目次
目次の生成を開始するヘッダーを追加する。
球体を準備するための代表的な技術がほとんどないことは、誰もが知っている。 メタリックパウダーガス自動化(GA)、プラズマ回転電極プロセス(prep)、プラズマ霧化(PA)、プラズマ球状化(PS)である。
球状金属粉の調製技術ベスト4:
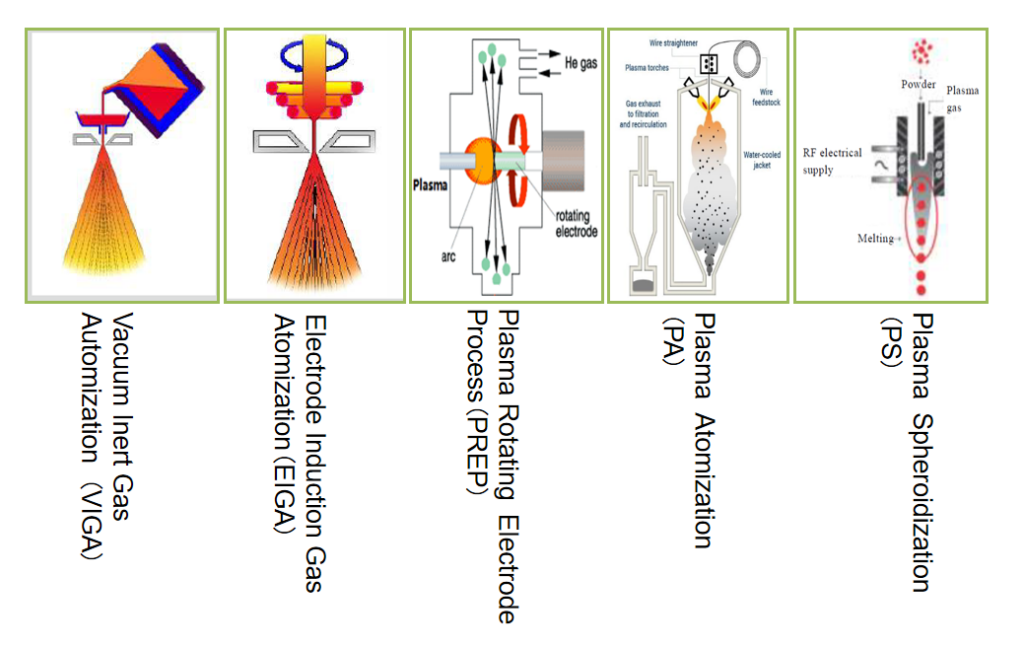
ガス自動化(GA)
エアロゾル化粉末製造は、高速気流を利用して液体金属流を小さな液滴に分解し、これを急速に凝縮して形状の整った粉末を製造するものである。
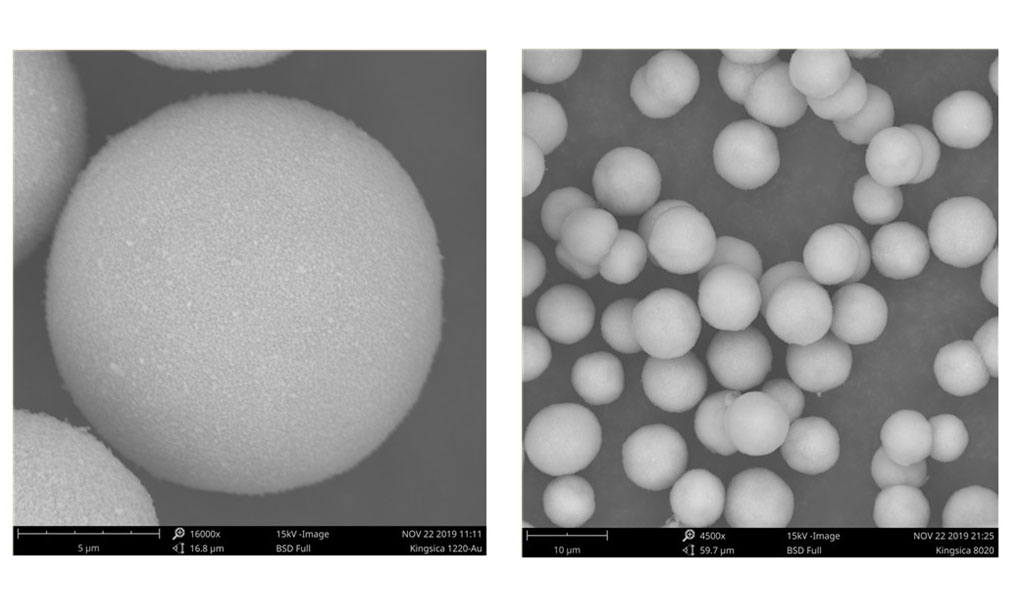
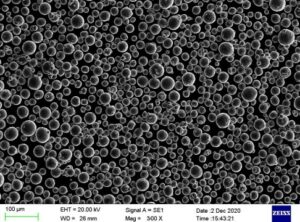
エアロゾリゼーションは、微細な球状の金属および合金粉末を調製するための最も重要な方法となっており、統計によると、アトマイゼーションによる金属粉末の生産量は、世界の粉末生産量の80%に達しています。アトマイズによって工業的に生産できる金属粉末には、タングステンやモリブデンなどの耐火性金属や非常に反応性の高い金属を除く、ほとんどすべての一般的な金属および合金系を含む、さまざまな種類があります。
この方法は、微粒子(<150μm)、良好な真球度、高純度、低酸素含有量、高速成形、低環境汚染の金属粉末を生成し、粉末冶金、金属射出成形、金属添加剤製造用の金属粉末の調製法の主流である。
プラズマアトマイズ(PA)
プラズマアトマイズ(PA)とは、金属原料(一般にワイヤー)を特殊な供給機構により一定速度で供給するプロセスである。原料は、炉の上部に左右対称に取り付けられた複数のプラズマトーチから発生する集束プラズマジェットによって超微細な液滴またはエアロゾルに急速に分散され、成膜プロセス中に冷却用の不活性ガスと熱交換することで、球形に近い粉末になります。
プラズマアトマイゼーション技術を用いると、粒径が小さく、純度が高く、流動性の良いチタン合金粉末を得ることができる。従来の粉末製造技術とは対照的に、プラズマアトマイゼーションでは、液体流を粉砕するために一般的に使用される水や気体媒体流を使用せず、高温プラズマを使用するため、急冷による溶融液滴の真球度不良の問題を回避することができます。さらに、この方法は従来のセラミックるつぼを使用する必要がなく、溶融可能なすべての金属材料、特にるつぼの汚染を引き起こすチタンを含む反応性の高い金属材料の粉末化に適している。
プラズマ回転電極プロセス(PREP)
プラズマ回転電極霧化法は、高純度で緻密な球状粉末材料を調製するための、より理想的な方法の一つである。そのメカニズムを簡単に説明すると、プラズマビームを熱源とし、金属または合金を自己消費型電極とし、同軸プラズマによって電極端部を溶融して液膜とし、それ自体の高速遠心力と表面張力の作用で球状粉末を得るというものである。
