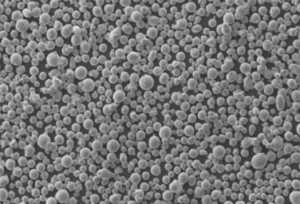
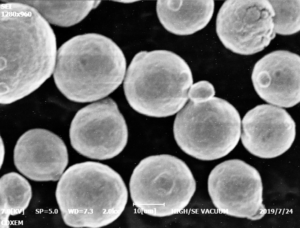
概要 ガス噴霧器
ガスアトマイザー装置は、航空宇宙、自動車、医療、エレクトロニクスなど、さまざまな産業で欠かせない金属粉末の製造に重要な役割を果たしています。これらの装置は、高圧ガスを用いて溶融金属を微細な粒子に分解し、高純度で均一、かつ流動性に優れた粉末を製造します。このプロセスは、材料特性の精度と一貫性が要求される用途に不可欠である。
ガスアトマイズにより、製造された金属粉末は、制御された粒度分布、高純度、球状形態などの望ましい特性を持つようになります。これらの特性により、ガスアトマイズ粉末は積層造形(3Dプリンティング)、金属射出成形(MIM)、その他の高度な製造技術に理想的なものとなる。

ガスアトマイザー装置の種類・構成・特性・特徴
ガス噴霧器の種類
| タイプ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 不活性ガス噴霧器 | アルゴンや窒素のような不活性ガスを使用し、アトマイズ工程での金属の酸化を防ぐ。 |
| 反応ガス噴霧器 | 水素などの反応性ガスを利用して、特定の合金を製造したり、粉末の特性を修正する。 |
| 水アトマイザー | ガスの代わりに高圧水ジェットを使用し、水との反応性が低い金属に適している。 |
| 真空噴霧器 | コンタミネーションを防ぐため、真空中で作動し、高純度の粉体製造に最適。 |
ガス噴霧器の構成
| コンポーネント | 素材 | 機能 |
|---|---|---|
| 噴霧ノズル | タングステンカーバイド, スチール | 溶融金属を分解するためにガスの流れを指示する。 |
| ガス供給システム | ステンレス鋼、合金 | ガスの流れを供給し、調整する。 |
| 溶解炉 | グラファイト、セラミックライニング | アトマイズ前に金属原料を溶解する。 |
| 粉体回収システム | ステンレス鋼、ポリマー | 金属粉を集め、保管する。 |
ガスアトマイザー装置の特性と特徴
| プロパティ | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 粒度分布 | 均一でコントロールされており、通常10~150ミクロンの範囲である。 |
| 粉体の形態 | 表面が滑らかな球状粒子で、流動性と充填密度を向上。 |
| 純度レベル | 不活性雰囲気処理により、コンタミネーションを最小限に抑えた高純度。 |
| 生産能力 | 実験室規模の小規模なものから大規模な産業用システムまでさまざま。 |
| 効率性 | 金属原料の粉末化効率が高い。 |
用途と使用法 ガス噴霧器
ガスアトマイズ粉末の用途
| 産業 | 申し込み |
|---|---|
| 航空宇宙 | 軽量で高強度の部品の製造。 |
| 自動車 | 複雑な形状の部品の製造。 |
| メディカル | 生体適合性インプラントや手術器具の開発。 |
| エレクトロニクス | 導電性ペーストと部品の製造。 |
| アディティブ・マニュファクチャリング(3Dプリンティング) | プロトタイプと最終使用部品の製造。 |
| 金属射出成形(MIM) | 複雑な金属部品を精密に成形。 |
ガスアトマイザー装置の仕様、サイズ、グレード、規格
ガス噴霧器の仕様
| 仕様 | 詳細 |
|---|---|
| ガス圧 | モデルにより10~50バールの範囲。 |
| ノズル径 | 通常0.2~2mm。 |
| 溶解能力 | バッチ当たり1kgから数トンまで。 |
| 粉体収率 | 粉体生産効率は最大95%。 |
金属粉末のサイズと等級
| グレード | サイズ範囲(ミクロン) | 典型的な構成 |
|---|---|---|
| ファイン | 10 – 30 | 高純度金属と合金。 |
| ミディアム | 30 – 60 | 汎用金属粉末。 |
