3Dプリンティングチタン粉末 は、航空宇宙、自動車、医療、その他の高度な用途向けの複雑で耐久性のある部品を3Dプリントするのに理想的な、強力で軽量、耐腐食性の金属です。この記事では、チタン粉末冶金、特性、用途、チタンによる積層造形のサプライヤーについて包括的な概要を提供します。
3dプリンティング・チタン粉末の概要
チタンは、その高い強度対重量比、耐疲労性、耐破壊性、生体適合性により、3Dプリンティングに望ましい材料です。チタンパウダーは、微細な形状や複雑な形状のパーツを粉末床融合プロセスでプリントすることを可能にします。
チタンのグレード AMに一般的に使用されるチタン合金には、Ti-6Al-4V(Ti64)、Ti64 ELI、商業純チタン(CP)グレード2、およびTi 6242が含まれます。
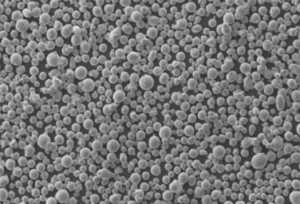
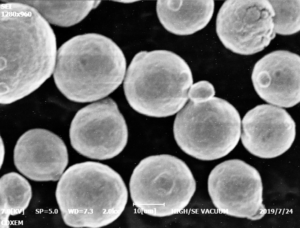
パウダー製造: チタンパウダーはガスアトマイズ法により製造され、溶融チタンを不活性ガスジェットにより微粒化し、粒度分布の狭い球状粒子にします。プラズマ回転電極法(PREP)も使用されます。
パウダーサイズ: 一般的なパウダーサイズは15~45ミクロンです。15ミクロン前後の細かいパウダーは解像度を向上させ、45ミクロンの粗いパウダーは造形速度を向上させます。
流動性と再利用: 球状の形態と制御された粒度分布により、良好な流動性が得られます。チタン粉末は、適切に取り扱えば、通常10~20回まで再利用が可能です。
安全だ: チタン粉末は非常に可燃性であり、その発火性により空気と反応する。不活性雰囲気での適切な取り扱いが重要です。
組成と微細構造
チタン粉末の組成、微細構造、存在する相、気孔率のような欠陥は、印刷部品の最終的な特性を決定する。
元素組成
| 合金 | チタン | アルミニウム | バナジウム | 鉄 | 酸素 | 窒素 | 水素 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V | バランス | 5.5-6.5% | 3.5-4.5% | 0.3% | 0.2% | 0.05 | 0.015 |
| Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo | バランス | 5.5-6.5% | – | – | – | – | – |
| CPグレード2 Ti | 99.2%分 | – | – | 0.最大3 | 0.最大25 | 0.最大03 | 0.最大015 |
フェーズ チタン合金はα六方最密充填相とβ体心立方相の混合相を含む。AMの冷却速度は非平衡相を生成する可能性がある。
欠陥: 融着不足、気孔、マイクロクラックが発生し、機械的特性が低下することがあります。熱間静水圧プレス(HIP)は、欠陥を減らし、一貫性を向上させるのに役立ちます。
粒構造: AMチタン合金では、急速な凝固とエピタキシャル成長により、ビルド方向に沿った柱状の先行β粒が見られる。柱状結晶粒の幅は強度に影響する。
表面粗さ: 粉末床溶融プロセスでは、部分的に溶融した粉末粒子により、印刷後の表面は半平滑になる。追加の仕上げ加工が必要になることが多い。
主要物件
印刷されたチタン部品の特性は、組成、気孔率、表面粗さ、造形方向、熱処理、および試験方向に影響されます。
物理的性質
| プロパティ | Ti-6Al-4V | CPグレード2 Ti |
|---|---|---|
| 密度 (g/cc) | 4.42 | 4.51 |
| 融点 (°C) | 1604-1660 | 1668 |
機械的性質
| プロパティ | 印刷済み | 熱間静水圧プレス(HIP) | 錬金アニール |
|---|---|---|---|
| 引張強さ(MPa) | 900-1300 | 950-1150 | 860-965 |
| 降伏強さ(MPa) | 800-1100 | 825-900 | 790-870 |
| 破断伸度(%) | 5-15 | 8-20 | 15-25 |
| 硬度(HRC) | 32-44 | 32-36 | 31-34 |
メリット
- 高い強度対重量比
- 高温下でも強度を維持
- 疲労、摩耗、腐食に強い
- バイオイナート – 医療用インプラントに最適
- 滅菌処理に耐える
制限事項
- 高価な材料とAM加工
- 反応性で可燃性の粉末
- 異方性
- 展伸材よりも延性が低い

積層造形チタン部品の用途
3Dプリンティングは、チタンの用途を、より軽く、より強く、より高性能な部品へと、産業界全体に拡大します。
航空宇宙 タービンブレード、機体およびエンジン構造、アンテナ、熱交換器
