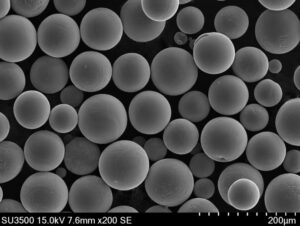
タングステン酸銅は、様々な産業および研究用途に適した汎用性の高い特性を持つ無機化合物です。本ガイドは、粉末状のタングステン酸銅に関する詳細なリファレンスとして役立ちます。組成と特性、規格基準、製造工程、サプライヤー、価格、各分野での用途、FAQなどを網羅しています。
概要 タングステン酸銅粉
タングステン酸銅粉は、化学式CuWO4で表される異種金属酸化物に分類される鮮やかな青色の無機塩です。主な特性は以下の通り:
- 組成銅、タングステン、酸素
- カラー:インテンス・ブルー
- 形状微粒子パウダー
- 主な特徴水溶性、酸化性、常磁性
- 分子量:331.602 g/mol
- 密度 4.28 g/cm3 at 20°C
様々な純度と粒度分布で提供されるタングステン酸銅パウダーは、ユニークな光物理学的、酸化的、低温学的、およびメカ化学的能力を発揮し、様々な産業で有用性を発揮します。
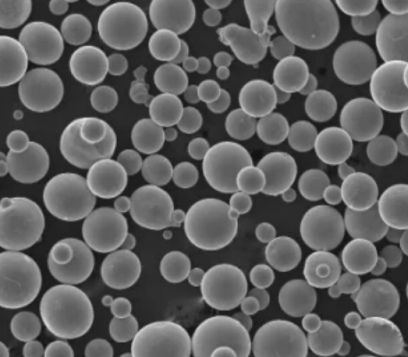
タングステン酸銅粉の組成
タングステン酸銅は、銅、タングステン、酸素の3つの元素を一定の化学量論比で含んでいます:
元素組成
| エレメント | パーセント |
|---|---|
| 銅(Cu) | 33.06% |
| タングステン(W) | 55.31% |
| 酸素 (O) | 11.63% |
表1: タングステン酸銅中の銅、タングステン、酸素組成
このトリメタルオキシド配列により、特徴的な濃い青色の着色、水やその他の溶媒への適度な溶解性、そして特筆すべき物理的特性が生まれる。
特性 タングステン酸銅粉
タングステン酸銅粉の技術的特徴は以下の通り:
物理的性質
| 特徴 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| カラー | インテンス・ブルー |
| フォーム | 微粒子、パウダー |
| 臭気 | 無臭 |
| 溶解度 | 酸とアンモニアに溶ける |
| 磁気 | パラマグネティック |
| 屈折率 | 2.030 |
化学的性質
| 属性 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| フォーミュラ | CuWO4 |
| 分子量 | 331.602 g/mol |
| 密度 | 4.20℃で28 g/cm3 |
| 融点 | データなし |
| 安定性 | 通常の条件下で安定 |
| ハザードクラス | 低毒性 |
表2A: タングステン酸銅粉の物理的・化学的性質
熱特性
| 測定 | 価値 |
|---|---|
| 分解 | 230°C |
| 熱容量 | 0.081 cal/g/°C |
| エントロピー | 38 cal/mol/K |
光学特性
| メートル | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| 反射率 | ブルーライト |
| エミッション | 青色蛍光 |
| バンドギャップ | 2.97eV |
表2B: タングステン酸銅粉の熱的・光学的特性
これらの技術的特性は、研究、光学、セラミックス、触媒、特殊化学品にまたがる材料の適切な用途を示唆している。
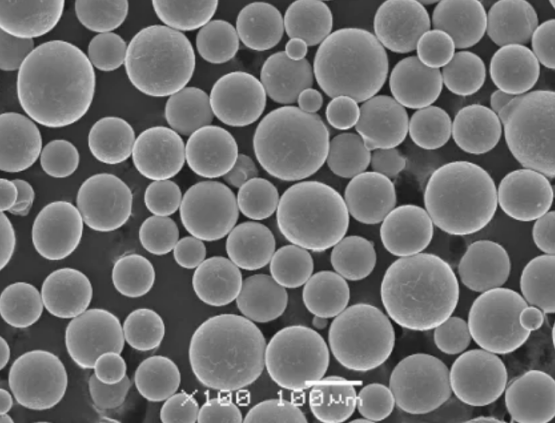

タングステン酸銅粉の仕様
市販のタングステン酸銅粉は、等級別に販売されている:
純度グレード基準
| グレード | 純度 |
|---|---|
| スタンダード | 90-95% |
| 高純度 | 97-99% |
| 超高純度 | 99.9-99.99% |
粒子径範囲
| メッシュサイズ | ミクロンレンジ |
|---|---|
| 200メッシュ | 75ミクロン以下 |
| 325メッシュ | 45ミクロン以下 |
| 400メッシュ | 38ミクロン以下 |
| 500メッシュ | 25ミクロン以下 |
表3: タングステン酸銅粉の代表的な純度等級と粒度規格
不純物レベルをより厳しく管理し、粒子径を小さくすることで、特定の用途の性能は向上するが、コストは増加する。
製造工程
タングステン酸銅粉の商業的生産は、タングステン酸銅に依存している:
- 固体反応
- 湿性化学沈殿物
- 水熱合成
- 電気化学的結晶化
- スプレー乾燥技術
前駆体化合物、温度プロファイル、溶媒管理、乾燥方法などの特定のプロセス条件に基づいて、粉末は純度、結晶形態、粒度分布、表面積、その他の重要な用途要件を満たすように調整することができる。
タングステン酸銅粉のサプライヤー
タングステン酸銅粉をグラムからトンまでのスケールで提供する化学メーカーが存在する:
| メーカー | ブランド名 | 価格帯 |
|---|---|---|
| アメリカの要素 | AEタングステン酸銅 | 100~500ドル/kg |
| スタンフォードマテリアルズ | SMC CuWO4 | 150~600ドル/kg |
| SATナノテクノロジー | CuWO4 | kgあたり120~450ドル |
| ホンウー・インターナショナル | HWI Cu-Tun-Ox | 90~375ドル/kg |
| カート・J・レスカー | KJL CuWO4 | 250~700ドル/kg |
表4: 評判の高いタングステン酸銅のサプライヤーと参考価格を選択する
