金属粉末は、積層造形から粉末冶金まで、さまざまな産業用途で重要な役割を果たしている。しかし、その性能にしばしば影響を与える重要な特性のひとつに 小気孔.これらの微細な空隙は、金属粉末の特性や使いやすさに影響を与えます。この包括的なガイドブックでは、金属粉末中の微小なガストラップ空隙の世界を深く掘り下げ、その影響、具体的な金属粉末モデル、用途などを探ります。
金属粉末中のマイナーガス捕捉細孔の概要
金属粉末は微小な粒子で構成されており、しばしばガスが閉じ込められた気孔を含んでいる。これらの気孔は、特にガスが完全に排出されない場合、製造プロセス中に形成される可能性があります。これらの気孔の特性と影響を理解することは、様々な用途における金属粉末の性能を最適化するために不可欠です。

の主な詳細 マイナーガス封入孔 金属粉末
| アスペクト | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| フォーメーション | ガスが完全に排出されないと、金属粉末の凝固中にガストラップ気孔が形成される。 |
| 物件への影響 | これらの気孔は、金属粉末の密度、機械的強度、熱伝導性、および全体的な性能に影響を与える可能性がある。 |
| 検出方法 | X線トモグラフィー、走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM)、レーザー回折などの方法が、これらの孔の検出と分析に用いられている。 |
| 軽減テクニック | 製造時のガスフローの最適化、加工後の処理、合金化などの技術は、こうした気孔の発生を抑えるのに役立つ。 |
| アプリケーションにおける重要性 | 航空宇宙産業、自動車産業、医療産業など、高い精度と性能を要求される用途では、気体を封じ込めた細孔を理解し制御することが不可欠である。 |
微小ガス捕捉孔を有する金属粉末の種類
金属粉末を扱う場合、ガスが捕捉された小孔を示す特定のモデルを考慮することが不可欠である。以下はその顕著な例である:
| 金属粉モデル | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 316Lステンレス鋼 | 耐食性と優れた機械的特性で知られるが、密度に影響する小さな気孔が見られることがある。 |
| Ti-6Al-4Vチタン合金 | 航空宇宙や医療用インプラントに広く使用され、疲労強度に影響を与えるガストラップ孔が発生しやすい。 |
| Inconel 718 | 高い強度と耐食性を持つニッケル基超合金だが、ガスが閉じ込められた気孔がクリープ特性や疲労特性に影響を及ぼすことがある。 |
| AlSi10Mg アルミニウム合金 | アディティブ・マニュファクチャリングでは一般的で、熱伝導率や機械的強度に影響を及ぼす可能性のある小さなガストラップ気孔を示す。 |
| コバルトクロム合金 | 医療用インプラントや歯科用途に使用される場合、ガスが閉じ込められた孔は生体適合性や機械的性能に影響を与える可能性がある。 |
| 銅粉 | 電気的な用途には不可欠だが、小さな気孔は導電性や熱特性に影響を与える。 |
| タングステン粉 | その高い密度と融点で知られる気孔は、熱伝導率や電気伝導率に影響を与える可能性がある。 |
| 鉄粉 | 粉末冶金で一般的に使用される気孔は、その磁気特性と密度に影響を与える可能性がある。 |
| ニッケル粉 | 電池やコーティングに使用される場合、小さな気孔が化学的・熱的安定性に影響を与えることがある。 |
| マグネシウム合金 | 軽量で優れた機械的特性を持つが、ガスが封じ込められた気孔は耐食性と強度に影響する。 |
金属粉末の組成と特性
金属粉末の組成と特性は、特に微小なガストラップ孔が存在する場合、その性能を決定する上で極めて重要である。
| 金属粉 | 構成 | 気体封入孔が影響する特性 |
|---|---|---|
| 316Lステンレス鋼 | 鉄、クロム、ニッケル、モリブデン | 密度、耐食性、機械的強度 |
| Ti-6Al-4V | チタン、アルミニウム、バナジウム | 疲労強度、引張強度、耐食性 |
| Inconel 718 | ニッケル、クロム、鉄 | 耐クリープ性、疲労強度、高温安定性 |
| AlSi10Mg | アルミニウム、シリコン、マグネシウム | 熱伝導性、機械的強度、延性 |
