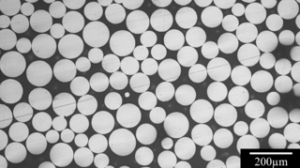
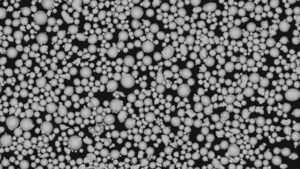
Poudres de cobalt-chromesouvent appelées poudres de CoCr, sont des matériaux essentiels dans une variété de processus de fabrication avancés, en particulier dans des industries telles que l'aérospatiale, les implants médicaux et l'automobile. Mais qu'est-ce qui rend ces poudres si spéciales ? Pourquoi sont-elles si couramment utilisées dans des applications de haute performance ? Plongeons dans le monde fascinant des poudres de cobalt-chrome, en explorant leurs propriétés, leurs applications et tout ce qu'il y a entre les deux.
Aperçu des poudres de cobalt-chrome
Les poudres de cobalt-chrome sont des alliages composés principalement de cobalt (Co) et de chrome (Cr), souvent avec de faibles ajouts d'autres éléments tels que le molybdène, le tungstène ou le carbone. Ces poudres sont réputées pour leur résistance exceptionnelle à l'usure, à la corrosion et aux températures élevées. Ces propriétés les rendent idéales pour les environnements où les matériaux sont soumis à des conditions extrêmes, comme dans la bouche (implants dentaires), dans le moteur (pales de turbine) ou même dans le corps humain (prothèses de hanche).

Composition des poudres de cobalt-chrome
La composition des poudres de cobalt-chrome peut varier en fonction des exigences spécifiques de l'application. La composition typique comprend
| Élément | Contenu (%) |
|---|---|
| Cobalt (Co) | 50-70% |
| Chrome (Cr) | 20-30% |
| Molybdène (Mo) | 5-10% |
| Tungstène (W) | 0-5% |
| Carbone (C) | 0.5-2% |
| Autres (Ni, Fe, etc.) | 0-5% |
Propriétés et caractéristiques des poudres de cobalt-chrome
Les poudres de cobalt-chrome présentent une combinaison unique de propriétés qui les rendent indispensables dans les applications de haute performance. Voici quelques-unes de leurs principales caractéristiques :
- Haute résistance à des températures élevées : Ces poudres conservent leur résistance mécanique même à des températures élevées, ce qui les rend idéales pour une utilisation dans les turbines et les moteurs.
- Excellente résistance à l'usure et à la corrosion : La présence de chrome offre une résistance exceptionnelle à la corrosion, tandis que la dureté de la matrice de cobalt assure une résistance à l'usure, parfaite pour les implants dentaires et orthopédiques.
- Biocompatibilité : Les alliages de CoCr sont biocompatibles, ce qui signifie qu'ils ne sont pas rejetés par le corps humain. Ceci est particulièrement important pour les implants médicaux.
- Résistance à la fatigue : Les alliages de cobalt-chrome peuvent résister à des contraintes répétées sans se fracturer, ce qui les rend appropriés pour les pièces soumises à des charges cycliques.
Modèles clés de Poudres de cobalt-chrome
Il existe plusieurs grades et modèles spécifiques de poudres de cobalt-chrome disponibles sur le marché, chacun étant adapté à des applications différentes. Voici un examen plus approfondi de dix modèles importants :
- CoCrMo (ASTM F75)
- Description : Il s'agit de l'alliage cobalt-chrome-molybdène le plus couramment utilisé pour les implants médicaux, en particulier pour les applications orthopédiques et dentaires.
- Propriétés : Haute biocompatibilité, résistance à la corrosion et excellente résistance à l'usure.
- CoCrW (Stellite 21)
- Description : Connu pour sa résistance exceptionnelle à l'usure, cet alliage est utilisé dans les sièges de soupapes, les roulements et les outils de coupe.
- Propriétés : Dureté élevée, excellente résistance aux températures élevées et bonne résistance à la corrosion.
- CoCrNiMo (ASTM F562)
- Description : Utilisé principalement dans les instruments chirurgicaux et les composants à haute résistance.
