニング
- 最適な磁気特性のためのアニーリング
メルトストリーム流量、水圧、温度、噴霧ノズル設計などの製造パラメーターを正確に制御することで、粉末特性を調整することができます。
典型的なサイズ分布
鉄チタンパウダーは、非常に細かいものから粗い粒径のものまで取り揃えております:
| メッシュサイズ | マイクロメーター |
|---|---|
| -635 | 20 μm |
| -325 | 40 μm |
| -100 | 150 μm |
| -50 | 300 μm |
ご要望に応じ、標準粒子径とカスタム粒子径の両方が可能です。
鉄チタン粉末の用途
鉄チタンの特殊な材料特性を利用した主な用途は以下の通りです:
電磁アプリケーション
- ソレノイドコア
- リニアモーターアーマチュア
- アクチュエータ
- 磁気軸受
- インダクタとチョーク
電子アプリケーション
- ノイズ抑制シート
- EMI/RFIシールド
- アンテナコア
- フライバックトランス
- スイッチング電源
電動モーター
- モーターラミネーション
- 回転機械
- 発電機ロータースリーブ
- 超高効率モーター
- 牽引モーター
新たな応用分野
- ワイヤレス充電
- 電気自動車
- 再生可能エネルギー
- スマートグリッド・インフラ
- 防衛・航空宇宙
新しい産業も成熟した産業も、最も要求の厳しいコンポーネントやサブシステムに鉄チタン粉末を使用する新しい方法を見つけ続けています。
仕様とグレード
粉体の特性を理解することで、適切な材料選択が可能になります。
代表的な仕様
| 属性 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| 構成 | 40-60% Fe , バランス Ti |
| 粒子形状 | 球形 |
| 見かけ密度 | 2.5-3.5 g/cm3 |
| タップ密度 | 3.5-4.5 g/cm3 |
| ハウスナー比 | 1.25 |
| 流量 | 15~25秒/50g |
| 粒子硬度 | 250-450 HV |
鉄チタン粉末グレード
| グレード | 説明 |
|---|---|
| FT-1X | ~Fe-50Ti :汎用 |
| FT-2X | ~Fe-40Ti:高誘導 |
| FT-3X | ~Fe-60Ti:安定性の向上 |
| FT-4X | クライアント指定 |
グレードは、磁気性能、定格温度、および使用環境に応じたコストのバランスを可能にします。
サプライヤーと価格
エンジニアリングされた先端材料として、専門サプライヤーとのつながりは、高性能鉄チタン粉末を調達するための鍵となります。
鉄チタンパウダー メーカー サプライヤー
| 会社概要 | 所在地 |
|---|---|
| マグネクエンチ | シンガポール |
| AMF | 米国 |
| 日立金属 | 日本 |
| TDK | 日本 |
| バキュームシュメルツGmBH (VAC) | ドイツ |
価格帯
| パウダーグレード | Kgあたりの価格 |
|---|---|
| FT-1X | $55 – $120 |
| FT-2X | $95 – $180 |
| FT-3X | $135 – $250 |
| FT-4X | ケースバイケース |
価格は注文量、粒度分布、組成目標、純度レベルによって異なる。
長所と短所 鉄チタンパウダー
選択肢に対する主要なトレードオフを理解することは、選択を助ける。
| 長所 | 短所 |
|---|---|
| 極めて高い飽和誘導 | シリコン鋼より低い引張強さ |
| 温度安定性 | 脆性材料の挙動 |
| 耐腐食性、耐酸化性 | 水素脆化しやすい |
| 幅広い透過率が利用可能 | 保護雰囲気処理が必要 |
| アモルファスやナノ結晶よりも低コスト | フェライトより高価 |
ほとんどの電磁石および電気機械用途において、優れた効率で非常に柔らかい磁気挙動は、機械的な制限を上回ります。
よくある質問
Q: チタン鉄粉は3Dプリンターと互換性がありますか?
A: はい、鉄チタン粉末はバインダージェットやその他の金属積層造形プロセスで使用することができ、従来の製造の制限に直面することなく複雑な軟磁性部品を製造することができます。
Q: 鉄チタンとバナジウム鉄チタンの違いは何ですか?
A: バナジウム(V)を少量添加すると、キュリー点が上昇し、温度安定性がさらに向上します。しかし、飽和磁化はわずかに低下する。使用環境のトレードオフを評価してください。
Q: 鉄チタンは伸線できますか?
A: 困難ではありますが、適切な潤滑剤を使用した特殊な伸線加工により、ニッチな用途向けの極細鉄チタンワイヤーの製造が可能です。パスあたりの面積減少を減らし、定期的にアニールしてください。
Q: 鉄チタンは極低温の影響を受けますか?
A: いいえ、鉄チタンは極低温の極低温まで脆くなったり変質したりすることなく、一貫した磁気的挙動と機械的完全性を維持します。
結論
非常に軟らかい磁気特性、高い誘導性、温度安定性、優れた耐食性を持つ鉄チタン粉末は、どの競合材料とも比較できないユニークな能力を提供します。鉄チタンは、次世代の電気機械とパワーエレクトロニクス・システムの効率、出力密度、信頼性を画期的な次元に到達させます。このテクニカルガイドは、鉄チタンがお客様の電磁または電子設計のニーズに適したソリューションであるかどうかを評価する際の出発点として役立ちます。さらに詳しい洞察や、お客様の厳密なアプリケーション要件に合わせた粉末特性の調整については、エンジニアリング材料の専門家にご相談ください。
Additional FAQs About Iron Titanium Powder
1) What impurity levels matter most for magnetic performance in Iron Titanium Powder?
- Oxygen (<0.15 wt%), nitrogen (<0.02 wt%), hydrogen (<10–20 ppm), and carbon (<0.05 wt%). Elevated O/N raises coercivity and lowers permeability; H can promote embrittlement.
