概要 噴霧化プラント
アトマイズ・プラントは、アトマイズ・プロセスによる金属粉末の生産を専門とする工業施設である。このプロセスでは、溶融金属を微細な液滴に分解し、凝固させて粉末にする。これらの金属粉末は、航空宇宙、自動車、電子機器、積層造形など、さまざまな産業で重要な役割を果たしている。
アトマイズ・プラントの主な構成要素
- 溶解炉:金属を加熱して溶融状態にする。
- 噴霧ノズル:溶融金属を微細な液滴に分解する。
- 冷却室:液滴を粉末に固める。
- コレクション・システム:金属粉を集める。
- ふるい分けユニット:粉体を粒度別に選別する。

製造される金属粉末の種類
1.ステンレススチール・パウダー
ステンレス鋼粉末は、その耐食性と強度で知られている。航空宇宙、医療機器、食品加工などの産業で使用されています。
2.チタンパウダー
チタン粉末は軽量で、優れた強度と耐食性を持っています。航空宇宙、医療用インプラント、スポーツ用品などに欠かせない。
3.アルミニウムパウダー
アルミニウム粉末は軽くて強く、耐食性に優れている。自動車や航空宇宙分野で広く使用されている。
4.銅粉
銅粉は導電性が高く、導電性インクやコーティングを含む電気・電子用途に使用されています。
5.ニッケルパウダー
ニッケル粉末は超合金や電池に使用され、高い強度と耐酸化性、耐腐食性を提供する。
6.コバルトパウダー
コバルト粉末は、切削工具や航空宇宙エンジンのような、高温で耐摩耗性の高い用途において極めて重要である。
7.鉄粉
鉄粉は自動車部品、磁性材料、焼結部品など様々な用途に使用されている。
8.亜鉛パウダー
亜鉛パウダーは主に亜鉛めっきや亜鉛を多く含む塗料の製造に使用される。
9.タングステンパウダー
タングステン粉末は融点と密度が高く、放射線遮蔽や高性能工具のような過酷な用途に最適です。
10.ブロンズ・パウダー
銅と錫の混合物である青銅粉は、装飾品、ベアリング、電気接点に使用される。
金属粉末の組成と特性
| 金属粉 | 構成 | プロパティ |
|---|---|---|
| ステンレス鋼粉末 | Fe、Cr、Ni、Mo | 耐食性、高強度 |
| チタン粉末 | Ti | 軽量、高強度、耐食性 |
| アルミニウムパウダー | Al | 軽量、優れた耐食性 |
| 銅粉末 | 銅 | 高い導電性 |
| ニッケル粉末 | Ni | 高強度、耐酸化性 |
| コバルト粉末 | Co | 耐摩耗性、高温安定性 |
| 鉄粉末 | Fe | 高い磁気特性 |
| 亜鉛パウダー | 亜鉛 | 亜鉛メッキに使用される耐食性 |
| タングステン粉末 | W | 高密度、高融点 |
| ブロンズ・パウダー | 銅、錫 | 良好な導電性、耐摩耗性 |
金属粉末の用途
| 金属粉 | 用途 |
|---|---|
| ステンレス鋼粉末 | 航空宇宙、医療機器、食品加工 |
| チタン粉末 | 航空宇宙、医療用インプラント、スポーツ用品 |
| アルミニウムパウダー | 自動車、航空宇宙 |
| 銅粉末 | 電気、電子 |
| ニッケル粉末 | 超合金、バッテリー |
| コバルト粉末 | 切削工具、航空宇宙エンジン |
| 鉄粉末 | 自動車部品、磁性材料 |
| 亜鉛パウダー | 亜鉛メッキ、亜鉛を多く含む塗料 |
| タングステン粉末 | 放射線遮蔽、高性能工具 |
| ブロンズ・パウダー | 装飾品、ベアリング、電気接点 |

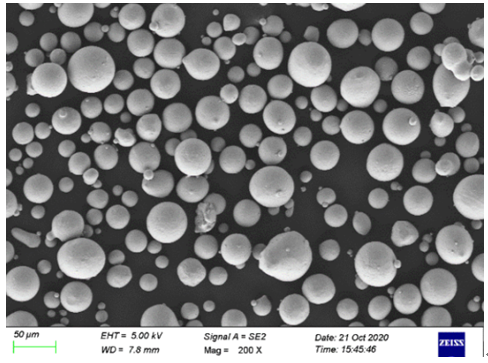
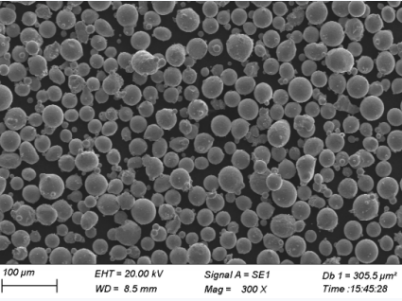
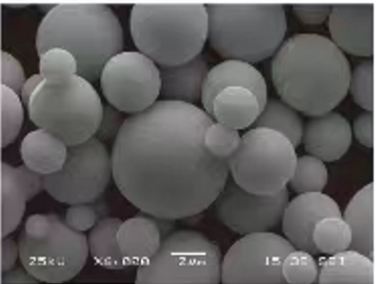
金属粉末の仕様と規格
| 金属粉 | 仕様 | サイズ (µm) | グレード | 規格 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ステンレス鋼粉末 | ASTM B214 | 1-150 | 304L、316L | ASTM、ISO |
| チタン粉末 | アストマ F67、F1580 | 15-45 | CP-Ti、Ti-6Al-4V | ASTM、ISO |
| アルミニウムパウダー | ASTM B212 | 10-100 | 1100, 7075 | ASTM、ISO |
