はじめに
チタン合金は、その優れた特性と幅広い用途により、様々な産業に革命をもたらしてきました。その中でも チタニオTC4 チタニオTC4は、最もポピュラーで汎用性の高いチタン合金の一つとして際立っている。この記事では、チタニオTC4の驚くべき特性、用途、そして課題を探求し、様々な分野で好まれる材料となった理由を明らかにします。
チタニオTC4とは?
チタニオTC4は、優れた強度、低密度、優れた耐食性で知られるチタン合金です。チタン(Ti)、アルミニウム(Al)、バナジウム(V)から成るTi-6Al-4V合金ファミリーに属します。これらの元素の組み合わせにより、顕著な機械的特性と生体適合性を持つ材料となり、多くの重要な用途に適しています。

チタニオTC4の特性
高い強度重量比
チタニオTC4の最も大きな利点の一つは、その驚くべき強度対重量比である。多くの鋼に匹敵する引張強度を誇りながら、重量は約半分であるため、航空宇宙、スポーツ用品など、重量が重視される用途に最適です。
耐食性
チタニオTC4は、特に他の材料が故障するような過酷な環境において、卓越した耐食性を示します。この特性は、海洋工学、化学処理、医療用インプラントなどの用途に不可欠であり、長寿命と信頼性を保証します。
生体適合性
チタニオTC4は生体適合性に優れているため、人工関節や歯科インプラントなどの医療用インプラントに最適です。チタニオTC4は、アレルギー反応や副作用のリスクを最小限に抑え、人体内での使用に成功した実績があります。
熱安定性
チタニオTC4は高温下でも強度と機械的特性を維持するため、航空機エンジンやガスタービンなど、高熱にさらされることが避けられない用途に適しています。
チタニオTC4の用途
航空宇宙産業
航空宇宙産業では、高強度、軽量、耐疲労性を兼ね備えたチタニオTC4が重用されている。航空機部品、エンジン部品、構造要素に使用され、性能と燃費の向上に貢献している。
医療用インプラント
先に述べたように、チタニオTC4は生体適合性に優れているため、医療用インプラントに最適である。整形外科用インプラント、歯科用器具、補綴物などに使用され、ヘルスケア分野を一変させた。
スポーツ用品
スポーツ用品業界では、チタニオTC4は軽量かつ耐久性のある用具の製造に利用されています。ゴルフクラブから自転車フレームに至るまで、この合金の特性はアスリートのパフォーマンス向上に役立っています。
海洋工学
チタニオTC4は耐食性、耐海水性に優れ、海洋用途に理想的な材料です。船舶部品、海洋構造物、水中装置などによく使用されています。
自動車部門
自動車産業は、チタニオTC4’の軽量特性の恩恵を受け、燃費向上と排出ガス削減に貢献しています。排気システム、サスペンション部品、エンジン部品などに使用されています。

チタニオTC4の加工と製造
溶解と合金化
チタニオTC4の製造には、チタン、アルミニウム、バナジウムを一緒に溶かし、均質な合金を形成することが必要である。合金元素の正確な制御は、望ましい材料特性を達成するために非常に重要です。
成形技術
チタニオTC4を様々な製品に成形するために、鍛造や押出などの様々な成形技術が採用されている。これらの工程は、材料の機械的特性を決定する上で重要な役割を果たします。
熱処理
チタニオTC4は、その機械的特性を最適化するために、一般的に熱処理が施されます。この熱処理は、合金の強度と延性を向上させ、特定の用途要件を満たすことを保証します。
