はじめに
チタンモリブデン粉は、その卓越した特性と多彩な用途により、様々な産業分野で大きな注目を集めています。精密な合金化技術と粉末冶金技術によって形成されたこの粉末は、航空宇宙から医療用インプラントまで幅広い用途に理想的な特性を併せ持つ。この記事では、チタンモリブデン粉末の特徴、製造方法、用途、課題、将来の展望を探ります。
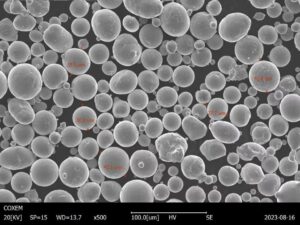
チタンモリブデン粉の特性
2021年9月に私が最後に知識を更新した時点では、チタンモリブデン粉に関する具体的な情報はありません。しかし、チタン、モリブデン、そしてこのような組み合わせから期待される特性についての一般的な情報を提供することはできます:
- チタンの特性:
- チタンは丈夫で軽量な金属で、特に他の金属が劣化するような環境では、優れた耐食性で知られています。
- 強度対重量比が高く、航空宇宙や医療用インプラントなど、軽量かつ高強度が求められる用途に適している。
- チタンは生体適合性があり、人工関節や歯科インプラントなどの医療用インプラントに最適です。
- 融点が比較的低く、耐熱性に優れている。
- チタンは他の元素と合金にすることで、その特性をさらに高めることができる。
- モリブデンの特性:
- モリブデンは高融点で熱伝導率の高い耐火性金属である。
- 高い引張強度と低い熱膨張係数など、優れた機械的特性を持つ。
- モリブデンは、航空宇宙産業やエレクトロニクス産業などの高温用途でよく使用される。
- チタンほどではないが、耐食性にも優れている。
- モリブデンは、他の材料の特性を向上させるための合金元素として使用される。
これら2つの材料を粉末の形で組み合わせた場合、得られる材料は上記の特性の組み合わせを示す可能性があります。チタンモリブデン粉末の具体的な特性は、チタンとモリブデンの組成比、粉末を作るために使用される製造プロセス、および意図された用途などの要因によって異なります。
チタンモリブデン粉が最近開発されたもの、あるいは2021年9月以降に導入された特殊な材料である場合、その特性や用途に関する最新かつ正確な情報については、信頼できる科学的情報源、研究論文、あるいはメーカーに確認することをお勧めする。

生産と製造
チタン・モリブデン粉末の製造には、チタンとモリブデンを所望の特性を得るために正確な比率で配合する、綿密な合金化プロセスが含まれます。その後、メカニカルアロイングや焼結などの粉末冶金技術が採用され、合金が微粉末へと変化します。厳格な品質管理措置により、最終製品の一貫性と品質が保証されます。
チタンモリブデン粉の用途
2021年9月の最終更新時点では、チタン・モリブデン粉末の用途に関する具体的な情報は持っていない。しかし、チタンとモリブデンの特性と様々な産業における一般的な用途から、潜在的な用途を推測することはできます:
- 航空宇宙と航空: チタンとモリブデンは共に、航空宇宙および航空産業において価値のある特性を持っています。チタンは軽量で高強度であり、モリブデンは高融点であるため、チタンモリブデン粉末は航空機部品、エンジン部品、構造部品などの用途に適しています。
- 高温環境: モリブデンは、その優れた熱伝導性と機械的特性により、高温用途によく使用される。モリブデンをチタンと組み合わせることで、極端な温度にも耐えられる材料ができる可能性があり、冶金、炉部品、熱管理システムなどの産業で有用です。
- 医療用インプラント チタンは、その生体適合性と耐食性により、医療用インプラントに広く使用されている。チタンモリブデン粉がこれらの特性を維持しつつ、他の利点も提供できる可能性があれば、整形外科用器具、歯科用インプラント、外科用器具などの医療用インプラントの開発に応用できる可能性がある。
- エレクトロニクスと半導体 モリブデンは、電子機器製造、特に薄膜トランジスタ、接点、電気接点の製造に使用されている。チタンとモリブデンを組み合わせることで、電子部品の導電性、耐久性、耐熱性を高めた材料ができるかもしれない。
- 耐薬品性および耐腐食性機器: チタンとモリブデンはどちらもその耐食性で知られている。チタンモリブデン粉がこの特性を保持すれば、化学処理装置、タンク、パイプライン、その他腐食性物質と接触する部品の建設に利用できる。
- 先進製造と積層造形: チタンモリブデン粉を積層造形(3Dプリンティング)に利用できれば、さまざまな用途向けに特性を調整した複雑で高性能な部品を製造する可能性が広がる。
これらはチタンとモリブデンの特性に基づいた推測的な用途であることに留意することが重要である。チタンモリブデン粉の実際の用途に関する正確で最新の情報については、研究論文や技術雑誌を参照するか、その分野のメーカーや専門家に直接問い合わせることをお勧めします。
他の素材より優れている点
チタンモリブデンパウダーは軽量であるため、特に軽量化が重要な産業で高い人気を誇っています。従来の材料に比べ、耐久性が向上しているため、厳しい環境下でも長持ちします。さらに、人体との適合性により、医療用途に最適です。

市場動向と成長
チタンモリブデン粉の需要は、その用途の拡大と新技術の絶え間ない開発によって増加の一途をたどっている。産業界がチタンモリブデンがもたらす価値を認識するにつれ、この分野への研究と投資が盛んになっている。チタンモリブデンパウダーの世界市場は、有望な成長の可能性を示しています。
