Aperçu de la poudre de CoNi7
Poudre de CoNi7 est une poudre d'alliage métallique unique composée principalement de cobalt (Co) et de nickel (Ni), souvent avec des traces d'autres éléments. Cette poudre est réputée pour sa solidité exceptionnelle, sa durabilité et sa résistance aux températures élevées et à la corrosion, ce qui la rend idéale pour les techniques de fabrication avancées telles que l'impression 3D et la métallurgie des poudres. Que vous travailliez dans le secteur aérospatial, électronique ou biomédical, le CoNi7 offre une série de propriétés qui peuvent être adaptées à des applications critiques.
Principales caractéristiques de la poudre de CoNi7
Pourquoi CoNi7 ? Cette poudre combine le meilleur du cobalt et du nickel. cobalt apporte une résistance supérieure à l'usure et une stabilité à haute température. nickel ajoute de la flexibilité et de la résistance à la corrosion. Ensemble, ils créent un matériau puissant pour des besoins industriels complexes.
- Point de fusion élevé: Parfait pour les environnements à forte chaleur.
- Résistant à la corrosion: Maintient l'intégrité même dans des conditions extrêmes.
- Résistant à l'usure: Performance durable, même en cas de stress.

Types de modèles de poudre de CoNi7 et leurs spécifications
Nous présentons ci-dessous quelques-uns des modèles et spécifications les plus courants disponibles sur le marché de la poudre de CoNi7.
| Modèle | Composition | Taille des particules (μm) | Point de fusion (°C) | Densité (g/cm³) | Utilisations courantes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoNi7-100 | 70% Co, 30% Ni | 15 – 30 | 1350 | 8.4 | Fabrication additive, pièces aérospatiales |
| CoNi7-200 | 65% Co, 35% Ni | 20 – 45 | 1400 | 8.6 | Implants biomédicaux, revêtements à haute température |
| CoNi7-300 | 60% Co, 40% Ni | 10 – 20 | 1300 | 8.5 | Électronique, équipements de précision |
| CoNi7-400 | 72% Co, 28% Ni | 25 – 50 | 1360 | 8.7 | Outillage industriel, roulements soumis à de fortes contraintes |
| CoNi7-500 | 75% Co, 25% Ni | 15 – 40 | 1380 | 8.8 | Génie maritime, traitement chimique |
| CoNi7-600 | 70% Co, 28% Ni, 2% Ti | 12 – 30 | 1370 | 8.9 | Composants de moteurs aérospatiaux |
| CoNi7-700 | 68% Co, 30% Ni, 2% Mo | 20 – 35 | 1340 | 8.6 | Contacts électriques, pièces résistantes à l'usure |
| CoNi7-800 | 66% Co, 34% Ni | 18 – 25 | 1320 | 8.5 | Impression 3D, prototypage |
| CoNi7-900 | 64% Co, 36% Ni, oligo-éléments | 25 – 40 | 1330 | 8.7 | Applications automobiles, stockage d'énergie |
| CoNi7-1000 | 70% Co, 28% Ni, 2% Cr | 15 – 30 | 1385 | 8.6 | Outils et matrices à haute performance |
Propriétés et caractéristiques des Poudre de CoNi7
Il est essentiel de comprendre les propriétés physiques et chimiques de la poudre de CoNi7 pour sélectionner le bon modèle pour des applications spécifiques. Le tableau suivant présente les principales caractéristiques qui font que cette poudre convient à une variété d'utilisations industrielles.
| Caractéristique | Description |
|---|---|
| Résistance aux hautes températures | Capable de résister à des températures allant jusqu'à 1400°C, il est idéal pour les environnements soumis à une chaleur extrême. |
| Résistance à la corrosion | Offre une excellente durabilité dans les environnements corrosifs, en particulier ceux qui impliquent une exposition à des produits chimiques ou à l'humidité. |
| Densité | varie entre 8,4 et 8,9 g/cm³, selon le modèle, ce qui permet d'obtenir un équilibre entre résistance et poids. |
| Résistance à l'usure | La teneur élevée en cobalt contribue à une meilleure résistance à l'usure, prolongeant ainsi la durée de vie des composants. |
| Conductivité thermique | Une conductivité thermique plus faible permet de maintenir la stabilité dans les applications à haute température. |
Aspects uniques de la poudre de CoNi7 par rapport à d'autres alliages
En quoi la poudre CoNi7 se distingue-t-elle des autres poudres à base de cobalt ou de nickel ? Le mélange de cobalt et de nickel offre un équilibre idéal entre robustesse et flexibilité, inégalé par les poudres monométalliques. C'est comme avoir l'endurance d'un athlète avec la précision d'un chirurgien, ce qui lui confère un avantage unique dans les applications soumises à de fortes contraintes et à des températures élevées.
Applications et utilisations de la poudre de CoNi7
| Domaine d'application | Utilisations spécifiques |
|---|---|
| Aérospatiale | Composants de moteurs à réaction, aubes de turbines et autres pièces à haute température. |
| Biomédical | Implants dentaires, prothèses articulaires et outils chirurgicaux. |
| Électronique | Contacts conducteurs, composants à haute résistance dans l'électronique. |
| Automobile | Pièces soumises à une forte friction, telles que les engrenages et les arbres d'entraînement. |
| Stockage de l'énergie | Piles à combustible et autres systèmes de stockage d'énergie à haut rendement. |
| Génie maritime | Composants résistants à la corrosion pour les applications sous-marines et côtières. |
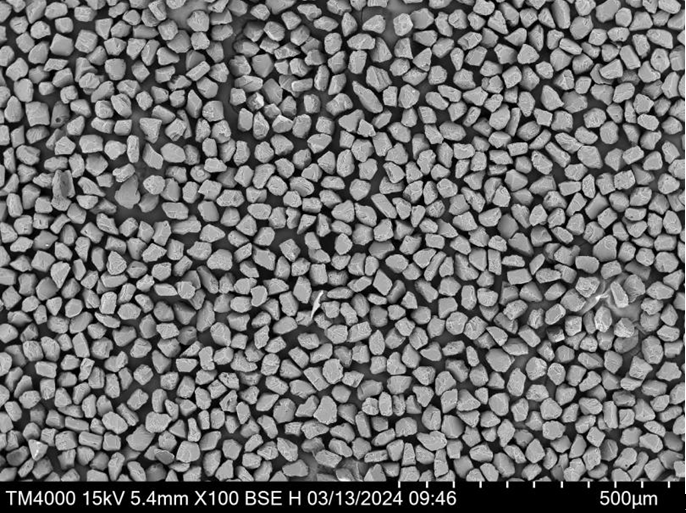


