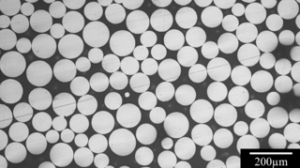
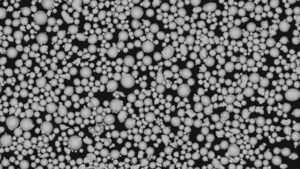
Lorsque l'on parle de matériaux de haute performance, la poudre de molybdène pur (Mo) vole souvent la vedette. Connue pour ses propriétés remarquables, telles qu'un point de fusion élevé, une excellente conductivité thermique et une résistance exceptionnelle à la corrosion, cette poudre métallique est une pierre angulaire dans diverses industries. Mais qu'est-ce qui la rend si spéciale ? Plongeons dans l'univers de la poudre de Poudre de Mo purele site Internet de la Commission européenne, qui explore ses types, ses caractéristiques, ses utilisations et bien d'autres choses encore.
Aperçu de la poudre de Mo pure
La poudre de Mo pur est une forme raffinée de molybdène, un métal de transition essentiel. Il est largement reconnu pour sa durabilité et sa résistance aux conditions extrêmes. Les ingénieurs et les fabricants l'apprécient pour sa capacité à maintenir l'intégrité structurelle sous une chaleur intense, ce qui en fait un choix de premier ordre dans les secteurs de l'aérospatiale, de l'électronique et de l'énergie.
Caractéristiques principales de Pure Mo Powder:
- Point de fusion élevé: Plus de 2 600°C (4 700°F), ce qui le rend adapté aux applications à haute température.
- Conductivité thermique et électrique: Assure un transfert d'énergie efficace.
- Résistance à la corrosion: Protège contre les réactions chimiques dans les environnements difficiles.
- Faible dilatation thermique: Réduit les risques de déformation dans les machines de précision.
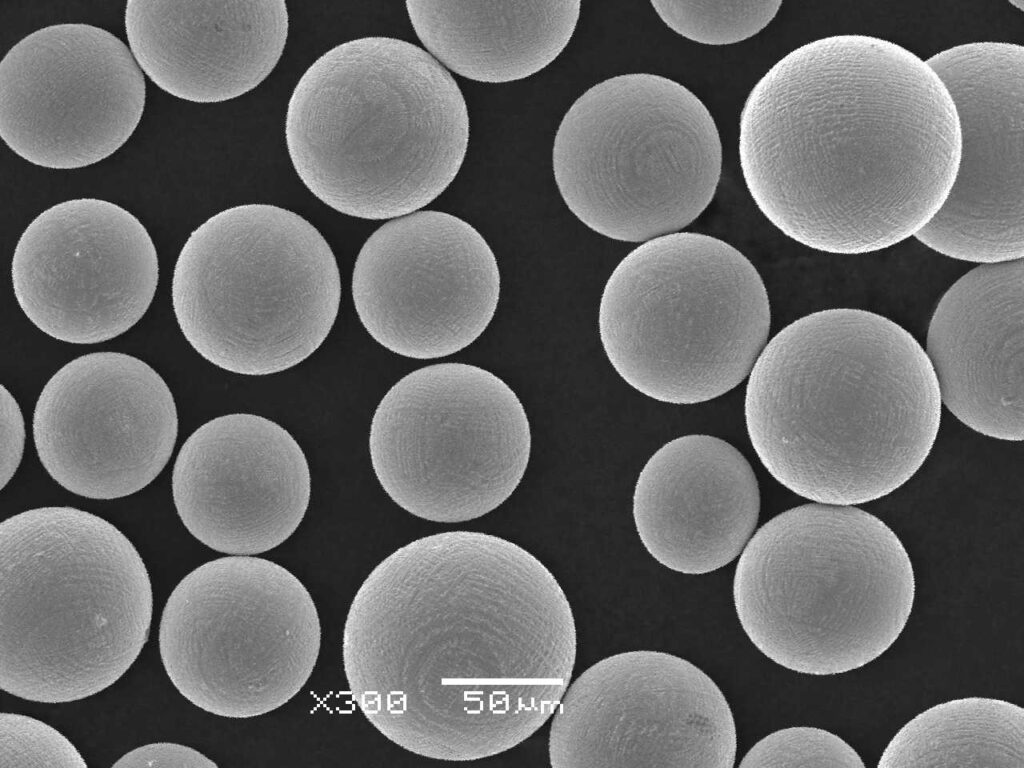

Types de modèles de poudre de Mo pure
Voici une ventilation des modèles spécifiques de poudre Pure Mo, chacun étant conçu pour des applications uniques :
| Modèle | Composition | Propriétés principales | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mo-100 | Molybdène pur | Grande pureté, faibles niveaux d'impureté | Électronique, revêtements par pulvérisation thermique |
| Mo-110 | Mo + 0,5 % de titane | Amélioration du raffinement des grains, meilleure ductilité | Composants aérospatiaux, tuyères de missiles |
