لمحة عامة عن تشكيل الشبكات الهندسية بالليزر (LENS)
يُعد التشكيل الصافي بالليزر الهندسي بالليزر، والمعروف باسم LENS، تقنية تصنيع مضافة متقدمة تستخدم أشعة الليزر عالية الطاقة لإنشاء أجزاء معدنية معقدة وعالية الأداء. وعلى عكس طرق التصنيع التقليدية، تشتهر تقنية LENS بقدرتها على بناء هياكل ثلاثية الأبعاد مباشرةً من المساحيق المعدنية التي يتم صهرها وترسيبها طبقة تلو الأخرى.
إن تعدد استخدامات LENS يجعلها ذات قيمة خاصة في الصناعات التي تتطلب أجزاء معدنية معقدة ذات خصائص ميكانيكية فائقة، مثل قطاعات الطيران والدفاع والطب الحيوي. ولكن ما الذي يميز LENS بالضبط عن طرق التصنيع الأخرى؟ ولماذا يجب أن تفكر في استخدامها لمشروعك القادم؟ دعنا نتعمق أكثر في عالم LENS الرائع.

كيف تعمل LENS؟
تخيل أنك تقوم ببناء منحوتة، ولكن بدلاً من إزميل كتلة من الحجر، فإنك تضيف طبقة من المواد طبقة تلو الأخرى حتى يظهر الشكل المطلوب. هذا هو جوهر LENS. إليك تفصيل خطوة بخطوة:
- تركيز شعاع الليزر: يتم تركيز شعاع ليزر عالي الطاقة على ركيزة.
- حقن المسحوق المعدني: يتم حقن المسحوق المعدني في النقطة البؤرية لشعاع الليزر باستخدام فوهة توصيل المسحوق.
- الذوبان والتصلب: يقوم الليزر بإذابة المسحوق المعدني، وعندما يبرد، يتصلب ليشكل طبقة جديدة.
- بناء طبقة تلو الأخرى: تتكرر هذه العملية حيث يتم بناء الجزء طبقة بعد طبقة، باتباع تصميم تم إنشاؤه بواسطة الكمبيوتر.
مزايا LENS:
- الدقة: تستطيع LENS إنتاج أجزاء ذات أشكال هندسية معقدة وتفاصيل دقيقة.
- كفاءة المواد: نظرًا لأن المواد تضاف فقط عند الحاجة إليها، فإن النفايات تكون في حدها الأدنى.
- التخصيص: يمكن تخصيص الأجزاء على الفور، وهو أمر مثالي للنماذج الأولية والتصنيع حسب الطلب.
المواد المستخدمة في العدسة: المساحيق المعدنية
أحد الجوانب الأكثر إثارة في LENS هو المجموعة الواسعة من المساحيق المعدنية التي يمكن استخدامها. تم تصميم هذه المساحيق خصيصًا لعملية LENS، مما يضمن أداءً متسقًا ومنتجات نهائية عالية الجودة.
المساحيق المعدنية الشائعة المستخدمة في العدسات
| المسحوق المعدني | التركيب | التطبيقات | خصائص فريدة من نوعها |
|---|---|---|---|
| سبائك التيتانيوم (Ti-6Al-4V) | 90% التيتانيوم، 6% الألومنيوم، 4% الفاناديوم | صناعة الطيران، الغرسات الطبية الحيوية | نسبة عالية من القوة إلى الوزن ومقاومة التآكل |
| انكونيل 718 | النيكل، والكروم، والحديد | الفضاء الجوي، شفرات التوربينات | مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية والمتانة |
| فولاذ مقاوم للصدأ 316L | الحديد والكروم والنيكل والنيكل | الأجهزة الطبية، التطبيقات البحرية | مقاومة التآكل، والتوافق الحيوي |
| ألومنيوم 6061 | الألومنيوم والمغنيسيوم والسيليكون | السيارات، والفضاء، والفضاء | خفة الوزن وخصائص ميكانيكية جيدة |
| الكوبالت والكروم (CoCr) | الكوبالت، والكروم، والموليبدينوم | زراعة الأسنان، التوربينات الغازية | مقاومة التآكل، قوة عالية |
| فولاذ مصهور (18Ni300) | الحديد والنيكل والكوبالت والنيكل والكوبالت | الأدوات، الفضاء الجوي | قوة عالية للغاية ومعالجة حرارية سهلة |
| كربيد التنجستن (WC-Co) | التنجستن، الكوبالت | أدوات القطع، معدات التعدين | صلابة فائقة، مقاومة للتآكل |
| سبائك النحاس (CuCrZr) | نحاس، كروم، زركونيوم، نحاس، كروم، زركونيوم | المكونات الكهربائية، المبادلات الحرارية | موصلية حرارية ممتازة، وقوة |
| هاستيلوي إكس | النيكل، الموليبدينوم، الكروم | المعالجة الكيميائية، المحركات النفاثة | مقاومة الأكسدة، قوة عالية |
| فولاذ الأدوات (H13) | الحديد، والكربون، والكروم | القوالب، والقوالب، والأدوات | المتانة ومقاومة التآكل |
تركيبة المساحيق المعدنية الشائعة لعدسات العدسات
عند اختيار المسحوق المعدني لـ LENS، من الضروري فهم التركيب المحدد لكل مادة، حيث يؤثر ذلك بشكل مباشر على الخواص الميكانيكية ومدى ملاءمتها لمختلف التطبيقات.