| 粗目 | 60 – 150 | 構造部品および重量部品。 |
ガスアトマイズ粉末の規格
| スタンダード | 組織 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM B243 | ASTMインターナショナル | 粉末冶金の標準用語。 |
| ISO 4497 | 国際標準化機構 | ふるい分けによる粒度分布の測定。 |
| MPIFスタンダード35 | 金属粉末工業連盟 | 金属粉末の材料規格。 |




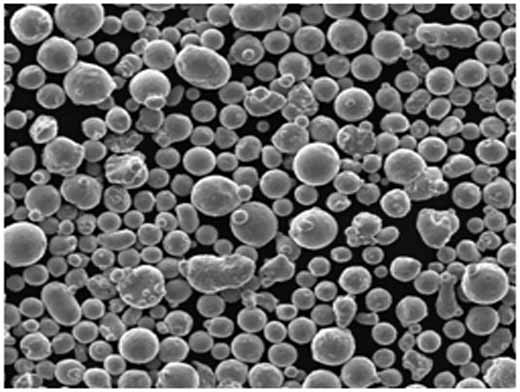

ガス噴霧器装置の納入業者と価格詳細
ガス噴霧器のサプライヤー
| サプライヤー | 所在地 | 専門性 |
|---|---|---|
| ヘガネスAB | スウェーデン | 高品質の金属粉末と噴霧装置。 |
| サンドビックAB | スウェーデン | 様々な金属に対応する高度な霧化技術。 |
| プラクセア・サーフェス・テクノロジー | アメリカ | 産業ガスソリューションとアトマイザー機器。 |
| AP&C(GEアディティブ) | カナダ | 航空宇宙グレードの金属粉末と噴霧システム。 |
価格詳細
| 設備タイプ | 価格帯 |
|---|---|
| ラボ用アトマイザー | 50,000ドル – 200,000米ドル |
| 工業用アトマイザー | 500,000ドル – 5,000,000ドル |
| 特注システム | 仕様により異なる |
ガス噴霧器の長所と短所
ガスアトマイザー装置の利点
| メリット | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 高純度 | コンタミネーションを最小限に抑えた金属粉末を製造。 |
| 均一な粒子径 | アプリケーションの一貫した品質とパフォーマンスを保証します。 |
| 汎用性 | 様々な金属や合金の加工が可能。 |
| スケーラビリティ | 小規模生産にも大規模生産にも適している。 |
ガスアトマイザー装置の限界
| 制限 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 高いイニシャルコスト | 設備のセットアップに多額の投資が必要。 |
| 複雑な操作 | 熟練したオペレーターと厳格な工程管理が必要。 |
| メンテナンス | 最適なパフォーマンスを確保するためには、定期的なメンテナンスが必要。 |
| エネルギー消費 | 霧化過程でのエネルギー使用量が多い。 |
特定金属粉末モデル
- Inconel 625
- 構成:ニッケル、クロム、モリブデン
- プロパティ:高耐食性、優れた疲労・熱疲労強度、耐酸化性。
- 用途:航空宇宙、海洋、化学処理。
- チタン合金 (Ti-6Al-4V)
- 構成:チタン、アルミニウム、バナジウム
- プロパティ:高強度対重量比、優れた耐食性、生体適合性。
- 用途:医療用インプラント、航空宇宙部品、自動車部品。
- 316Lステンレス鋼
- 構成:鉄、クロム、ニッケル、モリブデン
- プロパティ:優れた耐食性、良好な機械的特性。
- 用途:医療機器、食品加工機器、化学容器。
- アルミニウム合金 (AlSi10Mg)
- 構成:アルミニウム、シリコン、マグネシウム
- プロパティ:高強度、軽量、優れた熱特性。
- 用途:自動車、航空宇宙、構造部品。
- コバルトクロム(CoCr)
- 構成:コバルト、クロム、モリブデン
- プロパティ:高い耐摩耗性、生体適合性、優れた機械的特性。
- 用途:医療用インプラント、歯科機器、航空宇宙。
- 銅合金(CuNi2SiCr)
- 構成:銅、ニッケル、シリコン、クロム
- プロパティ:高い熱伝導性と電気伝導性、優れた機械的特性。
- 用途:電気部品、熱交換器、航空宇宙。
- マレージング鋼
- 構成:鉄、ニッケル、コバルト、モリブデン、チタン
