Poudres métalliques réfractaires sont une partie fascinante et essentielle de la science moderne des matériaux, jouant un rôle critique dans diverses industries de haute technologie. Ces matériaux sont connus pour leur résistance exceptionnelle à la chaleur et à l'usure, ce qui les rend inestimables dans les applications exigeantes. Dans ce guide complet, nous allons plonger dans le monde des poudres métalliques réfractaires, en explorant leurs types, leurs compositions, leurs propriétés, leurs applications et bien plus encore.
Aperçu des poudres métalliques réfractaires
Les poudres de métaux réfractaires sont dérivées d'éléments qui ont des points de fusion exceptionnellement élevés et qui sont résistants à l'usure, à la corrosion et à la déformation. Ces métaux comprennent le tungstène, le molybdène, le tantale, le niobium et le rhénium. Ils sont utilisés dans des environnements qui exigent des matériaux capables de résister à des conditions extrêmes, comme l'aérospatiale, les réacteurs nucléaires et les fours à haute température.

Types de poudres métalliques réfractaires
Pour bien comprendre les poudres métalliques réfractaires, examinons de plus près certains types spécifiques et leurs propriétés uniques :
| Métal | Description |
|---|---|
| Tungstène (W) | Connu pour son point de fusion et sa densité les plus élevés, il est idéal pour les applications à haute température. |
| Molybdène (Mo) | Excellente conductivité thermique et faible dilatation thermique, utilisées dans l'électronique et l'éclairage. |
| Tantale (Ta) | Très résistant à la corrosion, il est utilisé dans les appareils médicaux et les équipements de traitement chimique. |
| Niobium (Nb) | Haute ductilité et supraconductivité, utilisé dans les superalliages et l'électronique. |
| Rhénium (Re) | Point de fusion élevé et propriétés électriques uniques, utilisés dans les moteurs à réaction et l'électronique. |
| Zirconium (Zr) | Excellente résistance à la corrosion et solidité, utilisé dans les réacteurs nucléaires et les implants médicaux. |
| Hafnium (Hf) | Absorption élevée des neutrons, utilisée dans les réacteurs nucléaires et les composants aérospatiaux. |
| Vanadium (V) | Bonne résistance mécanique et thermique, utilisé dans les superalliages et les outils. |
| Chrome (Cr) | Excellente dureté et résistance à la corrosion, utilisée dans les revêtements et les superalliages. |
| Titane (Ti) | Rapport résistance/poids élevé, utilisé dans les applications aérospatiales, médicales et industrielles. |
Composition des Poudres de métaux réfractaires
La composition des poudres de métaux réfractaires est déterminante pour leurs performances. Ces métaux sont souvent combinés à d'autres éléments pour améliorer leurs propriétés spécifiques :
| Métal | Composition | Propriétés améliorées |
|---|---|---|
| Tungstène | Pur ou allié avec Ni, Fe, Cu | Amélioration de l'usinabilité et de la résistance. |
| Molybdène | Pure ou alliée avec Ti, Zr, C | Amélioration de la résistance au fluage et de la solidité. |
| Tantale | Pure ou alliée avec W, Hf | Résistance à la corrosion et solidité accrues. |
| Niobium | Pure ou alliée avec Ti, Al | Amélioration de la supraconductivité et de la résistance. |
| Rhénium | Pur ou allié avec Mo, W | Stabilité thermique et résistance accrues. |
Caractéristiques des poudres de métaux réfractaires
Les poudres métalliques réfractaires présentent des caractéristiques uniques qui les rendent adaptées à des applications de haute performance :
- Points de fusion élevés : Indispensable pour les applications impliquant une chaleur extrême.
- Dureté exceptionnelle : Assure la durabilité et la résistance à l'usure.
- Haute densité : Contribue à la résistance et à la stabilité sous contrainte.
- Résistance à la corrosion : Garantit la longévité dans les environnements difficiles.
- Bonne conductivité thermique et électrique : Important pour l'électronique et les applications à haute température.
