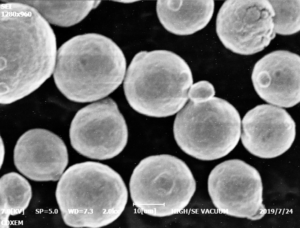
لمحة عامة عن مسحوق النيكل الموليبدينوم
مسحوق النيكل الموليبدينوم عبارة عن مسحوق سبيكة معدنية تتكون من النيكل والموليبدينوم. وهو يوفر مزيجًا فريدًا من الخصائص بما في ذلك القوة العالية ومقاومة التآكل ومقاومة التآكل والقدرة على تحمل درجات الحرارة العالية.
بعض التفاصيل الأساسية حول مسحوق الموليبدينوم النيكل:
- التركيب –؛ يحتوي عادةً على 60-70% نيكل و30-40% موليبدينوم بالوزن. يمكن تخصيص نسب محددة.
- طريقة الإنتاج –؛ عادةً ما يتم تصنيعها عن طريق السبك المسبق وتذرية النيكل والموليبدينوم لتكوين مسحوق متجانس ناعم.
- حجم الجسيمات –؛ يتراوح بين 10-150 ميكرون حسب الاستخدام. توفر المساحيق الأدق خصائص أكثر اتساقًا.
- الشكل –؛ تتيح جزيئات المسحوق الكروية كثافة تعبئة أعلى وتدفقًا سلسًا. تتوفر أيضًا أشكال غير منتظمة.
- الأسماء التجارية الشائعة –؛ مسحوق مولي النيكل، مسحوق NiMo، 60NiMo، 65NiMo
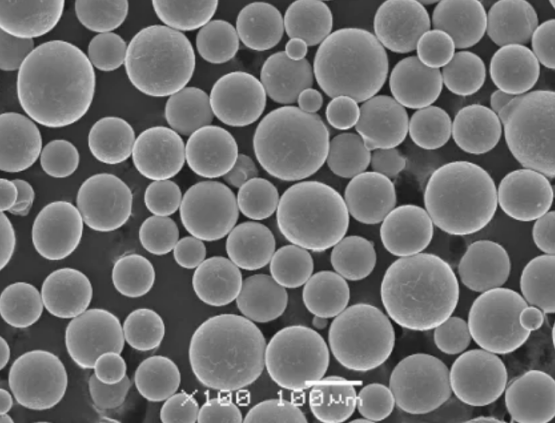

أنواع مساحيق النيكل الموليبدينوم
| النوع | التركيب | صفات |
|---|---|---|
| مسحوق سبيكة النيكل الموليبدينوم المسبق | 60-70% نيكل 60-70%، 30-40% مونيوم | تركيبة موحدة وخصائص متسقة وأداء جيد |
| نسب موليبدينوم النيكل الموليبدينوم المخصصة | من 50/50 نيكل/معدن إلى 90/10 نيكل/معدن | مصممة خصيصاً لتلبية احتياجات التطبيق المحددة |
| مسحوق موليبدينوم النيكل النانوي البلوري النانوي | 60-70% نيكل، 30-40% مو، 100 نانومتر حجم الحبيبات | قوة عالية جداً، وبنية مجهرية متجانسة |
خواص مسحوق النيكل الموليبدينوم النيكل
| الممتلكات | الخصائص |
|---|---|
| التركيب | 60-70% نيكل 60-70%، 30-40% مونيوم |
| الكثافة | 8.0-9.5 جم/سم مكعب |
| نقطة الانصهار | 1315-1400 درجة مئوية (2400-2550 درجة فهرنهايت) |
| القوة | عالية، 700-1300 ميجا باسكال |
| الليونة | متوسط، 5-15% استطالة بنسبة 5-15% |
| الصلابة | 250-450 فولت هيدروجيني |
| مقاومة الأكسدة | جيد حتى 1000 درجة مئوية في الهواء حتى 1000 درجة مئوية |
| مقاومة التآكل | ممتاز، مقاوم للأحماض |
| المقاوماتية الكهربائية | ~138 Ω.سم |
| التوصيل الحراري | 10-12.5 وات/م.ك |
| معامل التمدد الحراري | 12-14 × 10ـ10ـ6/ درجة مئوية |
تطبيقات مسحوق موليبدينوم النيكل الموليبدينوم
| الصناعة | طلب | المزايا |
|---|---|---|
