Poudre de TiCou poudre de carbure de titane, est un matériau essentiel dans diverses industries en raison de sa dureté exceptionnelle, de sa résistance à l'usure et de sa stabilité à haute température. Que vous travailliez dans l'aérospatiale, l'automobile ou l'industrie des outils de coupe, la poudre de TiC joue un rôle crucial dans l'amélioration des performances et de la durabilité. Ce guide complet se penche sur tous les aspects de la poudre de TiC - sa composition, ses caractéristiques, ses applications, ses avantages et ses spécifications - tout en explorant les modèles spécifiques disponibles sur le marché. Vous trouverez également des comparaisons détaillées et des FAQ qui vous permettront de mieux comprendre la poudre de TiC et son importance dans différentes industries.
Aperçu de la poudre de TiC
La poudre de carbure de titane (TiC) est un type de poudre céramique d'une dureté et d'une résistance à l'usure et à la corrosion exceptionnelles. Étant l'un des matériaux connus les plus durs, le TiC est souvent utilisé dans des applications de haute performance telles que les outils de coupe, les abrasifs, les revêtements et comme additif dans les composites à matrice métallique. Ses propriétés en font un matériau idéal pour les environnements exposés à des conditions extrêmes, telles que les températures élevées, l'usure importante et les environnements corrosifs.
La poudre de TiC est souvent synthétisée par divers procédés chimiques, généralement à l'aide de tétrachlorure de titane (TiCl4) et de sources de carbone à des températures élevées. La poudre de TiC obtenue peut être adaptée à différentes applications industrielles en fonction de facteurs tels que la taille des particules, la pureté et la composition.
Principales caractéristiques de la poudre de TiC
- Dureté: Le TiC est connu pour son extrême dureté, qui dépasse celle de nombreux autres matériaux. Il se classe à 9 sur l'échelle de dureté de Mohs, ce qui le rend approprié pour les outils de coupe, les abrasifs et les revêtements.
- Stabilité thermique: La poudre de TiC peut résister à des températures élevées, conservant son intégrité structurelle même en cas de chaleur extrême, ce qui en fait un matériau idéal pour les applications à haute température telles que les moteurs à réaction.
- Résistance à l'usure: En raison de sa dureté, la poudre de TiC est très résistante à l'abrasion et à l'usure. Cela en fait un excellent choix pour les machines à usage intensif, l'exploitation minière et les composants automobiles.
- Résistance à la corrosion: Le TiC présente une excellente résistance à la corrosion, en particulier dans les environnements à haute température et chimiquement agressifs, ce qui garantit la longévité des pièces et des composants.
- Conductivité électrique: Le TiC est également un bon conducteur d'électricité, ce qui le rend précieux pour les contacts électriques, les résistances et d'autres applications électroniques.
Composition des Poudre de TiC
La poudre de carbure de titane est principalement composée de deux éléments : le titane (Ti) et le carbone (C). La composition précise de la poudre peut varier en fonction de la méthode de production, mais le rapport entre le Ti et le C reste relativement constant, à savoir 1:1. Voici la composition de la poudre de TiC :
| Élément | Symbole | Pourcentage en poids | Rôle dans la composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| titane | Ti | ~50% | Assure la dureté et la stabilité thermique |
| Carbone | C | ~50% | Contribue à une dureté et une résistance à l'usure élevées |
Outre ces deux éléments primaires, la poudre de TiC peut également contenir des traces d'autres éléments tels que l'oxygène, l'azote ou des impuretés métalliques en fonction du processus de synthèse.
Types de poudre de TiC et modèles spécifiques
La poudre de TiC se décline en plusieurs types et qualités, chacun optimisé pour des applications industrielles différentes. Ces variations dépendent de facteurs tels que la taille des particules, la pureté et des propriétés spécifiques telles que la résistance à l'usure ou la conductivité électrique.
