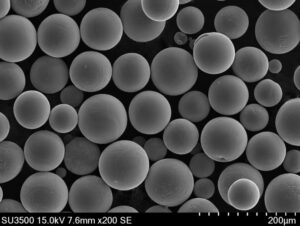
텅스텐 금속 분말 은 다양한 산업 분야에서 원료로 사용되는 미세 입자 형태의 텅스텐입니다. 고밀도, 강도, 내식성 및 높은 융점과 같은 고유한 특성으로 인해 중요한 엔지니어링 소재로 사용됩니다.
구성 및 제조
| 매개변수 | 세부 정보 |
|---|---|
| 원소 구성 | 순수 텅스텐(W) 또는 다른 금속과의 합금 |
| 생산 프로세스 | 텅스텐 막대에서 밀링하거나 텅스텐 산화물에서 환원합니다. |
| 입자 크기 | 일반적으로 1미크론에서 150미크론까지 다양합니다. |
| 순도 등급 | 99%~99.995% 순도 텅스텐 |
텅스텐 분말은 원하는 모양과 순도를 얻기 위해 수소 환원, 밀링 또는 열 플라즈마 구상화와 같은 다양한 공정을 통해 생산됩니다.
속성 및 특성
| 속성 | 가치 |
|---|---|
| 밀도 | 19.3g/cm3, 강철의 거의 두 배에 달하는 무게 |
| 녹는점 | 3422°C, 모든 금속 중 가장 높은 온도 |
| 힘 | 특히 소결 시 매우 높은 경도와 강도 |
| 전도성 | 낮은 전기 저항률, 높은 열 전도성 |
| 안정성 | 뛰어난 화학적 안정성 및 내식성 |

이러한 고유한 속성은 텅스텐 금속 분말 다양한 특수 애플리케이션으로 확장할 수 있습니다.
텅스텐 금속 분말의 응용 및 용도
| 애플리케이션 | 사용법 |
|---|---|
| 초경합금 공구 | 절삭 공구용 코발트 매트릭스에 바인딩됨 |
| 카운터 웨이트 | 무게추 및 밸러스트에 이상적인 고밀도 |
| 방사선 차폐 | X-선/감마선원으로부터 효과적으로 차폐 |
| 써미오닉 이미터 | 높은 융점으로 인한 필라멘트 |
| 3D 프린팅 파우더 | 고강도 텅스텐 부품 인쇄용 |
텅스텐 분말은 방위, 의료, 항공우주 및 기타 산업 전반에 걸쳐 미션 크리티컬한 요구 사항을 지원합니다.
사양 및 표준 등급
텅스텐 분말은 입자 크기 분포, 순도 수준, 제조 방법 등을 정의하는 다양한 국제 표준에 따라 제공됩니다. 몇 가지 일반적인 사양은 다음과 같습니다:
- ASTM B772 &8211; 순수 텅스텐 분말 유형
- ISO 5453 &8211; 화학 분석 및 크기 분류
- ICDD 00-001-1202 – 결정 구조 참조
공급업체 및 가격
| 공급업체 | kg당 가격 |
|---|---|
| 미드웨스트 텅스텐 | $70 – $500 |
| 버팔로 텅스텐 | $100 – $600 |
| 텅스텐 헤비 파우더 | $150 – $800 |
| 글로벌 텅스텐 분말 | $250 – $1500 |
가격은 순도 등급, 입자 모양/크기 일관성, 주문 수량, 부가가치 처리 여부에 따라 크게 달라집니다.

장점과 단점
| 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|
| 탁월한 경도와 밀도 | 다른 대안에 비해 비싼 가격 |
| 높은 온도에 견딜 수 있습니다. | 무거운 &8211; 제품에 사용할 경우 무게가 추가됩니다. |
| 부식 및 내마모성 | 제대로 처리하지 않으면 부서지기 쉬움 |
| 환경적으로 안정적 | 특정 형태로 가공하기 어려운 경우 |
| 균일한 파티클 분포 | 보호 분위기가 필요할 수 있습니다. |
자주 묻는 질문
텅스텐 금속 분말은 어떤 용도로 사용되나요?
특수한 특성으로 인해 공구, 분동, 방사선 차폐, 전자, 3D 프린팅 및 기타 고성능 영역에 응용되고 있습니다.
어떤 순도 등급을 사용할 수 있나요?
일반적인 순도 수준은 99%에서 99.995%까지입니다. 순도가 높을수록 훨씬 더 높은 가격이 책정됩니다.
일반적인 입자 크기는 어떻게 되나요?
입자 크기는 1마이크론에서 150마이크론까지 다양합니다. 원하는 크기는 적용 방법과 최종 사용 요구 사항에 따라 다릅니다.
텅스텐은 환경적으로 유해한가요?
아니요. 텅스텐 금속 분말은 일반적으로 무독성이며 친환경적입니다. 특정 가공에는 주의가 필요한 유해 화합물이 사용될 수 있습니다.
Additional FAQs: Tungsten Metal Powder
1) What particle morphology is best for different processes?
- Press-and-sinter: irregular/sponge for better green strength. Thermal spray and AM (LPBF): spherical for high flowability and packing. DED/wire-DED: coarser spherical or crushed granules.
2) How do oxygen and carbon impurities affect tungsten metal powder?
- Elevated O and C form WOx and carbides during sintering, increasing brittleness and porosity. For critical applications, target O ≤ 0.05 wt% and C ≤ 0.01 wt% unless intentionally alloyed.