自動車 コネクティングロッド、バルブ、ターボチャージャーホイール、ドライブトレインコンポーネント
医療と歯科: 整形外科用インプラント、人工関節、手術器具、患者適合器具
石油・ガス 耐食パイプ、バルブ、坑口部品、セパレーター
消費財: 自転車フレーム、ゴルフクラブヘッド、眼鏡フレームなどのスポーツ用品
工具: 金属射出成形金型、治具、固定具に統合された軽量コンフォーマル冷却チャンネル
ポピュラー 3Dプリンティングチタン粉末 AM用
| 合金 | 用途 | 印刷適性 | 表面仕上げ | 機械的特性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 航空宇宙部品、生物医学インプラント | 素晴らしい | 中程度 | 高強度、高硬度、疲労寿命 |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 航空宇宙構造部品、自動車 | 非常に良い | 中程度 | 強度、破壊靭性 |
| Ti 6242 | 高温部品 | グッド | 貧しい | 300℃における強度、耐クリープ性 |
| CPグレード2チタン | 医療用インプラント、化学プラント | 中程度 | 非常に良い | 延性、耐食性 |
仕様と規格
チタン粉末と印刷部品には、航空宇宙および医療規格に準拠した厳しい品質要件が課せられている。
パウダー仕様
| パラメータ | 必要条件 | 試験方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 粒子径 | 15-45 μm | レーザー回折 |
| 見かけ密度 | ≥ 2.7 g/cc | ホール流量計 |
| タップ密度 | ≥ 3.2 g/cc | タップ密度試験機 |
| 流量 | 15~25秒/50g | ホール流量計 |
| 化学組成 | 分析証明書 | GDMS、ICP-MS |
部品認定基準
| スタンダード | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| ASTM F3001 | AMチタン部品の標準 |
| ASTM F2924 | チタン合金 Ti-6Al-4V ELI |
| ASTM F3184 | 原料チタン合金粉末 |
| AMS7009 | 航空宇宙材料仕様 |
| ISO 13485 | 医療機器 – 品質管理 |
チタンAMの設計原則
チタンによる積層造形の利点を生かすには、適切な部品設計が極めて重要である。
- 支持構造を避けるため、オーバーハングを最小限に抑える。
- パウダーを落としやすくするために、パーツの向きを変える
- HIPや機械加工などの後処理を可能にする
- コンフォーマル冷却用チャンネル内蔵
- アセンブリを単一のチタン部品に統合
- 高応力領域を格子で補強する
- トポロジー最適化による軽量化のための形状最適化
サプライヤー 3Dプリンティングチタン粉末
| サプライヤー | 対象学年 | パウダーサイズ | 追加サービス |
|---|---|---|---|
| AP&C | Ti-6Al-4V、Ti-6Al-4V ELI、Ti64、CP-Tiグレード1~4 | 15-45 μm | 分析、試験、ふるい分け、混合、保管 |
| カーペンター添加剤 | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo | 15-45 μm | カスタム合金、パラメータ開発 |
| LPWテクノロジー | Ti-6Al-4V ELI、Ti-6Al-4V、CP-Tiグレード2 | 15-45 μm | 材料試験、粉体再利用分析 |
| プラクセア | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-4V ELI | 15-100 μm | ふるい分け、ブレンド、保管 |
| サンドビック | オスプレイ・チタン合金 | 15-45 μm | 粉体ライフサイクル管理 |
コストだ: ~1kgあたり500~1000ドルだが、注文量、グレード、粒度分布、ガス噴霧法、追加の取り扱い、試験要件によって異なる。

よくある質問
Q: チタン部品の3Dプリントにはどのような方法がありますか?
A: チタンは主に、選択的レーザー溶融(SLM)や電子ビーム溶融(EBM)を用いた粉末床溶融法によってプリントされます。レーザー金属蒸着(LMD)や溶接ベースの指向性エネルギー蒸着(DED)のようなワイヤーベースの方法も可能ですが、あまり一般的ではありません。
Q: AM用のチタンパウダーは特別な保管や取り扱いが必要ですか?