- Propriétés : Haute résistance, bonne ductilité et résistance à la corrosion.
- CoCrMoC (ASTM F90)
- Description : Une variante avec des ajouts de carbone pour améliorer la dureté.
- Propriétés : Résistance accrue à l'usure, convient aux applications soumises à de fortes contraintes.
- CoCrAlY (AMS 5894)
- Description : Utilisé dans les applications aérospatiales, en particulier dans les aubes de turbines.
- Propriétés : Résistance élevée à l'oxydation à des températures élevées, bonnes propriétés mécaniques.
- CoCrFeMnNi (alliage à haute entropie)
- Description : Un alliage plus récent utilisé dans des applications de recherche avancée pour ses propriétés uniques.
- Propriétés : Bonne ductilité, solidité et résistance à la corrosion.
- CoCrMoTi
- Description : L'ajout de titane améliore la biocompatibilité et réduit la densité.
- Propriétés : Léger, haute résistance à la corrosion, convient aux implants médicaux.
- CoCrSiW
- Description : Cet alliage est utilisé dans les revêtements résistants à l'usure pour les applications industrielles.
- Propriétés : Dureté élevée, excellente résistance à l'usure et bonne stabilité à haute température.
- CoCrMoNb
- Description : L'ajout de niobium renforce la solidité et la résistance à la fatigue.
- Propriétés : Propriétés mécaniques améliorées, adaptées aux composants aérospatiaux.
- CoCrZr
- Description : L'ajout de zirconium améliore la biocompatibilité et la résistance à la corrosion.
- Propriétés : Haute résistance à la corrosion, convient aux implants dentaires et orthopédiques.
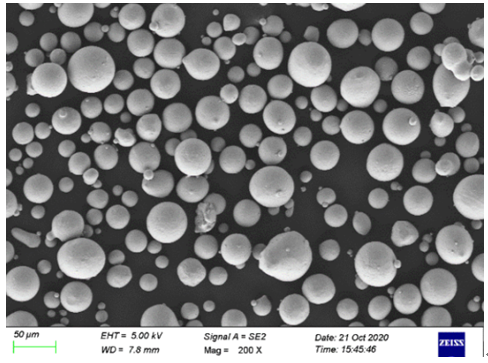
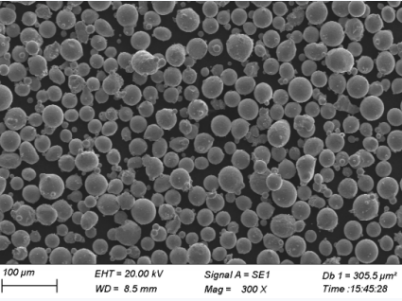
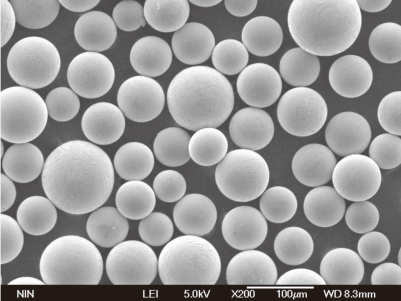
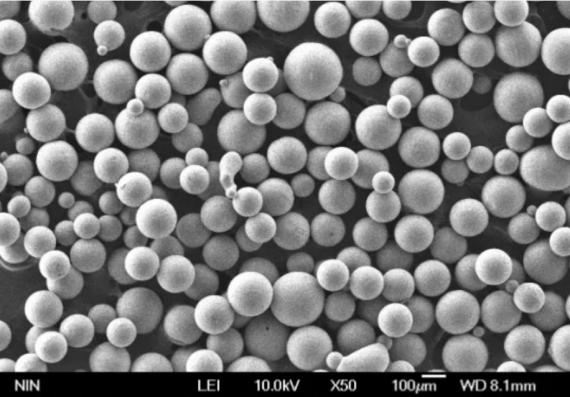
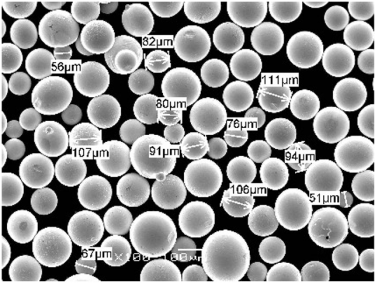
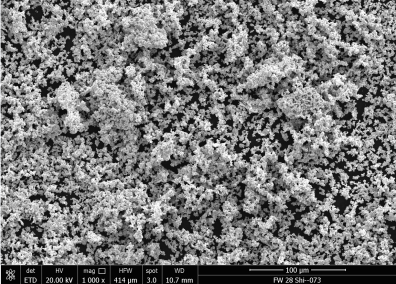
Applications des poudres de cobalt-chrome
Les poudres de cobalt-chrome sont des matériaux polyvalents utilisés dans diverses industries. Voici quelques-unes de leurs applications les plus courantes :
| application | L'industrie | Détails |
|---|---|---|
| Implants dentaires | Médical | Les alliages de CoCr sont utilisés dans les couronnes, les bridges et les armatures dentaires. |
| Implants de la hanche et du genou | Médical | En raison de leur biocompatibilité et de leur résistance à l'usure, les alliages de CoCr sont utilisés dans les prothèses articulaires. |
| Aubes de turbine | Aérospatiale | Les poudres de CoCr sont utilisées dans les moteurs à réaction en raison de leur résistance à haute température. |
| Sièges et paliers de soupapes | Automobile | Leur grande résistance à l'usure les rend idéales pour ces composants. |
| Outils de coupe | Industrie | Les alliages CoCr sont utilisés dans les outils pour leur dureté et leur durabilité. |
| Composants aérospatiaux | Aérospatiale | Utilisés dans les composants critiques soumis à de fortes contraintes en raison de leur résistance à la fatigue. |
