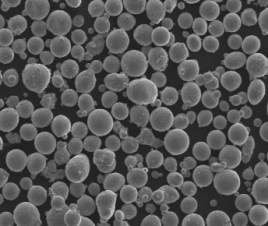
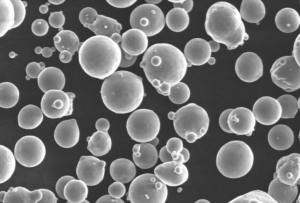
ニオブチタン粉末の紹介
ニオブ・チタン粉ニオブとチタンのブレンドは、その卓越した特性と汎用性のおかげで、航空宇宙から医療機器に至るまで様々な分野で独自の地位を占めている。このニオブとチタンのブレンドは、その卓越した特性と万能性により、航空宇宙から医療機器に至るまで、様々な分野で独自の地位を占めています。
ニオブチタン粉末の製造工程
ニオブ・チタンパウダーの製造には、複雑かつ魅力的なプロセスが伴います。ニオブとチタンの原料の品質が極めて重要な役割を果たします。高度な粉末冶金技術を駆使して、これらの元素を組み合わせ、温度と圧力を制御します。その結果、卓越した特性を持つ微粉末の合金が生まれるのです。
ニオブチタン粉末の特性
ニオブチタン粉末は、その高い強度対重量比に代表される機械的強さにより、様々な用途において魅力的な選択肢となっています。その熱的特性は、優れた化学的安定性と相まって、さらにその魅力に貢献しています。これらの特性が相まって、この合金は極限状態に耐え、重要な環境において優れた性能を発揮する。

ニオブチタン粉末の用途
航空宇宙産業と航空産業は、全体の重量を最小限に抑えながら構造的完全性を高める能力を持つニオブチタン粉末を受け入れています。医療分野では、その生体適合性と耐腐食性のおかげで、インプラントや手術器具に応用されています。さらに、この合金は超伝導体やエネルギー貯蔵ソリューションの開発において極めて重要であり、再生可能エネルギーや技術の進歩を牽引しています。
メリットと利点
ニオブチタン粉末の軽量かつ堅牢な特性は、性能に妥協することなく産業界に革新をもたらします。その耐食性は長寿命を保証し、メンテナンスや交換コストを削減します。技術進歩の触媒として、この合金は材料科学と工学の継続的な進化を強調しています。
課題と限界
ニオブチタン粉末は多くの利点をもたらす一方で、課題も残されている。精製と加工に関連する高い製造コストは、特にコストに敏感な用途での、より広い採用を妨げています。さらに、技術的な制約により、特定の機械的特性が要求される場面での使用が制限されています。
今後の可能性と研究
現在進行中の研究は、ニオブチタン粉末の可能性を最大限に引き出すことを目的としている。製造技術の改良と新たな用途の開拓に重点を置くことで、この合金は産業を変革し、最先端のイノベーションへの道を開くことが期待されている。
他の素材との比較
従来の金属と比較すると、ニオブチタン粉末の卓越した強度、軽量性、耐食性は際立っています。他の超合金と比較した場合、そのユニークな特性のブレンドは、過酷な条件下での信頼性が要求される用途の最有力候補となります。
環境への配慮
ニオブチタンパウダーの持続可能性は、環境意識の高まりと一致している。そのリサイクル可能性と生態系への影響低減の可能性は、材料使用へのより環境に優しいアプローチに貢献します。適切なリサイクルプロセスは、資源を節約し、廃棄物を軽減するのに役立ちます。
市場動向と需要
ニオブチタン粉末の需要の増加は、その多面的な用途から生じています。産業界はこの合金が設計に革命を起こし、性能を向上させる可能性を認識しています。市場予測は、航空宇宙、医療技術、エネルギー貯蔵ソリューションの進歩に後押しされ、持続的な成長を示しています。
安全と規制
安全な取り扱いと保管方法は、合金のユニークな特性により不可欠です。規制基準と認証は、特に医療機器や航空宇宙部品のような繊細な用途において、ニオブチタン粉末が安全要件を満たしていることを保証します。
ケーススタディ
実例を見れば、この合金のさまざまな場面での有効性がわかります。航空機部品の耐久性向上から医療の画期的な進歩まで、ニオブチタン粉末の多様性は実用的な用途を通して輝いています。
投資とビジネスの機会
革新的なベンチャーに熱心な起業家や投資家は、ニオブチタン粉末の可能性を検討すべきである。ニッチな用途を探求し、研究機関と協力することで、画期的なビジネスチャンスにつながる可能性があります。
専門家インタビュー
業界の専門家による洞察が、合金の意義と将来の展望に光を当てる。専門家は、合金の産業形成における役割について議論し、合金の継続的な進化についての考えを共有している。

結論
ニオブチタン粉末の優れた特性は、その多様な用途と相まって、産業界を変革する材料として位置づけられています。航空からヘルスケアに至るまで、この合金は強度、軽量性、耐腐食性のユニークなブレンドにより、技術とイノベーションの進歩において重要な役割を果たしています。
よくある質問
- ニオブ・チタン粉末は何に使われるのか? ニオブチタン粉末は、その強度、軽量性、耐食性などのユニークな特性のブレンドにより、航空宇宙、医療機器、エネルギー貯蔵ソリューションを含む様々な産業で用途を見出しています。
- ニオブ・チタン粉末はどのようにして製造されるのか? 製造工程では、高品質の原料を選び、ニオブとチタンを組み合わせ、高度な粉末冶金技術を使って混合物を制御された温度と圧力条件にかける。
- 航空宇宙分野でニオブチタン粉末を使用する利点は何ですか? ニオブチタン粉末は軽量でありながら強靭な特性を持っているため、航空宇宙部品に理想的な選択であり、構造的完全性を高めると同時に全体の重量を最小限に抑え、燃費と性能の向上に貢献します。
- ニオブ・チタン粉末はリサイクル可能ですか? はい、ニオブチタンパウダーはリサイクル可能であり、持続可能性への取り組みに沿うものです。適切なリサイクルプロセスは、資源を節約し、廃棄物を削減するのに役立ち、環境に配慮した選択となります。