التركيب التفصيلي للمساحيق المعدنية
| المسحوق المعدني | العناصر الأساسية | العناصر الإضافية | التطبيقات الشائعة |
|---|---|---|---|
| سبائك التيتانيوم (Ti-6Al-4V) | تيتانيوم (90%) | الألومنيوم (6%)، الفاناديوم (4%) | الطيران، الغرسات الطبية |
| انكونيل 718 | نيكل (50-55%) | الكروم (17-21%)، الحديد (5-9%) | التوربينات، المحركات النفاثة |
| فولاذ مقاوم للصدأ 316L | حديد (60-65%) | الكروم (16-18%)، النيكل (10-14%) | الأجهزة الطبية الحيوية والبحرية |
| ألومنيوم 6061 | ألومنيوم (97-98%) | المغنيسيوم (0.8 - 1.2%)، السيليكون (0.4 - 0.8%) | السيارات، والفضاء، والفضاء |
| الكوبالت والكروم (CoCr) | كوبالت (55-65%) | الكروم (26-30%)، الموليبدينوم (5-7%) | طب الأسنان، توربينات الغاز |
| فولاذ مصهور (18Ni300) | حديد (60-65%) | النيكل (18-20%)، الكوبالت (7-8%) | الأدوات، الفضاء الجوي |
| كربيد التنجستن (WC-Co) | تنجستن (85-90%) | كوبالت (6-10%) | أدوات القطع، التعدين |
| سبائك النحاس (CuCrZr) | نحاس (96-98%) | الكروم (0.5-1.5-1.2%)، الزركونيوم (0.1-0.2%) | الكهرباء، المبادلات الحرارية |
| هاستيلوي إكس | نيكل (47-52%) | الموليبدينوم (8-10%)، الكروم (20-23%) | الكيماويات، المحركات النفاثة |
| فولاذ الأدوات (H13) | حديد (85-90%) | الكربون (0.32-0.45%)، الكروم (4.75-5.5%) | القوالب، الأدوات |
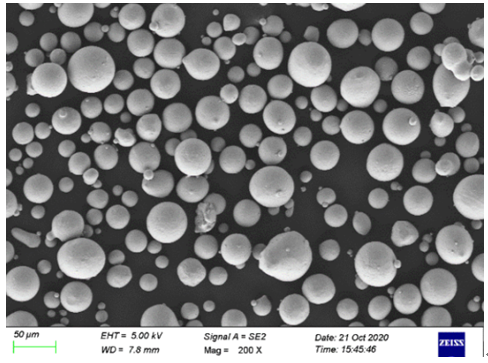
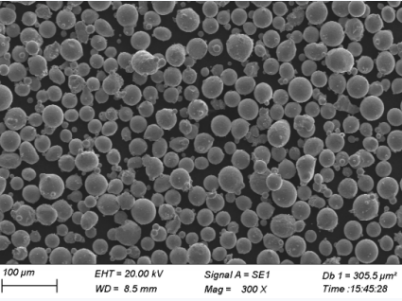
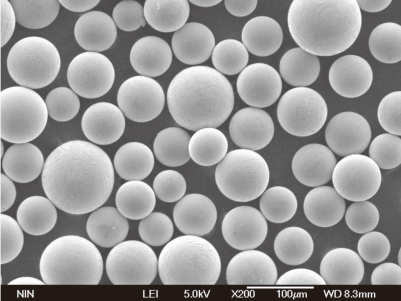



خصائص المكونات التي تنتجها LENS
تشتهر تقنية LENS بإنتاج أجزاء ذات خصائص فريدة تميزها عن تلك المصنوعة بالطرق التقليدية. دعونا نستكشف ما الذي يجعل هذه المكونات مميزة:
الخصائص الرئيسية لمكونات LENS
| الخصائص | الوصف | المزايا |
|---|---|---|
| دقة عالية | يمكن أن تنتج LENS قطعًا بتفاصيل معقدة وتفاوتات تفاوتات ضيقة. | مثالية للتصميمات المعقدة. |
| خصائص المواد المتفوقة | يمكن لعملية LENS تعزيز خصائص المواد، مثل القوة والمتانة. | أداء أفضل في التطبيقات الصعبة. |
| الحد الأدنى من المعالجة اللاحقة | غالبًا ما تتطلب أجزاء LENS معالجة لاحقة قليلة أو معدومة. | يقلل من وقت الإنتاج والتكاليف. |
| براعة في استخدام المواد | يمكن استخدام مجموعة كبيرة من المساحيق المعدنية في LENS. | المرونة في اختيار المادة المناسبة للوظيفة. |
| بناء طبقة تلو الأخرى | يتم بناء الأجزاء طبقة تلو الأخرى، مما يسمح بالتحكم الدقيق في الشكل النهائي. | التخصيص والضبط الدقيق للتصميمات. |
تطبيقات تقنية LENS
يتم اعتماد تقنية LENS في مختلف القطاعات نظرًا لقدراتها الفريدة. وفيما يلي جدول يسلط الضوء على التطبيقات الرئيسية لتقنية LENS في مختلف القطاعات:
التطبيقات الصناعية لتقنية LENS
| الصناعة | تطبيقات محددة | مزايا استخدام LENS |
|---|---|---|