| Prothèses | Médical | Les alliages de CoCr sont utilisés dans la production de prothèses durables et biocompatibles. |
| Revêtements résistants à l'usure | Industrie | Utilisé dans les revêtements pour prolonger la durée de vie des équipements exposés à des conditions difficiles. |
Spécifications, tailles, qualités et normes
Les poudres de cobalt-chrome sont disponibles en différentes spécifications, tailles et qualités, chacune étant adaptée à des applications spécifiques. Le tableau ci-dessous résume les principales spécifications :
| Spécifications | Grade | Taille des particules (µm) | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM F75 | Médical | 15-45 | ASTM F75 |
| AMS 5894 | Aérospatiale | 10-53 | AMS 5894 |
| ASTM F90 | Médical | 20-50 | ASTM F90 |
| Stellite 21 | Industrie | 15-63 | ASME BPVC |
| ASTM F562 | Médical | 25-45 | ASTM F562 |
| CoCrAlY | Aérospatiale | 10-50 | AMS 5894 |
| CoCrFeMnNi | Recherche | 10-45 | Sur mesure |
| CoCrMoTi | Médical | 20-45 | ISO 5832-4 |
| CoCrSiW | Industrie | 15-63 | ASME BPVC |
| CoCrMoNb | Aérospatiale | 10-50 | AMS 5894 |
Fournisseurs et prix
Le coût des poudres de cobalt-chrome varie en fonction de la qualité, de la taille des particules et du fournisseur. Voici une liste de quelques fournisseurs et de leurs prix :
| Fournisseur | Grade | Prix (USD/kg) | Pays |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technologie des charpentiers | ASTM F75 | $250 – $300 | ÉTATS-UNIS |
| Sandvik | Stellite 21 | $200 – $250 | Suède |
| Arcam AB (GE Additive) | CoCrMoTi | $300 – $350 | Suède |
| HC Starck | CoCrAlY | $400 – $450 | Allemagne |
| ATI Metals | ASTM F90 | $280 – $320 | ÉTATS-UNIS |
| Technologie LPW | CoCrFeMnNi | $350 – $400 | ROYAUME-UNI |
| EOS GmbH | ASTM F562 | $270 – $320 | Allemagne |
| Praxair Surface Technologies | CoCrSiW | $200 – $260 | ÉTATS-UNIS |
| Höganäs | CoCrMoNb | $320 – $380 | Suède |
| Kennametal | CoCrZr | $250 – $310 | ÉTATS-UNIS |
Avantages et limites de la Poudres de cobalt-chrome
Comme tout matériau, les poudres de cobalt-chrome ont leurs forces et leurs faiblesses. Explorons-les :
| Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|
| Résistance élevée à la corrosion | Coût : Le cobalt et le chrome sont des matériaux coûteux. |
| Excellente résistance à l'usure | Densité : Il est plus lourd que d'autres solutions telles que les alliages de titane. |
| Résistance à haute température | Usinabilité : Les alliages CoCr peuvent être difficiles à usiner. |
| Biocompatibilité | Disponibilité : Offre limitée par rapport aux alliages plus courants. |
| Résistance à la fatigue | Complexité de traitement : Nécessite un contrôle précis lors de la fabrication. |
| Polyvalence dans tous les secteurs d'activité | Impact sur l'environnement : L'extraction et le raffinage du cobalt peuvent avoir des conséquences importantes sur l'environnement. |

FAQ
Q1 : À quoi servent principalement les poudres de cobalt-chrome ?