| Mo-Spray | Mo de haute pureté | Particules fines, excellente fluidité | Pulvérisation thermique, revêtements pour aubes de turbines |
| Mo-Cu50 | Mo + 50 % de cuivre | Conductivité thermique améliorée, usinabilité | Dissipateurs thermiques, emballages électroniques |
| Mo-TZM | Mo + Ti + Zr + Carbone | Résistance supérieure, résistance au fluage | Pièces de four, réacteurs nucléaires |
| Mo-L | Molybdène à faible teneur en oxygène | Réduction du risque d'oxydation | Fabrication de semi-conducteurs |
| Nano-Mo | Nanoparticules de poudre de Mo | Surface extrêmement élevée | Catalyseurs, stockage de l'énergie |
| Mo-HighFlow | Mo avec grain optimisé | Propriétés d'écoulement supérieures pour la fabrication additive | impression 3D, composants de haute précision |
| Mo-AG | Alliage de Mo avec traces d'Ag | Propriétés anti-galling | Systèmes mécaniques sans lubrification |
| SuperMo-HT | Mo à haute température | Résistance accrue à la chaleur, déformation minimale | Fours à haute température, creusets |
Composition des Poudre de Mo pure
La poudre de Mo pure est principalement composée de molybdène, avec des niveaux variables d'additifs en fonction du modèle spécifique. Voici un aperçu de sa composition typique :
| Élément | Gamme typique (%) | Objectif |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdène (Mo) | 99.9%+ | Élément structurel principal |
| Oxygène (O) | < ; 0.02% | Contrôlé pour une meilleure résistance à la corrosion |
| Carbone (C) | < ; 0.01% | Maintient la pureté, réduit la fragilité |
| Titane (Ti) | 0-0,5 % (dans les alliages) | Raffinement des grains, ductilité accrue |
| Zirconium (Zr) | 0-0,2% (en TZM) | Renforce la structure du grain |
| Cuivre (Cu) | Jusqu'à 50 % (dans les alliages Mo-Cu) | Améliore l'usinabilité et la conductivité |
Caractéristiques de la poudre de Mo pure
Les caractéristiques uniques de la poudre de Mo pur la distinguent dans le monde des matériaux avancés :
| Caractéristique | Description |
|---|---|