プラズマ回転アトマイズ粉末製造の特徴:(1) 粉末の粒度分布が狭い、粒度が制御しやすい、真球度が高い ガスアトマイズ法で調製した合金粉末の粒度は主に0~150μmの範囲に集中する;プラズマ回転電極アトマイズ法で調製した合金粉末の粒度は主に20~200μmの範囲に集中する。(2)粉末は基本的に中空粉末、サテライト粉末は存在しない。 (3)粉末セラミック介在物が少なく、清浄度が高い。 (4)合金溶解工程がなく、粉末酸素増分が少ない。液体の流れを壊す高速不活性気流がない。エアロゾル化粉末酸素増分は100ppm以上、プラズマ回転アトマイズ粉末酸素増分は50ppm以下に制御できる。プラズマ回転霧化粉末製造技術の付加製造における利点 1)粉末固体、印刷プロセスは、空気の隙間、関与と析出孔、亀裂やその他の欠陥によってもたらされる中空球に存在しません、2)粉末粒子径、狭い粒度分布、印刷プロセスの少ない/ない球状化、凝集現象、より高い表面仕上げ、印刷の一貫性と均一性を完全に保証することができます。
プラズマ・スフェロイド化(PS)
プラズマ球状化技術は、プラズマの高温特性を利用して、プラズマ中に供給された不規則な形状の粉末粒子を急速に加熱・溶融し、表面張力と極めて高い温度勾配の複合効果により急速に凝固させて球状粉末を形成する。プラズマには、高温(~104K)、プラズマトーチの体積が大きい、エネルギー密度が高い、電極汚染がない、熱伝達と冷却が速い、などの利点がある。特に希少耐火金属、酸化物、窒化物、炭化物、その他の球状粉末の調製において、均一な成分、高い球形度、良好な流動性を持つ高品質の球状粉末を製造するのに適した方法です。
以上、数種類の3Dプリンティング用粉末製造装置の原理と特徴を簡単に紹介した。要約すると、アトマイズ粉末製造技術、特にVIGAとEIGAは、現在最も使用されている粉末製造技術であるが、他のいくつかの技術と比較すると、粉末の純度と真球度にはまだ限界がある。
PREP、PA、PSの技術を比較すると、PAはサテライトパウダーが多く、PSは原料の制約があり、PREPは他の2つの技術に比べて微粉収率が相対的に低い。
Additional FAQs on Spherical Metallic Powder
1) Which method yields the highest sphericity and cleanliness for reactive alloys like Ti or Ni superalloys?
PREP generally delivers the highest sphericity and lowest inclusion/oxygen pickup because there is no crucible and minimal melt exposure; EIGA/PA are also strong for reactivity control.
2) How do I choose between Gas Atomization (GA) and Plasma Atomization (PA) for AM powders?
Choose GA for broad alloy coverage and cost efficiency, especially steels and Ni alloys; choose PA for finer PSD, higher sphericity, and lower oxygen in Ti/CoCr, where flowability and purity are critical.
