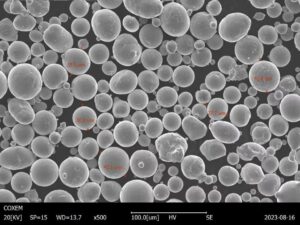
니오븀 티타늄 분말 소개
니오븀 티타늄 분말은 놀라운 합금으로, 산업 전반에 걸쳐 다양한 용도로 활용되어 큰 주목을 받고 있습니다. 니오븀과 티타늄이 혼합된 이 소재는 뛰어난 특성과 다용도성 덕분에 항공우주부터 의료기기에 이르기까지 다양한 분야에서 독보적인 위치를 차지하고 있습니다.
니오븀 티타늄 분말의 생산 공정
니오븀 티타늄 분말을 만드는 데는 복잡하면서도 흥미로운 공정이 필요합니다. 이 과정은 니오븀과 티타늄의 품질이 중추적인 역할을 하는 원료를 세심하게 선택하는 것에서 시작됩니다. 고급 분말 야금 기술을 사용하여 이러한 원소를 결합하고 제어된 온도 및 압력 조건을 적용합니다. 그 결과 뛰어난 특성을 지닌 미세한 분말 합금이 탄생합니다.
니오븀 티타늄 분말의 특성
니오븀 티타늄 분말의 높은 중량 대비 강도 비율로 대표되는 기계적 성능은 다양한 응용 분야에서 매력적인 선택이 될 수 있습니다. 우수한 화학적 안정성과 결합된 열적 특성 또한 니오븀 티타늄 분말의 장점입니다. 이러한 특성을 종합적으로 고려하면 이 합금은 극한 조건을 견디고 극한 환경에서 탁월한 성능을 발휘합니다.

니오븀 티타늄 분말의 응용 분야
항공우주 및 항공 산업에서는 전체 무게를 최소화하면서 구조적 무결성을 향상시키는 니오븀 티타늄 분말을 채택하고 있습니다. 의료 분야에서는 생체 적합성과 내식성 덕분에 임플란트 및 수술 도구에 응용되고 있습니다. 또한 이 합금은 초전도체 및 에너지 저장 솔루션 개발에 중추적인 역할을 하며 재생 에너지 및 기술 발전을 주도하고 있습니다.
장점 및 혜택
니오븀 티타늄 파우더의 가볍지만 견고한 특성은 산업계가 성능 저하 없이 혁신을 이룰 수 있도록 지원합니다. 내식성이 뛰어나 수명이 길어 유지보수 및 교체 비용이 절감됩니다. 기술 발전의 촉매제인 이 합금은 재료 과학 및 엔지니어링의 지속적인 진화를 강조합니다.
도전 과제와 한계
니오븀 티타늄 분말은 많은 장점을 제공하지만 여전히 과제가 남아 있습니다. 정제 및 가공과 관련된 높은 생산 비용은 특히 비용에 민감한 애플리케이션에서 더 폭넓게 채택되는 데 걸림돌이 됩니다. 또한 기술적 제약으로 인해 특정 기계적 특성이 요구되는 시나리오에서는 사용이 제한됩니다.
미래 잠재력 및 연구
니오븀 티타늄 분말의 잠재력을 최대한 활용하기 위한 지속적인 연구 노력이 진행 중입니다. 생산 기술을 개선하고 새로운 응용 분야를 탐색하는 데 중점을 두고 있는 이 합금은 산업을 변화시키고 최첨단 혁신의 길을 열 수 있는 가능성을 지니고 있습니다.
다른 자료와의 비교
기존 금속에 비해 니오븀 티타늄 분말의 뛰어난 강도, 가벼운 특성 및 부식에 대한 저항성은 눈에 띄게 두드러집니다. 다른 초합금과 비교했을 때, 니오븀 티타늄 분말의 독특한 특성 덕분에 극한 조건에서 신뢰성이 요구되는 응용 분야에 가장 적합한 소재입니다.
환경적 고려 사항
니오븀 티타늄 파우더의 지속 가능성은 환경에 대한 의식이 높아지는 추세와 맞닿아 있습니다. 재활용 가능성과 생태계에 미치는 영향을 줄일 수 있는 잠재력은 소재 사용에 대한 친환경적 접근 방식에 기여합니다. 적절한 재활용 프로세스는 자원을 절약하고 폐기물을 줄이는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
시장 동향 및 수요
니오븀 티타늄 분말에 대한 수요 증가는 다방면에 걸친 응용 분야에서 비롯됩니다. 업계에서는 설계를 혁신하고 성능을 개선할 수 있는 이 합금의 잠재력을 인정하고 있습니다. 시장 전망에 따르면 항공우주, 의료 기술 및 에너지 저장 솔루션의 발전에 힘입어 지속적인 성장이 예상됩니다.
