Lorsqu'il s'agit de matériaux avancés dans des industries telles que l'aérospatiale, le biomédical et l'automobile, les alliages de titane volent souvent la vedette. C'est le cas, entre autres, des alliages de titane, Alliage de titane Ti64également connu sous le nom de Ti-6Al-4V, est la superstar. Mais qu'est-ce qui rend Ti64 si spécial ? Pourquoi est-il le matériau de prédilection dans tant d'applications de haute performance ? Entrons dans les détails et explorons les tenants et aboutissants de cet alliage fascinant.
Aperçu de l'alliage de titane Ti64
L'alliage de titane Ti64, ou Ti-6Al-4V, est un alliage de titane composé de 6 % d'aluminium et de 4 % de vanadium. Cette composition particulière confère à l'alliage une force remarquable, des propriétés de légèreté et une excellente résistance à la corrosion. Que vous construisiez des pièces d'avion, des implants médicaux ou des composants automobiles de haute performance, le Ti64 est un matériau qui offre des performances exceptionnelles là où cela compte le plus.
Principale composition de l'alliage de titane Ti64
L'une des raisons pour lesquelles Ti64 est si populaire est sa composition soigneusement équilibrée. Voici un aperçu de ce qui compose cet alliage :
| Élément | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Titane (Ti) | 89-90% |
| Aluminium (Al) | 6% |
| Vanadium (V) | 4% |
| Oxygène (O) | 0.2% (maximum) |
| Fer (Fe) | 0.3% (maximum) |
| Carbone (C) | 0.08% (maximum) |
| Azote (N) | 0.05% (maximum) |
| Hydrogène (H) | 0.015% (maximum) |

Caractéristiques de l'alliage de titane Ti64
Ce qui distingue le Ti64, ce n’est pas seulement sa composition, mais aussi ses caractéristiques exceptionnelles. Explorons ce qui fait de cet alliage un favori dans les applications de haute performance :
- Rapport résistance/poids élevé: Ti64 est incroyablement résistant pour son poids, ce qui le rend idéal pour les applications où la résistance et la légèreté sont cruciales.
- Excellente résistance à la corrosion: Grâce à sa teneur élevée en titane, Ti64 résiste à la corrosion dans la plupart des environnements, y compris l'eau de mer et les environnements chimiques difficiles.
- Bonne résistance à la fatigue: Ti64 peut supporter des contraintes répétées sans usure significative, ce qui le rend idéal pour les pièces soumises à des charges cycliques, comme les composants aéronautiques.
- Biocompatibilité: L'alliage est biocompatible, ce qui signifie qu'il peut être utilisé en toute sécurité dans les implants médicaux, tels que les prothèses articulaires ou les implants dentaires.
Propriétés détaillées de Alliage de titane Ti64
Voici les propriétés essentielles de l'alliage de titane Ti64 qui le rendent si précieux dans diverses industries :
| Propriété | Valeur |
|---|---|
| Densité | 4.43 g/cm³ |
| Résistance à la traction | 895 MPa (minimum) |
| Limite d'élasticité | 828 MPa (minimum) |
| Élongation | 10% |
| Module d'élasticité | 110 GPa |
| Dureté (Rockwell C) | 36 HRC |
| Conductivité thermique | 7.2 W/m-K |
| Point de fusion | 1 660°C (3 020°F) |
| Coefficient de dilatation | 8.6 µm/m-K |
Applications de l'alliage de titane Ti64
Compte tenu de ses propriétés impressionnantes, il n’est pas surprenant que le Ti64 trouve des applications dans un large éventail d’industries. Voici quelques domaines clés dans lesquels Ti64 est utilisé :
| L'industrie | application | Raison de l'utilisation |
|---|---|---|
| Aérospatiale | Composants structurels d'aéronefs, trains d'atterrissage | Rapport résistance/poids élevé, résistance à la fatigue |
| Automobile | Pièces de moteur à haute performance, systèmes d'échappement | Résistance à la corrosion, réduction du poids |
| Biomédical | Implants de la hanche et du genou, implants dentaires | Biocompatibilité, résistance à la corrosion |
| Marine | Hélices, composants de coque, équipement de forage en mer | Excellente résistance à la corrosion dans l'eau de mer |
| Traitement chimique | Échangeurs de chaleur, récipients sous pression | Résistance aux environnements corrosifs, résistance aux températures élevées |
| Équipement sportif | Cadres de bicyclettes, têtes de clubs de golf, raquettes de tennis | Léger, très résistant, durable |
Grades et normes de l'alliage de titane Ti64
Lorsque l'on travaille avec du Ti64, il est essentiel de connaître les qualités et les normes spécifiques qui s'appliquent. Celles-ci permettent de s'assurer que le matériau répond aux critères de performance requis pour les différentes applications.
