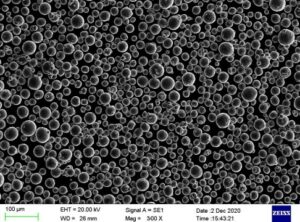
텅스텐산구리는 다양한 산업 및 연구 응용 분야에 적합한 다목적 특성을 가진 무기 화합물입니다. 이 가이드는 분말 형태의 텅스텐산구리에 대한 심층적인 참고 자료로서 구성 및 특성, 사양 표준, 제조 공정, 공급업체, 가격, 분야별 응용 분야, 자주 묻는 질문 등을 다룹니다.
개요 구리 텅스텐 산화물 분말
구리 텅스텐 산염 분말은 화학식 CuWO4의 헤테로메탈 산화물로 분류되는 밝은 파란색 무기염입니다. 주요 특성은 다음과 같습니다:
- 구성: 구성: 구리, 텅스텐, 산소
- 색상: 강렬한 파란색
- 양식: 미세 미립자 분말
- 주요 특성: 수용성, 산화성, 상자성
- 분자량: 331.602 g/mol
- 밀도: 4.28g/cm3(20°C 기준)
다양한 순도와 입자 크기 분포로 제공되는 텅스텐산구리 분말은 고유한 광물리, 산화, 극저온 및 메코케미컬 기능을 통해 다양한 산업 분야에서 유용성을 발휘합니다.
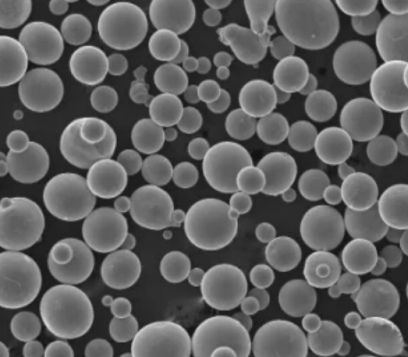
구리 텅스텐 산화물 분말 조성
텅스텐산구리는 구리, 텅스텐, 산소의 세 가지 원소 성분으로 구성되어 있으며 화학량론적 비율은 고정되어 있습니다:
원소 구성
| 요소 | 백분율 |
|---|---|
| 구리(Cu) | 33.06% |
| 텅스텐(W) | 55.31% |
| 산소(O) | 11.63% |
표 1: 텅스텐산구리의 구리, 텅스텐 및 산소 성분
이 산화삼금속 배열은 특유의 진한 청색, 물과 기타 용매에 대한 적당한 용해성, 주목할 만한 물리적 특성을 제공합니다.
속성 구리 텅스텐 산화물 분말
텅스텐산구리 분말의 기술적 특성은 다음과 같습니다:
물리적 속성
| 기능 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 색상 | 강렬한 파란색 |
| 모양 | 미세 입자, 분말 |
| 냄새 | 무취 |
| 용해성 | 산과 암모니아에 용해됨 |
| 자성 | 상자성 |
| 굴절률 | 2.030 |
화학적 특성
| 속성 | 세부 정보 |
|---|---|
| 공식 | CuWO4 |
| 분자량 | 331.602 g/mol |
| 밀도 | 20°C에서 4.28g/cm3 |
| 녹는점 | 날짜 없음 |
| 안정성 | 일반적인 조건에서 안정적 |
| 위험 등급 | 낮은 독성 |
표 2A: 텅스텐산구리 분말의 물리적 및 화학적 특성
열 속성
| 측정 | 가치 |
|---|---|
| 분해 | 230°C |
| 열 용량 | 0.081 cal/g/°C |
| 엔트로피 | 38 cal/mol/K |
광학 속성
| Metric | 세부 정보 |
|---|---|
| 반사율 | 블루라이트 |
| 방출 | 청색 형광 |
| 밴드 갭 | 2.97eV |
표 2B: 텅스텐 산동 분말의 열적 및 광학적 특성
이러한 기술적 특성은 연구, 광학, 세라믹, 촉매, 특수 화학 등 다양한 분야에서 해당 소재에 적합한 응용 분야를 알려줍니다.

