3D 프린팅 기술의 급속한 발전과 함께 3D 프린팅 소모품, 특히 3D 프린팅 금속 분말도 빠르게 발전하고 있습니다. 여기에는 티타늄 분말 및 티타늄 합금 분말, 티타늄 알루미늄 합금 분말 등의 사용이 포함되며 특히 주목할 만합니다.
구형 티타늄 합금 분말이 가장 널리 사용됩니다. 금속 분말 소재를 3D 프린팅에 사용할 수 있습니다. 따라서 이 기사에서는 구형 티타늄 합금 분말을 준비하는 몇 가지 방법과 향후 응용 분야에 대한 전망에 초점을 맞출 것입니다.
티타늄 합금은 저밀도, 고강도, 우수한 내식성, 높은 융점 등의 특성을 가지고 있습니다. 적층 제조 기술에 가장 일반적으로 사용되는 금속 중 하나이며 항공, 항공우주, 자동차, 생명공학 분야의 구조 부품으로 널리 사용됩니다.
티타늄 합금 분말의 제조
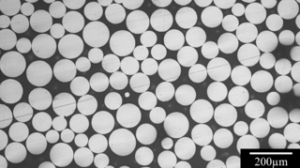
또한 3D 프린팅의 주요 기술 중 하나라는 것도 알고 있습니다, 선택적 레이저 용융(SLM)은 작고 정밀하며 복잡한 부품을 제조하는 데 적합합니다. 이 기술은 티타늄 합금 분말의 입자 크기가 좁아야 하며 분말의 구형도, 순도 및 유동성이 높아야 합니다.
진공 불활성 가스 분무(VIGA), 전극 유도 가스 분무(EIGA), 플라즈마 회전 전극 공정(PREP), 플라즈마 분무(PA), 플라즈마 스페로이드화(PS) 등 여러 일반적인 분말 제조 방법을 비교하면 PREP 장비가 구형도, 유동성 및 순도가 우수한 티타늄 합금 분말을 생산하여 사용 요건을 충족할 수 있음을 알 수 있습니다.
플라즈마 회전 전극 공정(PREP)은 구형 티타늄 합금 분말을 제조하는 가장 일반적인 방법 중 하나입니다. 원리는 티타늄 합금 바를 자체 소비 전극으로 사용하고 플라즈마를 열원으로 사용하여 전극을 서서히 녹이는 동안 전극을 고속으로 회전시키는 것입니다.
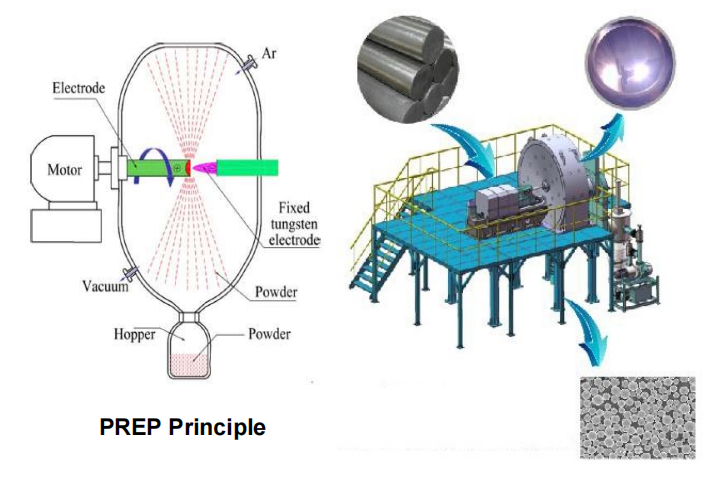
기존의 회전 전극 방식(REP)은 텅스텐 전극을 사용하는데, 금속 분무 중에 부식되어 불순물 성분으로 분말에 유입될 수 있습니다.
1985년, 노스웨스트 비철금속연구소는 중국 최초의 PREP 장비를 독자적으로 설계하고 개발했습니다.