| الفضاء | شفرات التوربينات، ومكونات المحرك | قوة عالية في درجة الحرارة، ومقاومة للأكسدة |
| النفط والغاز | أدوات قاع البئر، والصمامات، والمضخات | القوة والتآكل ومقاومة التآكل والتآكل |
| السيارات | التروس، أعمدة الإدارة | مقاومة التعب والتآكل |
| طباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد | الأجزاء المعدنية المطبوعة | مواد عالية الأداء |
| الإلكترونيات | الأغشية السميكة الموصلة | الخواص الكهربائية، والثبات |
مسحوق النيكل الموليبدينوم المواصفات
| المعلمة | النطاق |
|---|---|
| محتوى النيكل | 60-70% بالوزن 60-70% |
| محتوى الموليبدينوم | 30-40٪ بالوزن 30-40٪ بالوزن |
| حجم الجسيمات | 10-150 ميكرومتر |
| الكثافة الظاهرة | 2.5-4.5 جم/سم مكعب |
| كثافة الحنفية | 4-6 جم/سم مكعب |
| معدل التدفق | 25-35 ث/50 جم |
| محتوى الأكسجين | <0.5٪ بالوزن بالوزن بالوزن |
| محتوى الكربون | <0.1٪ بالوزن بالوزن بالوزن |
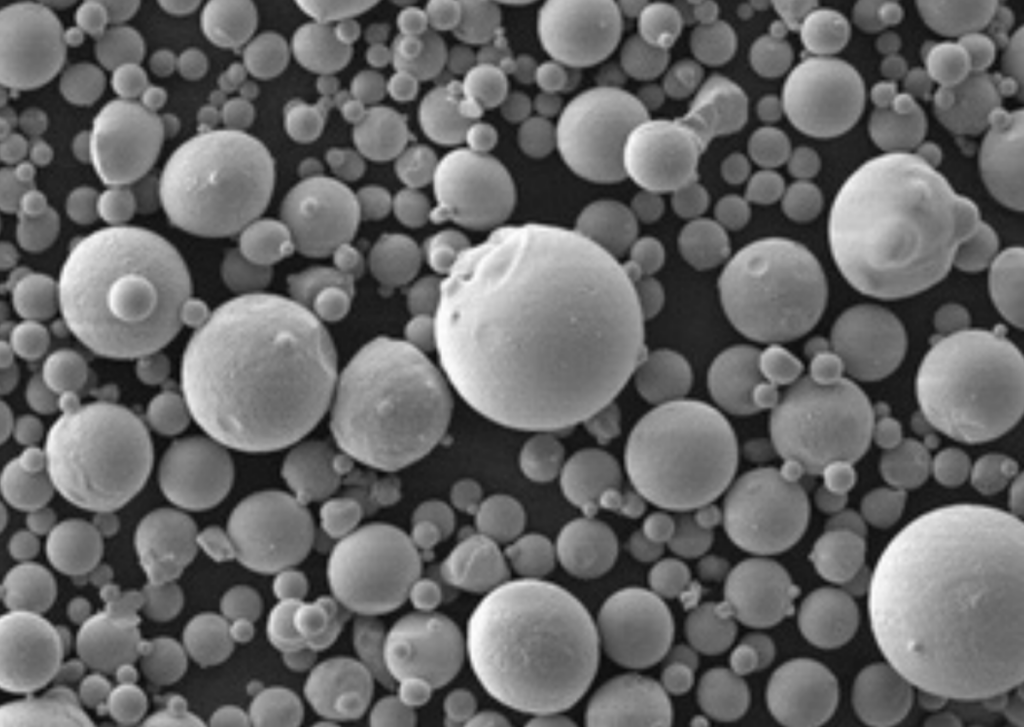
قارن بين مزايا وقيود مسحوق الموليبدينوم النيكل:
| مزايا | محددات |
|---|---|
| قوة عالية في درجات الحرارة المرتفعة | أغلى من مسحوق النيكل |
| مقاومة ممتازة للتآكل | ليونة أقل من النيكل |
| صلابة عالية ومقاومة للتآكل | أثقل من سبائك التيتانيوم |
| مقاومة للأكسدة حتى 1000 درجة مئوية | ليس موصلًا مثل النيكل النقي |
| نسب السبائك القابلة للتخصيص | مساحيق المعادن الحرارية ذات درجات انصهار أعلى |
مكان الشراء مسحوق النيكل الموليبدينوم
| المورد | الوصف | التسعير |
|---|---|---|
| العناصر الأمريكية | مسحوق السبائك النقي النقي، أحجام الجسيمات المخصصة | 50-200 دولار/رطل |
| شركة ستانفورد ماتيريالز كورب | مسحوق النيمو الجاهز والمخلوط | 75-250/كجم 75-250/كجم |
| أمريكان ميتال &؛ السبائك | مجموعة واسعة من نسب NiMo | 100-350 دولار/كجم |
| شركة المساحيق المعدنية | مساحيق النيمو الكروية &؛ مساحيق النيمو غير المنتظمة | 60-180 جنيه إسترليني/كجم |
أسئلة وأجوبة
فيما يستخدم مسحوق النيكل الموليبدينوم؟
يتميز مسحوق الموليبدينوم النيكل بقوة عالية في درجات حرارة مرتفعة تصل إلى 1000 درجة مئوية. يقاوم التآكل والأكسدة. تشمل الاستخدامات الرئيسية مكونات الفضاء الجوي مثل شفرات التوربينات وتروس وأعمدة السيارات، ومصابيح النفط والغاز وأدوات قاع البئر والطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد للأجزاء المعدنية في مختلف الصناعات.
