タングステン・コバルト粉炭化タングステン(WC)粉末を金属コバルトバインダー粉末と結合させた複合材料を指し、タングステンコバルト合金またはWC-Coとしても知られています。この粉末冶金製品は、硬度、靭性、耐熱性/耐摩耗性のユニークな組み合わせで高く評価されている一般的な超硬合金材料です。
タングステン・コバルト粉末の種類
タングステン・コバルト粉末は、様々な用途や加工方法に対応できるよう、様々な組成、サイズ、形状、グレードがあります。
| タイプ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 構成 | 通常、84~97重量%のWCに3~16%のコバルトを配合。比率は硬度、強度、耐久性、その他の特性を最適化するために調整される。 |
| 粒子形状 | 円形/球形のパウダーは、均一な金型充填のために流動性が良い。角のある粉体や粉砕された粉体は、成形強度が向上します。 |
| 粒子径 | サブミクロンのナノ構造パウダーから100ミクロン以上の粗粒子まで、最終的な部品のサイズと詳細に応じて対応。 |
| グレード | 純度、粒度分布、形状、残留炭化物およびその他のパラメータに基づく複数の品質等級。より高いグレードは、より要求の厳しい用途に使用される。 |
タングステン・コバルト加工法
WC-Coパウダーは、様々な圧密技術を経て、完成部品やコンポーネントとなる:
- プレス・焼結粉末冶金
- 金属射出成形
- バインダージェッティング、レーザー/電子ビーム粉末床融合などの積層造形
- 溶射コーティング
- 冷間/温間圧縮およびロールプレス
- クラッディング、ろう付け、溶接
適合性は、材料グレード、最終部品サイズ、複雑さ、性能要件、生産量などの要因によって異なります。
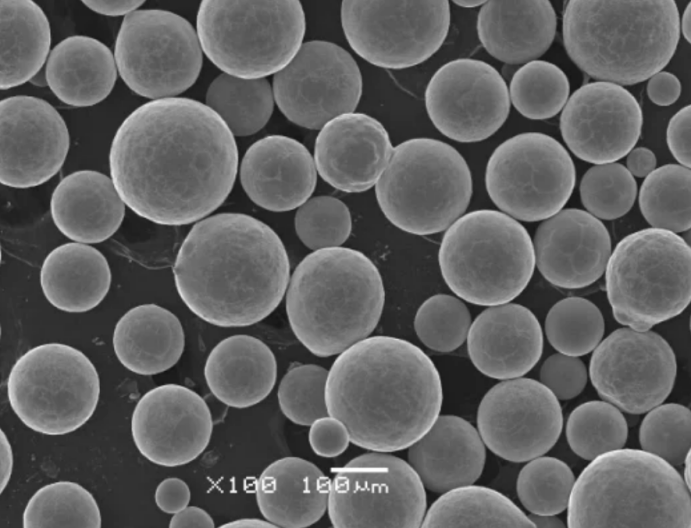

タングステン・コバルト組成
炭化タングステンとコバルト。他の元素は、アプリケーションのニーズに基づいて存在することがあります。
| 構成員 | 機能 | 重量 |
|---|---|---|
| 炭化タングステン(WC) | 極めて高い硬度、強度、耐摩耗性を実現 | 84-97% 標準 |
| コバルト | 炭化物を結合させる延性金属バインダー | 3~16%(一般的 |
| タンタル、チタン、ニオブカーバイド | 特定の用途に耐食性を付加 | オプションで5%まで |
| 炭化バナジウム | 熱処理中の粒成長抑制剤 | オプションで2%まで |
コバルトの役割
コバルト結合相は、炭化タングステン硬質金属において重要な機能を果たす:
- WC粒子を強靭な金属マトリックスでつなぎ合わせる
- 脆いWC粒子に破壊靭性と耐衝撃性を与える
- 変形を許容し、負荷分散をサポート
- 強度向上のための熱処理が可能
- 磁気特性を決定する
コバルト濃度が高いほど、一般的に強度と加工性が向上する一方で、硬度は低下する。WC-Co比は物理的、機械的、電気的、磁気的特性に直接影響する。
タングステン・コバルトの特性
炭化タングステン・コバルト硬質金属の主な特性は以下の通り:
| プロパティ | パフォーマンス |
|---|---|
| 硬度 | 最高1500HVまたは90HRA、最も硬い工業用素材のひとつ |
| 耐摩耗性 | 耐摩耗性、耐侵食性に優れる |
| タフネス | 最大30MPa√mの耐クラック伝播性 |
| 高温強度 | 制限時間内であれば1000℃まで動作可能 |
| 耐食性 | かなり不活性だが、特定のグレードはより優れた性能を発揮する |
| 熱伝導率 | 最大100W/mKの熱除去 |
| 電気伝導度 | グレードにより半導電性から金属に近いものまである。 |
| 熱膨張係数 | 5-7×10-lt;sup>-6-lt;/sup> K<sup>-1-lt;/sup>; |
| 密度 | 11-15 g/cc、チタン合金より重い |
