Vue d'ensemble Laser Engineering Net Shaping (LENS)
Le Laser Engineering Net Shaping, communément appelé LENS, est une technique avancée de fabrication additive qui utilise des lasers de grande puissance pour créer des pièces métalliques complexes et performantes. Contrairement aux méthodes de fabrication traditionnelles, le LENS est connu pour sa capacité à construire directement des structures en 3D à partir de poudres métalliques, qui sont fondues et déposées couche par couche.
La polyvalence de la technologie LENS la rend particulièrement précieuse dans les industries nécessitant des pièces métalliques complexes aux propriétés mécaniques supérieures, telles que l'aérospatiale, la défense et les secteurs biomédicaux. Mais qu'est-ce qui distingue exactement la technologie LENS des autres méthodes de fabrication ? Et pourquoi devriez-vous envisager de l'utiliser pour votre prochain projet ? Plongeons dans le monde fascinant de la technologie LENS.

Comment fonctionne LENS ?
Imaginez que vous construisiez une sculpture, mais qu'au lieu de ciseler un bloc de pierre, vous ajoutiez de la matière couche par couche jusqu'à ce que la forme souhaitée émerge. C'est l'essence même de LENS. Voici une description étape par étape :
- Focalisation du faisceau laser: Un faisceau laser de forte puissance est focalisé sur un substrat.
- Injection de poudre métallique: La poudre métallique est injectée dans le point focal du faisceau laser à l'aide d'une buse d'injection de poudre.
- Fusion et solidification: Le laser fait fondre la poudre métallique qui, en refroidissant, se solidifie pour former une nouvelle couche.
- Construction couche par couche: Ce processus se répète au fur et à mesure que la pièce est construite couche par couche, selon un dessin généré par ordinateur.
Avantages des LENS :
- Précision: LENS peut produire des pièces aux géométries complexes et aux détails fins.
- Efficacité des matériaux: Les matériaux n'étant ajoutés que là où ils sont nécessaires, les déchets sont minimes.
- Personnalisation: Les pièces peuvent être personnalisées à la volée, ce qui est idéal pour le prototypage et la fabrication sur mesure.
Matériaux utilisés dans les lentilles : poudres métalliques
L'un des aspects les plus intéressants du procédé LENS est la large gamme de poudres métalliques qui peuvent être utilisées. Ces poudres sont spécialement conçues pour le processus LENS, ce qui garantit des performances constantes et des produits finis de haute qualité.
Poudres métalliques courantes utilisées dans les LENS
| Poudre métallique | Composition | Applications | Propriétés uniques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alliage de titane (Ti-6Al-4V) | 90% Titane, 6% Aluminium, 4% Vanadium | Aérospatiale, implants biomédicaux | Rapport résistance/poids élevé, résistance à la corrosion |
| Inconel 718 | Nickel, chrome, fer | Aérospatiale, aubes de turbines | Résistance aux températures élevées, durabilité |
| Acier inoxydable 316L | Fer, chrome, nickel | Dispositifs médicaux, Applications marines | Résistance à la corrosion, biocompatibilité |
| Aluminium 6061 | Aluminium, magnésium, silicium | Automobile, aérospatiale | Léger, bonnes propriétés mécaniques |
| Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr) | Cobalt, chrome, molybdène | Implants dentaires, Turbines à gaz | Résistance à l'usure, haute résistance |
| Acier maraging (18Ni300) | Fer, nickel, cobalt | Outillage, aérospatiale | Très haute résistance, traitement thermique facile |
| Carbure de tungstène (WC-Co) | Tungstène, Cobalt | Outils de coupe, équipement minier | Dureté extrême, résistance à l'usure |
| Alliage de cuivre (CuCrZr) | Cuivre, chrome, zirconium | Composants électriques, échangeurs de chaleur | Excellente conductivité thermique, résistance |
| Hastelloy X | Nickel, molybdène, chrome | Traitement chimique, moteurs à réaction | Résistance à l'oxydation, haute résistance |
| Acier à outils (H13) | Fer, carbone, chrome | Moules, matrices, outillage | Ténacité, résistance à l'usure |
Composition des poudres métalliques courantes pour les LENS
Lors de la sélection d'une poudre métallique pour les LENS, il est essentiel de comprendre la composition spécifique de chaque matériau, car elle influe directement sur les propriétés mécaniques et l'adéquation aux différentes applications.