안전 및 규정
합금의 고유한 특성으로 인해 안전한 취급 및 보관 관행이 필수적입니다. 규제 표준 및 인증은 니오븀 티타늄 분말이 특히 의료 기기 및 항공 우주 부품과 같은 민감한 응용 분야에서 안전 요건을 충족하도록 보장합니다.
사례 연구
실제 사례는 다양한 시나리오에서 합금의 효과를 강조합니다. 항공기 부품의 내구성 강화부터 의료 분야의 혁신에 이르기까지 니오븀 티타늄 분말의 다재다능함은 실제 응용 분야에서 빛을 발합니다.
투자 및 비즈니스 기회
혁신적인 벤처에 관심이 있는 기업가와 투자자는 니오븀 티타늄 분말의 잠재력을 고려해야 합니다. 틈새 응용 분야를 탐색하고 연구 기관과 협력하면 획기적인 비즈니스 기회로 이어질 수 있습니다.
전문가 인터뷰
업계 전문가들의 인사이트를 통해 합금의 중요성과 미래 전망에 대해 알아보세요. 전문가들은 산업을 형성하는 데 있어 합금의 역할에 대해 논의하고 지속적인 진화에 대한 생각을 공유합니다.

결론
니오븀 티타늄 분말의 놀라운 특성과 다양한 응용 분야가 결합되어 산업 전반에 걸쳐 혁신적인 소재로 자리매김하고 있습니다. 항공에서 헬스케어에 이르기까지 이 합금은 강도, 경량성 및 부식에 대한 저항성이 독특하게 결합되어 있어 기술과 혁신을 발전시키는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다.
자주 묻는 질문
- 니오븀 티타늄 파우더의 용도는 무엇인가요? 니오븀 티타늄 분말은 강도, 경량성, 내식성과 같은 고유한 특성으로 인해 항공우주, 의료 기기, 에너지 저장 솔루션 등 다양한 산업 분야에서 활용되고 있습니다.
- 니오븀 티타늄 분말은 어떻게 생산되나요? 생산 공정에는 고품질 원료를 선택하고, 니오븀과 티타늄을 결합하고, 고급 분말 야금 기술을 사용하여 제어된 온도 및 압력 조건에 혼합물을 노출시키는 과정이 포함됩니다.
- 항공우주 분야에서 니오븀 티타늄 분말을 사용하면 어떤 이점이 있나요? 니오븀 티타늄 분말은 가볍지만 강한 특성을 가지고 있어 항공우주 부품에 이상적인 선택이며, 전체 무게를 최소화하면서 구조적 무결성을 향상시켜 연료 효율과 성능을 개선하는 데 기여합니다.
- 니오븀 티타늄 분말은 재활용이 가능한가요? 예, 니오븀 티타늄 분말은 재활용이 가능하므로 지속 가능성 노력에 부합합니다. 적절한 재활용 프로세스를 통해 자원을 절약하고 폐기물을 줄일 수 있으므로 환경을 고려한 선택이 될 수 있습니다.
- 니오븀 티타늄 분말의 광범위한 채택을 방해하는 과제는 무엇인가요? 특정 응용 분야에서 높은 생산 비용과 기술적 한계는 니오븀 티타늄 분말의 광범위한 채택을 저해하는 문제입니다. 이러한 요소는 비용에 민감한 시장과 특정 특성을 요구하는 응용 분야에서의 경쟁력에 영향을 미칩니다.
Additional FAQs About Niobium Titanium Powder
1) What makes Niobium Titanium Powder attractive for superconducting applications?
- Nb-Ti is a workhorse superconducting alloy used in MRI magnets and particle accelerators. As powder feedstock, it enables powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing routes to tailor microstructure, improving filament uniformity and enabling complex coil hardware. Its critical temperature (Tc ≈ 9.2 K) and high critical current density under magnetic fields make it reliable and cost-effective compared to higher-Tc but brittle alternatives.
2) Is Niobium Titanium Powder suitable for additive manufacturing (AM)?
- Yes. Gas/plasma-atomized Nb-Ti powders with high sphericity and low oxygen enable LPBF/EBM builds of lightweight brackets, implant components, and superconducting fixtures. Key controls: PSD suited to the process (e.g., 15–45 µm LPBF; 45–106 µm EBM), O/N/H below spec, and post-build heat treatments to optimize toughness and corrosion resistance.
3) How does oxygen and nitrogen content affect properties?
- Interstitials strengthen but embrittle Nb-Ti. For structural or biomedical uses, keeping O and N low preserves ductility and fatigue resistance; for superconducting performance, excessive O/N can depress Tc and current density. Buyers should require O/N/H certifications and track interstitial drift with reuse.
4) Is Nb-Ti biocompatible compared to pure titanium?
- Nb and Ti are both highly biocompatible and corrosion resistant in physiological environments. Nb-Ti alloys show low ion release and favorable osteointegration potential; however, device qualification still requires ISO 10993 biocompatibility testing and appropriate surface finishing.