Voici dix modèles populaires de poudre TiC et leurs caractéristiques spécifiques :
| Modèle de poudre de TiC | Description | Taille des particules (μm) | Pureté (%) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poudre de TiC standard | Poudre TiC à usage général avec des propriétés équilibrées | 10-50 | 99 | Outils de coupe, revêtements résistants à l'usure |
| Poudre de TiC ultra-fine | Poudre avec une taille de particule plus petite pour des revêtements de haute performance | 1-5 | 99.5 | Nanocoatings, matériaux abrasifs |
| Poudre recouverte de TiC | Revêtement en poudre de TiC avec d'autres matériaux pour une meilleure résistance à l'usure | 5-25 | 99.8 | Outillage industriel, applications de rectification |
| Poudre de TiC de haute pureté | Poudre de TiC ultra-pure avec un minimum d'impuretés | 10-30 | 99.9 | Aérospatiale, militaire, environnements à haute température |
| Poudre nanométrique de carbure de titane | Particules de TiC nanométriques aux propriétés améliorées | <1 | 99 | Électronique, fabrication avancée |
| Poudre composite TiC-métal | Poudre composite combinant TiC et métaux pour une plus grande robustesse | 20-40 | 97 | Composites à matrice métallique, pièces automobiles |
| Poudre sphérique de TiC | Poudre de TiC de forme sphérique pour une meilleure fluidité et un meilleur frittage | 15-45 | 99.5 | Impression 3D, métallurgie des poudres |
| TiC pour la poudre de rechargement | Conçu pour les revêtements résistants à l'usure dans les machines à usage intensif | 30-60 | 98 | Exploitation minière, construction, machines |
| Poudre composite à base de TiC | Poudre combinée à d'autres matériaux céramiques pour une résistance accrue | 10-50 | 98.5 | Revêtements haute performance, applications militaires |
| Poudre de carbonitrure de titane (TiCN) | TiC combiné à l'azote pour une meilleure résistance à l'usure et à la corrosion | 20-50 | 99 | Outils de coupe, industries abrasives |
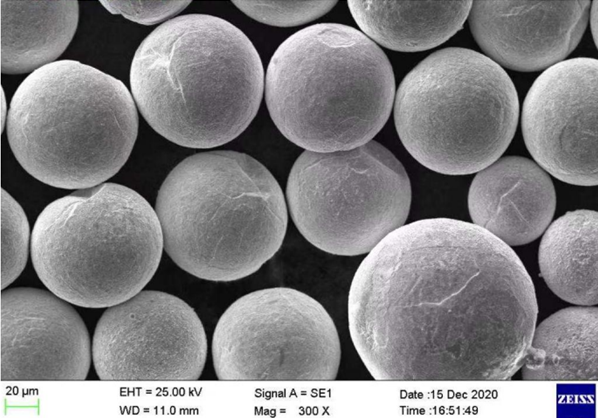
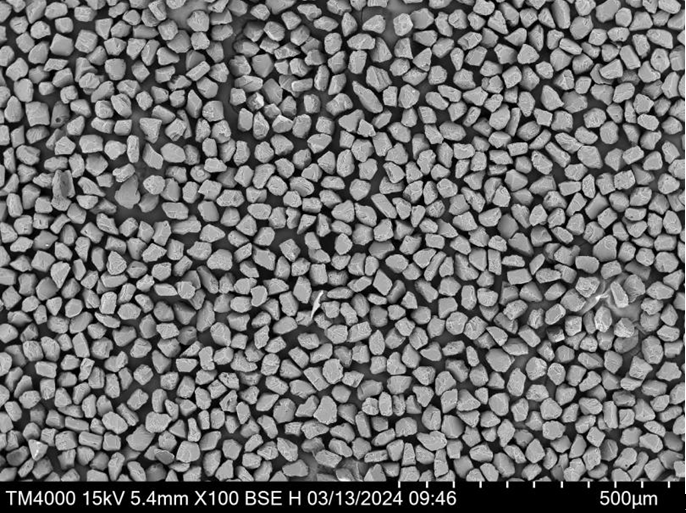




Applications de la poudre de TiC
La poudre de TiC est utilisée dans un large éventail d'industries en raison de sa dureté et de sa durabilité remarquables. Voici quelques-unes des principales applications de la poudre de TiC, classées par industrie :
Applications industrielles
| L'industrie | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aérospatiale | Revêtements haute performance, composants de moteurs, boucliers thermiques |
| Automobile | Plaquettes de frein, revêtements résistants à l'usure pour moteurs et engrenages |
| Exploitation minière | Outils de coupe, forets, matériaux de rechargement |
| Travail des métaux | Outils d'usinage CNC, outils de coupe, plaquettes et matériaux abrasifs |
| Électronique | Revêtements conducteurs, contacts électriques, résistances |
| L'énergie | Composants à haute température pour centrales électriques, aubes de turbines et réacteurs |
Applications médicales et biotechnologiques
| application | Détails |
|---|---|
| Implants médicaux | Revêtements à base de TiC pour améliorer la résistance à l'usure des implants orthopédiques |
| Biocompatibilité | En raison de la nature inerte du TiC, il peut être utilisé pour des applications médicales à long terme. |
Spécifications, tailles et qualités des Poudre de TiC
Lors de la sélection de la poudre de TiC, il est important de prendre en compte des spécifications telles que la taille des particules, la qualité et la pureté. Voici un aperçu des principales spécifications et tailles disponibles :
