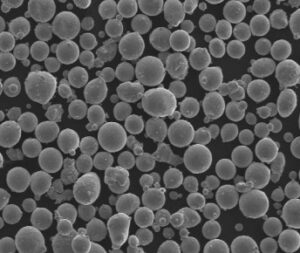
La poudre d'acier faiblement allié est un matériau polyvalent et essentiel dans diverses industries, de l'automobile à l'aérospatiale. Ces poudres sont conçues avec des compositions chimiques et des propriétés spécifiques pour répondre aux exigences de l'ingénierie moderne. Que vous soyez un ingénieur cherchant à optimiser les performances de votre produit, un fabricant à la recherche du matériau adéquat ou simplement curieux du sujet, ce guide vous plongera dans le monde des poudres d'acier faiblement allié.
Vue d'ensemble Aciers faiblement alliés Poudre
La poudre d'aciers faiblement alliés est produite par diverses méthodes, notamment l'atomisation, la réduction et l'électrolyse, ce qui permet d'obtenir une poudre fine et uniforme utilisée dans diverses applications. Contrairement aux aciers fortement alliés, les aciers faiblement alliés contiennent un pourcentage plus faible d'éléments d'alliage, généralement inférieur à 8%. Cela permet d'obtenir un équilibre entre la résistance, la dureté et la soudabilité, ce qui les rend idéaux pour les applications nécessitant des propriétés mécaniques spécifiques.
Qu'est-ce qui rend la poudre d'acier faiblement allié si spéciale ?
Les poudres d'acier faiblement allié sont conçues pour obtenir des propriétés spécifiques, telles qu'une solidité, une ténacité et une résistance à l'usure accrues. La composition précise de ces poudres permet aux fabricants de créer des composants à la fois durables et légers, sans compromettre les performances.

Types d'aciers faiblement alliés Poudre
La diversité des poudres d'aciers faiblement alliés est immense. Nous examinerons ci-dessous quelques-uns des modèles les plus couramment utilisés, en analysant leur composition, leurs propriétés et leurs applications.
| Modèle | Composition | Propriétés principales | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 4130 | Chrome, molybdène | Haute résistance, ténacité, bonne soudabilité | Pièces d'avion, automobile, pétrole et gaz |
| AISI 4340 | Nickel, chrome, molybdène | Excellente résistance à la fatigue, grande ténacité | Engrenages, vilebrequins, machines soumises à de fortes contraintes |
| AISI 6150 | Chrome, Vanadium | Bonne résistance aux chocs et à l'usure | Ressorts, arbres, couteaux |
| AISI 8620 | Nickel, chrome, molybdène | Cémentation, bonne ténacité | Engrenages, vilebrequins, bagues |
| AISI 5140 | Chrome | Résistance élevée à la traction, ténacité | Boulons, écrous, essieux |
| AISI 5120 | Chrome | Résistance élevée à l'usure, dureté | Engrenages, cames, pièces hydrauliques |
| AISI 50B44 | Bore | Amélioration de la trempabilité et de la résistance | Composants structurels, fixations |
| AISI 5145 | Chrome | Haute trempabilité, bonne ténacité | Automobile, machines d'ingénierie |
| AISI 5160 | Chrome | Excellente résistance à la fatigue, ténacité | Ressorts à lames, barres de torsion |
| AISI 52100 | Chrome | Résistance élevée à l'usure, robustesse | Roulements, outils, pièces soumises à de fortes contraintes |
Composition des Aciers faiblement alliés Poudre
La composition de la poudre d'aciers faiblement alliés est un facteur essentiel dans la détermination de ses propriétés. L'ajout d'éléments tels que le chrome, le molybdène, le nickel, le vanadium et le bore contribue aux caractéristiques mécaniques du matériau, telles que la dureté, la ténacité et la résistance à la corrosion.
- Chrome (Cr) : Améliore la dureté, la résistance à la corrosion et la résistance à l'usure.
- Molybdène (Mo) : Augmente la résistance à haute température, améliore la ténacité.
- Nickel (Ni) : Ajoute de la ténacité, améliore la résistance aux chocs.
- Vanadium (V) : Améliore la solidité, la résistance à l'usure et la ténacité.
- Bore (B) : Améliore la trempabilité, permettant un durcissement plus profond du matériau.
Tableau de composition détaillé
| Élément | Fonction | Effet sur les propriétés |
|---|---|---|
| Chrome | Agent de durcissement | Augmente la dureté, la résistance à l'usure et à la corrosion |
| Molybdène | Agent de renforcement | Améliore la résistance à haute température, la ténacité |
| Nickel | Agent tensioactif | Améliore la ténacité et la résistance aux chocs |
| Vanadium | Amélioration de la force et de la résistance | Améliore la résistance à l'usure et la solidité |
| Bore | Agent de durcissement | Augmente la trempabilité, la profondeur de trempe |
Caractéristiques des poudres d'aciers faiblement alliés
Il est essentiel de comprendre les caractéristiques des poudres d'acier faiblement allié pour sélectionner le matériau adéquat pour votre application. Vous trouverez ci-dessous les principales caractéristiques qui distinguent ces poudres.