| 磁気特性 | WC-Co比によって決まる。 |
超硬合金は、硬度、摩耗性能、破壊靭性のユニークなバランスにより、極端な圧力、温度、衝撃、摩擦、腐食環境に耐える理想的な材料です。特性は、特定の用途と使用条件に応じて選択された組成と加工パラメータに基づいて微調整されます。
タングステン・コバルトの用途
タングステンカーバイトコバルト材料は、その卓越した硬度と摩耗特性に加え、強度と耐熱性を兼ね備えているため、次のような分野で非常に幅広い産業用途に使用されています:
| 産業 | 一般的なアプリケーション |
|---|---|
| 鉱業 | 掘削工具およびビット、削岩インサートおよび歯、スクリーニング媒体 |
| 石油・ガス | ダウンホールツール、ワイヤーラインツール、フラックボール、スリーブ、坑井穿孔 |
| 建設 | 道路切削・計画用工具、溝掘り用工具、丸鋸 |
| 金属加工 | 旋削チップ、冷間成形金型、回転バリ、スリッター、ローラースケール |
| 木工 | 切削工具、丸鋸、チッパー、プレーナー、ジョインターナイフ |
| 自動車 | 燃料噴射ノズルホルダー、バルブ、シート |
| 航空宇宙 | 伸線ダイス、押出ダイス、スウェージングツール |
| エレクトロニクス | 半導体ウェハーダイシングブレード |
| メディカル&デンタル | 手術用ブレードとドリルビット |
| 食品加工 | ミートチョッパープレート、押出ダイス |
炭化コバルトタングステンのユニークな特性は、過酷な使用条件下で、従来の工具鋼、ステンレス鋼、その他の競合材料よりも優れた性能を発揮します。
タングステンコバルト粉仕様
プレス・焼結用炭化コバルトタングステン粉末は、各種国際規格に適合しています:
| スタンダード | 説明 |
|---|---|
| ISO 2768 | 超硬合金粉末の幾何公差 |
| ISO 4499 | 超硬合金の粒度測定方法 |
| ASTM B771 | 射出成形用銅タングステンカーバイド粉の規格 |
| JIS R 1601 | 超硬合金粉末の分類 |
ISO 2768に準拠した主要な粉体メトリクスとその代表値:
| パラメータ | 典型的な範囲 |
|---|---|
| 粒子径 | 0.2~120ミクロン |
| 粒子形状 | 丸型、角型、破砕型 |
| 見かけ密度 | 3-8 g/cc |
| タップ密度 | 4-12 g/cc |
| 比表面積 | 0.1~20m<sup>2</sup>/g |
| 固溶体含有量 | オプションで5%まで |
| 残留炭素 | 0.最大1 |
| 残留酸素 | 0.最大6 |
メーカー各社は、化学組成、物理的特性、および検査基準を明記した詳細なTDSおよびCOAを、対象用途に合わせた各粉末グレードに提供しています。独自のニーズにはカスタムブレンドも提供します。
炭化タングステンとコバルト硬質金属の比較
標準的な炭化タングステングレードとコバルトリッチな硬質金属粉末を比較した場合の主な相違点:
| パラメータ | 炭化タングステン | コバルト・ハードメタル |
|---|---|---|
| 構成 | 94~97%WC、3~6%Co含有 | WC84~90%、Co10~16 |
| 硬度 | 最大92HRA (>1500 HV) | 最大62HRA(~700HV) |
| タフネス | 脆性骨折のリスクが高い | 最大30MPa√mの耐クラック伝播性 |
| 強さ | 2,000~3,000MPaの横破断強度 | 4,500~5,500MPaの横破断強度 |
| 耐摩耗性 | 極めて高い耐摩耗性と耐侵食性 | 低めだが優れた摩耗性能 |
| 耐食性 | バインダーで保護されていない場合、酸化やケミカル・アタックを受けやすい。 | 厚いコバルト層による優れた耐食性 |
| 磁気応答 | 微量のコバルトバインダーによる微弱な磁性 | コバルト含有量が高いため強磁性 |