| コバルト・クロム | コバルト、クロム | 生体適合性、機械的強度、耐摩耗性 |
| 銅 | 銅 | 電気伝導率、熱伝導率、機械的強度 |
| タングステン | タングステン | 密度、熱伝導率、電気伝導率 |
| 鉄 | 鉄 | 磁気特性、密度、機械的強度 |
| ニッケル | ニッケル | 化学的安定性、熱安定性、機械的強度 |
| マグネシウム合金 | マグネシウム、アルミニウム、亜鉛 | 耐食性、機械的強度、密度 |
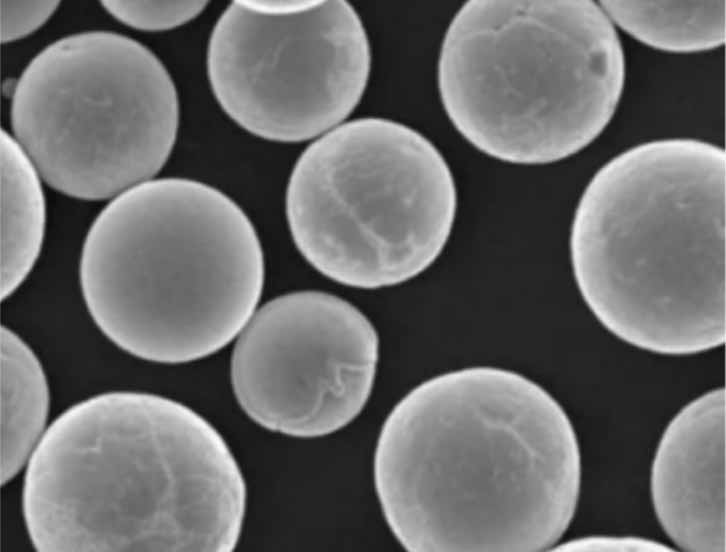




金属粉末の用途 マイナーガス封入孔
微小な気孔を持つ金属粉末は、様々な産業で使用され、それぞれに特有の特性や性能が要求される。
| 申し込み | 金属粉モデル | ガストラップ孔の影響 |
|---|---|---|
| 付加製造 | 316Lステンレス鋼、AlSi10Mg、Ti-6Al-4V | 層の密着性、密度、機械的特性に影響 |
| 航空宇宙部品 | Ti-6Al-4V、インコネル718 | 疲労強度、高温性能、信頼性に影響 |
| 医療用インプラント | コバルトクロム、Ti-6Al-4V | 生体適合性、機械的完全性、寿命に影響を与える |
| 導体 | 銅、アルミニウム | 電気伝導性、熱管理、機械的強度に影響 |
| 自動車部品 | アルミニウム合金、マグネシウム合金 | 軽量化、機械的強度、耐食性に影響 |
| 金型 | タングステン、インコネル718 | 耐摩耗性、熱伝導性、機械的安定性に影響する。 |
| 電池とエネルギー貯蔵 | ニッケル、コバルトクロム | 化学的安定性、エネルギー密度、熱管理への影響 |
| 粉末冶金 | 鉄、銅 | 密度、機械的強度、磁気特性に影響 |
| コーティングと表面処理 | ニッケル、アルミニウム、銅 | 接着性、耐摩耗性、表面仕上げに影響 |
| バイオ医療機器 | チタン合金、コバルトクロム | 生体適合性、機械的性能、耐食性に影響を及ぼす |
金属粉末の仕様、サイズ、等級、規格
金属粉末の仕様は、その用途や気体封入孔の有無によって異なる。
| 金属粉 | 仕様 | サイズ | グレード | 規格 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316Lステンレス鋼 | A276, ISO 5832-1 | 15-45ミクロン | 316L, 1.4404 | ASTM F138、ISO 5832-1 |
| Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM B348、ISO 5832-3 | 20~50ミクロン | グレード5 | アストマ F136、ISO 5832-3 |
| Inconel 718 | ASMB637、AMS5662 | 15-53ミクロン | 午前5662、午前5663 | AMS5662、ASM B637 |
| AlSi10Mg | ISO 3522 | 20-63ミクロン | AlSi10Mg | ISO 3522 |
| コバルト・クロム | ASTM F1537、ISO 5832-4 | 10~45ミクロン | CoCrMo | ASTM F75、ISO 5832-4 |
| 銅 | アストレムB170、アストレムB216 | 15-63ミクロン | Cu-ETP、Cu-DHP | アストレムB170、アストレムB216 |
| タングステン | ASTM B777、ISO 5457 | 5-50ミクロン | W1, W2 | ASTM B777、ISO 5457 |
| 鉄 | ASTM B783、ISO 10085 | 10-100ミクロン | Fe-1、Fe-2 | ASTM B783、ISO 10085 |
| ニッケル | ASMB160、ISO6280 | 10~45ミクロン | Ni-201、Ni-200 | ASMB160、ISO6280 |
| マグネシウム合金 | アストレムB93、アストレムB403 | 20-100ミクロン | AZ31B、AZ91D | アストレムB93、アストレムB403 |
金属粉末のサプライヤーと価格詳細
金属粉末を調達するには、適切なサプライヤーを見つけ、価格設定の詳細を理解することが極めて重要である。
| サプライヤー | 金属粉モデル | 価格(1kgあたり) | 地域 | 追加サービス |