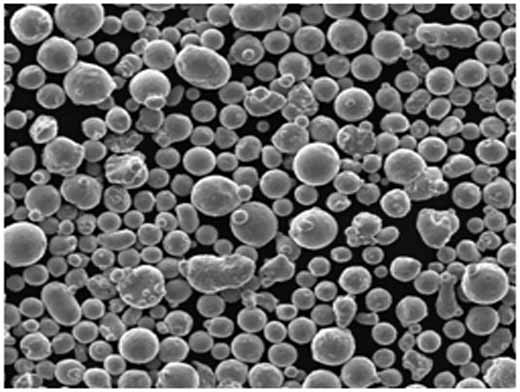


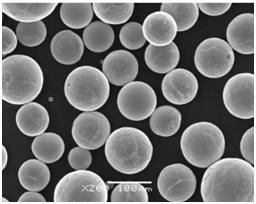


Applications des poudres métalliques réfractaires
Les poudres de métaux réfractaires sont utilisées dans diverses industries en raison de leurs propriétés remarquables :
| L'industrie | application |
|---|---|
| Aérospatiale | Composants de moteurs à réaction, tuyères de fusées, boucliers thermiques. |
| Électronique | Dispositifs semi-conducteurs, filaments, contacts. |
| Médical | Instruments chirurgicaux, implants, appareils dentaires. |
| Nucléaire | Composants du réacteur, blindage contre les radiations, gaine de combustible. |
| Traitement chimique | Équipement résistant à la corrosion, catalyseurs, cuves de réaction. |
| Industrie | Outils de coupe, moules, matrices, revêtements résistants à l'usure. |
Spécifications, tailles, qualités, normes
La compréhension des spécifications et des normes relatives aux poudres métalliques réfractaires est cruciale pour leur application :
| Métal | Tailles (microns) | Notes | Normes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungstène | 1-100 | W1, W2, W3 | ASTM B777, ISO 4497 |
| Molybdène | 1-50 | Mo1, Mo2, TZM | ASTM B386, ISO 5755 |
| Tantale | 1-40 | Ta1, Ta2 | ASTM B708, ISO 13782 |
| Niobium | 1-60 | Nb1, Nb2, Nb3 | ASTM B393, ISO 13782 |
| Rhénium | 1-20 | Re1, Re2 | ASTM B708, ISO 13782 |
Fournisseurs et détails des prix
Trouver des fournisseurs fiables et comprendre les prix est essentiel pour l'approvisionnement :
| Fournisseur | Métal | Prix (par kg) | Informations sur le contact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungstène mondial | Tungstène | $250 | [email protected] |
| Molybdène du Midwest | Molybdène | $150 | [email protected] |
| Approvisionnement en tantale | Tantale | $300 | [email protected] |
| Sources de Niobium | Niobium | $200 | [email protected] |
| Rhénium Rare | Rhénium | $400 | [email protected] |
Avantages et limites des poudres métalliques réfractaires
Si les poudres métalliques réfractaires offrent de nombreux avantages, elles présentent également certaines limites :
| Avantages | Limites |
|---|---|
| Résistance aux températures élevées | Coût élevé |
| Excellente résistance mécanique | Difficile à usiner |
| Résistance supérieure à la corrosion | Disponibilité limitée |
| Bonne conductivité électrique et thermique | Lourd et dense |
| Longue durée de vie et durable | Risques potentiels pour la santé lors de la manipulation |
Comparaison des poudres de métaux réfractaires
Lorsqu'il s'agit de choisir entre différentes poudres métalliques réfractaires, il est important de comparer leurs propriétés et leur adéquation à des applications spécifiques :
| Métal | Point de fusion (°C) | Densité (g/cm³) | Résistance à la corrosion | Conductivité thermique (W/m-K) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tungstène | 3422 | 19.25 | Excellent | 173 | Aérospatiale, électronique, éclairage |
| Molybdène | 2623 | 10.28 | Bon | 138 | Électronique, fusion du verre, éclairage |
| Tantale | 3017 | 16.65 | Supérieure | 57 | Dispositifs médicaux, traitement chimique |
| Niobium | 2477 | 8.57 | Bon | 54 | Superalliages, électronique, médical |
| Rhénium | 3186 | 21.02 | Excellent | 48 | Moteurs à réaction, électronique, chimie |
Analyse détaillée d'un projet spécifique Poudres de métaux réfractaires
Nous allons maintenant approfondir les spécificités de certaines poudres métalliques réfractaires clés, en mettant en évidence leurs propriétés, applications et avantages uniques.
poudre de tungstène
La poudre de tungstène est réputée pour son point de fusion et sa densité incroyablement élevés. Elle est donc idéale pour les applications qui exigent que les matériaux résistent à des températures et à des contraintes mécaniques extrêmes. Le tungstène est couramment utilisé dans l'aérospatiale pour les composants des moteurs à réaction, dans l'électronique pour les filaments et dans les appareils médicaux pour le blindage contre les radiations.
Poudre de molybdène
La poudre de molybdène est connue pour son excellente conductivité thermique et sa faible dilatation thermique. Ces propriétés en font un matériau adapté aux applications électroniques, telles que les dissipateurs thermiques et les transistors, ainsi qu'aux industries de l'éclairage et de la fusion du verre. La capacité du molybdène à conserver sa résistance à des températures élevées est un avantage clé.
poudre de tantale
La poudre de tantale se distingue par sa résistance supérieure à la corrosion. Cela lui confère une valeur inestimable dans le traitement chimique et les applications médicales. Le tantale est souvent utilisé dans les instruments chirurgicaux, les implants et les équipements qui manipulent des substances hautement corrosives. Sa capacité à résister à la corrosion est un gage de longévité et de fiabilité.
poudre de niobium
La poudre de niobium se distingue par sa grande ductilité et sa supraconductivité. Cela en fait un composant essentiel des superalliages utilisés dans l'aérospatiale et l'électronique. Les propriétés supraconductrices du niobium sont utilisées dans les appareils d'imagerie médicale et les accélérateurs de particules, où le maintien de basses températures et de performances efficaces est crucial.