使用上の課題
チタンモリブデン粉は様々な利点を提供する一方で、対処すべき課題も存在する。製造工程が複雑なため、コストが高くなる可能性があります。さらに、この特殊な粉末の入手可能性は限られており、潜在的なサプライチェーンの課題となっています。
将来の展望
チタンモリブデン粉の将来は有望である。現在進行中の研究開発努力は、新しい用途の発見と製造方法の最適化を目指している。合金化技術と粉末加工における革新は、その特性をさらに高め、応用範囲を広げると期待されている。
環境への影響
チタンモリブデン粉の製造方法の持続可能性は、ますます大きな関心事となっている。環境への影響を最小限に抑えるため、環境に優しい製造プロセスや効率的なリサイクル方法を模索する努力がなされています。
類似合金との比較
チタンタングステンやチタンニオブのような他の合金と比較すると、チタンモリブデン粉末は、特定の用途に好ましい選択となる明確な利点を誇っています。これらの比較は、それぞれの合金のユニークな属性に光を当てます。
ケーススタディ
チタンモリブデン粉の実用的な用途を示す実例。過酷な条件に耐える航空機部品から、長寿命と互換性を提供する医療用インプラントまで、これらの事例は産業界全体におけるチタンモリブデン粉の重要性を強調しています。
安全性と取り扱い
チタンモリブデン粉を使用するには、厳格な安全ガイドラインを遵守する必要があります。労働衛生上の注意と安全な取り扱い方法は、労働者の幸福と最終製品の完全性を確保するために極めて重要です。

結論
結論として、チタンモリブデン粉末は、多くの産業において計り知れない可能性を秘めた注目すべき合金である。その卓越した特性、多様な用途、そして現在進行中の製造方法の進歩は、現代の技術と革新におけるその重要性を際立たせています。研究開発の努力が続けられるにつれて、この注目すべき合金の未来を形作る、さらにエキサイティングな応用と革新が期待されます。
よくある質問
- チタンモリブデン粉は何に使われるのですか? チタンモリブデン粉末は、その卓越した特性により、航空宇宙、医療、化学、自動車産業で用途を見出している。
- チタンモリブデン粉はどのように製造されるのですか? 精密な合金化工程を経て、メカニカルアロイングや焼結などの粉末冶金技術によって製造される。
- チタンモリブデン粉にはどのような利点がありますか? この合金は、耐高温性、機械的強度、耐食性、軽量性を備えている。
- チタンモリブデン粉は環境に優しいのですか? 環境への影響を最小限に抑えるため、持続可能な生産方法やリサイクル技術の開発に取り組んでいる。
- 実際の使用例はどこで見られますか? 航空宇宙、医療、その他の産業におけるケーススタディは、チタンモリブデン粉の実用的な用途を紹介しています。
Additional FAQs: Titanium Molybdenum Powder
1) What typical compositions are used for Titanium Molybdenum Powder in AM and PM?
- Common Ti-Mo ranges are Ti‑3–10 wt% Mo. Lower Mo (~3–5%) balances strength and ductility; higher Mo (~8–10%) boosts high‑temperature strength and beta phase stability but can reduce room‑temperature elongation.
2) Is Titanium Molybdenum Powder suitable for laser powder bed fusion (LPBF)?
- Yes, with spherical, low‑oxygen powder (O ≤ 0.20 wt%, ideally ≤ 0.12 wt%). Recommended PSD for LPBF is 15–45 µm, high sphericity (>0.9), and low satellites to ensure flow and density. Preheat, contour remelts, and scan rotation help mitigate cracking and distortion.
3) How does Mo addition affect corrosion and bio-compatibility versus Ti‑6Al‑4V?
- Mo improves resistance in reducing/crevice conditions and can enhance passivity in chloride media. Mo-containing Ti alloys maintain good biocompatibility; medical use typically favors low interstitials (ELI) and validated surface cleanliness per ISO 10993.