機械加工と仕上げ
チタニオTC4は熱伝導率が低く、加工硬化しやすいため、加工には特別な配慮が必要です。精密で滑らかな表面を実現するために、高度な加工技術と仕上げ工程が用いられます。
チタニオTC4の他の素材に対する優位性
チタン合金とスチール合金の比較
TC4のようなチタン合金を従来のスチール合金と比較すると、強度を損なうことなく重量を減らすという点で大きな利点があることがわかります。この利点により、チタン合金は航空宇宙や自動車用途で好まれる選択肢となっています。
ティタニオTC4 vs. ティタニオTC1
チタニオTC4は、従来のTC1に比べて靭性と溶接性が向上しています。この改良により、様々な産業分野での適用が拡大しました。
アルミニウム合金との比較
チタニオTC4は、強度と耐食性の点でアルミニウム合金を凌駕しており、軽量性と耐久性が重要な要素となる用途に適した選択肢となっている。
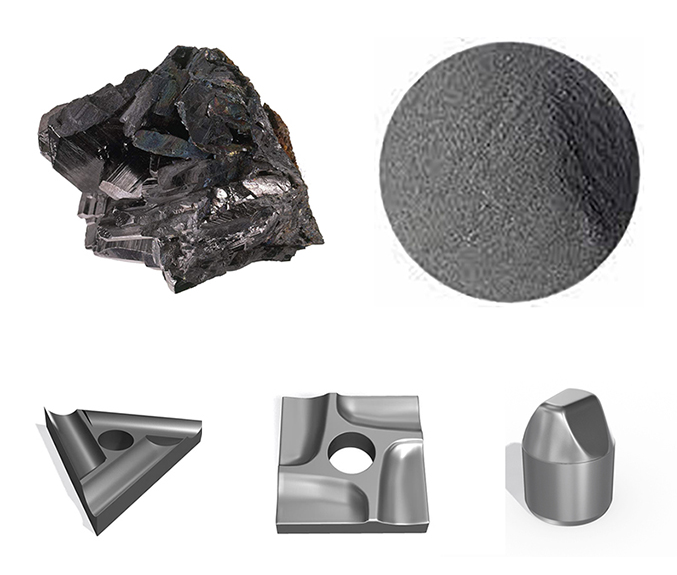

チタニオTC4の課題と限界
コスト
チタニオTC4を含むチタン合金は、他の材料と比較して高価であるため、コストに敏感な産業での採用に影響を与える可能性があります。
複雑な製造
チタニオTC4の製造と加工には、特殊な設備と専門知識が必要であり、製造に複雑さを加えている。
ギャリング
チタニオTC4を使用した特定の用途では、金属同士の接触における摩耗の一形態であるギャリングが発生する可能性があります。この問題を軽減するには、適切な潤滑と表面処理が必要です。
溶接の難しさ
チタン合金は、その困難な溶接性で知られており、チタニオTC4も例外ではありません。チタニオTC4部品の溶接継手の完全性を確保するためには、熟練した溶接工と正確な溶接技術が必要です。
将来の展望とイノベーション
技術の進歩と材料科学の研究が進むにつれて、チタニオTC4の生産と加工における更なる革新が期待できる。研究者たちは、チタニオTC4の特性を向上させ、コストを削減するための新しい合金元素や加工技術を探求しており、より幅広い産業への利用を可能にしています。さらに、チタニオTC4を用いた3Dプリンティングのような付加製造の進歩は、材料の無駄を最小限に抑えながら複雑な部品を製造する有望な可能性を秘めている。
環境への影響と持続可能性
チタニオTC4’の持続可能性は、その長寿命とリサイクル性にあります。耐食性に優れているため、部品の寿命が長く、頻繁な交換の必要性を減らすことができます。さらに、TC4を含むチタン合金はリサイクル可能であるため、新たな原材料の需要を減らし、環境への影響を最小限に抑えることができます。様々な産業において、環境に優しく持続可能な材料が注目されており、チタニオTC4への関心と採用がさらに進むと予想される。
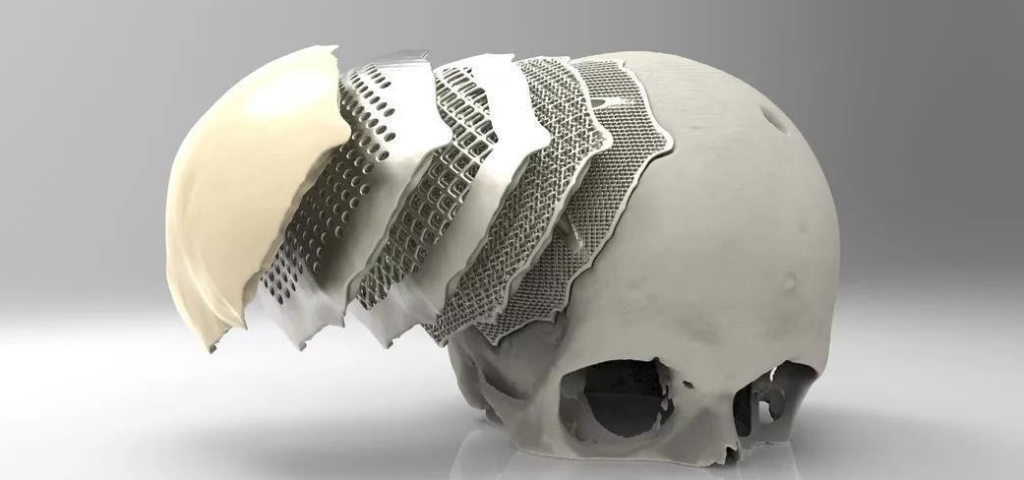
結論
チタニオTC4は、その卓越した特性と汎用性により、多くの産業を変革してきた注目すべきチタン合金です。航空宇宙から医療用インプラント、海洋工学からスポーツ用品に至るまで、この合金は要求の厳しい用途においてその価値を証明してきました。その高い強度対重量比、耐食性、生体適合性、熱安定性は、様々な重要部品にとって魅力的な選択肢となっている。コストや複雑な製造方法といった課題が存在する一方で、現在進行中の研究と技術革新は、チタニオTC4の明るい未来を約束している。
よくある質問
1.チタニオTC4は鉄よりも強いのか?