| الفضاء | شفرات التوربينات، والمكونات الهيكلية، وإصلاح الأجزاء البالية | مكونات خفيفة الوزن وعالية المتانة وقابلة للإصلاح |
| الطبية | زراعة الأسنان حسب الطلب، تركيبات الأسنان الاصطناعية | المواد المتوافقة حيويًا والدقة والتخصيص |
| السيارات | المكونات خفيفة الوزن، النماذج الأولية، النماذج الأولية | النماذج الأولية السريعة وكفاءة المواد |
| الدفاع | مكونات الدروع، أنظمة الأسلحة، أنظمة الأسلحة | متانة محسّنة وأشكال هندسية معقدة |
| الطاقة | أجزاء التوربينات، والمبادلات الحرارية، وخلايا الوقود | مقاومة درجات الحرارة العالية، كفاءة المواد |
| الأدوات | القوالب، والقوالب، وأدوات القطع | المتانة، ومقاومة التآكل، وتقليل المهل الزمنية |
| النفط والغاز | أدوات قاع البئر، والصمامات، والمضخات | مقاومة التآكل، قوة المادة |
| الإلكترونيات | المشتتات الحرارية، والمكونات الموصلة | التوصيل الحراري، الهندسة الدقيقة |
| البحرية | أعمدة المروحة، وأجزاء الدفة، ومكونات المضخة | مقاومة التآكل والقوة |
| المعالجة الكيميائية | مكونات المفاعل، المبادلات الحرارية، المبادلات الحرارية | مقاومة التآكل، والأداء في درجات الحرارة العالية |
المواصفات والمقاسات والدرجات والمعايير في LENS
عند العمل باستخدام تقنية LENS، من المهم فهم المواصفات والأحجام والدرجات والمعايير المرتبطة بالمساحيق المعدنية والمكونات.
المواصفات والمعايير الخاصة بمواد العدسات
| المواد | المواصفات/الدرجة | قياسي | المقاسات النموذجية |
|---|---|---|---|
| سبائك التيتانيوم (Ti-6Al-4V) | ASTM F1472، الدرجة 5 | منظمة ASTM الدولية | المسحوق: 15-45 ميكرومتر |
| انكونيل 718 | AMS 5662، UNS N07718 | شركة SAE الدولية | المسحوق: 10-53 ميكرومتر |
| فولاذ مقاوم للصدأ 316L | A240STM A240، S31603 uns S31603 | منظمة ASTM الدولية | المسحوق: 10-45 ميكرومتر |
| ألومنيوم 6061 | A96061 A96061 ASTM B209، A96061 | منظمة ASTM الدولية | المسحوق: 15-63 ميكرومتر |
| الكوبالت والكروم (CoCr) | astm f75, uns r30075 | منظمة ASTM الدولية | المسحوق: 15-45 ميكرومتر |
| فولاذ مصهور (18Ni300) | AMS 6514، UNS K93120 | شركة SAE الدولية | المسحوق: 10-45 ميكرومتر |
| كربيد التنجستن (WC-Co) | ISO 9001:2008 | معايير الأيزو | المسحوق: 20-70 ميكرومتر |
| سبائك النحاس (CuCrZr) | أستم B422، وSNSS C18150 | منظمة ASTM الدولية | المسحوق: 10-45 ميكرومتر |
| هاستيلوي إكس | AMS 5754، UNS N06002 | شركة SAE الدولية | المسحوق: 15-53 ميكرومتر |
| فولاذ الأدوات (H13) | A681STM A681, uns t20813 | منظمة ASTM الدولية | المسحوق: 10-45 ميكرومتر |
مزايا وقيود عدسة LENS
تقدم تقنية LENS العديد من الفوائد، ولكن من المهم أيضًا إدراك حدودها. إليك مقارنة:
مزايا مقابل قيود عدسة LENS
| مزايا | محددات |
|---|---|
| دقة عالية | التكلفة: يمكن أن تكون العدسات مكلفة بسبب المعدات والمواد المستخدمة. |