- Haute résistance : Les aciers faiblement alliés offrent une résistance supérieure, ce qui les rend adaptés aux applications structurelles exigeantes.
- Bonne résistance : L'équilibre des éléments d'alliage garantit que le matériau reste résistant, même sous forte contrainte.
- Résistance à l'usure : Ces poudres sont conçues pour résister à l'usure et prolonger la durée de vie des composants.
- Soudabilité : Contrairement à certains aciers fortement alliés, les aciers faiblement alliés peuvent être soudés assez facilement, ce qui les rend idéaux pour les fabrications complexes.
- Rentable : Les poudres d'acier faiblement allié offrent une solution économique sans compromis sur les performances.
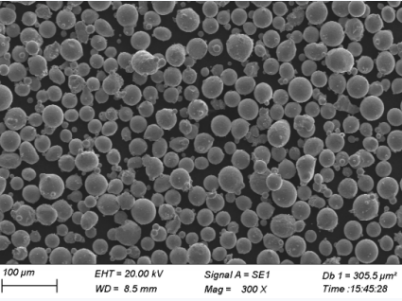
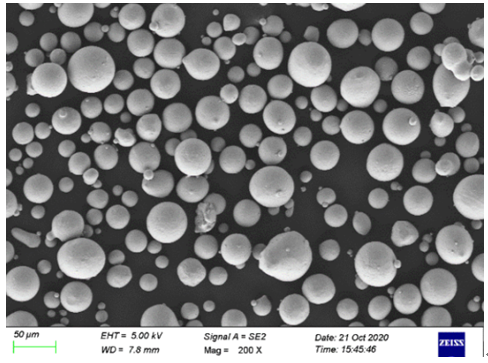



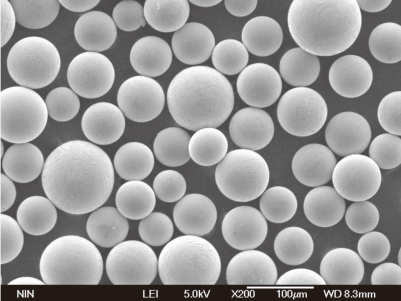
Tableau comparatif des caractéristiques
| Caractéristique | Description | Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|---|---|
| La force | Résistance élevée à la traction | Convient aux applications lourdes | Peut nécessiter un traitement thermique |
| Solidité | Capacité à résister aux chocs | Idéal pour les composants structurels | Diminue avec l'augmentation de la teneur en carbone |
| Résistance à l'usure | Résistance à l'abrasion | Prolonge la durée de vie des composants | Peut nécessiter un alliage avec des éléments plus durs |
| Soudabilité | Facilité de soudage | Simplifie la fabrication | Nécessite un traitement thermique avant/après la soudure |
| Rapport coût-efficacité | Coût abordable des matériaux | Réduction des coûts globaux de fabrication | Peut nécessiter un traitement supplémentaire |
Avantages des aciers faiblement alliés Poudre
La poudre d'aciers faiblement alliés offre plusieurs avantages qui en font un choix intéressant pour diverses industries :
- Polyvalence : Convient à une large gamme d'applications, de l'automobile à l'aérospatiale.
- Durabilité : Une résistance accrue à l'usure et à la corrosion garantit des performances durables.
- Personnalisation : La possibilité d'adapter la composition permet d'obtenir des propriétés mécaniques spécifiques.
- Le rapport coût-efficacité : Il offre un équilibre entre performance et coût, ce qui en fait un choix économique pour les fabricants.
Applications des poudres d'aciers faiblement alliés
Les poudres d'acier faiblement allié sont utilisées dans de nombreuses industries en raison de leurs propriétés uniques. Voici un aperçu détaillé de quelques-unes des applications les plus courantes.
| L'industrie | application | Pourquoi un acier faiblement allié ? |
|---|---|---|
| Automobile | Engrenages, arbres, vilebrequins | Haute résistance, résistance à la fatigue |
| Aérospatiale | Composants structurels, train d'atterrissage | Robustesse, légèreté |
| Pétrole et gaz | Trépans, pipelines | Résistance à l'usure, ténacité |
| Défense | Plaques d'armure, armement | Haute résistance, durabilité |
| La construction | Poutres structurelles, fixations | Soudabilité, résistance |
Utilisations spécifiques dans les industries
| L'industrie | Utilisation spécifique | Exemple de modèle |
|---|---|---|
| Automobile | Vilebrequins | AISI 4340 |
| Aérospatiale | Train d'atterrissage | AISI 4130 |
| Pétrole et gaz | Mèches | AISI 8620 |
| Défense | Plaques d'armure | AISI 5140 |
| La construction | Poutres structurelles | AISI 6150 |
Spécifications, tailles, qualités et normes
Lors de la sélection des poudres d'acier faiblement allié, il est essentiel de tenir compte des spécifications, des dimensions, des qualités et des normes qui s'appliquent à votre cas d'utilisation particulier. Le tableau ci-dessous résume ces aspects.