- プロパティ:超高強度、良好な靭性、熱処理が容易。
- 用途:工具、航空宇宙、高性能エンジニアリング。
- Hastelloy X
- 構成:ニッケル、クロム、モリブデン、鉄
- プロパティ:優れた耐酸化性、高温強度。
- 用途:航空宇宙、ガスタービン、工業炉用途。
- ニッケル合金718
- 構成:ニッケル、クロム、鉄、ニオブ、モリブデン
- プロパティ:高い引張強さ、降伏強さ、クリープ強さ
破断特性。
- 用途:ジェットエンジン、高応力部品、石油・ガス。
- 工具鋼(H13)
- 構成:鉄、クロム、モリブデン、バナジウム
- プロパティ:高い靭性、良好な耐熱疲労性。
- 用途:工具、金型、熱間加工用金型
比較分析 ガス噴霧器
| 特徴 | 不活性ガス噴霧器 | 反応ガス噴霧器 | 水アトマイザー | 真空噴霧器 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粉末の純度 | 高い | 中~高 | 中程度 | 非常に高い |
| 粒子の形態学 | 球形 | 球形 | 不規則 | 球形 |
| コスト | 中~高 | 高い | 低~中程度 | 非常に高い |
| 適切な金属 | 幅広い | 特定の合金 | 反応性の低い金属 | 高純度金属 |
| 酸化防止 | 素晴らしい | グッド | 後処理が必要 | 素晴らしい |
各タイプの長所と短所
| タイプ | メリット | デメリット |
|---|---|---|
| 不活性ガス噴霧器 | 高純度、幅広い用途 | 運用コストが高く、不活性ガスの供給が必要 |
| 反応ガス噴霧器 | アトマイズ中の合金化を可能にする | 複雑性が高く、特殊なガスの取り扱いが必要 |
| 水アトマイザー | 低コスト、シンプルなセットアップ | 不規則な粒子が発生し、汚染の危険性がある |
| 真空噴霧器 | 最高純度、酸化と汚染を防ぐ | 非常に高いコスト、複雑なメンテナンス |

よくある質問
| 質問 | 回答 |
|---|---|
| ガスアトマイズとは? | ガスアトマイズは、溶融金属を高圧ガス流によって微細な液滴に分解し、金属粉末を形成するプロセスである。 |
| なぜアトマイズに不活性ガスを使うのか? | アルゴンのような不活性ガスは、金属粉末の酸化や汚染を防ぎ、高い純度と品質を保証する。 |
| ガスアトマイザーはあらゆる種類の金属に対応できますか? | ほとんどのガスアトマイザーは広範囲の金属と合金を扱うことができるが、反応性金属や高融点金属には特別なセットアップが必要な場合がある。 |
| ガスアトマイズ粉末はどのような産業に役立つか? | 航空宇宙、自動車、医療、エレクトロニクス、積層造形などの産業は、ガスアトマイズ粉末から大きな恩恵を受けている。 |
| 粒径は金属粉末の用途にどのような影響を与えるのか? | 3Dプリンティングのような精密な用途では、小さくて均一な粒子が好まれるが、従来のプロセスではより大きな粒子が使用されることもある。 |
| ガスアトマイズの環境への配慮は? | ガスアトマイゼーションは、特に金属と反応しない不活性ガスを使用する場合、他の方法に比べて環境への影響が少ない。 |
| 製造中の金属粉末の品質はどのように確保されるのですか? | 管理された雰囲気、正確なガス流量調整、製造後の粒子径と組成の厳格な検査によって品質が保証される。 |
| ガス霧化と水霧化の違いは何ですか? | ガスアトマイズは高圧ガスを使用し、より微細で球状の粉末を製造するのに対し、ウォーターアトマイズはウォータージェットを使用し、より不規則な形状を製造する。 |
| ガス噴霧技術に新しい進歩はありますか? | ノズル設計の改良、ガス流量制御の改善、デジタル・モニタリング・システムとの統合による精度の向上などだ。 |
| 自分のニーズに合ったガスアトマイザーを選ぶには? | ガスアトマイザーを選ぶ際には、金属の種類、要求される純度、粒度分布、生産能力、予算などの要素を考慮する。 |