トレードオフ
コバルト含有量を増やすと、靭性と耐食性が向上する一方で、硬度と摩耗性能は低下します。極めて高い硬度対強度および耐久性。
超硬タングステンと超硬コバルトの比較
炭化タングステンを区別することは重要である。 パウダー (コバルトバインダーなしの純粋なWC)と炭化タングステン コバルト (複合WC+Coパウダー)。
| メートル | 炭化タングステン | 炭化タングステン コバルト |
|---|---|---|
| 成分 | コバルトを含まない純タングステンカーバイド | インティメイトWC+Coパウダーミックス |
| 硬度 | 極めて硬度が高く、非常に脆い。 | コバルトによる靭性向上で硬度低下を相殺 |
| 用途 | バインダーを使用しない純粋なWC形態での使用は限定的である。 | ほとんどの商業用途ではバインダーとしてコバルトが必要 |
| 加工 | 純粋なWC粉末の焼結に挑戦 | コバルトとの統合が容易になり、製品が強化される |
| 価格 | 単一部品としては安価 | コバルト含有によるコスト高 |
| 空室状況 | あまり一般的ではない | 非常に広く入手可能 |
したがって、炭化タングステン・コバルト粉末はより汎用性が高く、硬質金属部品製造の大半の使用例に適用できる。
タングステン・コバルト粉のグレード
炭化タングステン・コバルト粉末は、性能のニーズを満たすために、標準化された幅広い組成と等級で市販されています:
| グレード | 説明 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| マイクログレイン | 非常に微細な1ミクロンパウダーは、より小さく複雑な部品に適しています。 | 小型工具、エレクトロニクス |
| サブミクロン | 適度な表面積を持つ1ミクロン以下の粒子 | 刃先交換式チップ、絞りダイス |
| ウルトラファイン | ~1~5ミクロンのパウダーで特性向上 | 切削工具、採掘用ピック |
| ファイン | 5~10ミクロンの中粒子が、より良い流動性とパッキングを実現 | 金属除去ツール、摩耗部品 |
| スタンダード | 汎用10-30ミクロンパウダー | 建設、木工、成形工具 |
| 中/粗 | 靭性の高い30ミクロン粒子 | 鉱業、石油・ガス、大型部品 |
より高いグレードの指定は、粒度分布、形状、純度レベル、酸素/炭素含有量、微細構造などの重要な粉体測定基準をより厳しく管理した、より優れた品質を示します。
プレミアムパウダーは、超硬合金部品の焼結密度、性能の安定性、信頼性を向上させます。しかし、高度な用途に最適化された、より微細で純度の高いタングステン・コバルトのグレードでは、コストも大幅に上昇します。
タングステン・コバルト粉末のコスト分析
価格は組成、等級、注文量、市況によって異なる:
| パウダーグレード | 平均価格帯 |
|---|---|
| 標準的な業務用10~30ミクロン | ポンドあたり27~37ドル |
| 微粒子サブミクロン 1~5ミクロン | ポンドあたり45~55ドル |
| 高純度超微粉 <1 ミクロン | ポンドあたり90~110ドル |
| 特殊バインダー強化またはコバルトグレード | ポンドあたり80ドルから250ドル以上 |
- タングステン価格の変動はパウダーのコストに直接影響する
- より高純度の医療用および航空宇宙用グレードは、割高な価格設定となっている。
- 数千ポンド単位の大量注文で大幅なコスト削減を実現
エネルギー、原材料、輸送コストの上昇に伴い、炭化タングステン・コバルト粉末の価格は上昇圧力に直面しているが、市場が需給のバランスを取るにつれて安定すると予想される。考察 ライフサイクルコスト分析 より高い性能のグレードは、優れた生産性と耐久性を提供し、部品あたりのコストを低減することができるため、意思決定のために使用されます。
よくある質問
超硬合金とは?