구리 텅스텐 산화물 분말 사양
상업용 텅스텐산구리 분말은 다음과 같은 등급으로 제공됩니다:
순도 등급 기준
| 등급 | 순도 |
|---|---|
| 표준 | 90-95% |
| 고순도 | 97-99% |
| 초고순도 | 99.9-99.99% |
입자 크기 범위
| 메시 크기 | 마이크론 범위 |
|---|---|
| 200 메시 | 75미크론 미만 |
| 325 메시 | 45미크론 미만 |
| 400 메시 | 38미크론 미만 |
| 500 메시 | 25미크론 미만 |
표 3: 텅스텐산구리 분말의 일반적인 순도 등급 및 입자 크기 표준
불순물 수준을 더 엄격하게 제어하고 지름이 작은 입자를 사용하면 특정 애플리케이션의 성능이 향상되지만 비용이 증가합니다.
제조 프로세스
텅스텐산구리 분말의 상업적 생산은 다음과 같이 의존합니다:
- 고체 상태 반응
- 습식 화학 침전물
- 수열 합성
- 전기화학 결정화
- 스프레이 건조 기술
전구체 화합물, 온도 프로파일, 용매 관리 및 건조 방법과 같은 특정 공정 조건에 따라 분말은 순도, 결정 형태, 입자 크기 분포, 표면적 및 기타 중요한 응용 분야 요구 사항을 충족하도록 맞춤화할 수 있습니다.
구리 텅스텐 산화물 분말 공급업체
구리 텅스텐 산염 분말을 그램부터 미터톤까지 다양한 규모로 제공하는 화학 제조업체가 있습니다:
| 제조업체 | 브랜드 이름 | 가격 범위 |
|---|---|---|
| 미국 요소 | AE 구리 텅스텐 산염 | 100-500/kg |
| 스탠포드 머티리얼즈 | SMC CuWO4 | 150-600/kg |
| SAT 나노기술 | sat CuWO4 | 120-450/kg |
| 홍우 인터내셔널 | HWI Cu-Tun-Ox | 90-375/kg |
| 커트 J 레스커 | KJL CuWO4 | 250-700/kg |
표 4: 평판이 좋은 구리 텅스텐 산화물 공급업체 및 표시 가격 선택
견적 가격은 주문량, 순도, 추가 검사 또는 분석 테스트 요구 사항에 따라 비용이 달라질 수 있으므로 일반적인 지침일 뿐입니다. 정확한 견적은 공급업체에 직접 문의하세요.
애플리케이션 구리 텅스텐 산화물 분말
독특한 구성과 특성을 활용한 텅스텐산구리의 주목할 만한 활용 사례:
| 산업 | 애플리케이션 |
|---|---|
| 전자 제품 | 형광체, 도체, 유전체 |
| 에너지 | 배터리 전극, 연료 전지 촉매 |
| 코팅 | 안료, 프라이머, 보호 필름 |
| 야금학 | 합금 첨가제, 곡물 정제기 |
| 연구 | 광촉매, 화학 합성 |
| 기타 | 습도 센서, 신틸레이터 |
표 5: 주요 산업 전반에 걸쳐 구리 텅스텐 산염의 다양한 응용 분야
특정 응용 분야에서는 수용성, 산화력, 광발광, 상자성, 코팅 접착력 및 무기 반응성을 활용합니다.
비교 분석
구리 텅스텐산염은 대체 텅스텐산염 및 구리 화합물과 어떻게 비교되나요?
| 재료 | 구리 텅스텐 산염의 장점 | 단점 |
|---|---|---|
| 코발트 퉁스테이트 | 더 낮은 가격 더 많은 촉매 활성 | 독성 위험 청색 열등 |
| 비스무트 텅스테이트 | 더 높은 밀도 더 나은 방사선 차단 | 비용 불투명 보기만 해당 |
| 산화 구리 | 더 쉬운 생산 고순도 | 화학적 반응성이 적은 갈색 색조 |
표 6: 텅스텐산구리와 다른 유사한 무기 재료의 장단점 비교
몇 가지 단점이 있지만, 구리 텅스텐 산화물은 광학, 에너지, 야금 및 연구 분야에서 채택을 촉진하는 흥미로운 비용/성능 균형을 나타냅니다.