| ヘガネスAB | 316Lステンレス鋼、鉄、銅 | $20 – $50 | ヨーロッパ、北米 | カスタム合金開発、技術サポート |
| サンドビック | Ti-6Al-4V、インコネル718、アルミニウム合金 | $100 – $300 | グローバル | 積層造形ソリューション、材料分析 |
| GKN粉末冶金 | 鉄、銅、ニッケル | $10 – $30 | グローバル | 粉末冶金ソリューション、プロトタイピング |
| カーペンター・テクノロジー | Ti-6Al-4V、コバルトクロム、インコネル718 | $150 – $400 | 北米、ヨーロッパ | 先進材料エンジニアリング、カスタムソリューション |
| エッカ顆粒 | アルミニウム合金、銅、マグネシウム合金 | $15 – $45 | グローバル | 高純度パウダー、カスタマイズされた粒子径 |
| ATIメタルズ | ニッケル、チタン合金、ステンレス鋼 | $80 – $250 | グローバル | 航空宇宙材料、技術コンサルティング |
| LPWテクノロジー | Ti-6Al-4V、インコネル718、アルミニウム合金 | $120 – $350 | グローバル | 積層造形用パウダー、リサイクルソリューション |
| スタルクHC | タングステン、コバルトクロム、鉄 | $50 – $150 | グローバル | 高性能素材、技術サポート |
| カイメラ・インターナショナル | 銅、鉄、アルミニウム合金 | $20 – $60 | グローバル | カスタム合金粉末、材料特性評価 |
| アルカムAB | Ti-6Al-4V、インコネル718、コバルトクロム | $200 – $500 | グローバル | 電子ビーム溶解、積層造形ソリューション |
金属粉末中の微小ガス捕捉孔の利点と欠点
ガストラップ孔の長所と短所を理解することは、材料の選択と応用について十分な情報を得た上での決断に役立つ。
| アスペクト | メリット | デメリット |
|---|---|---|
| 機械的特性 | 強度重量比の高い軽量構造物を作ることができる。 | 密度の低下、機械的強度の潜在的低下。 |
| 熱特性 | ガスが封じ込められた小さな孔は断熱材として機能し、用途によっては熱性能を向上させる。 | 熱伝導率の低下は、高熱用途では不利になることがある。 |
| 製造業 | 細孔は、制御された製造プロセスを通じて、所望の特性を達成するために調整することができる。 | コントロールや予測が難しく、特性のばらつきにつながる。 |
| コスト | 材料の使用量を減らすことで、特定の製造工程におけるコスト削減の可能性。 | 気孔含有量を管理するための追加処理または品質管理措置によるコスト増。 |
| 用途 | 軽量で断熱性を必要とする用途に有効。 | 気孔の存在が有害な高強度、高導電性、高精度の用途では限界がある。 |
マイナーガス封入孔の緩和技術
金属粉末中の微小なガストラップ孔の影響を緩和し、より優れた性能と信頼性を確保するために、いくつかの技術が採用されている。
1.製造時のガスフローの最適化
粉末製造工程で適切なガスフローを確保することは、ガストラップ孔の発生を最小限に抑えるのに役立つ。真空溶解や不活性ガスアトマイズなどの技術が一般的に使用されている。
2.後処理
熱間等方圧加圧(HIP)のようなプロセスは、高い圧力と温度を加えることによって、ガスが閉じ込められた気孔を大幅に減少または除去することができ、その結果、より緻密で均質な材料を得ることができる。
3.合金元素と添加元素
特定の合金元素を導入することで、ガスが閉じ込められた気孔の形成と分布を制御することができる。例えば、特定の合金に希土類元素を添加すると、ガス溶解性が向上し、気孔の形成が抑制される。
4.高度な製造技術
レーザー焼結や電子ビーム溶解などの技術は、金属粉末の微細構造をよりよく制御することを可能にし、ガストラップ孔の可能性を低減する。
金属粉末の比較分析
様々なパラメータで異なる金属粉末を比較することで、特定の用途に対する適性を洞察することができる。
| パラメータ | 316Lステンレス鋼 | Ti-6Al-4V | Inconel 718 | AlSi10Mg | コバルト・クロム | 銅 | タングステン | 鉄 | ニッケル | マグネシウム合金 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 密度 | 中程度 | 低い | 高い | 低い | 高い | 中程度 | 非常に高い | 高い | 中程度 | 非常に低い |