3) When is Plasma Spheroidization (PS) preferable?
PS is ideal for converting irregular feedstocks (e.g., milled, hydride–dehydride Ti, refractory/ceramic powders) to high-sphericity particles, improving flowability without fully remelting large ingots.
4) What PSD ranges are typical for LPBF vs. L-DED from each method?
LPBF: D10–D90 ≈ 15–45 μm (PA, PREP, fine GA, PS-refined). L-DED: 45–150 μm (coarser GA/PREP cuts). Binder jetting often prefers 5–25 μm with tight tails.
5) How does satellite powder formation impact print quality and how can it be minimized?
Satellites reduce flowability and increase porosity risk. Mitigate via optimized atomization pressure/temperature, nozzle design, post-process classification/sieving, and PS reconditioning for GA/PA lots.
2025 Industry Trends in Spherical Metallic Powder
- Multi-laser AM drives tighter PSD control and lower oxygen specs for GA and PA powders.
- Blue/green laser compatibility pushes demand for high-reflectivity Cu/Al spherical metallic powder with enhanced sphericity and oxide control (e.g., EIGA + PS).
- Sustainability: Powder genealogy, higher recycle blend-back with inline O2/H2O monitoring, and EPDs requested by aerospace/medical OEMs.
- Hybrid routes: GA base powder reconditioned by PS to reduce satellites and narrow PSD; PREP used for premium lots where defect tolerance is minimal.