A: はい、チタンは空気と反応しやすいので、パウダーはアルゴンガスや窒素ガスを使用した不活性雰囲気下で保管・加工する必要があります。可燃性の環境や発火源は避けなければなりません。作業者はチタン粉末を取り扱う際、保護具を着用する必要があります。
Q:チタンAM部品の気孔率の問題は何が原因ですか?
A: 冷却速度が速いとガスが巻き込まれ、融合欠陥が発生しやすくなる。気孔率を最小化するには、出力、速度、ハッチ間隔、フォーカスオフセット、粉末層密度などのパラメーターの最適化が必要です。また、熱間静水圧プレス(HIP)は、初期印刷後の部品の高密度化に役立ちます。
Q:AM加工後に直接チタンの表面を滑らかにするのが難しいのはなぜですか?
A: 部分的に溶けたチタンパウダーは表面に付着し、ざらざらした仕上がりになります。タンブリング、サンドブラスト、フライス加工、研削、研磨は、チタンプリント部品を滑らかにするために使用される二次加工です。化学的または電気化学的な仕上げ加工も使用されます。
Q: 市販の純チタンを3Dプリントできますか?
A: はい、組成と粒度分布に関するB348のようなASTM規格を満たすグレード1から4の非合金CPチタン粉末は、骨インプラントや化学プラントのような高い延性を必要とする用途の純チタン部品の印刷に使用することができます。
Additional FAQs on 3D Printing Titanium Powder
1) How many reuse cycles are safe for 3D printing titanium powder without degrading quality?
With strict oxygen/nitrogen control, sieving (e.g., 45 μm), and lot traceability, many aerospace shops qualify 5–15 reuse cycles. Stop reuse if O increases >0.03 wt% from baseline, flow degrades, or defect rates rise. Follow ISO/ASTM 52907 and internal MPS.
2) Which AM processes work best for titanium powders and why?
Laser powder bed fusion (LPBF/SLM) and electron beam melting (EBM) are dominant. LPBF offers fine features and broad parameter sets; EBM runs at elevated temperature, reducing residual stress and is favored for porous implants. Binder jetting for Ti is emerging but typically requires careful de-oxygenation and sinter-HIP.
3) What post-processing is essential for fatigue-critical Ti-6Al-4V parts?
Stress relief (650–750°C), hot isostatic pressing (HIP ~920–930°C, 100–120 MPa, 2–4 h), machining of critical surfaces, and polishing/electropolishing to Ra ≤1 μm. Fatigue performance often doubles versus as-printed.
4) How do powder size distributions affect build outcomes?
Finer cuts (15–25 μm) improve surface quality and detail but can reduce flowability and build rate. Coarser cuts (25–45 μm) raise throughput and stability but increase stair-stepping and roughness. Choose distribution to match feature size and machine recoating behavior.
5) What safety controls are mandatory for titanium powder handling?
Inert gas cabinets/Gloveboxes, Class D fire extinguishers, bonded/grounded equipment, dust collection with spark arrestors, ATEX-rated components where applicable, antistatic PPE, O2 monitoring, and documented spill/ignition procedures. Reference NFPA 484 and local regulations.
2025 Industry Trends in 3D Printing Titanium Powder
- Accelerated qualification: AMS 7015/7016 adoption expands, shortening time-to-flight for LPBF Ti parts via standardized process control and in-situ monitoring requirements.
- Multi-laser productivity: 8–12 laser LPBF systems push cost per part down; scan strategies mitigate lack-of-fusion at hatch boundaries.
- Powder lifecycle management: Inline O/N analysis and automated sieve stations standardize reuse; more closed-loop powder traceability integrated with MES/QMS.
- EBM for orthopedics: Growth in porous Ti implants due to faster build rates and temperature-managed microstructures.
- Binder jetting pilots: Early 2025 pilots show competitive cost for simple Ti geometries after de-binding and HIP, with ongoing work on oxygen pickup mitigation.
