概要 ニッケルモリブデン粉
ニッケルモリブデン粉末は、ニッケルとモリブデンからなる金属合金粉末です。高強度、耐食性、耐摩耗性、高温耐性など、ユニークな特性を兼ね備えています。
ニッケル・モリブデン・パウダーに関するいくつかの重要な詳細:
- 組成 – 通常、重量で 60-70% のニッケルと 30-40% のモリブデンを含む。特定の比率はカスタマイズすることができます。
- 製造方法 – 通常、ニッケルとモリブデンを予備合金化し、アトマイズして微細な均質粉末を作ることによって製造される。
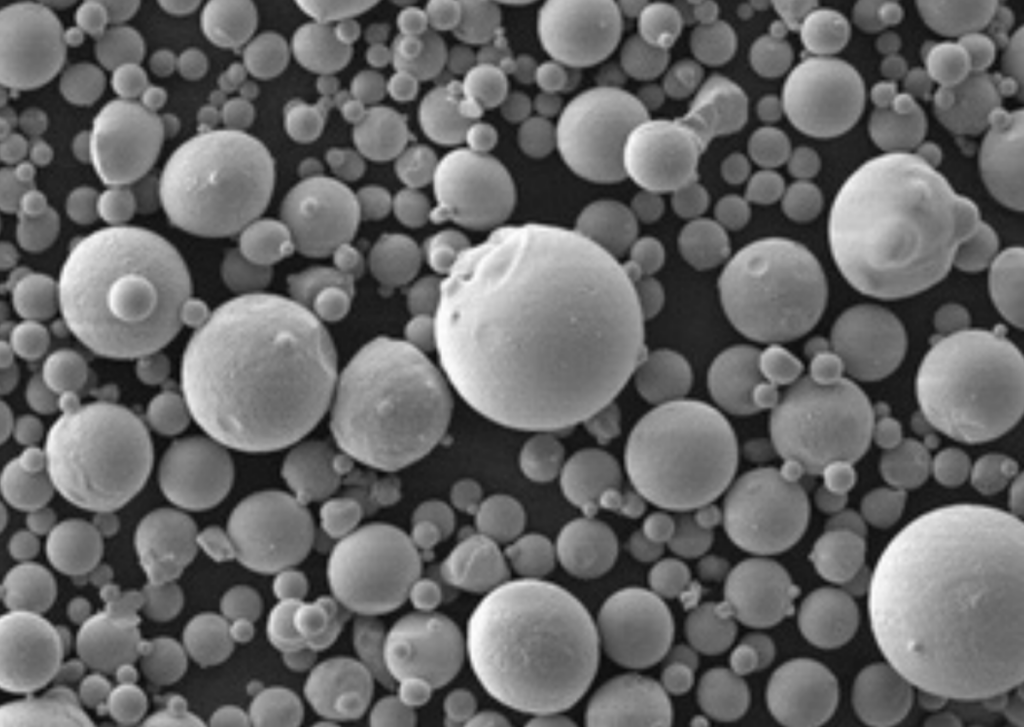
- 粒子径 – 用途に応じて10-150ミクロンの範囲。より微細な粉末は、より均一な特性を提供します。
- 形状 – 球状の粉末粒子は、より高い充填密度とスムーズな流動性を可能にします。不規則な形状も可能です。
- 一般商品名 – ニッケルモリパウダー、NiMo パウダー、60NiMo、65NiMo
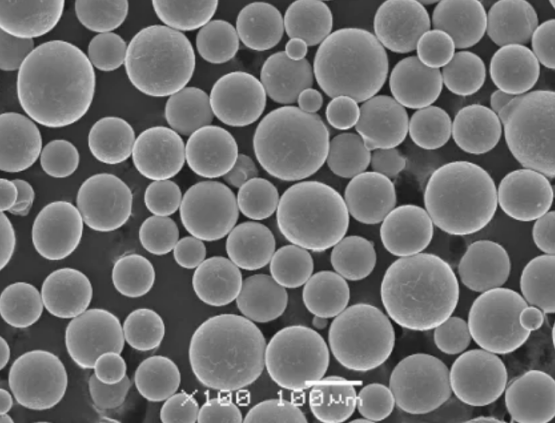

ニッケルモリブデン粉の種類
| タイプ | 構成 | 特徴 |
|---|---|---|
| ニッケルモリブデン合金粉末 | 60-70%ニッケル、30-40%モリブデン | 均一な組成、安定した特性、優れた性能 |
| カスタム・ニッケル・モリブデン比 | 50/50ニッケル/モリブデン~90/10ニッケル/モリブデン | 特定のアプリケーションのニーズに対応 |
| ナノ結晶ニッケルモリブデン粉 | Ni60~70%、Mo30~40%、粒径100nm | 非常に高い強度、均質な微細構造 |
ニッケルモリブデン粉の特性
| プロパティ | 特徴 |
|---|---|
| 構成 | 60-70%ニッケル、30-40%モリブデン |
| 密度 | 8.0-9.5 g/cc |
| 融点 | 1315-1400°C (2400-2550°F) |
| 強さ | 高、700~1300MPa |
| 延性 | 中程度、5~15%の伸び |
| 硬度 | 250-450 HV |
| 耐酸化性 | 大気中1000℃まで良好 |
| 耐食性 | 優れた耐酸性 |
| 電気抵抗率 | ~138 μΩ.cm |
| 熱伝導率 | 10-12.5 W/m.K |
| 熱膨張係数 | 12-14 x 10ˉ6/°C |
ニッケルモリブデン粉の用途
| 産業 | 申し込み | メリット |
|---|---|---|
| 航空宇宙 | タービンブレード、エンジン部品 | 温度に対する高い強度、耐酸化性 |
| 石油・ガス | ダウンホールツール、バルブ、ポンプ | 強度、耐摩耗性、耐食性 |
| 自動車 | ギア、ドライブシャフト | 耐疲労性と耐摩耗性 |
| 3Dプリンティング | プリント金属部品 | 高性能素材 |
| エレクトロニクス | 導電性厚膜 | 電気的特性、安定性 |
ニッケルモリブデン粉 仕様
| パラメータ | レンジ |
|---|---|
| ニッケル含有量 | 60-70 wt |
| モリブデン含有量 | 30-40 wt |
| 粒子サイズ | 10-150 μm |
| 見かけ密度 | 2.5-4.5 g/cc |
| タップ密度 | 4-6 g/cc |
| 流量 | 25~35秒/50g |
| 酸素含有量 | 0.5 wt |
| 炭素含有量 | 0.1 wt |
ニッケルモリブデン粉の利点と限界を比較する:
| メリット | 制限事項 |
|---|---|
| 高温での高い強度 | ニッケル粉より高価 |
| 優れた耐食性 | ニッケルより延性が低い |