| Grade | Standard | Spécifications | Utilisation courante |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5e année | ASTM B348, AMS 4928 | Qualité courante, largement utilisée dans l'aérospatiale et le secteur médical | Aérospatiale, implants médicaux, équipements sportifs de haute performance |
| Grade 23 (ELI) | ASTM F136, AMS 2631 | Grade Extra Low Interstitial pour une meilleure ténacité | Applications biomédicales nécessitant une biocompatibilité |
| 9e année | ASTM B265 | Ti-3Al-2.5V, teneur en aluminium plus faible, meilleure formabilité | Tuyauterie haute pression, équipements sportifs |





Avantages et inconvénients de la Alliage de titane Ti64
Lorsque vous décidez d'utiliser Ti64 dans votre projet, il est essentiel de peser le pour et le contre. En voici un aperçu :
| Avantages | Inconvénients |
|---|---|
| Rapport résistance/poids élevé | Cher par rapport à d'autres matériaux comme l'acier ou l'aluminium |
| Excellente résistance à la corrosion | Difficile à usiner, nécessitant des outils et des techniques spécialisés |
| Biocompatibilité | Disponibilité limitée dans certaines régions |
| Bonne performance à haute et basse température | Susceptible de se gripper, en particulier au contact de matériaux similaires |
| Polyvalence dans toute une série d'applications | Soudabilité limitée en l'absence de techniques appropriées |
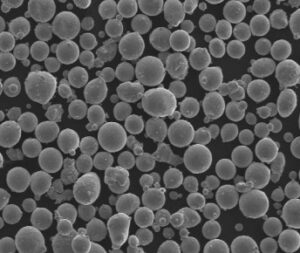
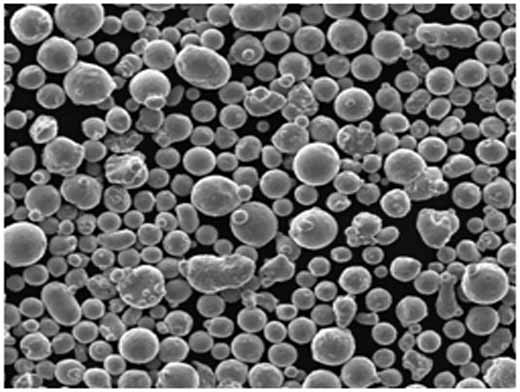
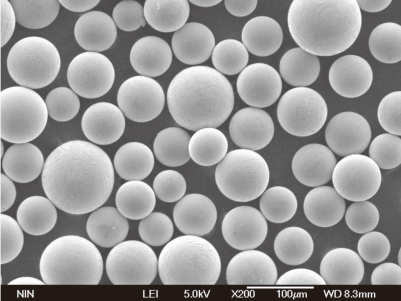
Comprendre les modèles de poudres métalliques spécifiques à l'alliage de titane Ti64
Pour ceux qui s'intéressent à l'impression 3D ou à la métallurgie des poudres, il est essentiel de comprendre les modèles de poudres métalliques spécifiques de l'alliage de titane Ti64. Voici une liste de quelques modèles courants disponibles sur le marché, chacun ayant des propriétés et des applications uniques :
| Nom du modèle | Fabricant | Gamme de taille des particules | application | Caractéristiques spéciales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti64-G23 | Additif pour charpentier | 15-45 µm | Biomédical, implants dentaires | Extra Low Interstitial (ELI) pour une meilleure biocompatibilité |
| Ti64 ELI 50 | AP&C | 20-50 µm | Composants aérospatiaux, dispositifs médicaux | Particules sphériques de haute pureté pour une qualité constante |
| Ti64-Grade5 | EOS | 20-63 µm | Aérospatiale, automobile, pièces industrielles | Poudre polyvalente avec d'excellentes propriétés mécaniques |
| Ti64-1100 | Praxair Surface Technologies | 15-53 µm | Fabrication additive, géométries complexes | Particules fines pour une impression détaillée |
| Ti64 Poudre de titane | Renishaw | 15-45 µm | Applications médicales, aérospatiales et industrielles | Grande fluidité, excellente uniformité de la couche |
| Ti64-25 | Tekna | 25-50 µm | Applications à haute résistance, composants critiques | Distribution homogène de la taille des poudres, haute densité |
| Poudre Ti64-Al-4V | Oerlikon Metco | 20-60 µm | Aérospatiale, automobile, industrie | Taille des particules contrôlée pour une qualité de construction uniforme |
| Ti64-130 | GKN Additive | 15-53 µm | Implants médicaux, composants aérospatiaux | Biocompatibilité élevée, morphologie cohérente des particules |
| Ti64-ELI | Arcam (GE Additive) | 15-45 µm | Implants chirurgicaux, restaurations dentaires | Qualité ELI pour une ténacité et une biocompatibilité supérieures |