Composition détaillée des poudres métalliques
| Poudre métallique | Éléments primaires | Éléments supplémentaires | Applications courantes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alliage de titane (Ti-6Al-4V) | Titane (90%) | Aluminium (6%), Vanadium (4%) | Aérospatiale, Implants médicaux |
| Inconel 718 | Nickel (50-55%) | Chrome (17-21%), Fer (5-9%) | Turbines, moteurs à réaction |
| Acier inoxydable 316L | Fer (60-65%) | Chrome (16-18%), Nickel (10-14%) | Marine, Dispositifs biomédicaux |
| Aluminium 6061 | Aluminium (97-98%) | Magnésium (0,8-1,2%), Silicium (0,4-0,8%) | Automobile, aérospatiale |
| Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr) | Cobalt (55-65%) | Chrome (26-30%), molybdène (5-7%) | Dentaire, Turbines à gaz |
| Acier maraging (18Ni300) | Fer (60-65%) | Nickel (18-20%), Cobalt (7-8%) | Outillage, aérospatiale |
| Carbure de tungstène (WC-Co) | Tungstène (85-90%) | Cobalt (6-10%) | Outils de coupe, exploitation minière |
| Alliage de cuivre (CuCrZr) | Cuivre (96-98%) | Chrome (0.5-1.2%), Zirconium (0.1-0.2%) | Électricité, échangeurs de chaleur |
| Hastelloy X | Nickel (47-52%) | Molybdène (8-10%), Chrome (20-23%) | Produits chimiques, moteurs à réaction |
| Acier à outils (H13) | Fer (85-90%) | Carbone (0,32-0,45%), Chrome (4,75-5,5%) | Moules, outillage |



Caractéristiques des composants produits dans les LENS
La technologie LENS est connue pour produire des pièces aux caractéristiques uniques qui les distinguent des pièces fabriquées par des méthodes traditionnelles. Voyons ce qui fait la spécificité de ces composants :
Principales caractéristiques des composants LENS
| Caractéristique | Description | Bénéfice |
|---|---|---|
| Haute précision | LENS peut produire des pièces avec des détails complexes et des tolérances serrées. | Idéal pour les conceptions complexes. |
| Propriétés supérieures des matériaux | Le processus LENS peut améliorer les propriétés des matériaux, telles que la résistance et la durabilité. | Meilleures performances dans les applications exigeantes. |
| Post-traitement minimal | Les pièces LENS ne nécessitent souvent que peu ou pas de post-traitement. | Réduit les délais et les coûts de production. |
| Polyvalence des matériaux | Une large gamme de poudres métalliques peut être utilisée dans les LENS. | Flexibilité dans le choix du matériau approprié pour le travail. |
| Construction couche par couche | Les pièces sont construites couche par couche, ce qui permet un contrôle précis de la forme finale. | Personnalisation et mise au point des conceptions. |
Applications de la technologie LENS
La technologie LENS est adoptée dans divers secteurs en raison de ses capacités uniques. Le tableau ci-dessous présente les principales applications de la technologie LENS dans différents secteurs :
Applications industrielles de la technologie des LENS
| L'industrie | Applications spécifiques | Avantages de l'utilisation des LENS |
|---|---|---|
| Aérospatiale | Aubes de turbines, composants structurels, réparation de pièces usées | Légèreté, composants à haute résistance, réparabilité |
| Médical | Implants sur mesure, prothèses dentaires | Matériaux biocompatibles, précision, personnalisation |
| Automobile | Composants légers, Prototypage | Prototypage rapide, efficacité des matériaux |
| Défense | Composants de blindage, systèmes d'armes | Durabilité accrue, géométries complexes |
| L'énergie | Pièces de turbines, échangeurs de chaleur, piles à combustible | Résistance aux températures élevées, efficacité des matériaux |
| Outillage | Moules, matrices, outils de coupe | Durabilité, résistance à l'usure, délais réduits |
| Pétrole et gaz | Outils de fond de puits, vannes, pompes | Résistance à la corrosion, résistance des matériaux |
| Électronique | Dissipateurs thermiques, composants conducteurs | Conductivité thermique, mécanique de précision |
| Marine | Arbres d'hélices, pièces de gouvernail, composants de pompes | Résistance à la corrosion, solidité |
| Traitement chimique | Composants de réacteurs, échangeurs de chaleur | Résistance à la corrosion, performances à haute température |
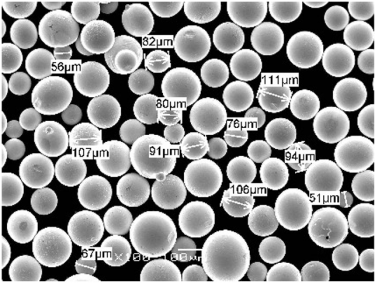
Spécifications, tailles, qualités et normes dans les LENS
Lorsque l'on travaille avec la technologie LENS, il est important de comprendre les spécifications, les tailles, les qualités et les normes associées aux poudres métalliques et aux composants.