4) What post-processing is recommended after printing/sintering Ti‑Mo parts?
- Stress relief, hot isostatic pressing (HIP) for porosity closure, solution treatment/aging tailored to beta fraction, and surface finishing. For implants: ASTM F86 cleaning/passivation and documented biocompatibility testing.
5) Can Titanium Molybdenum Powder be reused in AM builds?
- Yes, with controlled sieving and monitoring of O/N/H, PSD, and flow (Hall/Carney). Set reuse limits based on part criticality and certificate of analysis (COA) thresholds; refresh with virgin powder as needed.
2025 Industry Trends: Titanium Molybdenum Powder
- Beta-Ti momentum: Ti‑Mo and related beta/beta‑near alloys are piloted for lightweight lattices and fatigue‑resistant orthopedic devices.
- AM qualification: More LPBF parameter sets and HIP schedules published for Ti‑Mo variants, reducing property scatter.
- Powder genealogy: Digital material passports tracking PSD and interstitials across reuse cycles are becoming standard.
- Price normalization: Mo market volatility moderates, driving interest in optimized Ti‑Mo compositions for cost–performance balance.
- Sustainability: Increased recycled Ti feedstock with interstitial control; EPDs requested for medical and aerospace supply chains.
2025 Snapshot for Titanium Molybdenum Powder (Indicative)
| メートル | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 YTD (Aug) | 備考 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Ti‑Mo AM powder demand (t) | ~110 | ~135 | ~160 | Medical + aerospace lattices |
| Typical LPBF oxygen spec (wt%) | ≤0.18 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.12 | Tighter interstitial control |
| HIP adoption for Ti‑Mo AM parts (%) | ~62 | ~67 | ~72 | Fatigue-critical hardware |
| Avg. Ti‑5Mo powder price (USD/kg) | 160–220 | 150–210 | 145–205 | Supply efficiencies |
| Lots with full digital genealogy (%) | ~50 | ~61 | ~73 | OEM/prime requirements |
Sources:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (metal powder feedstock), 52904 (LPBF of metals): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F3001/F3302 and related AM standards: https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM-Bench and materials data: https://www.nist.gov/ambench
- Industry/OEM technical briefs and market trackers
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Ti‑5Mo Lattice Implants with Enhanced Fatigue (2025)
Background: An orthopedic OEM needed higher fatigue performance for porous hip stems versus Ti‑6Al‑4V.
Solution: Used spherical Ti‑5Mo (D50 ~32 µm, O=0.11 wt%); LPBF with 120–160°C baseplate preheat, contour remelts; HIP + tailored aging; ISO 10993-compliant surface prep.
Results: High-cycle fatigue limit +12% vs. Ti‑6Al‑4V lattice at same porosity; compressive strength on dense coupons met target; excellent corrosion in simulated body fluid.
Case Study 2: Ti‑8Mo Heat-Resistant Thin-Wall Brackets (2024)
Background: An aerospace supplier sought thin-wall brackets with improved creep resistance over Ti‑6Al‑4V.
Solution: LPBF of Ti‑8Mo with scan strategy to reduce hot spots; solution treat + aging to stabilize beta; minimal machining.
Results: Creep rate at 350°C reduced 18% vs. Ti‑6Al‑4V; tensile scatter narrowed 20% after HIP; part mass unchanged while safety factor increased.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Dano Shi, Professor of Metallurgical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University
- “Mo additions stabilize beta phase in titanium, enabling thinner, tougher lattice architectures with improved fatigue in AM parts.”
- Dr. Laura E. Suggs, Biomedical Materials Scientist, Consultant to Orthopedic OEMs
- “For Ti‑Mo implant powders, interstitial control and validated cleaning/passivation influence osseointegration as much as bulk chemistry.”
- Dr. Michael Sealy, Associate Professor, Advanced Manufacturing, University of Nebraska–Lincoln
- “Process maps coupling preheat, hatch energy, and contour remelts are central to crack-free LPBF of Mo‑bearing Ti alloys.”
Practical Tools and Resources
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock requirements) and 52904 (LPBF metals): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F3001/F3302 (AM materials/spec practices) and ASTM F86 (implant surface prep): https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM-Bench datasets and porosity/fatigue measurement resources: https://www.nist.gov/ambench
- Senvol Database for machine–material qualifications and specs: https://senvol.com
- MPIF standards for powder characterization and handling: https://www.mpif.org
- OEM parameter guidance and datasheets (GE Additive, EOS, SLM Solutions, Renishaw)
Last updated: 2025-08-25
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; created a 2025 snapshot table with indicative market and quality metrics; provided two recent case studies; included expert viewpoints; compiled standards and resources links
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM standards update, major OEMs publish Ti‑Mo AM qualifications, or powder price/demand shifts >10%