3) Can tungsten metal powder be used in laser powder bed fusion?
- Yes, but it requires preheating and optimized parameters to mitigate cracking due to high stiffness and thermal gradients. Typical LPBF PSD: 15–45 µm spherical, with low O/N and tight PSD.
4) What are common tungsten composites and why use them?
- W-Ni-Fe/W-Ni-Cu heavy alloys for radiation shielding and kinetic energy components; W-Cu for thermal management and EDM electrodes; WC-Co for cutting tools. Composites balance density, ductility, and conductivity.
5) How should tungsten powder be stored and handled safely?
- Keep sealed and dry, under inert gas if possible; use local exhaust ventilation, antistatic grounding, and explosion-rated dust controls. Although tungsten is not highly reactive, fine powders can pose a dust explosion hazard.
2025 Industry Trends: Tungsten Metal Powder
- Semiconductor and medical growth: Demand up for W-Cu heat spreaders and high-density shielding components.
- Advanced manufacturing: More spherical, plasma-atomized W powders available for LPBF/DED; crack-mitigation strategies mature.
- Sustainability: Increased closed-loop recycling and take-back programs for W scrap/powders with certified impurity control.
- Standards tightening: Stricter impurity and PSD specs for AM-grade W and W-heavy alloys; wider adoption of in-line O/N/H analysis.
- Defense/aerospace: Continued shift from lead to tungsten-based shielding/ballast and kinetic components.
2025 Tungsten Powder Market Snapshot (Indicative)
| Metric | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD (Aug) | 참고 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global W powder demand (kt) | ~18.5 | ~19.3 | ~20.1 | Semiconductor + defense |
| Spherical W (15–45 µm) price (USD/kg) | 180–320 | 190–340 | 200–360 | PA/spheroidized, low O/N |
| Irregular W (-325 mesh) price (USD/kg) | 70–140 | 75–150 | 80–160 | Hydrogen-reduced |
| Typical O spec (AM-grade W) | ≤0.06 wt% | ≤0.05 wt% | ≤0.04 wt% | Tighter QC, in-line analyzers |
| AM adoption (W/W-alloys programs) | 신규 | Early pilots | Pilot-to-production | LPBF + DED parameter maturity |
| W-Cu demand growth (YoY) | +6% | +8% | +9–11% | Power electronics, EDM |
Sources:
- USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (Tungsten): https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- ASTM/ISO powder standards: https://www.astm.org, https://www.iso.org
- Supplier technical notes (Global Tungsten & Powders, H.C. Starck Solutions, Plansee) and industry trackers
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Crack-Resistant LPBF of Tungsten for Collimators (2025)
Background: A medical device OEM needed dense, fine-featured W collimators with reduced post-machining.
Solution: Used plasma-atomized W powder (D50 ~28 µm, O=0.035 wt%) with build plate preheat >600°C, beam shaping, and contour-remelting; stress-relief + hot isostatic pressing (HIP).
Results: Relative density 99.5–99.8%, microcrack incidence reduced by 70% vs. baseline; dimensional accuracy ±60 µm on 2 mm walls; machining time cut 25%.
Case Study 2: W-Cu Heat Spreaders via PM Infiltration for SiC Power Modules (2024)
Background: An EV inverter supplier sought CTE-matched plates with high thermal conductivity.
Solution: Sintered porous W skeletons from -325 mesh W, followed by capillary Cu infiltration to 15–30 vol% Cu; final surface lapped.
Results: Thermal conductivity 200–230 W/m·K; CTE 7.5–8.5 ppm/K (25–200°C); warpage <8 µm over 50 mm; yield +10% compared to prior route.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Dirk N. Schwab, Head of R&D, Plansee High Performance Materials
- “For AM-grade tungsten metal powder, controlling interstitials and applying elevated preheat are decisive to suppress solidification cracking and achieve near-wrought density.”
- Prof. Susanne Wurster, Materials Processing, TU Munich
- “W–Cu and W–Ni–Fe heavy alloys continue to expand as lead replacements. Process route selection—PM infiltration vs. AM—should follow CTE and flatness tolerance needs.”
- Dr. Kevin J. Hemker, Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University
- “Grain boundary engineering and beam shaping are enabling finer W features with improved toughness, opening opportunities in radiation optics and micro heat exchangers.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- ASTM B777 (tungsten heavy alloys), B772 (tungsten powder), B214/B212 (sieve/flow), E1019 (O/N/H): https://www.astm.org
- ISO 4497 (particle size by sieving), ISO 13320 (laser diffraction), ISO 7637-equivalent PM methods: https://www.iso.org
- USGS Tungsten Statistics and Information: https://www.usgs.gov
- OSHA/NIOSH guidance for metal powder handling and combustible dust: https://www.osha.gov, https://www.cdc.gov/niosh
- MatWeb materials database for W and W-composites: https://www.matweb.com
- Senvol Database for AM machine–material compatibility: https://senvol.com
- Supplier technical libraries: Global Tungsten & Powders, H.C. Starck Solutions, Plansee, Midwest Tungsten
Last updated: 2025-08-25
Changelog: Added 5 FAQs; inserted 2025 market snapshot table; provided two recent case studies; included expert opinions; compiled practical tools/resources with standards and datasets
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if USGS data revises demand/pricing >10%, new ASTM/ISO standards for AM-grade tungsten publish, or major LPBF/DED breakthroughs reduce cracking further