| Grade | Spécifications | Gamme de tailles (µm) | Normes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 4130 | ASTM A829 | 10-100 | ASTM, ISO |
| AISI 4340 | AMS 6415 | 15-150 | AMS, ASTM |
| AISI 6150 | ASTM A231 | 20-200 | ASTM, ISO |
| AISI 8620 | AMS 6274 | 10-120 | AMS, SAE |
| AISI 5140 | ASTM A322 | 15-180 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 5120 | ASTM A29 | 10-100 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 50B44 | ASTM A331 | 20-160 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 5145 | ASTM A108 | 10-120 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 5160 | ASTM A689 | 15-150 | ASTM, SAE |
| AISI 52100 | AMS 6440 | 10-110 | AMS, SAE |
Fournisseurs et prix des Aciers faiblement alliés Poudre
Les informations sur les prix et les fournisseurs sont cruciales pour les fabricants qui cherchent à s'approvisionner en poudres d'acier faiblement allié. Vous trouverez ci-dessous un résumé des principaux fournisseurs et des prix indicatifs.
| Fournisseur | Localisation | Modèle disponible | Prix par kg (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hoganas AB | Suède | AISI 4340, AISI 8620 | $15 – $25 |
| GKN Hoeganaes | ÉTATS-UNIS | AISI 4130, AISI 6150 | $12 – $22 |
| Technologie des matériaux Sandvik | Suède | AISI 5140, AISI 52100 | $18 – $30 |
| Technologie des charpentiers | ÉTATS-UNIS | AISI 5120, AISI 5160 | $20 – $28 |
| Rio Tinto Metal Powders | Canada | AISI 5145, AISI 50B44 | $14 – $26 |
Comparaison des poudres d'aciers faiblement alliés
Choisir la bonne poudre d'acier faiblement allié peut s'avérer difficile, surtout si l'on tient compte de divers facteurs tels que le coût, la disponibilité et les propriétés spécifiques. Vous trouverez ci-dessous une comparaison pour vous aider à prendre une décision en connaissance de cause.
| Paramètres | AISI 4130 | AISI 4340 | AISI 8620 | AISI 5140 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| La force | Haut | Très élevé | Modéré | Haut |
| Solidité | Haut | Haut | Haut | Modéré |
| Résistance à l'usure | Modéré | Haut | Modéré | Haut |
| Soudabilité | Bon | Juste | Excellent | Bon |
| Coût | Modéré | Haut | Faible | Modéré |

Avantages et limites des aciers faiblement alliés Poudre
Il est essentiel de comprendre les avantages et les limites des poudres d'acier faiblement allié pour sélectionner le matériau adapté à votre application. Le tableau ci-dessous résume ces aspects.
| Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|
| Haute résistance : Assure une solide intégrité structurelle. | Traitement thermique requis : Peut nécessiter un traitement supplémentaire. |
| Bonne résistance : Peut absorber une énergie élevée sans se fracturer. | Coût : Certains alliages peuvent être plus chers. |
| Résistance à l'usure : Prolonge la durée de vie des composants. | Disponibilité : La disponibilité de certaines classes peut être limitée. |
| Soudabilité : Plus facile à fabriquer et à assembler. | La complexité : Nécessite une sélection minutieuse en fonction de l'application. |
| Personnalisation : Peut être adapté à des besoins spécifiques. | Traitement : Peut nécessiter un contrôle précis pendant la fabrication. |
FAQ
À quoi servent les poudres d'acier faiblement allié ?
Les poudres d'acier faiblement allié sont utilisées dans une variété d'applications, y compris les composants automobiles tels que les engrenages et les vilebrequins, les structures aérospatiales, les équipements pétroliers et gaziers, les matériaux de défense et les éléments de construction.
Comment les aciers faiblement alliés se comparent-ils aux aciers fortement alliés ?
Les aciers faiblement alliés contiennent un pourcentage plus faible d'éléments d'alliage (généralement moins de 8%) que les aciers fortement alliés, ce qui les rend plus économiques et plus faciles à souder, mais leur confère une moindre résistance à la corrosion.
Les aciers faiblement alliés peuvent-ils être soudés facilement ?
Oui, les aciers faiblement alliés présentent généralement une bonne soudabilité, surtout par rapport aux aciers fortement alliés. Toutefois, des traitements thermiques avant et après le soudage peuvent être nécessaires pour obtenir les meilleurs résultats.
Quel est le rôle du chrome dans les aciers faiblement alliés ?
Le chrome améliore la dureté, la résistance à l'usure et la résistance à la corrosion des aciers faiblement alliés, ce qui en fait un élément essentiel dans la composition de nombreuses poudres d'acier faiblement allié.
Où puis-je acheter des poudres d'acier faiblement allié ?
Les poudres d'acier faiblement allié peuvent être achetées auprès de divers fournisseurs tels que Höganäs AB, GKN Hoeganaes, Sandvik Materials Technology, Carpenter Technology et Rio Tinto Metal Powders. Les prix varient en fonction de la qualité et du fournisseur.