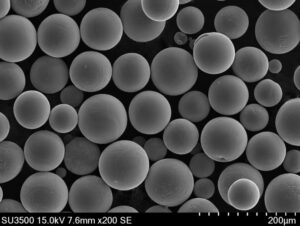
タングステン金属粉 は、様々な工業用途の原料として使用されるタングステンの微粒子です。高密度、高強度、耐食性、高融点のようなそのユニークな特性は、それが重要なエンジニアリング材料になります。
組成と製造
| パラメータ | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| 元素組成 | 純タングステン(W)または他の金属との合金 |
| 生産プロセス | タングステン棒からの粉砕またはタングステン酸化物からの還元 |
| 粒子径 | 通常1ミクロンから150ミクロンまで |
| 純度グレード | 純度99%から99.995%のタングステン |
タングステン粉末は、所望の形状と純度を達成するために、水素還元、粉砕、または熱プラズマ球状化のような様々なプロセスによって製造される。
特性と特徴
| プロパティ | 価値 |
|---|---|
| 密度 | 19.3 g/cm3 で、鋼鉄のほぼ2倍 |
| 融点 | 3422 °C、全金属中最高 |
| 強さ | 非常に高い硬度と強度、特に焼結した場合 |
| 導電率 | 低い電気抵抗率、高い熱伝導率 |
| 安定性 | 優れた化学的安定性と耐食性 |

これらのユニークな特性は タングステン金属粉末 から様々な特殊用途まで。
タングステン金属粉末の用途と使用例
| 申し込み | 使用方法 |
|---|---|
| 超硬工具 | 切削工具用コバルトマトリックスに結合 |
| カウンターウェイト | ウエイトやバラストに最適な高密度 |
| 放射線遮蔽 | X線/ガンマ線源からの効果的なシールド |
| サーミオニック・エミッター | 高融点によるフィラメント |
| 3Dプリンティング粉末 | 高強度タングステン部品の印刷用 |
タングステン粉末は、防衛、医療、航空宇宙、その他の産業におけるミッションクリティカルなニーズをサポートしています。
仕様と標準グレード
タングステン粉末は、粒度分布、純度レベル、製造方法等を定義する様々な国際規格の下で利用可能です。いくつかの一般的な仕様が含まれます:
- ASTM B772 – 純タングステン粉末の種類
- ISO 5453 – 化学分析およびサイズ分類
- ICDD 00-001-1202 – 結晶構造リファレンス
サプライヤーと価格
| サプライヤー | kgあたりの価格 |
|---|---|
| 中西部タングステン | $70 – $500 |
| バッファロー・タングステン | $100 – $600 |
| タングステンヘビーパウダー | $150 – $800 |
| 世界のタングステン粉 | $250 – $1500 |
価格は、純度等級、粒子形状/サイズの一貫性、注文量、付加価値加工によって大きく左右される。

長所と短所
| 長所 | 短所 |
|---|---|
| 卓越した硬度と密度 | 代替品に比べて高価 |
| 高温に耐える | 重い –製品に使用すると重量が増す |
| 耐食性、耐摩耗性 | 適切に処理しないと脆くなる |
| 環境的に安定している | 機械加工が難しい形状もある |
| 均一な粒子分布 | 保護雰囲気が必要な場合がある |
よくある質問
タングステン金属粉末は何に使われるのか?
その特殊な特性により、工具、重り、放射線遮蔽、エレクトロニクス、3Dプリンティング、その他の高性能領域で応用されている。
どのような純度グレードがありますか?
一般的な純度の範囲は99%から99.995%である。純度が高いほど価格も高くなります。
典型的な粒子径は?
粒子径は1ミクロンから150ミクロンまで。ご希望のサイズは、適用方法と最終用途の要件によって異なります。
タングステンは環境に有害か?
いいえ、タングステン金属粉末は一般的に無毒で、環境に優しいです。加工によっては有害な化合物を使用する場合があり、注意が必要です。
Additional FAQs: Tungsten Metal Powder
1) What particle morphology is best for different processes?
- Press-and-sinter: irregular/sponge for better green strength. Thermal spray and AM (LPBF): spherical for high flowability and packing. DED/wire-DED: coarser spherical or crushed granules.
2) How do oxygen and carbon impurities affect tungsten metal powder?
- Elevated O and C form WOx and carbides during sintering, increasing brittleness and porosity. For critical applications, target O ≤ 0.05 wt% and C ≤ 0.01 wt% unless intentionally alloyed.
3) Can tungsten metal powder be used in laser powder bed fusion?
- Yes, but it requires preheating and optimized parameters to mitigate cracking due to high stiffness and thermal gradients. Typical LPBF PSD: 15–45 µm spherical, with low O/N and tight PSD.
4) What are common tungsten composites and why use them?
- W-Ni-Fe/W-Ni-Cu heavy alloys for radiation shielding and kinetic energy components; W-Cu for thermal management and EDM electrodes; WC-Co for cutting tools. Composites balance density, ductility, and conductivity.