A1 : Les poudres de cobalt-chrome sont principalement utilisées dans des applications de haute performance nécessitant des matériaux très solides, résistants à l'usure et à la corrosion. Elles sont largement utilisées dans les secteurs médical, aérospatial et industriel.
Q2 : Les alliages cobalt-chrome sont-ils sûrs pour les implants médicaux ?
A2 : Oui, les alliages cobalt-chrome sont biocompatibles, ce qui permet de les utiliser en toute sécurité dans les implants médicaux tels que les couronnes dentaires, les prothèses de hanche et de genou.
Q3 : Comment les poudres de cobalt-chrome se comparent-elles aux alliages de titane ?
A3 : Les poudres de cobalt-chrome offrent une meilleure résistance à l'usure et une plus grande solidité à des températures élevées que les alliages de titane. Cependant, le titane est plus léger et souvent plus facile à usiner.
Q4 : Quel est le coût typique des poudres de cobalt-chrome ?
A4 : Le coût varie en fonction de la qualité et du fournisseur, mais se situe généralement entre $200 et $450 par kilogramme.
Q5 : Quels sont les défis posés par le traitement des poudres de cobalt-chrome ?
A5 : Les défis de la transformation comprennent le coût élevé des matières premières, la complexité de l'usinage et la nécessité d'un contrôle précis pendant la fabrication afin d'éviter les défauts.
Q6 : Quelles sont les industries qui bénéficient le plus des poudres de cobalt-chrome ?
A6 : Les industries médicale et aérospatiale bénéficient considérablement de l'utilisation de poudres de cobalt-chrome en raison de leurs exigences élevées en matière de performance des matériaux.
Q7 : Les poudres de cobalt-chrome posent-elles des problèmes environnementaux ?
A7 : Oui, l'extraction et le traitement du cobalt et du chrome peuvent avoir des incidences sur l'environnement, en particulier dans les régions minières d'où proviennent ces métaux.
Q8 : Les poudres de cobalt-chrome peuvent-elles être utilisées dans l'impression 3D ?
A8 : Absolument ! Les poudres de CoCr sont couramment utilisées dans la fabrication additive pour produire des composants complexes et de haute performance.
Q9 : Comment les poudres de cobalt-chrome améliorent-elles les performances des outils de coupe ?
A9 : La résistance à l'usure et la dureté élevées des alliages CoCr en font des outils de coupe idéaux, permettant une durée de vie plus longue et des coupes plus précises.
Q10 : Quel est l'avenir des poudres de cobalt-chrome dans l'industrie manufacturière ?
A10 : Avec les progrès constants de la science des matériaux, les poudres de cobalt-chrome devraient rester essentielles dans les applications de pointe, en particulier dans la fabrication additive et l'ingénierie biomédicale.
Conclusion
Les poudres de cobalt-chrome sont plus qu'un simple mélange de métaux ; elles sont la pierre angulaire de l'ingénierie moderne et des progrès médicaux. Que ce soit dans le moteur d'un avion à réaction ou à l'intérieur du corps d'un patient, les propriétés uniques de ces poudres garantissent qu'elles répondent aux exigences rigoureuses des applications de haute performance.