Poudre de rhénium
La poudre de rhénium est appréciée pour son point de fusion élevé et ses propriétés électriques uniques. Elle est utilisée dans les moteurs à turbine à haute température et dans l'électronique qui nécessitent des matériaux capables de résister à des conditions extrêmes. La stabilité thermique et la résistance exceptionnelles du rhénium en font un matériau essentiel dans les environnements exigeants.
Analyse comparative : Tungstène et molybdène
Si l'on compare le tungstène au molybdène, les deux métaux offrent une résistance aux températures élevées, mais le point de fusion plus élevé du tungstène (3422°C contre 2623°C) lui confère un avantage dans les applications à ultra-haute température. Cependant, la conductivité thermique supérieure du molybdène et sa densité plus faible en font un meilleur choix pour les applications nécessitant une dissipation efficace de la chaleur et un poids plus léger.
Analyse comparative : Tantale et Niobium
Le tantale et le niobium excellent tous deux dans la résistance à la corrosion, mais la densité plus élevée du tantale (16,65 g/cm³ contre 8,57 g/cm³) le rend plus adapté aux applications où le poids est moins important et où une résistance maximale à la corrosion est requise. La ductilité élevée et la supraconductivité du niobium en font le choix préféré pour les applications électroniques et aérospatiales de pointe.
Analyse comparative : Rhénium et tungstène
Le rhénium et le tungstène sont tous deux utilisés dans des applications à haute température, mais les propriétés électriques uniques du rhénium et son prix plus élevé le rendent idéal pour l'électronique spécialisée et les moteurs à réaction. La densité plus élevée et le coût plus faible du tungstène le rendent plus pratique pour les applications générales à haute température et à haute résistance.

FAQ
| Question | Réponse |
|---|---|
| Que sont les poudres métalliques réfractaires ? | Les poudres métalliques réfractaires sont des matériaux ayant un point de fusion élevé et une résistance exceptionnelle à la chaleur, à l'usure et à la corrosion. |
| Quelles sont les applications courantes des poudres métalliques réfractaires ? | Ils sont utilisés dans l'aérospatiale, l'électronique, les appareils médicaux, les réacteurs nucléaires et les équipements de traitement chimique. |
| Comment les poudres de métaux réfractaires sont-elles produites ? | Ils sont généralement produits par des procédés tels que l'alliage mécanique, le dépôt chimique en phase vapeur et la réduction des oxydes métalliques. |
| Quelles sont les principales propriétés de la poudre de tungstène ? | La poudre de tungstène est connue pour son point de fusion élevé, sa densité et sa résistance, ce qui la rend idéale pour les applications à haute température. |
| Pourquoi la poudre de molybdène est-elle utilisée en électronique ? | La poudre de molybdène présente une excellente conductivité thermique et une faible dilatation thermique, ce qui la rend appropriée pour les dissipateurs thermiques et les composants électroniques. |
| Qu'est-ce qui rend la poudre de tantale résistante à la corrosion ? | La poudre de tantale possède une couche d'oxyde protectrice qui résiste à la corrosion, même dans des environnements chimiques difficiles. |
| Comment la poudre de niobium est-elle utilisée dans les applications aérospatiales ? | La poudre de niobium est utilisée dans les superalliages pour les moteurs à réaction et d'autres composants aérospatiaux de haute performance en raison de sa résistance et de sa ductilité élevées. |
| Quels sont les avantages de l'utilisation de la poudre de rhénium dans l'électronique ? | La poudre de rhénium offre des propriétés électriques uniques et une grande stabilité thermique, ce qui la rend idéale pour les composants électroniques de haute performance. |
| La manipulation de poudres métalliques réfractaires présente-t-elle des risques pour la santé ? | Oui, certaines poudres de métaux réfractaires peuvent présenter des risques pour la santé en cas d'inhalation ou d'ingestion. Des mesures de sécurité appropriées doivent être prises lors de la manipulation et de la transformation. |
| Où puis-je acheter des poudres de métaux réfractaires ? | Les poudres de métaux réfractaires peuvent être achetées auprès de fournisseurs spécialisés tels que Global Tungsten, Midwest Molybdenum, Tantalum Supply, Niobium Sources et Rhenium Rare. |
Conclusion
Le choix de la poudre de métal réfractaire appropriée dépend des exigences spécifiques de votre application. Prenez en compte des facteurs tels que le point de fusion, la conductivité thermique, la résistance à la corrosion, la densité et le coût. La compréhension de ces propriétés vous aidera à prendre une décision éclairée et à garantir la réussite de votre projet.