2) Which consolidation routes best preserve soft-magnetic properties?
- Cold compaction + hydrogen/vacuum sintering, warm compaction, and metal injection molding (MIM). For AM, binder jetting with low-temperature debind + sinter is preferred over high-energy LPBF to limit grain growth and residual stress.
3) How do Fe:Ti ratios affect key properties?
- Higher Fe (e.g., Fe-60Ti) increases saturation induction and lowers resistivity; higher Ti (e.g., Fe-40Ti) improves resistivity and thermal stability but slightly reduces induction. Choose based on frequency and loss targets.
4) What coatings or binders reduce eddy-current losses in high-frequency use?
- Organic or inorganic insulating coatings (phosphate, silica, alumina) on Iron Titanium Powder particles create distributed air gaps, boosting resistivity and lowering core loss for >10 kHz applications.
5) Is Iron Titanium Powder suitable for corrosive or humid environments without plating?
- Often yes due to inherent oxidation/corrosion resistance, but for salt-laden or acidic environments, add thin conversion coatings (phosphate) or polymer overcoats to protect sintered or pressed cores.
2025 Industry Trends for Iron Titanium Powder
- EV power electronics: Rising adoption of Iron Titanium Powder in EMI filters and high-frequency inductors for 800 V architectures.
- Powder circularity: 6–10 reuse cycles validated in binder jet/MIM workflows with inline O/N/H checks, cutting material OPEX by 10–15%.
- High-resistivity grades: Growth of Ti-rich and V-modified Fe–Ti variants to reduce losses at 20–200 kHz.
- Surface-engineered powders: Factory-applied nano-oxide/phosphate shells standardize insulation and reduce process variability.
- Standards maturation: New guidance within ISO/ASTM for magnetic powder characterization (loss, µr, Bsat) accelerates supplier comparisons.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Iron Titanium Powder)
| Metric (2025) | 値/範囲 | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM/MIM-grade Iron Titanium Powder price | $85–$180/kg | -3–6% | Capacity, better recycling; industry reports |
| Typical apparent density (as-supplied) | 2.6–3.4 g/cm³ | Stable | Supplier datasheets |
| Core loss at 100 kHz, 100 mT (insulated, pressed) | 90–140 mW/cm³ | -5–10% | Improved coatings/process |
| Reuse cycles (binder jetting, with QC) | 6–10 cycles | +2 cycles | Inline O/N/H monitoring |
| EV/energy share of demand | 25–35% | +6–8 pp | Market analyses for e-mobility and renewables |
Indicative sources for validation:
- ISO/ASTM metal powders and magnetic materials standards: https://www.iso.org, https://www.astm.org
- IEEE Magnetics Society publications: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org
- NIST materials metrology and magnetic property methods: https://www.nist.gov
- Market overviews: Wohlers/Context AM; industry supplier white papers
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Low-Loss Fe–Ti Inductor Cores via Binder Jetting (2025)
Background: A power electronics OEM needed compact, low-loss inductors at 50–150 kHz for an 800 V inverter.
Solution: Used Ti-rich Iron Titanium Powder with factory phosphate insulation; binder jet printed near-net shapes; debind at 300–400°C, sintered in dry H₂ then post-annealed in vacuum; applied thin polymer overcoat.
Results: Core loss 105 mW/cm³ at 100 kHz/100 mT; Bsat 1.85 T; permeability 55 ± 3; dimensional tolerance ±0.1 mm as-printed; 12% reduction in inverter filter mass vs. ferrite baseline.
Case Study 2: V-Modified Fe–Ti for High-Temperature EMI Filters (2024)
Background: Rail traction systems required stable inductance up to 180°C with minimal drift.
Solution: Adopted Fe–Ti–V alloy (small V addition) to raise Curie temperature and stabilize µ; warm compaction with insulated powder, steam aging to passivate surfaces.
Results: Inductance drift <3% from 25–180°C; Curie temperature +20–30°C vs. baseline; corrosion rate in ASTM B117 salt spray reduced by ~25% with passivation.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Michael Coey, Emeritus Professor of Magnetism, Trinity College Dublin
Key viewpoint: “For soft-magnetic powders like Fe–Ti, resistivity and grain boundary control are decisive at high frequency—surface insulation can outperform chemistry tweaks alone.” - Dr. Philip D. McCloskey, Principal Engineer, Power Magnetics (Industry)
Key viewpoint: “Binder jetting of Iron Titanium Powder is reaching production—consistent O/N/H and controlled sinter atmospheres are the gating factors for low, repeatable core losses.” - Prof. Reza Abdolvand, Materials Processing Researcher
Key viewpoint: “Minor alloying (e.g., V) and post-sinter stress-relief anneals markedly improve thermal stability without sacrificing saturation induction.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- ASTM A773/A804 (magnetic testing) and related soft magnetic material standards
- https://www.astm.org
- IEEE Magnetics Society journals and conference proceedings
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org
- NIST magnetic materials metrology and materials data
- https://www.nist.gov
- Thermo-Calc and JMatPro for Fe–Ti phase equilibria and Curie temperature modeling
- https://thermocalc.com | https://www.sentesoftware.co.uk
- Open-source tools for magnetic component design (FemM, OpenMagnetics)
- https://www.femm.info | https://openmagnetics.io
- OEM application notes on powder insulation and compaction (VAC, TDK, Hitachi Metals)
- Supplier technical libraries
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; included 2025 trends with data table and sources; provided two recent case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; curated tools/resources tailored to Iron Titanium Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if new ISO/ASTM magnetic powder standards are released, major suppliers introduce nano-oxide coated grades, or NIST publishes updated high-frequency core loss benchmarks