- Cost-down focus: Improved yield in PREP (adaptive electrode control) and PA (torch optimization) narrowing price gap with GA for Ti-6Al-4V.
| 2025 Metric (Spherical Metallic Powder) | Typical Range/Value | Relevance | ソース |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF PSD target (D10–D90) | 15–45 μm | Flowability and layer quality | ISO/ASTM 52907 |
| Tap density of premium Ti-6Al-4V PA/PREP powders | 2.5-2.9 g/cm³ | Packing, density | OEM datasheets |
| Oxygen spec (Ti AM-grade) | ≤0.13 wt% (ELI), ≤0.20 wt% (Grade 5) | Ductility, fatigue | ASTM F136/F3001 |
| Satellite content (post-PS reconditioning) | <3–5% by count | Flow/defect control | Supplier QC notes |
| Indicative lot yield in PREP (20–200 μm) | 55–70% after classification | Cost and availability | Vendor application notes |
| Market price band (Ti-6Al-4V powder) | ~$80–$200/kg (GA) vs. ~$120–$300/kg (PA/PREP) | Budgeting | Market trackers/suppliers |
Authoritative references and further reading:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Additive manufacturing feedstock): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F2924, F3001 (Ti alloys for AM): https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench datasets: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM Handbook: Powder Metallurgy and Additive Manufacturing: https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: PS Reconditioning of GA Inconel 718 to Reduce Satellites (2025)
Background: An aerospace supplier experienced recoater streaks and variable density from GA IN718 due to satellite-rich lots.
Solution: Applied plasma spheroidization to re-melt particle surfaces, followed by tight classification; implemented inline O2/H2O monitoring and argon recirculation.
Results: Satellite count reduced from ~12% to <3%; Hall flow improved by 18%; LPBF porosity fell from 0.45% to 0.12% without parameter change.
Case Study 2: PREP Titanium Alloy Powder for Thin‑Wall LPBF Lattice Structures (2024)
Background: A medical OEM required high ductility and fatigue life in Ti‑6Al‑4V ELI lattices.
Solution: Switched to PREP powder with narrow PSD (20–40 μm) and O ≤0.12 wt%; applied low‑energy contour scans and stress relief.
Results: 10–15% higher elongation, 25% improvement in HCF endurance at 10⁷ cycles; surface defect incidence reduced, enabling lower CT sampling.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. John Campbell, Casting and Atomization Specialist (Emeritus), University of Birmingham
Key viewpoint: “Control of melt cleanliness and turbulence during atomization is as decisive as gas velocity for minimizing satellites and inclusions.” - Dr. Martina Zimmermann, Head of Additive Materials, Fraunhofer IWM
Key viewpoint: “PS as a secondary step is proving cost‑effective to lift GA powder quality to PA/PREP performance for many aerospace parts.” - Dr. Brent Stucker, AM standards contributor and industry executive
Key viewpoint: “Powder passports tying PSD, O/N/H, and in‑process monitoring to acceptance are accelerating serial qualification of spherical metallic powder.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- University of Birmingham: https://www.birmingham.ac.uk
- Fraunhofer IWM: https://www.iwm.fraunhofer.de
- ASTM AM CoE: https://amcoe.org
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and QC
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock), ASTM B214/B822 (PSD), ASTM B212/B329 (apparent/tap density)
- NFPA 484 (combustible metals safety): https://www.nfpa.org
- Characterization labs and equipment
- LECO O/N/H analyzers: https://www.leco.com
- Laser diffraction and SEM services at accredited labs
- Process and design tools
- Ansys Additive, Simufact Additive for parameter optimization and distortion control
- nTopology for lattice design tailored to powder PSD
- Market/data
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- NIST AM Bench datasets: https://www.nist.gov
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 trends with metrics table and sources, two recent case studies on PS and PREP routes, expert viewpoints with citations, and practical tools/resources relevant to spherical metallic powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM feedstock standards update, major OEMs publish new PSD/oxygen specs, or significant price/yield shifts occur in GA/PA/PREP/PS routes.