| 高い硬度と耐摩耗性 | チタン合金より重い |
| 1000℃までの耐酸化性 | 純ニッケルほどの導電性はない |
| カスタマイズ可能な合金比 | 耐火性金属粉末は融点が高い |
購入先 ニッケルモリブデン粉
| サプライヤー | 説明 | 価格 |
|---|---|---|
| アメリカの要素 | 純プレアロイ粉末、カスタム粒度 | 50~200ドル/ポンド |
| スタンフォードマテリアルズ | プレハブ・ブレンドNiMo粉末 | 75~250ドル/kg |
| アメリカン・メタル&アンプ; 合金 | 幅広いニッケルモリブデン比 | 100~350ドル/kg |
| メタル・パウダー・カンパニー | 球状&不規則なNiMo粉末 | 60~180ポンド/kg |
よくある質問
ニッケルモリブデン粉は何に使われるのか?
ニッケルモリブデン粉末は、1000℃までの高温で高い強度を持つ。腐食や酸化にも強い。主な用途は、タービンブレードのような航空宇宙部品、自動車のギアやシャフト、石油・ガス用ダウンホールツール、および業界全体の金属部品の3Dプリントなどです。
ニッケルモリブデン粉は導電性ですか?
はい、ニッケルモリブデン粉は、約138μΩ.cmという高いニッケル含有量のおかげで良好な導電性を持っています。そのため、導電性厚膜用途に有用です。
ニッケル・モリブデンの組成は?
一般的な組成は、60~70重量%のニッケルと30~40重量%のモリブデンである。正確な比率は、アプリケーションの要件に応じてカスタマイズすることができます。
ニッケルモリブデンとインコネルの違いは何ですか?
インコネルは、ニッケル・クロムをベースとする超合金の一群である。ニッケルモリブデン合金は、クロムの代わりにモリブデンを使用することで、高い強度、硬度、耐食性を実現しています。
ニッケル・モリブデンより強い合金は?
タングステンやレニウムのような耐火金属合金は、ニッケル・モリブデンよりも融点が高い。炭化コバルトタングステン粉末は、非常に高い硬度と耐摩耗性を提供します。しかし、ニッケルモリブデンは高温強度、延性、耐酸化性の最高の組み合わせを提供します。
Additional FAQs About Nickel Molybdenum Powder
1) What PSD and morphology are recommended for additive manufacturing?
- For LPBF, use spherical Nickel Molybdenum Powder with PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.92, satellites <5%. For DED, 45–150 µm with tight sieving and low hollow fraction verified by CT.
2) How does Ni:Mo ratio affect properties?
- Higher Mo (35–40 wt%) increases solid-solution strengthening and acid corrosion resistance (reduces pitting/crevice attack) but can reduce ductility and raise flow stress during processing. Higher Ni improves ductility and thermal conductivity.
3) What environments benefit most from Ni–Mo alloys?