見積価格は、注文量、純度、追加スクリーニングまたは分析試験の要件によってコストが異なるため、一般的なガイダンスに過ぎません。正確な見積もりについては、直接ベンダーにお問い合わせください。
応用例 タングステン酸銅粉
ユニークな組成と特性を生かしたタングステン酸銅の注目すべき用途:
| 産業 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| エレクトロニクス | 蛍光体、導体、誘電体 |
| エネルギー | 電池電極、燃料電池触媒 |
| コーティング | 顔料、プライマー、保護フィルム |
| 冶金学 | 合金添加剤、穀物精製剤 |
| リサーチ | 光触媒, 化学合成 |
| その他 | 湿度センサ、シンチレータ |
表5: 主要産業におけるタングステン酸銅の多様な用途
具体的な用途としては、水溶性、酸化力、フォトルミネッセンス、常磁性、塗膜密着性、無機反応性などが挙げられる。
比較分析
タングステン酸銅と他のタングステン酸銅化合物との比較は?
| 素材 | タングステン酸銅の利点 | デメリット |
|---|---|---|
| タングステン酸コバルト | 低価格 触媒活性が高い | 毒性有害性 青色劣性 |
| タングステン酸ビスマス | より高い密度 より良い放射線遮断 | 費用 放射線不透過ビューのみ |
| 酸化銅 | 製造が容易 純度が高い | 化学反応性が低い 褐色の色調 |
表6: タングステン酸銅と他の類似無機材料との長所と短所の比較
タングステン酸銅にはいくつかの欠点がありますが、コストと性能のバランスは魅力的です。
よくある質問
Q:タングステン酸銅は天然に存在するのですか、それとも純粋な合成ですか?
A: マラカイトのような鉱物とは異なり、タングステン酸銅は自然には生成しません。市販されているものはすべて化学的な製造工程で作られたものです。
Q: タングステン酸銅粉の保存可能期間はどのくらいですか?
A: タングステン酸銅粉は湿気を避け、気密性の高い容器で適切に保管すれば、最低でも1-2年はもちます。純度の高いグレードほど安定性が高くなります。
Q: タングステン酸銅粉は有毒ですか?
A: タングステン酸銅は、経口 LD50 が 1000mg/kg を超える比較的低い毒性を示します。ただし、無機化合物を取り扱う際の標準的な注意事項(手袋、ゴーグル、微粒子に遭遇した場合のマスクなど)を守ってください。
Q: タングステン酸銅と酸化タングステンの違いは何ですか?
A:重要な違いは、銅タングステートは銅とタングステンの酸化物を異種金属配列で一緒に含むのに対し、酸化タングステンは銅を含まないWOx化合物を指すことです。
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1) What makes Copper Tungstate Powder (CuWO4) attractive for photocatalysis?
- Its indirect band gap near ~2.3–2.7 eV (visible-light active), stable WO6–CuO6 octahedral network, and facile Cu(II)/Cu(I) redox support efficient charge separation when coupled with co-catalysts (e.g., Pt, NiFeOx) or heterojunctions (e.g., g‑C3N4, TiO2).
2) How should Copper Tungstate Powder be stored to maintain stability?
- Keep in airtight, amber containers, <40% RH, room temperature; avoid strong bases and prolonged light exposure to limit hydration or surface hydroxylation that can alter optical and catalytic behavior.
3) Can Copper Tungstate Powder be used in battery electrodes?
- Yes. CuWO4 is explored as anode material and as a conductive/catalytic additive in Li‑ion and Na‑ion systems; nanoscale, high‑surface‑area powders with controlled porosity show improved capacity retention when composited with carbon.
4) What particle size is recommended for coatings and inks?
- Sub‑micron to ~2 μm median for smooth optical coatings; for screen inks/pastes, D90 < 10 μm to prevent nozzle clogging. Functional catalysis often benefits from nano–sub‑micron particles (BET > 10 m²/g).