Spécifications et normes pour les matériaux des LENS
| Matériau | Spécification/Grade | Standard | Tailles typiques |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alliage de titane (Ti-6Al-4V) | ASTM F1472, Grade 5 | ASTM International | Poudre : 15-45 µm |
| Inconel 718 | AMS 5662, UNS N07718 | SAE International | Poudre : 10-53 µm |
| Acier inoxydable 316L | ASTM A240, UNS S31603 | ASTM International | Poudre : 10-45 µm |
| Aluminium 6061 | ASTM B209, UNS A96061 | ASTM International | Poudre : 15-63 µm |
| Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr) | ASTM F75, UNS R30075 | ASTM International | Poudre : 15-45 µm |
| Acier maraging (18Ni300) | AMS 6514, UNS K93120 | SAE International | Poudre : 10-45 µm |
| Carbure de tungstène (WC-Co) | ISO 9001:2008 | Normes ISO | Poudre : 20-70 µm |
| Alliage de cuivre (CuCrZr) | ASTM B422, UNS C18150 | ASTM International | Poudre : 10-45 µm |
| Hastelloy X | AMS 5754, UNS N06002 | SAE International | Poudre : 15-53 µm |
| Acier à outils (H13) | ASTM A681, UNS T20813 | ASTM International | Poudre : 10-45 µm |
Avantages et limites des LENS
La technologie LENS offre de nombreux avantages, mais il est également important de reconnaître ses limites. Voici une comparaison :
Avantages et limites des LENS
| Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|
| Haute précision | Coût: Les LENS peuvent être coûteux en raison de l'équipement et des matériaux nécessaires. |
| Efficacité des matériaux | Complexité: Le processus est techniquement complexe et nécessite des opérateurs qualifiés. |
| Personnalisation | Finition de la surface: Les pièces peuvent nécessiter un post-traitement supplémentaire pour obtenir la finition de surface souhaitée. |
| Large gamme de matériaux | Limitation de la taille: LENS est généralement limité à des pièces plus petites en raison de la nature du processus. |
| Réparabilité | Vitesse: LENS peut être plus lent que d'autres méthodes de fabrication pour la production à grande échelle. |
| Propriétés mécaniques améliorées | Configuration initiale: Les coûts d'installation initiaux élevés peuvent constituer un obstacle pour les petites entreprises. |
Comparaison entre LENS et d'autres techniques de fabrication additive
LENS est souvent comparé à d'autres méthodes de fabrication additive telles que le frittage direct de métaux par laser (DMLS) et la fusion sélective par laser (SLM). Voyons quelles sont les différences :
LENS par rapport à d'autres méthodes de fabrication additive
| Fonctionnalité | LENTILLE | DMLS | slm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gamme de matériaux | Large gamme, y compris les alliages à haute performance | Principalement des métaux, moins de matériaux exotiques | Large gamme, similaire à LENS |
| Précision | Élevée, avec possibilité de détails fins | Très élevé, idéal pour les dessins complexes | Élevée, comparable à LENS |
| Coût | Installation coûteuse, rentable pour les pièces de grande valeur | Moyennement cher | Semblable à LENS, en fonction du matériau |
| Vitesse | Modéré, adapté aux pièces complexes | Généralement plus rapide pour les petites pièces | Plus rapide que les LENS pour certaines applications |
| Post-traitement | Minimum requis | Un peu de post-traitement est nécessaire | Nécessite un post-traitement important |
| Applications | Aérospatiale, médecine, outillage | Aérospatiale, Automobile, Médical | Aérospatiale, médecine, industrie |
Fournisseurs et détails des prix pour les matériaux LENS
Il est essentiel de savoir où s'approvisionner en matériaux LENS et quels sont les coûts associés pour établir un budget et planifier vos projets.