이들이 사용하는 PREP의 제조 공정은 고속 회전 전극(원료)을 고순도 불활성 대기의 보호 아래 플라즈마 아크에 의해 녹이고, 녹은 금속을 큰 원심력에 의해 내보내 불활성 대기에 의해 원자화되어 저온실 내벽에 닿으면 구형의 분말로 응축되는 방식입니다.
이 기술과 시스템을 사용하면 높은 분말 구형도(90% 이상), 낮은 다공성 및 위성 분말을 얻을 수 있습니다. 이는 우리가 필요로 하는 티타늄 합금 분말의 요구 사항을 완전히 충족합니다.
티타늄 합금 분말의 응용
위에서 언급했듯이 티타늄 합금 분말은 다양한 용도로 사용되므로 여기에서는 참고용으로 일부만 나열하겠습니다.
티타늄 합금은 의료 분야에서 관절 임플란트, 보철물 등을 만드는 데 널리 사용됩니다. 티타늄 합금의 높은 가공성으로 인해 기존 디자인에서 벗어나 개인별 차이를 구현할 수 있어 의료 기기의 적응성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 또한 3D 프린팅 티타늄의 짧은 가공 주기는 골종양과 같은 질병을 앓고 있는 환자에게 장기적인 영향을 미칩니다.
티타늄과 티타늄 합금의 고강도, 고온 및 내식성으로 인해 항공우주 분야에서 새롭게 주목받고 있으며, 최근 3D 프린팅 기술의 개발과 적용으로 빠르게 채택되고 있습니다. 항공우주 분야에서 티타늄과 티타늄 합금은 일반 소재보다 가볍고 강하며 연성이 뛰어납니다. 또한 내식성이 뛰어나 해양 및 항공기 분야에서 경쟁력이 점점 더 높아지고 있습니다.
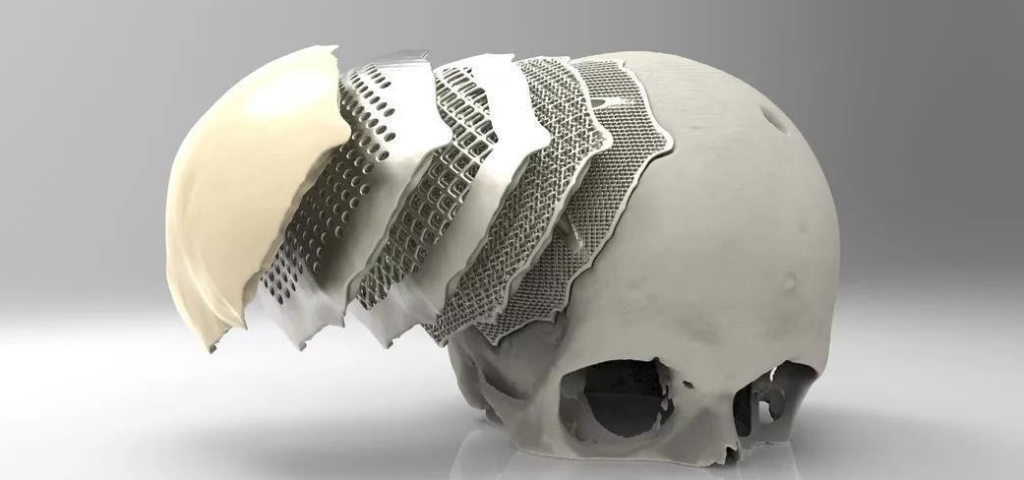
3D 프린팅의 중요한 소모품인 티타늄 합금은 항공우주, 자동차 및 바이오 의료 산업에서 응용 및 개발되면서 3D 프린팅 기술의 발전을 주도했습니다.
의 발전 전망 티타늄 합금 분말
4차 기술 혁명으로 정의되는 적층 제조는 이미 업계에서 스마트 제조의 가장 첨단적이고 유망한 기술 개발 중 하나로 널리 알려져 있으며, 이에 따라 인쇄 소모품으로 금속 소재의 개발이 빠르게 성장하고 있습니다.