| Point de fusion | L'une des températures les plus élevées parmi les métaux, plus de 2 600°C, ce qui permet de l'utiliser dans des applications de chaleur extrême. |
| Densité | Environ 10,28 g/cm³, offrant une intégrité structurelle robuste dans des espaces compacts. |
| Conductivité thermique | Élevé (138 W/m-K), ce qui facilite la dissipation efficace de la chaleur dans les composants électroniques. |
| Résistance à la corrosion | Résistant à l'oxydation et aux réactions chimiques, même dans des environnements acides ou basiques difficiles. |
| Faible dilatation thermique | Garantit la stabilité dimensionnelle en cas de fluctuations de température, idéal pour la mécanique de précision. |
| Usinabilité | Lorsqu'il est allié, il devient plus facile à usiner, ce qui lui confère une grande polyvalence pour les conceptions complexes. |
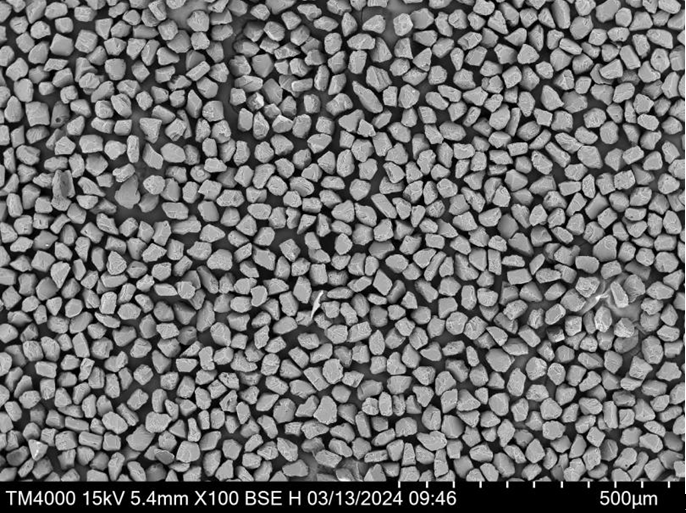
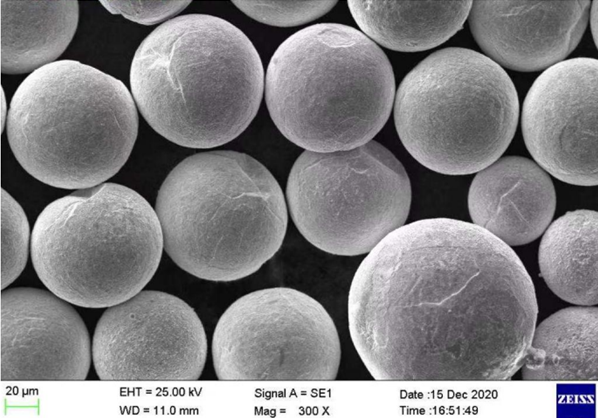
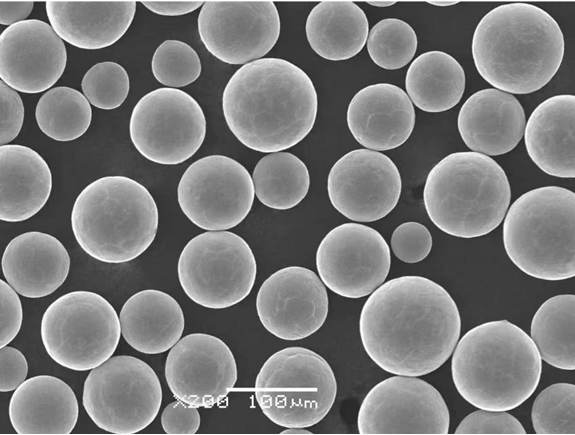



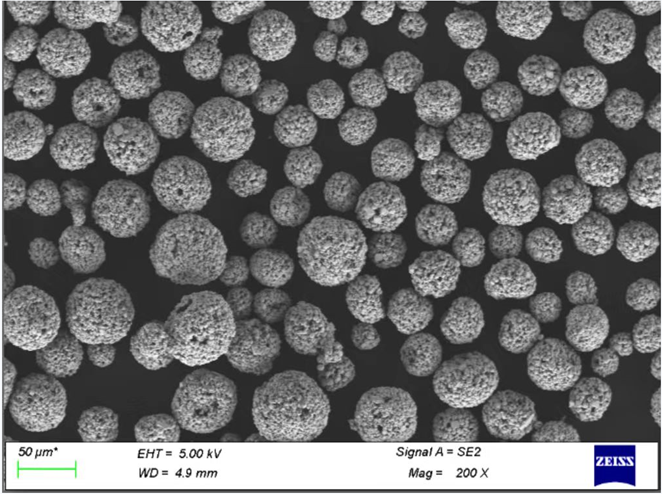

Applications de la poudre de Mo pure
La poudre de Mo pur est utilisée dans de nombreuses applications, allant de la haute technologie à l'industrie :
| application | Rôle de la poudre de Mo pure |
|---|---|
| Aérospatiale | Composants tels que les pales de turbines et les tuyères de fusées, grâce à une résistance élevée à la chaleur. |
| Électronique | Dissipateurs thermiques et semi-conducteurs pour une gestion thermique efficace. |
| L'énergie | Utilisé dans les réacteurs nucléaires et comme matériau dans les panneaux solaires. |
| Médical | Protection contre les rayonnements dans les appareils de radiologie et de traitement du cancer. |
| Industrie | Fours à haute température, outils de coupe et revêtements pour la résistance à l'usure. |
| Automobile | Pièces pour moteurs diesel et composants pour véhicules électriques. |
| Catalyse | Poudre de Nano-Mo pour les réactions chimiques et la production d'hydrogène. |
| Fabrication additive | impression 3D de pièces à haute résistance et résistantes à la température. |
Spécifications, tailles et normes
Voici un résumé des spécifications communes pour Poudre de Mo pure:
| Spécifications | Détails |