超硬合金とは、炭化物粒子と結合相(通常はコバルト)を混合して作られる複合材料のことである。炭化物成分として炭化タングステン粉末を使用した炭化タングステンコバルト(タングステンコバルト、WC-Coまたはカーバイドコバルトとも呼ばれる)は、そのユニークな特性のおかげで、超硬合金の非常に人気のあるタイプです。
炭化タングステンのグレードにはどのようなものがありますか?
炭化タングステン粉末自体は、純度、粒子径、炭素/酸素含有量やその他の指標に基づいて異なるグレードで利用可能です。一般的な炭化タングステン粉末の指定は、微小粒、サブミクロン、微細、標準および粗い粒子径が含まれます。さらに、超硬合金は組成によって区別されます – より高いコバルト含有量は、硬度と摩耗性能を最適化する標準的なグレードと比較して、改善された強度と靭性を持つコバルトリッチなグレードになります。特殊グレードには、タンタル、チタン、ニオブなどの炭化物が含まれることもあります。
超硬部品の製造方法
タングステンカーバイド・コバルトの完成部品を製造するための好ましい圧密プロセスには、プレス・焼結粉末冶金が含まれる:
- WCパウダーとCoパウダーを適量計量する。
- ボールミルによる密な混合と均質化
- 金型を使用し、圧力を加えることでグリーンパーツを成形。
- ハンドリング強度を向上させるための脱バインダーとプレシンター加工
- コバルト融点直下の高温焼結
- さらに熱処理を加えることで、特性をさらに向上させることができる。
粉末冶金の柔軟性と優れた炭化物特性により、この技術は商業規模の製造に非常に人気がある。
炭化タングステンの色は?
粉末状では、炭化タングステンコバルトは、一般的に暗い灰色を示す。コバルトを含まない純粋な炭化タングステンは薄い灰色に見えるかもしれません。より高いコバルト含有量は、より金属色を付与する。完全に焼結炭化タングステン部品は、出発粉末比の違いを反映しています。全体的に、灰色のいくつかの色合いが最も代表的な色です。
炭化タングステンは磁性を持つのか?
炭化タングステン自体は非磁性である。しかし、磁気反応はWC-Co合金中のコバルト結合剤の割合によって決まります。コバルトが6%以下のグレードは、一般的に弱い磁気吸引力しか示さない。Coが10%を超えるコバルトリッチな組成は強磁性になる。このため、磁気分離技術により、摩耗した超硬合金部品や使用済みの超硬合金部品をリサイクル用に回収することが容易になる。
炭化タングステンは危険か?