Fournisseurs et prix des matériaux pour LENS
| Matériau | Fournisseur | Prix approximatif par kg |
|---|---|---|
| Alliage de titane (Ti-6Al-4V) | Technologie Carpenter, Oerlikon AM | $300 – $500 |
| Inconel 718 | Praxair Surface Technologies, Sandvik | $150 – $300 |
| Acier inoxydable 316L | Sandvik, Carpenter Technology | $50 – $100 |
| Aluminium 6061 | Oerlikon AM, LPW Technology | $30 – $60 |
| Cobalt-Chrome (CoCr) | Arcam AB, Sandvik | $400 – $600 |
| Acier maraging (18Ni300) | LPW Technology, EOS GmbH | $200 – $350 |
| Carbure de tungstène (WC-Co) | H.C. Starck, Global Tungsten & Powders (en anglais) | $500 – $700 |
| Alliage de cuivre (CuCrZr) | Sandvik, Praxair Surface Technologies | $100 – $200 |
| Hastelloy X | Technologie Carpenter, Technologie LPW | $300 – $500 |
| Acier à outils (H13) | EOS GmbH, LPW Technology | $50 – $100 |
FAQ
| Question | Réponse |
|---|---|
| À quoi sert LENS ? | LENS est utilisé pour fabriquer des pièces métalliques de haute performance, réparer des composants usés et créer des prototypes. |
| En quoi LENS diffère-t-il de la fabrication traditionnelle ? | LENS construit des pièces couche par couche à partir de poudre métallique, offrant une plus grande précision et une meilleure efficacité des matériaux par rapport aux méthodes traditionnelles. |
| Quels matériaux peuvent être utilisés dans LENS ? | Une large gamme de poudres métalliques, y compris les alliages de titane, l'acier inoxydable, l'aluminium et les superalliages à base de nickel, peut être utilisée. |
| Les LENS sont-ils rentables ? | Les LENS peuvent être rentables pour les pièces complexes de grande valeur, mais peuvent être coûteux pour une production simple et à grande échelle. |
| Quels sont les secteurs qui bénéficient le plus de LENS ? | Les secteurs de l'aérospatiale, de la médecine, de l'automobile et de la défense bénéficient considérablement de la précision et de la personnalisation offertes par LENS. |
| Y a-t-il des limitations de taille avec les LENS ? | Oui, LENS est généralement plus adapté aux pièces de petite taille, bien que les progrès technologiques élargissent ses capacités. |
| Comment LENS se compare-t-il aux autres méthodes de fabrication additive ? | LENS offre des propriétés matérielles et une personnalisation supérieures, mais peut être plus lent et plus coûteux que des méthodes telles que DMLS ou SLM. |
| Quels sont les principaux défis posés par les LENS ? | Les coûts d'installation initiaux élevés, la complexité technique et la nécessité de disposer d'opérateurs qualifiés sont des défis courants. |
| Les LENS peuvent-ils être utilisés pour la production de masse ? | Si la technologie LENS est idéale pour les pièces spécialisées de grande valeur, elle n'est généralement pas utilisée pour la production de masse en raison de sa lenteur et de son coût plus élevé. |
| Quel post-traitement est nécessaire pour les pièces LENS ? | Les pièces LENS ne nécessitent généralement qu'un post-traitement minimal, bien qu'une finition de surface puisse être nécessaire en fonction de l'application. |