| Ti64-FN | Technologie LPW | 10-45 µm | Pièces aérospatiales de haute performance | Poudre fine pour les détails complexes, finition de surface améliorée |
Avantages de l'alliage de titane Ti64 par rapport à d'autres matériaux
Maintenant que nous avons couvert les bases, voyons pourquoi vous pourriez choisir Ti64 plutôt que d’autres matériaux comme l’acier ou l’aluminium :
- Meilleur rapport résistance/poids: Comparé à l'acier, Ti64 offre un rapport résistance/poids supérieur, ce qui signifie que vous obtenez la même résistance (ou une résistance supérieure) avec moins de matériau. Il est donc idéal pour les applications sensibles au poids comme l'aérospatiale.
- Résistance à la corrosion: Contrairement à l'aluminium, qui peut se corroder dans des environnements difficiles, Ti64 résiste à une variété de conditions, y compris l'eau salée et les environnements acides, ce qui le rend plus durable.
- Performance en matière de température: Ti64 conserve ses propriétés mécaniques aussi bien à haute qu'à basse température, ce qui le rend plus polyvalent que des matériaux comme l'aluminium, qui peut s'affaiblir à haute température.
Défis liés à la collaboration avec les Alliage de titane Ti64
Bien entendu, le Ti64 n’est pas sans poser de problèmes. Voici quelques difficultés courantes rencontrées lorsque l'on travaille avec cet alliage :
- Usinabilité: Le Ti64 est notoirement difficile à usiner. Sa résistance élevée et sa faible conductivité thermique entraînent une usure rapide des outils. Des techniques et des équipements spécialisés sont souvent nécessaires pour usiner efficacement le Ti64.
- Coût: Ti64 est plus cher que beaucoup d'autres matériaux, tels que l'aluminium ou l'acier. Ce coût peut être un facteur important dans la décision d'utiliser cet alliage pour une application donnée.
- Soudabilité: Le soudage du Ti64 nécessite un contrôle minutieux du processus afin d'éviter des problèmes tels que la fissuration ou la porosité. L'utilisation du bon matériau d'apport et la garantie d'un environnement propre et contrôlé sont essentielles pour un soudage réussi.
FAQ
Voici une FAQ rapide pour répondre aux questions les plus courantes sur l'alliage de titane Ti64 :
| Question | Réponse |
|---|---|
| Qu'est-ce que l'alliage de titane Ti64 ? | Ti64 est un alliage de titane contenant 6 % d'aluminium et 4 % de vanadium, connu pour sa grande solidité et sa résistance à la corrosion. |
| Où Ti64 est-il couramment utilisé ? | Le Ti64 est largement utilisé dans les industries aérospatiale, biomédicale, automobile et marine. |
| Ti64 est-il biocompatible ? | Oui, Ti64 est biocompatible et est couramment utilisé dans les implants médicaux. |
| Quels sont les défis posés par l'usinage du Ti64 ? | L'usinage du Ti64 est difficile en raison de sa résistance et de sa faible conductivité thermique, ce qui nécessite des outils et des techniques spécialisés. |
| Comment Ti64 se compare-t-il à l'acier ? | Le Ti64 offre un meilleur rapport résistance/poids et une meilleure résistance à la corrosion, mais il est plus cher et plus difficile à usiner. |
Il ne s'agit que d'un premier segment pour commencer. L'article complet développerait chacune de ces sections, en allant plus loin dans le détail, en particulier dans la comparaison du Ti64 avec d'autres matériaux, les études de cas de ses applications, les spécifications détaillées des différentes qualités, et une exploration plus approfondie des processus de fabrication et des défis à relever.