多くの工業用粉末と同様、炭化タングステン・コバルトの取り扱いには、一定の安全衛生上の注意が必要です:
- 粉塵の吸入を避けること
- 十分な換気を確保する
- 必要に応じてマスク、手袋、ゴーグルを着用する。
- 皮膚への接触や摂取を防ぐ
- リスクを適切に管理するためにSDSを見直す
固体状では、炭化タングステン自体は比較的不活性で、毒性はないと考えられている。しかし、典型的なコバルト・バインダーは、人によっては皮膚や呼吸器の感作を引き起こす可能性がある。全体として、超硬合金は、ガイドラインに従って注意深く取り扱えば、重大な健康被害をもたらすことはない。
結論
非常に高い硬度と強度、靭性、摩耗性能を併せ持つタングステンカーバイトコバルトは、金属加工、鉱業、建設、エネルギー、その他多くの産業用途で主力超硬合金となっています。WCとCoの粉末組成と圧密プロセスをカスタマイズすることで、オーダーメイドの特性プロファイルが可能になります。コンポーネントの信頼性、一貫性、工具寿命はすべて、原料として選択されたタングステン・コバルト粉末の品質と等級によって決まります。パイオニアが性能の限界を押し広げ続ける中、超硬合金の進歩は、多様な最先端技術における将来のブレークスルーを支えるだろう。
Frequently Asked Questions (Supplemental)
1) How does cobalt content affect Tungsten Cobalt Powder performance?
- Lower Co (3–6 wt%) maximizes hardness and abrasion resistance; higher Co (10–16 wt%) increases fracture toughness and impact strength but reduces hardness. Choose based on dominant failure mode: abrasive wear vs. chipping/impact.
2) What powder characteristics matter most for MIM vs. press‑and‑sinter?
- MIM: very fine PSD (often D50 < 5 μm), tight PSD, high apparent/tap density ratio, controlled oxygen/carbon, excellent de‑binder behavior. Press‑and‑sinter: slightly coarser PSD (D50 ≈ 5–15 μm), good flowability and die fill, consistent green strength.
3) Can Tungsten Cobalt Powder be used in additive manufacturing?
- Yes. Binder jetting is most common; PBF of WC‑Co typically requires a laser with optimized parameters or pre‑alloyed feedstock and often benefits from HIP to reduce porosity. Powder sphericity and low oxygen are critical.
4) How is grain growth controlled during WC‑Co sintering?
- Add small amounts of VC/Cr3C2/TaC as inhibitors, use rapid ramp and optimized dwell, and apply sinter‑HIP. These limit WC grain coarsening, preserving hardness while maintaining toughness.
5) What are best practices for handling WC‑Co powders safely?
- Control dust with local exhaust, use conductive/grounded equipment, wear appropriate PPE (P3/N100 respirators, gloves), avoid skin contact with cobalt, and follow NFPA 484 and SDS guidance. Implement medical surveillance where cobalt exposure is significant.
2025 Industry Trends and Data
- ESG and recycling: Closed‑loop carbide recycling programs increase reclaimed WC content without compromising properties.
- Fine‑scale control: Wider adoption of sinter‑HIP and grain inhibitors for micrograin and submicron grades in high‑precision tooling.
- AM adoption: Binder‑jetted WC‑Co with post HIP achieves near‑wrought properties for wear plates and conformal‑cooled dies.
- Cobalt stewardship: More suppliers disclose cobalt provenance and reduce free Co surface area via post‑sinter treatments for improved biocompatibility in certain applications.
- Predictive quality: Inline oxygen/carbon analytics and AI‑assisted PSD control improve lot‑to‑lot consistency.