- Sustainability: Buy-to-fly ratios near 1.2 for AM vs. 8–12 for subtractive, plus increased regional atomization capacity to stabilize supply.
| 2025 Metric (Ti-6Al-4V unless noted) | 典型的な範囲 | Relevance/Notes | ソース |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPBF build rate per laser | 10–60 cm³/h | Multi-kW, multi-laser platforms improve throughput | OEM specs (EOS, SLM Solutions, Trumpf) |
| As-built density (LPBF) | 99.0–99.9% | With optimized power/speed/hatch and contour scans | Peer-reviewed AM studies |
| HIP + polished HCF strength | 400–600 MPa at 10⁷ cycles | Critical for aerospace brackets/implants | Literature averages |
| Qualified powder reuse cycles | 5–15 | With O ≤0.15 wt% total and tight PSD control | ISO/ASTM 52907 guidance |
| Ti powder price (atomized) | $450–$900/kg | Varies by grade, lot size, and certification | Market trackers, USGS context |
| EBM porous implant pore size | 300–700 μm | Target for osseointegration lattice regions | Orthopedic device literature |
Authoritative sources and references:
- ASTM and ISO/ASTM AM standards: https://www.astm.org and https://www.iso.org
- SAE AMS 7015/7016: https://saemobilus.sae.org
- USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries (Titanium): https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
- FDA device database for AM implants: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfpmn/pmn.cfm
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: Cost-Down of Aerospace Ti Brackets via Multi-Laser LPBF and Closed-Loop Powder Reuse (2025)
Background: An aerospace Tier-1 supplier needed to reduce piece cost and lead time for Ti-6Al-4V brackets while meeting AMS 7016.
Solution: Implemented 8-laser LPBF platform, automated powder recycle with inline O/N analysis, stress relief + HIP, and critical surface machining.
Results: Cost per part down 22%, buy-to-fly 1.25, first-pass yield 98.6%, and fatigue at 10⁶ cycles improved 30% over 2023 baseline. Internal qualification aligned to AMS 7015/7016 and customer MPS.
Case Study 2: EBM-Printed Porous CP-Ti Grade 2 Acetabular Cups for Enhanced Osseointegration (2024)
Background: Hospital consortium sought better primary stability and reduced revision risk in complex hip cases.
Solution: Designed 60% lattice porosity with 500 μm pores; EBM at elevated temperature to reduce residual stress; post-cleaning and sterilization per ISO 13485; verification to ASTM F3001/F67.
Results: Bench push-out strength +25% vs. machined-and-coated cups; early 12-month follow-up indicated improved stability with no adverse ion release beyond ISO 10993 limits. Device data supported premarket submission.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Iain Todd, Professor of Metallurgy and Materials Processing, University of Sheffield
Key viewpoint: “For titanium powders, controlling oxygen pickup across the entire lifecycle is the single biggest lever for reliable ductility and fatigue; inline gas analysis and strict reuse rules are now best practice.” - Dr. Martina Zimmermann, Head of Additive Manufacturing Materials, Fraunhofer IWM
Key viewpoint: “Multi-laser LPBF increases productivity, but scan synchronization and defect mapping must be tied to acceptance criteria like AMS 7016 to prevent hatch-boundary lack-of-fusion.” - Dr. Gaurav Lalwani, Materials Scientist (Biomedical Implants), independent consultant
Key viewpoint: “EBM-produced porous Ti surfaces deliver reproducible osseointegration without post-coatings, provided pore size and surface energy are tightly controlled.”
Citations for expert profiles:
- University of Sheffield AMRC/Materials: https://www.sheffield.ac.uk
- Fraunhofer IWM: https://www.iwm.fraunhofer.de
- Consultant profile/context: https://scholar.google.com (publication records)
Practical Tools and Resources
- Data and standards
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (feedstock characterization) and 52910 (design guidelines): https://www.iso.org
- ASTM F3001, F2924, F3184 (Ti powders/parts): https://www.astm.org
- SAE AMS 7015/7016 (AM Ti qualification): https://saemobilus.sae.org
- Process and simulation
- Ansys Additive Suite (distortion, support, microstructure): https://www.ansys.com
- Autodesk Netfabb and Fusion Additive features: https://www.autodesk.com
- nTopology for topology optimization and lattices: https://ntop.com
- Powder management and QC
- Senvol Database (machines/materials): https://senvol.com/database
- LECO O/N/H analyzers for powder/part gas content: https://www.leco.com
- Bodycote HIP services: https://www.bodycote.com
- Safety and compliance
- NFPA 484 (combustible metals guidance): https://www.nfpa.org
- AMPP (formerly NACE) resources on titanium corrosion and finishing: https://www.ampp.org
- Market intelligence
- USGS titanium summaries and trends: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs
Last updated: 2025-08-21
Changelog: Added 5 new FAQs, 2025 trend table with metrics and sources, two recent case studies, expert commentary, and curated tools/resources specific to 3D printing titanium powder.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if AMS/ASTM/ISO standards are revised, multi-laser LPBF parameters materially change, or titanium powder pricing/supply experiences significant volatility.