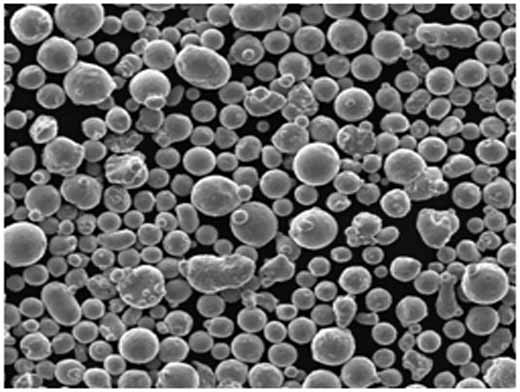


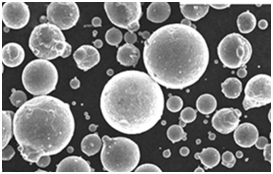



Spécifications, tailles et qualités de la poudre de CoNi7
Pour sélectionner la bonne poudre de CoNi7, il faut choisir les spécifications adéquates pour votre projet particulier. Vous trouverez ci-dessous les spécifications et les qualités typiques disponibles sur le marché.
| Spécifications | Détails |
|---|---|
| Options de notation | Industrie, biomédical, aérospatial |
| Taille des particules | Gammes de 10 à 50 μm, en fonction de l'application. |
| Niveau de pureté | Typiquement ≥99.5% pour les grades à haute performance |
| Normes respectées | ASTM F75, ISO 5832-12 (pour les applications médicales) |
Comparaison des avantages et des inconvénients de la Poudre de CoNi7
La poudre CoNi7 présente de nombreux avantages, mais aussi des limites en fonction des exigences de votre projet. En voici un aperçu :
| Aspect | Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|---|
| Durabilité | Extrêmement résistant aux fortes contraintes, il convient donc aux pièces lourdes. | Peut être surdimensionné pour des applications à faible contrainte, ce qui entraîne des coûts plus élevés. |
| Résistance à la chaleur | Contrairement à de nombreux autres alliages, il résiste bien aux températures extrêmes. | Pas toujours nécessaire pour les applications à température ambiante. |
| Coût | Le coût supérieur reflète la performance supérieure, en particulier dans les qualités aérospatiales et médicales. | Souvent plus chères que les poudres monométalliques. |
| Personnalisation | Différentes qualités et spécifications sont disponibles pour différentes industries. | Il peut être difficile de se procurer des qualités spécifiques, selon le fournisseur. |
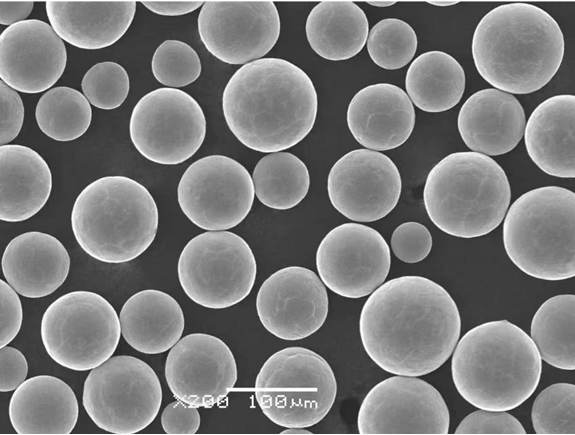
FAQ
| Question | Réponse |
|---|---|
| À quoi sert la poudre de CoNi7 ? | Il est utilisé dans les applications aérospatiales, médicales et électroniques en raison de sa durabilité et de sa résistance à la chaleur. |
| Comment la poudre de CoNi7 se compare-t-elle à la poudre de cobalt pur ? | Le CoNi7 a une meilleure flexibilité et une meilleure résistance à la corrosion, grâce à sa teneur en nickel. |
| La poudre de CoNi7 peut-elle être imprimée en 3D ? | Oui, il est couramment utilisé dans la fabrication additive de pièces complexes. |
| La poudre de CoNi7 est-elle biocompatible ? | Certaines qualités répondent aux normes de biocompatibilité pour les implants médicaux. |