| KPI (Tungsten Cobalt Powder & Parts), 2025 | 2023 Baseline | 2025 Typical/Target | Why it matters | Sources/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC grain size (micrograin grades, μm) | 0.8–1.2 | 0.4–0.8 | Hardness/edge retention | ISO 4499; supplier QC |
| TRS (transverse rupture strength, MPa) | 3,500–4,500 | 4,800–5,500 | Chipping resistance | Grade and Co% dependent |
| Hardness (HRA) across portfolios | 86–91 | 88–92 | 耐摩耗性 | Composition + grain control |
| Binder‑jetted WC‑Co final density (%) | 96–98 | 98.5–99.5 | Mechanical reliability | Sinter‑HIP optimization |
| Recycled WC content in feed (%) | 5–15 | 15-35 | ESG, cost stability | Supplier EPD/LCA |
| Cobalt (free surface) reduction after treatment (%) | - | 20–40 | Health/safety, corrosion | Post‑sinter surface mods |
Authoritative resources:
- ISO 4499 (carbide grain size), ISO 3327 (hardmetals—TRS): https://www.iso.org
- MPIF standards for powder testing: https://www.mpif.org
- NFPA 484 (combustible metals): https://www.nfpa.org
- REACH/OSHA cobalt guidance: https://echa.europa.eu | https://www.osha.gov
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Binder‑Jetted WC‑10Co Wear Plates with Sinter‑HIP (2025)
- Background: A mining OEM sought faster lead times on wear plates while maintaining service life.
- Solution: Spherical WC‑10Co powder (D50 ≈ 12 μm), binder jetting with high green density, hydrogen dewax/sinter followed by HIP; VC + Cr3C2 inhibitors to control grain growth.
- Results: Final density 99.2%; hardness 91.2 HRA; TRS 5,050 MPa; field life +14% vs. pressed‑sinter baseline; lead time −35%.
Case Study 2: Micrograin WC‑6Co End Mills via Sinter‑HIP and Nano‑Coating (2024)
- Background: Precision machining customer needed longer tool life in hardened steels.
- Solution: Submicron WC‑6Co powder (mean grain ≈ 0.6 μm) with VC inhibitor; vacuum sinter‑HIP; AlTiN‑based nano‑coating; edge prep via micro‑honing.
- Results: Tool life +28% in 60 HRC steel; flank wear rate −22%; chipping defects reduced by 30% per lot SPC.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Barbara L. Boyce, Materials Engineer (Hardmetals), independent consultant; former national lab researcher
- Viewpoint: “Grain size control and carbon/oxygen balance dominate WC‑Co performance—small deviations shift hardness–toughness trade‑offs more than modest Co changes.”
- Dr. Michael R. Khonsari, Distinguished Professor of Mechanical Engineering, tribology specialist, Louisiana State University
- Viewpoint: “Surface engineering of WC‑Co—edge preparation and nano‑multilayer coatings—often doubles life without changing the base grade.”
- Dr. Christina Friedrichs, Head of Powder R&D, industrial carbide manufacturer
- Viewpoint: “Binder‑jet plus HIP is maturing for complex WC‑Co geometries; powder sphericity and inhibitor chemistry are the gating variables.”
Affiliation links:
- LSU Mechanical Engineering: https://www.lsu.edu
- MPIF: https://www.mpif.org
Practical Tools/Resources
- Standards/QC: ISO 4499 (grain size), ISO 3327 (TRS), MPIF test methods; ASTM E1019 for O/N/H in powders
- Design/data: Kennametal and Sandvik Coromant grade application guides; MatWeb property data (https://www.matweb.com)
- Process modeling: Thermo‑Calc/DICTRA for phase and carbon window; Ansys/Simufact for sinter shrinkage/distortion prediction
- Metrology: SEM + EBSD for grain and binder mapping; microhardness (HV), HRA; CT for porosity/defects in AM parts
- Safety/ESG: NFPA 484 handling; SDS for cobalt exposure; supplier EPD/LCA disclosures for recycled content
Last updated: 2025-08-22
Changelog: Added 5 supplemental FAQs targeting composition effects, process selection, AM suitability, grain control, and safety; introduced a 2025 KPI table and trend insights; provided two recent case studies (binder‑jet wear plates; micrograin end mills); included expert viewpoints with affiliations; compiled standards, modeling, metrology, and safety/ESG resources for Tungsten Cobalt Powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/MPIF standards update, major suppliers revise WC‑Co grain inhibitor chemistries, or new field data on binder‑jet/HIP WC‑Co performance is published.