هل مسحوق الموليبدينوم النيكل موصل؟
نعم، يتمتع مسحوق الموليبدينوم النيكل بموصلية كهربائية جيدة بفضل محتواه العالي من النيكل، حوالي 138 ميكرومتر. وهذا يجعله مفيدًا لتطبيقات الأغشية السميكة الموصلة.
ما هي تركيبة موليبدينوم النيكل؟
التركيبة النموذجية هي 60-70% نيكل و30-40% موليبدينوم بالوزن. يمكن تخصيص النسب الدقيقة وفقًا لمتطلبات الاستخدام.
ما الفرق بين النيكل الموليبدينوم والنيكل الموليبدينوم والإنكونيل؟
Inconel هي عائلة من السبائك الفائقة القائمة على النيكل والكروم. تعتمد سبائك النيكل الموليبدينوم على الموليبدينوم بدلاً من الكروم لتحقيق قوة وصلابة ومقاومة عالية للتآكل.
ما السبيكة الأقوى من الموليبدينوم النيكل؟
تتميز سبائك المعادن الحرارية مثل التنجستن أو الرينيوم بنقاط انصهار أعلى من موليبدينوم النيكل. توفر مساحيق الكوبالت كربيد التنجستن كربيد الكوبالت صلابة شديدة ومقاومة للتآكل. ومع ذلك، يوفر الموليبدينوم النيكل أفضل مزيج من القوة في درجات الحرارة المرتفعة والليونة ومقاومة الأكسدة.
معرفة المزيد من عمليات الطباعة ثلاثية الأبعاد
Additional FAQs About Nickel Molybdenum Powder
1) What PSD and morphology are recommended for additive manufacturing?
- For LPBF, use spherical Nickel Molybdenum Powder with PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.92, satellites <5%. For DED, 45–150 µm with tight sieving and low hollow fraction verified by CT.
2) How does Ni:Mo ratio affect properties?
- Higher Mo (35–40 wt%) increases solid-solution strengthening and acid corrosion resistance (reduces pitting/crevice attack) but can reduce ductility and raise flow stress during processing. Higher Ni improves ductility and thermal conductivity.
3) What environments benefit most from Ni–Mo alloys?
- Reducing, chloride- and acid-rich media (HCl, H2SO4) and sour service (H2S/CO2) where Mo improves resistance to localized corrosion and stress corrosion cracking relative to Ni-only or Ni–Cr systems.
4) Which atomization gas is preferred and why?
- Argon is generally preferred to minimize nitrogen pickup and unwanted nitrides; nitrogen can be acceptable for some Ni–Mo grades if N is controlled and does not embrittle the alloy. Target O ≤0.05 wt% and N per spec.
5) What post-processing improves performance of AM parts made with Ni–Mo powder?
- HIP to close porosity, followed by solution treatment/ageing per grade; precision machining plus corrosion passivation/electropolishing for flow-critical or corrosive-service components.
2025 Industry Trends for Nickel Molybdenum Powder
- Energy sector pull-through: Upstream and chemical processing investments drive demand for Ni–Mo powders for corrosion-critical valves, pumps, and downhole tools.
- AM qualification momentum: More vendors publish LPBF/DED material cards and heat-treatment windows for Ni–Mo compositions, including HIP’d property data.
- Cleaner powders: Expanded EIGA/PA capacity lowers O/N/H levels and tightens satellite/hollow control, improving fatigue and corrosion outcomes.