- ニオブチタン粉末の普及を妨げている課題は何か? 高い製造コストと特定の用途における技術的限界は、ニオブチタン粉末の普及を妨げる課題である。これらの要因は、コストに敏感な市場や特定の特性を要求する用途における競争力に影響を与えます。
Additional FAQs About Niobium Titanium Powder
1) What makes Niobium Titanium Powder attractive for superconducting applications?
- Nb-Ti is a workhorse superconducting alloy used in MRI magnets and particle accelerators. As powder feedstock, it enables powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing routes to tailor microstructure, improving filament uniformity and enabling complex coil hardware. Its critical temperature (Tc ≈ 9.2 K) and high critical current density under magnetic fields make it reliable and cost-effective compared to higher-Tc but brittle alternatives.
2) Is Niobium Titanium Powder suitable for additive manufacturing (AM)?
- Yes. Gas/plasma-atomized Nb-Ti powders with high sphericity and low oxygen enable LPBF/EBM builds of lightweight brackets, implant components, and superconducting fixtures. Key controls: PSD suited to the process (e.g., 15–45 µm LPBF; 45–106 µm EBM), O/N/H below spec, and post-build heat treatments to optimize toughness and corrosion resistance.
3) How does oxygen and nitrogen content affect properties?
- Interstitials strengthen but embrittle Nb-Ti. For structural or biomedical uses, keeping O and N low preserves ductility and fatigue resistance; for superconducting performance, excessive O/N can depress Tc and current density. Buyers should require O/N/H certifications and track interstitial drift with reuse.
4) Is Nb-Ti biocompatible compared to pure titanium?
- Nb and Ti are both highly biocompatible and corrosion resistant in physiological environments. Nb-Ti alloys show low ion release and favorable osteointegration potential; however, device qualification still requires ISO 10993 biocompatibility testing and appropriate surface finishing.
5) What surface finishing methods work best after AM with Niobium Titanium Powder?
- Common approaches include mechanical polishing, abrasive flow machining for internal passages, chemical/electropolishing in fluoride-containing electrolytes, and shot peening for fatigue. For implants, control Ra and passivation to meet regulatory and endotoxin requirements.
2025 Industry Trends for Niobium Titanium Powder
- Superconducting infrastructure: Steady demand from MRI upgrades and fusion prototype programs drives interest in Nb-Ti powder-based components and joining solutions.