- Reducing, chloride- and acid-rich media (HCl, H2SO4) and sour service (H2S/CO2) where Mo improves resistance to localized corrosion and stress corrosion cracking relative to Ni-only or Ni–Cr systems.
4) Which atomization gas is preferred and why?
- Argon is generally preferred to minimize nitrogen pickup and unwanted nitrides; nitrogen can be acceptable for some Ni–Mo grades if N is controlled and does not embrittle the alloy. Target O ≤0.05 wt% and N per spec.
5) What post-processing improves performance of AM parts made with Ni–Mo powder?
- HIP to close porosity, followed by solution treatment/ageing per grade; precision machining plus corrosion passivation/electropolishing for flow-critical or corrosive-service components.
2025 Industry Trends for Nickel Molybdenum Powder
- Energy sector pull-through: Upstream and chemical processing investments drive demand for Ni–Mo powders for corrosion-critical valves, pumps, and downhole tools.
- AM qualification momentum: More vendors publish LPBF/DED material cards and heat-treatment windows for Ni–Mo compositions, including HIP’d property data.
- Cleaner powders: Expanded EIGA/PA capacity lowers O/N/H levels and tightens satellite/hollow control, improving fatigue and corrosion outcomes.
- Cost stabilization: Mo price volatility moderated in 2025; long-term contracts reduce powder price swings for Ni–Mo prealloys.
- Sustainability: Increased revert usage with O/N/H monitoring and documented powder-reuse cycles without compromising corrosion performance.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Nickel Molybdenum Powder)
| Metric (2025) | Typical Value/Range | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM-grade Ni–Mo powder price | $70–$160/kg | -2–6% | Supplier quotes; moderated Mo pricing |
| Recommended PSD (LPBF / DED) | 15–45 µm / 45–150 µm | Stable | OEM parameter guides |
| Sphericity (SEM/image analysis) | ≥0.92–0.97 | Slightly up | Supplier CoAs |
| Oxygen content (AM-grade) | ≤0.03–0.05 wt% | Down | EIGA/PA adoption |
| Typical LPBF density after HIP | 99.7–99.95% | +0.1–0.2 pp | OEM/academic datasets |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 6–8 cycles | Stable | O/N/H tracking + sieving |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards (52900 series; 52907 powders; 52908 machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench and powder metrology: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM International Handbooks (Nickel Alloys; Corrosion; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Ni–Mo Impellers for Acid Transfer Pumps (2025)
Background: A chemical processor needed corrosion‑resistant impellers with internal channels for HCl service.
Solution: Argon gas‑atomized Ni–Mo powder (65Ni–35Mo), PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.95; 280°C plate heating; island scan with contour-first; HIP + solution treat; electropolish of flow paths.
Results: Density 99.9% post‑HIP; CT showed zero through‑wall porosity; corrosion rate in 10% HCl at 60°C reduced by 35% vs. cast Ni alloy baseline; pump efficiency +4.2%.
Case Study 2: DED Repair of Ni–Mo Valve Seats in Sour Gas (2024)
Background: Oil & gas operator sought on‑site repair with high sour‑service resistance.
Solution: DED using 45–125 µm Ni–Mo powder with controlled O ≤0.04 wt%; preheat and interpass temperature control; post‑weld HIP surrogate (high‑pressure heat treat) + finish machining.
Results: Hardness 320–360 HV; no sulfide stress cracking in NACE TM0177 testing; service life projected +25% vs. prior weld overlay.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Tresa Pollock, Distinguished Professor of Materials, UC Santa Barbara
Key viewpoint: “Powder cleanliness and morphology—especially low hollow and satellite fractions—are decisive for fatigue and corrosion reliability in Ni–Mo AM components.” - Dr. John R. Scully, Charles Henderson Professor of Materials Science, University of Virginia
Key viewpoint: “Molybdenum’s role in stabilizing passive films under reducing acids makes Ni–Mo alloys uniquely suited to aggressive chloride environments.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “Inline O/N/H trending and CT quantification of defects are now standard for qualifying Ni–Mo powder lots for aerospace and chemical service.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and corrosion guidance
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders) and 52908 (Machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NACE/AMPP standards for sour service corrosion testing: https://www.ampp.org
- Handbooks and data
- ASM Handbooks (Nickel and High‑Temperature Alloys; Corrosion; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
- Metrology and QC
- Interstitials: LECO O/N/H analyzers
- PSD/shape: Malvern Mastersizer, SEM image analysis
- CT for hollow/satellite fraction: industrial CT solutions
- Electrochemical test methods for corrosion rate and pitting potential
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced 2025 trends with data table and sources; provided two recent Ni–Mo case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; listed practical tools/resources for Nickel Molybdenum Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM or AMPP publish updated powder/corrosion standards, major OEMs release validated Ni–Mo AM property cards, or new datasets on powder cleanliness–corrosion correlations become available