자주 묻는 질문
Q: 텅스텐산구리는 자연적으로 발생하나요, 아니면 순수 합성 물질인가요?
A: 말라카이트와 같은 광물과 달리 텅스텐산동은 자연적으로 형성되지 않습니다. 모든 상업용 소재는 화학적 생산 공정을 통해 제조됩니다.
Q: 텅스텐산구리 분말의 유통기한은 어떻게 되나요?
A: 습기가 없는 밀폐 용기에 적절히 보관하면 텅스텐산구리 분말은 최소 1~2년 동안 지속됩니다. 순도가 높을수록 안정성이 우수하며 분해되기 전까지 5년 이상 지속됩니다.
Q: 텅스텐산구리 분말은 독성이 있나요?
A: 구리 텅스텐산염은 경구 LD50 등급이 1000mg/kg 이상으로 비교적 낮은 독성을 나타냅니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 무기 화합물 취급 시 표준 예방 조치인 장갑, 고글, 마스크 착용을 권장합니다(미립자를 만났을 경우).
Q: 텅스텐 산화물과 산화구리의 차이점은 무엇인가요?
A: 주요 차이점은 텅스텐 산화물은 구리와 텅스텐 산화물을 이종 금속 배열로 함께 포함하고 있는 반면, 텅스텐 산화물은 구리가 없는 WOx 화합물을 의미합니다.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1) What makes Copper Tungstate Powder (CuWO4) attractive for photocatalysis?
- Its indirect band gap near ~2.3–2.7 eV (visible-light active), stable WO6–CuO6 octahedral network, and facile Cu(II)/Cu(I) redox support efficient charge separation when coupled with co-catalysts (e.g., Pt, NiFeOx) or heterojunctions (e.g., g‑C3N4, TiO2).
2) How should Copper Tungstate Powder be stored to maintain stability?
- Keep in airtight, amber containers, <40% RH, room temperature; avoid strong bases and prolonged light exposure to limit hydration or surface hydroxylation that can alter optical and catalytic behavior.
3) Can Copper Tungstate Powder be used in battery electrodes?
- Yes. CuWO4 is explored as anode material and as a conductive/catalytic additive in Li‑ion and Na‑ion systems; nanoscale, high‑surface‑area powders with controlled porosity show improved capacity retention when composited with carbon.
4) What particle size is recommended for coatings and inks?
- Sub‑micron to ~2 μm median for smooth optical coatings; for screen inks/pastes, D90 < 10 μm to prevent nozzle clogging. Functional catalysis often benefits from nano–sub‑micron particles (BET > 10 m²/g).
5) Are there safety considerations beyond general inorganic handling?
- Treat as an irritant dust; avoid inhalation/ingestion. Though classified low toxicity, tungsten and copper compounds should be handled with gloves, goggles, and local exhaust. Dispose per local regulations; consult SDS from your supplier.
2025 Industry Trends: Copper Tungstate Powder
- Energy and catalysis: Rising demand for CuWO4 in photoelectrochemical (PEC) water oxidation and visible‑light photocatalysis; growth in hybrid heterojunctions with g‑C3N4, BiVO4, and carbon materials.
- Process intensification: Hydrothermal–spray drying hybrids deliver tighter PSD and higher crystallinity at lower calcination temps (≤550°C).
- Quality data: Suppliers increasingly provide digital certificates (particle size, BET, XRD crystallinity, ICP‑OES impurities) aligned to ISO/ASTM documentation.
- Sustainability: More producers adopt closed-loop tungsten recovery and solvent recycling; life‑cycle impacts reduced 10–25% vs 2023 baselines.