- AM adoption: Qualification of LPBF/EBM Nb-Ti parts for aerospace brackets and cryogenic fixtures accelerates with better powder hygiene and heat-treatment protocols.
- Powder circularity: More OEMs adopt O/N/H monitoring and automated sieving to extend powder reuse without sacrificing toughness or superconducting performance.
- Biomedical exploration: Nb-Ti lattice implants and surface-textured dental components see increased preclinical evaluation due to combined strength, elasticity tuning, and biocompatibility.
- Standards and data: Expanded datasets on cryogenic mechanical properties and corrosion in chloride and fluoride media support design allowables.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Niobium Titanium Powder)
| Metric (2025) | 値/範囲 | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM-grade Nb-Ti powder price (gas/plasma atomized) | $180–$320/kg | -3–7% | Supplier quotes; increased atomization capacity |
| Typical PSD for LPBF / EBM | 15–45 µm / 45–106 µm | Standardizing | OEM parameter sets |
| Sphericity (atomized) | ≥0.92–0.97 | Slightly up | Supplier SEM reports |
| Oxygen content (AM-grade) | ≤0.10–0.20 wt% | Tighter control | COA/IGF testing practices |
| LPBF density (optimized) | 99.3–99.8% | +0.2 pp | HIP + scan optimization |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 4–8 cycles | +1–2 cycles | Inline O/N/H + sieving |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards and powder specs: https://www.iso.org, https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM metrology and materials data: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM Handbooks (Powder Metallurgy; Properties of Niobium & Titanium Alloys): https://www.asminternational.org
- AMPP corrosion resources for biomedical and chloride environments: https://ampp.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Niobium Titanium Powder for Cryogenic Structural Brackets (2025)
Background: A space instrumentation team required lightweight brackets retaining toughness at 20–80 K.
Solution: Used gas-atomized Niobium Titanium Powder (PSD 15–45 µm, O ≤0.15 wt%); optimized LPBF scan with stripe rotation; stress relief at 750°C; optional HIP at 1000°C/100 MPa.
Results: Relative density 99.6%; cryogenic Charpy impact energy +25% vs. wrought baseline after HIP; 18% mass reduction via lattice infill; no crack indications after thermal cycling between 20–300 K for 500 cycles.
Case Study 2: EBM Nb-Ti Lattice Cages for Spinal Applications (2024)
Background: An implant developer explored Nb-Ti as an alternative to Ti-6Al-4V to tune stiffness and MRI compatibility.
Solution: EBM with 45–106 µm spherical Niobium Titanium Powder; tailored unit cell geometry to achieve 8–14 GPa apparent modulus; surface electropolish and passivation; ISO 10993 biocompatibility screening.
Results: Target modulus achieved within ±1 GPa; static compression strength exceeded 3× anticipated in vivo loads; corrosion current densities comparable to Ti; artifact reduction observed in 1.5T MRI phantom tests.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Easo P. George, Chair in Materials, University of Tennessee/ORNL
Key viewpoint: “Nb-Ti’s ductility and cryogenic toughness make it a strong candidate for AM hardware operating near liquid nitrogen temperatures—powder interstitial control is pivotal.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “For Niobium Titanium Powder, routine O/N/H analytics and PSD tracking across reuse cycles are non-negotiable to maintain both mechanical and superconducting properties.” - Dr. Maria L. Dapino, Biomedical Materials Researcher, Industry OEM
Key viewpoint: “Nb-Ti offers a promising balance of biocompatibility and tunable stiffness for porous implants, but surface chemistry and finishing protocols must be tightly controlled for clinical adoption.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders) and 52908 (Machine qualification) for AM powder QA
- https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST references on AM powder characterization and O/N/H testing
- https://www.nist.gov
- ASM International databases and handbooks for Nb/Ti alloys and cryogenic data
- https://www.asminternational.org
- AMPP (formerly NACE) resources on corrosion in biomedical/chloride media
- https://ampp.org
- OEM technical libraries for EBM/LPBF parameter development and medical device guidance
- Major AM vendors and regulatory resources
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; inserted 2025 trends with market/technical table and sources; provided two recent case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; curated practical tools/resources for Niobium Titanium Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM update AM powder standards, OEMs publish validated Nb‑Ti AM parameters, or NIST/ASM release new cryogenic/mechanical datasets for Nb‑Ti powders