컨설팅 업체인 SmarTech에 따르면 금속 분말 적층 제조의 글로벌 시장 규모는 2024년까지 110억 달러에 달할 것으로 예상됩니다.
티타늄 및 티타늄 합금은 우수한 강도와 인성, 내식성, 저밀도 및 생체 적합성으로 인해 항공 우주, 자동차, 바이오 의료 및 기타 분야에서 널리 사용되고 있으며 시장 수요는 매우 유망합니다.
플라즈마 기술의 적용 및 개발은 티타늄 합금 분말의 제조에 대한 기술 지원을 제공합니다.
플라즈마 회전 전극 공정은 전극 속도와 얻어진 분말의 거친 입자 크기와 같은 요인에 의해 제한되지만, 일부 분말 제조 장비 연구 기관에서는 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 노력하고 있습니다.
플라즈마 회전 장비의 개발 및 홍보로 3D 프린팅 분야에서 티타늄 및 티타늄 합금 분말의 비용이 점차 감소하고 적층 제조 분야에서 금속 분말의 광범위한 응용을 촉진 할 것입니다.
우리는 3D 프린팅이 앞으로 더 많은 분야에서 우리의 삶을 변화시킬 것이며, 티타늄 합금 분말의 준비와 개발이 이 과정에 큰 영향을 미칠 것이라고 믿을 만한 이유가 있습니다.
Additional FAQs: Titanium Alloy Powder and 3D Printing
1) Which titanium alloy powder grades are most used for AM and why?
- Ti6Al4V (Grade 5/23 ELI) dominates due to strength-to-weight, weldability, and biocompatibility. Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo and Ti-5553 appear in aerospace for higher temperature or strength; CP-Ti (Grade 2) is used for corrosion resistance and formability.
2) What particle size and sphericity are optimal for common AM processes?
- LPBF: 15–45 µm, high sphericity (>90%) for flowability and packing.
- EBM: 45–105 µm to suit elevated preheats and larger melt pools.
- DED: 50–150 µm with consistent flow. PREP/EIGA/PA routes yield excellent sphericity and low satellites.
3) How do oxygen and nitrogen contents affect titanium alloy powder performance?
- Interstitials (O, N) raise strength but reduce ductility and fatigue life. AM-grade Ti6Al4V ELI often targets O ≤ 0.13 wt% and N ≤ 0.05 wt%. Tight humidity control limits O pickup during storage/reuse.
4) PREP vs. VIGA/EIGA/PA: when to choose each for titanium alloy powder?
- PREP: clean, high-sphericity powder with very low inclusions—excellent for medical/aerospace; typically narrower PSD, higher cost.
- VIGA/EIGA: scalable gas atomization; EIGA avoids electrode/contact contamination.
- PA/PS: very spherical, fine PSD; favored for LPBF where low satellites and flow are critical.
5) What post-processing is typical for AM titanium parts?
- Stress relief, HIP for defect closure and isotropy, machining, surface finishing (grit blasting, chemical milling/electropolish), and tailored heat treatments to tune alpha/beta microstructure. For implants: cleaning, passivation, and validation per medical QMS.
2025 Industry Trends: Titanium Alloy Powder
- Medical scale-up: More lattice implants in Grade 23 with validated powder genealogy and in-line O/N/H monitoring.
- Aerospace productivity: Multi-laser LPBF and software-driven scan strategies cut cycle times 10–20% for Ti6Al4V brackets and ducts.
- Feedstock sustainability: Closed-loop recycling of oversize/unused powder with certified impurity limits; EPDs requested by OEMs.
- Process convergence: PREP and EIGA powders increasingly co-qualified as suppliers demonstrate consistent PSD and interstitial control.
- Design maturation: Functionally graded lattices and thin-wall heat exchangers push demand for tighter PSD and low-satellite content.