| Spécifications | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Taille des particules | Taille des particules de poudre | 1-100 μm |
| La pureté | La quantité d'impuretés dans la poudre de TiC | 97%-99.9% |
| Densité | Masse par unité de volume de la poudre | 4,9-5,1 g/cm³ |
| Dureté | La capacité de la poudre de TiC à résister à l'indentation | 9 sur l'échelle de Mohs |
| Point de fusion | Température de fusion de la poudre de TiC | 3,300°C |
| Grade | La classification de la qualité en fonction de la pureté et de la taille | Élevé, Moyen, Faible |
Fournisseurs et informations sur les prix de la poudre de TiC
La poudre de TiC est disponible auprès de plusieurs fournisseurs, chacun proposant des qualités, des tailles et des prix différents. Voici un bref aperçu des fournisseurs de poudre de TiC et des fourchettes de prix habituelles :
| Fournisseur | Grade | Fourchette de prix | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | Haute pureté | $500-$1500 par kg | Recherche, applications de haute performance |
| H.C. Starck | Pureté moyenne | $300-$700 par kg | Revêtements industriels, composites à matrice métallique |
| Éléments américains | Faible pureté | $200-$500 par kg | Utilisation industrielle en vrac, abrasifs |
| Matériaux avancés | Ultra fin | $1000-$3000 par kg | Nanocouches, fabrication avancée |
| Treibacher Industrie | Grade standard | $250-$600 par kg | Outils de coupe, matériaux de rechargement |
Avantages et inconvénients de la poudre de TiC
Comme tout matériau, la poudre de TiC a ses forces et ses faiblesses. Examinons les avantages et les limites de l'utilisation de la poudre de TiC dans diverses applications.
| Pour | Cons |
|---|---|
| Dureté et résistance à l'usure exceptionnelles | Cher par rapport à d'autres matériaux |
| Stabilité thermique élevée pour les températures extrêmes | Peut être difficile à transformer en formes complexes |
| Résistance à la corrosion dans les environnements difficiles | Peut nécessiter un équipement spécialisé pour la manipulation et la synthèse |
| Peut être utilisé dans diverses industries | Flexibilité limitée en termes d'application pour certains dessins ou modèles |

FAQ
| Question | Réponse |
|---|---|
| Quel est le point de fusion de la poudre de TiC ? | La poudre de TiC a un point de fusion d'environ 3 300°C. |
| La poudre de TiC est-elle utilisée dans l'impression 3D ? | Oui, la poudre sphérique de TiC est souvent utilisée dans les processus d'impression 3D. |
| Comment le TiC se compare-t-il au carbure de tungstène ? | Le TiC est généralement plus dur mais plus fragile que le carbure de tungstène, ce qui le rend plus adapté aux revêtements et aux applications résistantes à l'usure. |
| Quels sont les principaux avantages de la poudre de TiC dans les applications industrielles ? | Ses principaux avantages sont sa dureté, sa résistance à l'usure et sa stabilité thermique, ce qui le rend idéal pour les environnements difficiles. |
| La poudre TiC peut-elle être utilisée dans des applications aérospatiales ? | Oui, la poudre de TiC est largement utilisée dans les applications aérospatiales en raison de sa résistance aux températures élevées et de sa durabilité. |
Conclusion
La poudre de TiC est un matériau incroyablement polyvalent utilisé dans de nombreuses industries, de l'aérospatiale à l'exploitation minière en passant par l'automobile. Grâce à sa dureté, sa résistance à l'usure et sa stabilité thermique remarquables, la poudre de TiC est essentielle pour créer des composants de haute performance capables de résister à des conditions extrêmes.