そう、チタニオTC4は、多くのスチール合金に匹敵する強度を示しながら、重量は約半分であり、優れた強度対重量比を実現している。
2.チタニオTC4の主な用途は?
チタニオTC4は、航空宇宙産業、医療用インプラント、スポーツ用品、海洋工学、自動車分野などで使用されている。
3.チタニオTC4は他のチタン合金と比較してどうですか?
チタニオTC4は、チタニオTC1のような以前のバージョンと比較して、靭性と溶接性が改善されています。また、強度と耐食性の面でもアルミニウム合金を凌駕しています。
4.Titanio TC4を使う上での課題はありますか?
課題としては、比較的高価であること、製造上の要件が複雑であること、用途によってはカジリが発生すること、溶接が難しいことなどが挙げられる。
5.チタニオTC4は環境的に持続可能ですか?
チタニオTC4は長寿命でリサイクル可能なため、環境負荷の低減を重視する産業にとって魅力的な選択肢となっている。
Additional FAQs on Titanio TC4
1) Can Titanio TC4 be 3D-printed for end-use parts?
Yes. Ti-6Al-4V (Titanio TC4) is the most widely used titanium powder in metal additive manufacturing (LPBF/SLM, EBM, DED). It achieves 94–99.5% relative density with proper process parameters and post-heat treatment, suitable for aerospace brackets, medical implants, and heat-exchangers.
2) What are optimal heat treatments for 3D-printed Titanio TC4?
Typical sequences include stress-relief (650–750°C, 1–3 h, Ar/vacuum), hot isostatic pressing (HIP: ~920–930°C, 100–120 MPa, 2–4 h), and aging as needed. HIP closes internal porosity and improves fatigue life significantly.
3) How does surface finish impact fatigue in Titanio TC4?
Surface roughness strongly affects high-cycle fatigue. Shot peening, micro-blasting, chemical milling, electropolishing, and laser polishing can boost fatigue strength by 20–60% versus as-printed or as-machined surfaces.
4) Is Titanio TC4 suitable for chloride-rich marine environments?
Yes. The passive TiO2 film provides excellent resistance to seawater and chlorides. Crevice corrosion risk increases in hot, stagnant chloride solutions; use tight crevice design, cathodic protection, or coatings where applicable.
5) What certifications govern Titanio TC4 for critical applications?
Common references include ASTM B348 (bars), ASTM F136/F1472 (medical), AMS 4928/4911 (aerospace), and ISO 5832-3 (implants). For AM powders/parts, see ASTM F2924/F3001 and AMS 7015/7016 for process and quality controls.
2025 Industry Trends for Titanio TC4
- Additive manufacturing maturation: Widespread adoption of LPBF/HIP workflows for flight hardware and patient-specific implants; expanded use of EBM for thick sections with lower residual stress.
- Powder sustainability: Closed-loop powder recycling and traceability systems reduce buy-to-fly ratios and material cost volatility.
- Cost-down via near-net-shape: Increased uptake of additive, forging + machining hybrids, and DED repair of high-value components.
- Weldability improvements: Narrow-gap GTAW with trailing shields, laser welding with active gas control, and friction stir variants reduce defect rates.
- Biomedical surface engineering: Nano-textured and bioactive coatings (e.g., CaP, TiO2 nanotubes) to accelerate osseointegration while controlling ion release.