2025 Titanium Alloy Powder Snapshot (Indicative)
| Metric | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD (Aug) | 참고 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global titanium AM powder demand (kt) | ~10.4 | ~11.2 | ~12.1 | Driven by aerospace + medical |
| AM-grade Ti6Al4V price (USD/kg) | 180–260 | 170–240 | 160–230 | Scale, reuse, competition |
| Typical O spec (Grade 23, wt%) | ≤0.13 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.11 | Tighter interstitial control |
| LPBF average build-rate gain vs. 2023 | - | +8–12% | +10–20% | Multi-laser and scan tuning |
| Share of PREP/EIGA in medical Ti powders (%) | ~46 | ~50 | ~54 | Inclusion control emphasis |
| Reused powder share in AM builds (%) | 30–40 | 35–45 | 40–50 | With genealogy + O/N/H limits |
Sources:
- ASTM/ISO AM standards: https://www.astm.org, https://www.iso.org
- FDA device databases and AM guidance: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices
- MPIF and industry trackers (Context/Wohlers-type reports)
- Supplier technical notes (AP&C/GE Additive, EOS, Höganäs, Carpenter Additive)
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: High-Fatigue Ti6Al4V ELI Lattice Implants via LPBF (2025)
Background: A medical OEM needed higher fatigue performance and osseointegration for acetabular cups.
Solution: Used ELI powder (D50 ~30 µm, O=0.10 wt%) from EIGA route; gradient lattice (60–80% porosity), contour remelts, HIP, and surface roughening (Ra 20–35 µm) with validated cleaning.
Results: 25–30% increase in high-cycle fatigue life; early osseointegration improved in pilot cohort; powder reuse extended to 10 cycles with O ≤ 0.12 wt%.
Case Study 2: Thin-Wall Ti6Al4V Heat Exchangers with PREP Powder (2024)
Background: An aerospace supplier targeted compact, leak-tight exchangers for bleed-air cooling.
Solution: PREP Ti6Al4V powder (15–45 µm, high sphericity) with adaptive hatch/contour and 200°C plate preheat; selective HIP for core; chemical milling to uniformize walls.
Results: Helium leak ≤1×10^-9 mbar·L/s, density ≥99.7% in HIPed zones; mass reduced 18% vs. brazed assembly; build time -12% using optimized scan order.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Amy J. Clarke, Professor of Metallurgy, Colorado School of Mines
- “Powder PSD stability and interstitial control across reuse cycles are as critical to fatigue scatter as the post-build HIP for Ti6Al4V.”
- Dr. Martin Wegener, Head of Materials and Processes, EOS GmbH
- “For titanium alloy powder, scan strategy and preheat management now rival hardware in achieving density and consistent surface quality on thin walls.”
- Dr. Dirk N. Schwab, Head of R&D, Plansee High Performance Materials
- “PREP and EIGA powders can both meet medical/aerospace needs when oxygen and inclusions are tightly controlled—supplier genealogy is decisive.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (AM feedstock requirements), ISO/ASTM 52904 (LPBF of metals): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F3001 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI AM), ASTM F2924 (PBF Ti-6Al-4V), ASTM F3302 (AM material specs): https://www.astm.org
- FDA Technical Considerations for Additive Manufactured Medical Devices: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices
- NIST AM-Bench (datasets for melt pool/porosity studies): https://www.nist.gov/ambench
- Senvol Database for machine–material mapping: https://senvol.com
- OEM application notes: GE Additive/AP&C, EOS, SLM Solutions, Renishaw
- OSHA/NIOSH combustible dust and metal powder handling: https://www.osha.gov, https://www.cdc.gov/niosh
Last updated: 2025-08-25
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; inserted a 2025 trends snapshot with metrics table and sources; provided two recent case studies; included expert viewpoints; curated standards and resource links
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ASTM/ISO/FDA guidance updates, major OEM qualifications change reuse limits, or market demand shifts >10% in aerospace/medical segments