|---|---|
| La pureté | 99.9% à 99,99% |
| Taille des particules | Nano (10-50 nm), Micro (1-100 µm), Macro (>100 µm) |
| Normes | ASTM B387, ISO 9001 |
| Options d'emballage | 1kg, 5kg, 10kg, conteneurs en vrac |
| Variantes de grade | Mo, TZM, Mo-Cu, Nano-Mo |
Comparaison : Avantages et limites
| Aspect | Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|---|
| Résistance à la chaleur | Gère sans effort les températures extrêmes. | Cher par rapport aux métaux de base. |
| Conductivité | Excellentes performances thermiques et électriques. | Nécessite une expertise pour l'intégration correcte de l'alliage. |
| Résistance à la corrosion | Résiste aux environnements chimiques difficiles. | Il n'est pas idéal pour les environnements de réduction. |
| Usinabilité | Facile à usiner lorsqu'il est allié. | Le Mo pur peut être cassant et doit être manipulé avec précaution. |

Fournisseurs et détails des prix
| Fournisseur | Région | Fourchette de prix (par kg) | Caractéristiques principales |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungstène et poudres à l'échelle mondiale | ÉTATS-UNIS | $200 – $350 | Poudres de molybdène de haute pureté. |
| Groupe Plansee | L'Europe | $250 – $400 | Spécialisé dans les alliages TZM et Mo-Cu. |
| H.C. Starck Tungstène | Allemagne | $300 – $450 | Offre des poudres de nano-Mo pour des applications avancées. |
| Combat de Luoyang | Chine | $150 – $300 | Prix compétitifs pour les grandes quantités. |
FAQ
| Question | Réponse |
|---|---|
| De quoi est composée la poudre Pure Mo ? | Principalement du molybdène avec un minimum d'impuretés ou d'éléments d'alliage. |
| La poudre Pure Mo peut-elle être imprimée en 3D ? | Oui, surtout avec des modèles comme Mo-HighFlow pour la fabrication additive. |
| Quelles sont les industries qui utilisent la poudre de Mo ? | Les secteurs de l'aérospatiale, de l'électronique, de la médecine, de l'automobile et de l'énergie, entre autres. |
| Comment conserver la poudre Mo ? | Conserver dans un endroit frais et sec avec une exposition minimale à l'air et à l'humidité pour éviter l'oxydation. |