5) How should tungsten powder be stored and handled safely?
- Keep sealed and dry, under inert gas if possible; use local exhaust ventilation, antistatic grounding, and explosion-rated dust controls. Although tungsten is not highly reactive, fine powders can pose a dust explosion hazard.
2025 Industry Trends: Tungsten Metal Powder
- Semiconductor and medical growth: Demand up for W-Cu heat spreaders and high-density shielding components.
- Advanced manufacturing: More spherical, plasma-atomized W powders available for LPBF/DED; crack-mitigation strategies mature.
- Sustainability: Increased closed-loop recycling and take-back programs for W scrap/powders with certified impurity control.
- Standards tightening: Stricter impurity and PSD specs for AM-grade W and W-heavy alloys; wider adoption of in-line O/N/H analysis.
- Defense/aerospace: Continued shift from lead to tungsten-based shielding/ballast and kinetic components.
2025 Tungsten Powder Market Snapshot (Indicative)
| メートル | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD (Aug) | 備考 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global W powder demand (kt) | ~18.5 | ~19.3 | ~20.1 | Semiconductor + defense |
| Spherical W (15–45 µm) price (USD/kg) | 180–320 | 190–340 | 200–360 | PA/spheroidized, low O/N |
| Irregular W (-325 mesh) price (USD/kg) | 70–140 | 75–150 | 80–160 | Hydrogen-reduced |
| Typical O spec (AM-grade W) | ≤0.06 wt% | ≤0.05 wt% | ≤0.04 wt% | Tighter QC, in-line analyzers |
| AM adoption (W/W-alloys programs) | エマージング | Early pilots | Pilot-to-production | LPBF + DED parameter maturity |
| W-Cu demand growth (YoY) | +6% | +8% | +9–11% | Power electronics, EDM |
Sources:
- USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (Tungsten): https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- ASTM/ISO powder standards: https://www.astm.org, https://www.iso.org
- Supplier technical notes (Global Tungsten & Powders, H.C. Starck Solutions, Plansee) and industry trackers
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Crack-Resistant LPBF of Tungsten for Collimators (2025)
Background: A medical device OEM needed dense, fine-featured W collimators with reduced post-machining.
Solution: Used plasma-atomized W powder (D50 ~28 µm, O=0.035 wt%) with build plate preheat >600°C, beam shaping, and contour-remelting; stress-relief + hot isostatic pressing (HIP).
Results: Relative density 99.5–99.8%, microcrack incidence reduced by 70% vs. baseline; dimensional accuracy ±60 µm on 2 mm walls; machining time cut 25%.
Case Study 2: W-Cu Heat Spreaders via PM Infiltration for SiC Power Modules (2024)
Background: An EV inverter supplier sought CTE-matched plates with high thermal conductivity.
Solution: Sintered porous W skeletons from -325 mesh W, followed by capillary Cu infiltration to 15–30 vol% Cu; final surface lapped.
Results: Thermal conductivity 200–230 W/m·K; CTE 7.5–8.5 ppm/K (25–200°C); warpage <8 µm over 50 mm; yield +10% compared to prior route.
Expert Opinions
- Dr. Dirk N. Schwab, Head of R&D, Plansee High Performance Materials
- “For AM-grade tungsten metal powder, controlling interstitials and applying elevated preheat are decisive to suppress solidification cracking and achieve near-wrought density.”
- Prof. Susanne Wurster, Materials Processing, TU Munich
- “W–Cu and W–Ni–Fe heavy alloys continue to expand as lead replacements. Process route selection—PM infiltration vs. AM—should follow CTE and flatness tolerance needs.”
- Dr. Kevin J. Hemker, Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University
- “Grain boundary engineering and beam shaping are enabling finer W features with improved toughness, opening opportunities in radiation optics and micro heat exchangers.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- ASTM B777 (tungsten heavy alloys), B772 (tungsten powder), B214/B212 (sieve/flow), E1019 (O/N/H): https://www.astm.org
- ISO 4497 (particle size by sieving), ISO 13320 (laser diffraction), ISO 7637-equivalent PM methods: https://www.iso.org
- USGS Tungsten Statistics and Information: https://www.usgs.gov
- OSHA/NIOSH guidance for metal powder handling and combustible dust: https://www.osha.gov, https://www.cdc.gov/niosh
- MatWeb materials database for W and W-composites: https://www.matweb.com
- Senvol Database for AM machine–material compatibility: https://senvol.com
- Supplier technical libraries: Global Tungsten & Powders, H.C. Starck Solutions, Plansee, Midwest Tungsten
Last updated: 2025-08-25
Changelog: Added 5 FAQs; inserted 2025 market snapshot table; provided two recent case studies; included expert opinions; compiled practical tools/resources with standards and datasets
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if USGS data revises demand/pricing >10%, new ASTM/ISO standards for AM-grade tungsten publish, or major LPBF/DED breakthroughs reduce cracking further