- Supply-chain resilience: More regional melt and powder atomization capacity to manage aerospace/defense demand.
| Metric (2025) | Typical Range/Value | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|
| LPBF build rate for Ti-6Al-4V | 10–60 cm³/h per laser | New 1–4 kW multi-laser systems; see OEM specs (EOS, SLM Solutions, Trumpf) |
| As-built LPBF UTS (Ti-6Al-4V) | 900–1100 MPa | Depends on scan strategy; post-HIP ~930–1000 MPa UTS with higher ductility |
| High-cycle fatigue (HIP + polished) | 400–600 MPa at 10⁷ cycles | Literature averages; geometry/surface dependent |
| Powder reuse cycles (qualified) | 5–15 cycles | With oxygen control <0.15 wt% and sieving; see ASTM F2924 guidance |
| Aerospace Ti price trend YoY | +3–7% | Driven by demand and sponge supply; see USGS, market reports |
| Buy-to-fly ratio (AM vs. subtractive) | 1.1–1.5 vs. 8–12 | AM significantly reduces scrap in Ti components |
Authoritative data sources:
- ASTM International standards: https://www.astm.org
- SAE/AMS specs: https://saemobilus.sae.org
- USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (Titanium & Titanium Dioxide): https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- FDA device database (implants): https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Topology-Optimized LPBF Ti-6Al-4V Bracket for Regional Jet (2025)
Background: An aerospace supplier sought 20–30% mass reduction for a load-bearing systems bracket with tight fatigue requirements.
Solution: Designed a topology-optimized lattice–solid hybrid in Titanio TC4, printed via LPBF on a 1 kW multi-laser system; applied stress relief + HIP; surface finished critical fillets to Ra < 1.0 µm.
Results: 28% weight reduction, 35% increase in fatigue life at 10⁶ cycles versus legacy machined plate; buy-to-fly dropped from ~9 to 1.3. Component passed qualification per AMS 7016 and airline DOA procedures. Reference: OEM technical paper and internal qualification report (2025).
Case Study 2: Patient-Specific Acetabular Cup with Porous Ti-6Al-4V (2024)
Background: Hospital network needed improved osseointegration and reduced revision rates for complex hip cases.
Solution: EBM-printed Titanio TC4 cups with 60–70% porous trabecular structures; surface cleaned and sterilized per ISO 13485; validated per ASTM F3001.
Results: Early clinical follow-up at 12 months showed improved primary stability and reduced migration; push-out tests revealed >30% higher fixation strength vs. machined-and-coated cups. Reference: Multicenter pilot study preprint and device manufacturer data (2024).
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Michael Sealy, Director, Nebraska Engineering Additive Manufacturing Lab
Key viewpoint: “For Titanio TC4, HIP plus targeted surface conditioning is now the baseline for flight and implant-grade fatigue performance. The focus in 2025 is on repeatable in-situ monitoring tied to AMS 7016 acceptance.” - Dr. Lluís Llanes, Professor of Materials Science, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC)
Key viewpoint: “Galling and fretting remain practical concerns for Ti-6Al-4V in contact interfaces. Solid lubricants and textured surfaces can mitigate wear without compromising corrosion resistance.” - Dr. Sarah Boyer, Senior Materials Engineer, FDA CDRH (opinions personal)
Key viewpoint: “Patient-specific AM Ti-6Al-4V devices benefit from robust design controls and powder traceability. Compliance with ASTM F2924/F3001 and ISO 10993 biocompatibility remains essential for submissions.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- Nebraska Engineering: https://engineering.unl.edu
- UPC Materials Science faculty: https://etseib.upc.edu
- FDA CDRH overview: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices
Practical Tools and Resources
- Process parameters databases:
- Senvol Database for AM machines/materials: https://senvol.com/database
- Granta EduPack/Ansys Materials: https://www.ansys.com/products/materials
- Standards and qualification:
- ASTM F2924, F3001, F136, F1472: https://www.astm.org
- AMS 7015/7016 (AM material and process): https://saemobilus.sae.org
- Design and simulation for Titanio TC4:
- nTopology (lightweighting/topology optimization): https://ntop.com
- Autodesk Netfabb/ Fusion with Metal AM utilities: https://www.autodesk.com
- Ansys Additive Suite (distortion & support simulation): https://www.ansys.com
- Powder handling and quality:
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock characterization) overview: https://www.iso.org
- Oxygen/nitrogen analyzers (LECO systems): https://www.leco.com
- Post-processing and finishing:
- HIP service providers directories: https://www.bodycote.com
- Electropolishing and chemical milling guides for Ti: https://www.nace.org (AMPP resources)
- Market and pricing intelligence:
- USGS titanium summaries: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- IEA materials for clean energy tech (context): https://www.iea.org
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 new FAQs, 2025 trend table with metrics, two recent case studies, expert opinions with sources, and a tools/resources list focused on Titanio TC4 and 3D printing processes.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ASTM/AMS standards are revised, new OEM parameter sets are released, or significant price/supply changes occur in titanium sponge/powder markets.