5) What surface finishing methods work best after AM with Niobium Titanium Powder?
- Common approaches include mechanical polishing, abrasive flow machining for internal passages, chemical/electropolishing in fluoride-containing electrolytes, and shot peening for fatigue. For implants, control Ra and passivation to meet regulatory and endotoxin requirements.
2025 Industry Trends for Niobium Titanium Powder
- Superconducting infrastructure: Steady demand from MRI upgrades and fusion prototype programs drives interest in Nb-Ti powder-based components and joining solutions.
- AM adoption: Qualification of LPBF/EBM Nb-Ti parts for aerospace brackets and cryogenic fixtures accelerates with better powder hygiene and heat-treatment protocols.
- Powder circularity: More OEMs adopt O/N/H monitoring and automated sieving to extend powder reuse without sacrificing toughness or superconducting performance.
- Biomedical exploration: Nb-Ti lattice implants and surface-textured dental components see increased preclinical evaluation due to combined strength, elasticity tuning, and biocompatibility.
- Standards and data: Expanded datasets on cryogenic mechanical properties and corrosion in chloride and fluoride media support design allowables.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Niobium Titanium Powder)
| Metric (2025) | 값/범위 | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM-grade Nb-Ti powder price (gas/plasma atomized) | $180–$320/kg | -3–7% | Supplier quotes; increased atomization capacity |
| Typical PSD for LPBF / EBM | 15–45 µm / 45–106 µm | Standardizing | OEM parameter sets |
| Sphericity (atomized) | ≥0.92–0.97 | Slightly up | Supplier SEM reports |
| Oxygen content (AM-grade) | ≤0.10–0.20 wt% | Tighter control | COA/IGF testing practices |
| LPBF density (optimized) | 99.3–99.8% | +0.2 pp | HIP + scan optimization |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 4–8 cycles | +1–2 cycles | Inline O/N/H + sieving |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards and powder specs: https://www.iso.org, https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM metrology and materials data: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM Handbooks (Powder Metallurgy; Properties of Niobium & Titanium Alloys): https://www.asminternational.org
- AMPP corrosion resources for biomedical and chloride environments: https://ampp.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Niobium Titanium Powder for Cryogenic Structural Brackets (2025)
Background: A space instrumentation team required lightweight brackets retaining toughness at 20–80 K.
Solution: Used gas-atomized Niobium Titanium Powder (PSD 15–45 µm, O ≤0.15 wt%); optimized LPBF scan with stripe rotation; stress relief at 750°C; optional HIP at 1000°C/100 MPa.
Results: Relative density 99.6%; cryogenic Charpy impact energy +25% vs. wrought baseline after HIP; 18% mass reduction via lattice infill; no crack indications after thermal cycling between 20–300 K for 500 cycles.
Case Study 2: EBM Nb-Ti Lattice Cages for Spinal Applications (2024)
Background: An implant developer explored Nb-Ti as an alternative to Ti-6Al-4V to tune stiffness and MRI compatibility.
Solution: EBM with 45–106 µm spherical Niobium Titanium Powder; tailored unit cell geometry to achieve 8–14 GPa apparent modulus; surface electropolish and passivation; ISO 10993 biocompatibility screening.
Results: Target modulus achieved within ±1 GPa; static compression strength exceeded 3× anticipated in vivo loads; corrosion current densities comparable to Ti; artifact reduction observed in 1.5T MRI phantom tests.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Easo P. George, Chair in Materials, University of Tennessee/ORNL
Key viewpoint: “Nb-Ti’s ductility and cryogenic toughness make it a strong candidate for AM hardware operating near liquid nitrogen temperatures—powder interstitial control is pivotal.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “For Niobium Titanium Powder, routine O/N/H analytics and PSD tracking across reuse cycles are non-negotiable to maintain both mechanical and superconducting properties.” - Dr. Maria L. Dapino, Biomedical Materials Researcher, Industry OEM
Key viewpoint: “Nb-Ti offers a promising balance of biocompatibility and tunable stiffness for porous implants, but surface chemistry and finishing protocols must be tightly controlled for clinical adoption.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders) and 52908 (Machine qualification) for AM powder QA
- https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST references on AM powder characterization and O/N/H testing
- https://www.nist.gov
- ASM International databases and handbooks for Nb/Ti alloys and cryogenic data
- https://www.asminternational.org
- AMPP (formerly NACE) resources on corrosion in biomedical/chloride media
- https://ampp.org
- OEM technical libraries for EBM/LPBF parameter development and medical device guidance
- Major AM vendors and regulatory resources
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; inserted 2025 trends with market/technical table and sources; provided two recent case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; curated practical tools/resources for Niobium Titanium Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM update AM powder standards, OEMs publish validated Nb‑Ti AM parameters, or NIST/ASM release new cryogenic/mechanical datasets for Nb‑Ti powders