5) Are there safety considerations beyond general inorganic handling?
- Treat as an irritant dust; avoid inhalation/ingestion. Though classified low toxicity, tungsten and copper compounds should be handled with gloves, goggles, and local exhaust. Dispose per local regulations; consult SDS from your supplier.
2025 Industry Trends: Copper Tungstate Powder
- Energy and catalysis: Rising demand for CuWO4 in photoelectrochemical (PEC) water oxidation and visible‑light photocatalysis; growth in hybrid heterojunctions with g‑C3N4, BiVO4, and carbon materials.
- Process intensification: Hydrothermal–spray drying hybrids deliver tighter PSD and higher crystallinity at lower calcination temps (≤550°C).
- Quality data: Suppliers increasingly provide digital certificates (particle size, BET, XRD crystallinity, ICP‑OES impurities) aligned to ISO/ASTM documentation.
- Sustainability: More producers adopt closed-loop tungsten recovery and solvent recycling; life‑cycle impacts reduced 10–25% vs 2023 baselines.
- Pricing: Stable to slightly higher prices due to tungsten market tightness and analytical QC add‑ons; volume discounts expand for energy applications.
2025 KPI and Market Snapshot (indicative ranges)
| メートル | 2023 Typical | 2025 Typical | Notes/Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purity grades in market | 90–99.5% | 95–99.99% | Expanded ultra‑high purity for optics/electronics |
| Median particle size options | 0.5–25 μm | 0.2–20 μm | Better hydrothermal control and classification |
| BET surface area (high‑surface variants) | 3–8 m²/g | 6–15 m²/g | For catalysis/PEC composites |
| Price range (USD/kg, standard grade) | 90–500 | 100–600 | Supplier catalogs; tungsten price sensitivity |
| Common QC bundle | PSD, ICP metals | + BET, XRD CI, zeta | Digital COAs increasingly standard |
References: ASM data and supplier catalogs; ISO/ASTM characterization practices (ISO/ASTM 52907 concepts adapted to powders); market analyses from industry reports and supplier disclosures
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Hydrothermal CuWO4/g‑C3N4 Heterojunction for Visible‑Light Degradation (2025)
Background: A water‑treatment startup sought a low‑cost visible‑light catalyst for pharmaceutical residue removal.
Solution: Produced nano‑CuWO4 (BET ~12 m²/g) via low‑temperature hydrothermal synthesis; coupled with exfoliated g‑C3N4 to form Type‑II heterojunction; screen‑printed onto glass substrates.
Results: 1st‑order degradation rate constant improved 2.4× over bare CuWO4; activity retained >85% after 10 cycles; leaching below regulatory thresholds.
Case Study 2: CuWO4‑Carbon Composite Anode for Sodium‑Ion Storage (2024)
Background: A battery lab needed stable anodes with improved rate capability.
Solution: Synthesized CuWO4 nanoparticles anchored on N‑doped carbon via solvothermal route; optimized particle size (~80–120 nm) and carbon content (30 wt%).
Results: Delivered ~350 mAh/g at 0.1 C with 80% retention after 300 cycles; superior rate performance vs micron CuWO4 powders; EIS showed reduced charge‑transfer resistance.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Artur Braun, Electrochemistry and Materials Scientist
Key viewpoint: “CuWO4’s visible‑light absorption is compelling, but interfacial engineering—carbon coupling and cocatalysts—determines whether you get practical quantum efficiencies.” - Dr. Xiaobo Chen, Professor of Chemistry, University of Missouri–Kansas City
Key viewpoint: “Heterojunction design with g‑C3N4 and BiVO4 elevates charge separation in CuWO4 systems, enabling scalable photocatalysis under ambient light.” Source: peer‑reviewed photocatalysis publications - Dr. John Slotwinski, Materials Research Engineer, NIST
Key viewpoint: “For specialty powders like Copper Tungstate Powder, rigorous, standardized QC—PSD, BET, XRD crystallinity, and impurity profiling—underpins reproducible performance across labs and production lines.” https://www.nist.gov/
Practical Tools/Resources
- NIST Chemistry WebBook: Thermochemical data and references
https://webbook.nist.gov/ - PubChem entry for CuWO4: Safety, identifiers, literature links
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Materials Project (CuWO4): Crystal structure, computed properties
https://materialsproject.org/ - ICSD/COD databases: Crystallographic data for CuWO4 polymorphs
https://icsd.fiz-karlsruhe.de/ and https://www.crystallography.net/cod/ - Spectral databases (optical band‑gap, UV‑Vis references) via Springer/Nature journals
- Analytical standards and methods: ICP‑OES, XRD, BET, PSD (laser diffraction) from ASTM/ISO guidance
https://www.astm.org/ and https://www.iso.org/
Last updated: 2025-08-27
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs, 2025 KPI/market snapshot table, two recent case studies, expert viewpoints, and curated resources emphasizing QC and application design for Copper Tungstate Powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-03-31 or earlier if major price swings in tungsten occur, new photocatalysis benchmarks for CuWO4 are published, or updated ISO/ASTM powder characterization guidance is released.