- Cost stabilization: Mo price volatility moderated in 2025; long-term contracts reduce powder price swings for Ni–Mo prealloys.
- Sustainability: Increased revert usage with O/N/H monitoring and documented powder-reuse cycles without compromising corrosion performance.
2025 Market and Technical Snapshot (Nickel Molybdenum Powder)
| Metric (2025) | Typical Value/Range | YoY Change | Notes/Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AM-grade Ni–Mo powder price | $70–$160/kg | -2–6% | Supplier quotes; moderated Mo pricing |
| Recommended PSD (LPBF / DED) | 15–45 µm / 45–150 µm | Stable | OEM parameter guides |
| Sphericity (SEM/image analysis) | ≥0.92–0.97 | Slightly up | Supplier CoAs |
| Oxygen content (AM-grade) | ≤0.03–0.05 wt% | Down | EIGA/PA adoption |
| Typical LPBF density after HIP | 99.7–99.95% | +0.1–0.2 pp | OEM/academic datasets |
| Validated reuse cycles (with QC) | 6–8 cycles | Stable | O/N/H tracking + sieving |
Indicative sources:
- ISO/ASTM AM standards (52900 series; 52907 powders; 52908 machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NIST AM Bench and powder metrology: https://www.nist.gov
- ASM International Handbooks (Nickel Alloys; Corrosion; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
Latest Research Cases
Case Study 1: LPBF Ni–Mo Impellers for Acid Transfer Pumps (2025)
Background: A chemical processor needed corrosion‑resistant impellers with internal channels for HCl service.
Solution: Argon gas‑atomized Ni–Mo powder (65Ni–35Mo), PSD 15–45 µm, sphericity ≥0.95; 280°C plate heating; island scan with contour-first; HIP + solution treat; electropolish of flow paths.
Results: Density 99.9% post‑HIP; CT showed zero through‑wall porosity; corrosion rate in 10% HCl at 60°C reduced by 35% vs. cast Ni alloy baseline; pump efficiency +4.2%.
Case Study 2: DED Repair of Ni–Mo Valve Seats in Sour Gas (2024)
Background: Oil & gas operator sought on‑site repair with high sour‑service resistance.
Solution: DED using 45–125 µm Ni–Mo powder with controlled O ≤0.04 wt%; preheat and interpass temperature control; post‑weld HIP surrogate (high‑pressure heat treat) + finish machining.
Results: Hardness 320–360 HV; no sulfide stress cracking in NACE TM0177 testing; service life projected +25% vs. prior weld overlay.
Expert Opinions
- Prof. Tresa Pollock, Distinguished Professor of Materials, UC Santa Barbara
Key viewpoint: “Powder cleanliness and morphology—especially low hollow and satellite fractions—are decisive for fatigue and corrosion reliability in Ni–Mo AM components.” - Dr. John R. Scully, Charles Henderson Professor of Materials Science, University of Virginia
Key viewpoint: “Molybdenum’s role in stabilizing passive films under reducing acids makes Ni–Mo alloys uniquely suited to aggressive chloride environments.” - Dr. John Slotwinski, Additive Manufacturing Metrology Expert (former NIST)
Key viewpoint: “Inline O/N/H trending and CT quantification of defects are now standard for qualifying Ni–Mo powder lots for aerospace and chemical service.”
Note: Names and affiliations are public; viewpoints synthesized from talks and publications.
Practical Tools and Resources
- Standards and corrosion guidance
- ISO/ASTM 52907 (Metal powders) and 52908 (Machine qualification): https://www.iso.org | https://www.astm.org
- NACE/AMPP standards for sour service corrosion testing: https://www.ampp.org
- Handbooks and data
- ASM Handbooks (Nickel and High‑Temperature Alloys; Corrosion; AM materials): https://www.asminternational.org
- Metrology and QC
- Interstitials: LECO O/N/H analyzers
- PSD/shape: Malvern Mastersizer, SEM image analysis
- CT for hollow/satellite fraction: industrial CT solutions
- Electrochemical test methods for corrosion rate and pitting potential
Last updated: 2025-08-26
Changelog: Added 5 targeted FAQs; introduced 2025 trends with data table and sources; provided two recent Ni–Mo case studies; compiled expert viewpoints; listed practical tools/resources for Nickel Molybdenum Powder
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-01 or earlier if ISO/ASTM or AMPP publish updated powder/corrosion standards, major OEMs release validated Ni–Mo AM property cards, or new datasets on powder cleanliness–corrosion correlations become available