| 機械的強度 | 高い | 非常に高い | 非常に高い | 中程度 | 非常に高い | 中程度 | 高い | 高い | 中程度 | 中程度 |
| 熱伝導率 | 中程度 | 低い | 低い | 高い | 中程度 | 非常に高い | 高い | 中程度 | 中程度 | 中程度 |
| 耐食性 | 非常に高い | 高い | 非常に高い | 中程度 | 高い | 低い | 非常に高い | 中程度 | 高い | 中程度 |
| コスト | 中程度 | 高い | 非常に高い | 低い | 高い | 中程度 | 非常に高い | 低い | 高い | 低い |
| アプリケーションの適合性 | 積層造形、医療 | 航空宇宙、医療 | 航空宇宙、高温 | 積層造形 | 医療、歯科 | 電気、熱 | 工具、高温 | 粉末冶金 | バッテリー、コーティング | 自動車、航空宇宙 |
詳細な事例とケーススタディ
ケーススタディ1:航空宇宙分野におけるTi-6Al-4V
Ti-6Al-4Vは、航空宇宙用途で一般的に使用されるが、しばしば以下のような問題に直面する。 小気孔.詳細な研究によると、電子ビーム溶解プロセスを最適化することで、このような気孔の発生が大幅に減少し、その結果、部品の疲労強度と信頼性が向上した。
ケーススタディ2:医療用インプラントにおける316Lステンレス鋼
316Lステンレス鋼は、その優れた耐食性と生体適合性により、医療用インプラントに広く使用されている。しかし、ガスが封じ込められた気孔の存在は、その機械的特性に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。熱間等方圧加圧(HIP)を用いて粉末を処理することで、機械的特性が向上した高密度の材料が得られ、荷重を支えるインプラントに適している。
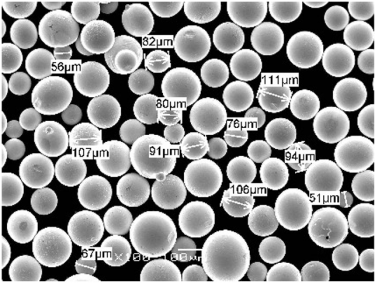
よくある質問
| 質問 | 回答 |
|---|---|
| 金属粉のガストラップ細孔とは? | 微小ガストラップ気孔とは、製造工程でガスが十分に排出されない場合に金属粉末粒子内に形成される微小な空隙のことである。 |
| ガストラップされた細孔は、金属粉末の性能にどのような影響を与えるのか? | これらは密度、機械的強度、熱伝導率などの特性に影響を与え、金属粉末の全体的な性能に影響を与える。 |
| ガスが溜まった毛穴を完全になくすことはできるのか? | これを完全に除去することは難しいが、熱間等方圧加圧(HIP)や最適化された製造工程のような技術によって、その存在を大幅に減らすことができる。 |
| 金属粉末中のガストラップ気孔が最も影響を受ける産業は? | 航空宇宙産業、医療産業、自動車産業、積層造形産業は、ガストラップ孔の影響を特に受けやすい。 |
| 金属粉末にガストラップされた細孔があることには、何か利点があるのでしょうか? | 場合によっては、特定の用途に有益な断熱性や軽量性をもたらすこともある。しかし、こうした利点は多くの場合、状況に左右される。 |
| 金属粉末中のガストラップされた細孔を検出するには、どのような方法があるのか? | X線トモグラフィー、走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM)、レーザー回折などの技術は、これらの細孔の検出と分析に一般的に使用されている。 |
| サプライヤーはどのようにして、ガストラップ孔を最小限に抑えた金属粉末の品質を確保するのだろうか? | サプライヤーは、高度な製造技術、厳格な品質管理措置、およびこれらの孔の存在を最小限に抑えるための後処理を使用しています。 |
結論
金属粉末中のマイナーなガストラップ気孔を理解し管理することは、様々な用途においてその性能を最適化するために極めて重要である。様々な金属粉末モデル、その特性、用途、緩和技術を探求することで、産業界は製品の信頼性と効率を高めるための情報に基づいた決定を下すことができます。航空宇宙、医療、付加製造のいずれにおいても、これらの微細な空隙を制御することで、材料性能の大幅な向上とアプリケーションの成功につながります。