| 銅粉末 | ASTM B833 | 5-100 | C11000 | ASTM、ISO |
| ニッケル粉末 | ASTM B330 | 5-100 | ニッケル200、ニッケル201 | ASTM、ISO |
| コバルト粉末 | ASTM B330 | 10-100 | Co-27、Co-28 | ASTM、ISO |
| 鉄粉末 | ASTM B213 | 1-150 | Fe-99、Fe-100 | ASTM、ISO |
| 亜鉛パウダー | ASTM B852 | 5-100 | Zn-1、Zn-2 | ASTM、ISO |
| タングステン粉末 | ASTM B777 | 1-50 | W-1、W-2 | ASTM、ISO |
| ブロンズ・パウダー | ASTM B213 | 5-100 | CuSn8, CuSn10 | ASTM、ISO |
金属粉末のサプライヤーと価格
| サプライヤー | 金属粉末 | 価格帯(kgあたり) | 地域 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ヘガネスAB | ステンレススチール、鉄 | $10 – $100 | ヨーロッパ、アメリカ |
| GKNホエガネス | チタン、アルミニウム | $50 – $500 | グローバル |
| サンドビック・オスプレイ | ニッケル、コバルト | $30 – $400 | グローバル |
| アメテック | 銅、ブロンズ | $20 – $150 | 米州 |
| カーペンター | タングステン、亜鉛 | $100 – $1000 | グローバル |
金属粉末の利点と限界
| 金属粉 | メリット | 制限事項 |
|---|---|---|
| ステンレス鋼粉末 | 高強度、耐食性 | 高い、重い |
| チタン粉末 | 軽量、生体適合性 | 高コスト、加工が難しい |
| アルミニウムパウダー | 軽量、優れた熱特性 | 鋼鉄に比べて強度が低い |
| 銅粉末 | 優れた導電性 | 高価、酸化しやすい |
| ニッケル粉末 | 高温安定性、強度 | コストが高く、機械加工が難しい |
| コバルト粉末 | 耐摩耗性、高温能力 | 高価で加工が難しい |
| 鉄粉末 | コストパフォーマンス、磁気特性 | 腐食に弱い |
| 亜鉛パウダー | 耐食性、低コスト | 強度が低く、高荷重用途には適さない |
| タングステン粉末 | 高密度、高融点 | 非常に硬く、加工が難しい |
| ブロンズ・パウダー | 良好な導電性、美的魅力 | 中程度の強度、変色することがある |
噴霧化プラントの構成
アトマイズプラントの構成は、特定のニーズと生産される金属粉末の種類によって異なる。しかし、核となる構成要素には一般的に以下が含まれる:
- 溶解炉:誘導炉、アーク炉、ガス焚き炉などがあり、金属の融点や特性によって選択される。
- 霧化チャンバー:高温・高圧に耐えるよう設計されており、通常はステンレス鋼などの耐熱性材料で作られている。
- 冷却システム:水冷式、ガス冷却式、空冷式があり、金属粉に必要な冷却速度によって使い分ける。
- コレクション・システム:多くの場合、サイクロン、バッグフィルター、ホッパーを使用して微粉を効率的に集める。
- ふるい分けユニット:振動スクリーンや遠心分級機を使って粉体を粒度別に選別する。
噴霧化プラントの特徴
霧化プラントは、いくつかの重要な特徴を備えている:
- 生産能力:少量生産から大規模な工業生産まで。
- 柔軟性:様々な金属粉末の製造が可能。
- 効率性:廃棄物を最小限に抑え、高い歩留まりを実現。
- 精密:安定した粒子径と粒度分布の粉体を製造。
- 安全性:高温・高圧に対応する高度な安全機能を装備。
の利点 噴霧化プラント
効率と収量
アトマイズプラントは高効率に設計されており、原料からの最大収率を保証します。これは、より少ない廃棄物でより多くの金属粉が生産されることを意味します。
汎用性
これらのプラントは、さまざまな産業ニーズに対応し、多種多様な金属粉を生産することができます。航空宇宙用途にステンレス鋼が必要であろうと、電気部品に銅が必要であろうと、アトマイズプラントなら対応できます。
高品質