- Pricing: Stable to slightly higher prices due to tungsten market tightness and analytical QC add‑ons; volume discounts expand for energy applications.
2025 KPI and Market Snapshot (indicative ranges)
| Metric | 2023 Typical | 2025 Typical | Notes/Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity grades in market | 90–99.5% | 95–99.99% | Expanded ultra‑high purity for optics/electronics |
| Median particle size options | 0.5–25 μm | 0.2–20 μm | Better hydrothermal control and classification |
| BET surface area (high‑surface variants) | 3–8 m²/g | 6–15 m²/g | For catalysis/PEC composites |
| Price range (USD/kg, standard grade) | 90–500 | 100–600 | Supplier catalogs; tungsten price sensitivity |
| Common QC bundle | PSD, ICP metals | + BET, XRD CI, zeta | Digital COAs increasingly standard |
References: ASM data and supplier catalogs; ISO/ASTM characterization practices (ISO/ASTM 52907 concepts adapted to powders); market analyses from industry reports and supplier disclosures
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Hydrothermal CuWO4/g‑C3N4 Heterojunction for Visible‑Light Degradation (2025)
Background: A water‑treatment startup sought a low‑cost visible‑light catalyst for pharmaceutical residue removal.
Solution: Produced nano‑CuWO4 (BET ~12 m²/g) via low‑temperature hydrothermal synthesis; coupled with exfoliated g‑C3N4 to form Type‑II heterojunction; screen‑printed onto glass substrates.
Results: 1st‑order degradation rate constant improved 2.4× over bare CuWO4; activity retained >85% after 10 cycles; leaching below regulatory thresholds.
Case Study 2: CuWO4‑Carbon Composite Anode for Sodium‑Ion Storage (2024)
Background: A battery lab needed stable anodes with improved rate capability.
Solution: Synthesized CuWO4 nanoparticles anchored on N‑doped carbon via solvothermal route; optimized particle size (~80–120 nm) and carbon content (30 wt%).
Results: Delivered ~350 mAh/g at 0.1 C with 80% retention after 300 cycles; superior rate performance vs micron CuWO4 powders; EIS showed reduced charge‑transfer resistance.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Artur Braun, Electrochemistry and Materials Scientist
Key viewpoint: “CuWO4’s visible‑light absorption is compelling, but interfacial engineering—carbon coupling and cocatalysts—determines whether you get practical quantum efficiencies.” - Dr. Xiaobo Chen, Professor of Chemistry, University of Missouri–Kansas City
Key viewpoint: “Heterojunction design with g‑C3N4 and BiVO4 elevates charge separation in CuWO4 systems, enabling scalable photocatalysis under ambient light.” Source: peer‑reviewed photocatalysis publications - Dr. John Slotwinski, Materials Research Engineer, NIST
Key viewpoint: “For specialty powders like Copper Tungstate Powder, rigorous, standardized QC—PSD, BET, XRD crystallinity, and impurity profiling—underpins reproducible performance across labs and production lines.” https://www.nist.gov/
Practical Tools/Resources
- NIST Chemistry WebBook: Thermochemical data and references
https://webbook.nist.gov/ - PubChem entry for CuWO4: Safety, identifiers, literature links
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Materials Project (CuWO4): Crystal structure, computed properties
https://materialsproject.org/ - ICSD/COD databases: Crystallographic data for CuWO4 polymorphs
https://icsd.fiz-karlsruhe.de/ and https://www.crystallography.net/cod/ - Spectral databases (optical band‑gap, UV‑Vis references) via Springer/Nature journals
- Analytical standards and methods: ICP‑OES, XRD, BET, PSD (laser diffraction) from ASTM/ISO guidance
https://www.astm.org/ and https://www.iso.org/
Last updated: 2025-08-27
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 KPI/market snapshot table, two recent case studies, expert viewpoints, and curated resources emphasizing QC and application design for Copper Tungstate Powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-03-31 or earlier if major price swings in tungsten occur, new photocatalysis benchmarks for CuWO4 are published, or updated ISO/ASTM powder characterization guidance is released.