製造されるパウダーは高品質で、粒子径が均一、純度も優れている。そのため、様々なハイテク産業における要求の厳しい用途に適しています。
スケーラビリティ
研究開発のための小規模生産から大規模な工業生産まで、噴霧プラントはさまざまな生産要件に合わせて拡張することができる。
費用対効果
初期設定費用は高いかもしれないが、
長期的なメリットと効率性により、アトマイズプラントは金属粉末製造のための費用対効果の高いソリューションとなります。
噴霧化プラントの欠点
高額な初期投資
噴霧化プラントの設置には多額の資本投資が必要である。設備、設置、インフラにかかる費用は相当なものになる。
複雑な操作
噴霧化プラントの運転は複雑で、熟練工を必要とする。効率的で安全な運転を確保するには、適切な訓練と経験が不可欠です。
メンテナンス
プラントを円滑に稼動させるには、定期的なメンテナンスが欠かせない。これは運転コストを増加させる可能性があり、専門のメンテナンス・チームが必要になります。
エネルギー消費
特にタングステンやチタンのような高融点金属を含むアトマイズ・プロセスは、エネルギー集約型である。これは高い操業コストにつながる。
金属粉末の比較:長所と短所
| 金属粉 | 長所 | 短所 |
|---|---|---|
| ステンレス鋼粉末 | 強靭、耐食性 | 高い、重い |
| チタン粉末 | 軽量、高強度 | 非常に高価で、加工が難しい |
| アルミニウムパウダー | 軽量、良好な耐食性 | 他の金属に比べて弱い |
| 銅粉末 | 優れた導電性 | コスト高、酸化しやすい |
| ニッケル粉末 | 強力な耐高温性 | 高コスト、機械加工が難しい |
| コバルト粉末 | 耐久性、耐熱性 | 高価で処理が難しい |
| 鉄粉末 | 手頃な価格、マグネット式 | 腐食しやすい |
| 亜鉛パウダー | 安価、耐食性 | 弱く、高ストレス用途には不向き |
| タングステン粉末 | 非常に緻密、高融点 | 非常に硬く、加工が難しい |
| ブロンズ・パウダー | 良好な導電性、審美性 | 中程度の強度、変色することがある |
よくある質問
霧化プラントとは?
アトマイズ・プラントは、溶融金属を微細な液滴に分解して粉末状に凝固させ、金属粉末を製造する工業設備である。
噴霧プラントの主な構成部品は何ですか?
主な構成部品には、溶解炉、噴霧ノズル、冷却室、回収システム、ふるい分け・分級装置などがある。
アトマイズ工場で製造された金属粉を使用する産業は?
航空宇宙、自動車、エレクトロニクス、積層造形などの産業は、金属粉末に大きく依存している。
霧化プラントを使う利点は何ですか?
利点としては、高い効率性、粉体製造の多様性、粉体の高い品質、拡張性、長期的な費用対効果などが挙げられる。
製造される金属粉の主な種類は?
主な種類は、ステンレス、チタン、アルミニウム、銅、ニッケル、コバルト、鉄、亜鉛、タングステン、青銅粉など。
アトマイズ工場では、金属粉はどのように分類されるのですか?
金属粉末は、粒度によって粉末を選別するふるい分け装置や分級装置を用いて分級される。
霧化プラントを運営する上での課題は何ですか?
課題としては、初期投資の高さ、複雑な運用、メンテナンスの必要性、エネルギー消費の多さなどが挙げられる。
霧化プロセスはどのように行われるのですか?
アトマイズ・プロセスでは、金属を溶かし、アトマイズ・ノズルを使って溶融金属を微細な液滴に分解し、その後冷却して液滴を粉末状に凝固させる。
アトマイズ・プラントはすべての金属に使用できますか?
アトマイズプラントでは多種多様な金属粉末を製造できるが、プロセスパラメーターは各金属の特性に基づいて調整する必要がある。
アトマイズ工場で生産される金属粉末のコスト範囲は?
コストは金属粉末の種類によって大きく異なり、1キログラム当たり10ドルから1000ドル程度である。
結論
噴霧プラント は、さまざまな産業に不可欠な高品質の金属粉を生産することで、現代の製造業において重要な役割を果たしている。高い初期投資と運用の複雑さにもかかわらず、効率性、汎用性、拡張性といった利点により、貴重な資産となっています。航空宇宙、自動車、エレクトロニクスのいずれにおいても、これらのプラントで生産される粉末は、製品やイノベーションに不可欠なものです。