| كفاءة المواد | التعقيد: العملية معقدة تقنيًا وتتطلب مشغلين مهرة. |
| التخصيص | تشطيب السطح: قد تتطلب القِطع معالجة إضافية بعد المعالجة لتحقيق تشطيب السطح المطلوب. |
| مجموعة واسعة من المواد | تحديد الحجم: تقتصر LENS عادةً على الأجزاء الأصغر حجمًا بسبب طبيعة العملية. |
| قابلية الإصلاح | السرعة: يمكن أن تكون LENS أبطأ مقارنة بطرق التصنيع الأخرى للإنتاج على نطاق واسع. |
| خواص ميكانيكية محسّنة | الإعداد الأولي: يمكن أن تشكل تكاليف الإعداد الأولية المرتفعة عائقاً أمام الشركات الصغيرة. |
مقارنة بين LENS وتقنيات التصنيع المضافة الأخرى
غالبًا ما تتم مقارنة LENS بطرق التصنيع المضافة الأخرى مثل التلبيد المباشر للمعادن بالليزر (DMLS) والذوبان الانتقائي بالليزر (SLM). دعونا نفصل الاختلافات:
عدسة LENS مقابل طرق التصنيع المضافة الأخرى
| الميزة | العدسة | DMLS | SLM |
|---|---|---|---|
| نطاق المواد | مجموعة واسعة، بما في ذلك السبائك عالية الأداء | المعادن في المقام الأول، عدد أقل من المواد الغريبة | نطاق واسع، على غرار LENS |
| الدقة | عالية، مع إمكانية الحصول على تفاصيل دقيقة | عالية جداً، مثالية للتصاميم المعقدة | مرتفع، يضاهي LENS |
| التكلفة | إعداد مكلف وفعال من حيث التكلفة للأجزاء عالية القيمة | باهظة الثمن إلى حد ما | على غرار LENS، حسب المادة |
| السرعة | معتدل، مناسب للأجزاء المعقدة | أسرع بشكل عام للأجزاء الأصغر حجمًا | أسرع من LENS لتطبيقات معينة |
| المعالجة اللاحقة | الحد الأدنى المطلوب | يلزم إجراء بعض المعالجة اللاحقة | يتطلب معالجة لاحقة كبيرة بعد المعالجة |
| التطبيقات | الفضاء، والفضاء، والطب، والأدوات | الفضاء والسيارات والطب والفضاء | الفضاء والطيران والطب والصناعة |
الموردون وتفاصيل تسعير مواد العدسة LENS
إن فهم مصدر مواد LENS والتكاليف المرتبطة بها أمر بالغ الأهمية لوضع الميزانية والتخطيط لمشاريعك.
الموردون وأسعار مواد العدسات
| المواد | المورد | السعر التقريبي للكيلوغرام الواحد |
|---|---|---|
| سبائك التيتانيوم (Ti-6Al-4V) | كاربنتر تكنولوجي، أورليكون AM | $300 – $500 |
| انكونيل 718 | براكسير للتقنيات السطحية، ساندفيك | $150 – $300 |
| فولاذ مقاوم للصدأ 316L | ساندفيك، كاربنتر تكنولوجي | $50 – $100 |
| ألومنيوم 6061 | أورليكون إيه إم، إل بي دبليو تكنولوجي | $30 – $60 |
| الكوبالت والكروم (CoCr) | أركام AB، ساندفيك | $400 – $600 |
| فولاذ مصهور (18Ni300) | LPW Technology, EOS GmbH | $200 – $350 |
| كربيد التنجستن (WC-Co) | إتش سي ستارك، التنجستن والمساحيق العالمية | $500 – $700 |
| سبائك النحاس (CuCrZr) | ساندفيك، براكسير للتكنولوجيا السطحية | $100 – $200 |
| هاستيلوي إكس | كاربنتر تكنولوجي، تقنية LPW | $300 – $500 |
| فولاذ الأدوات (H13) | EOS GmbH، LPW Technology | $50 – $100 |
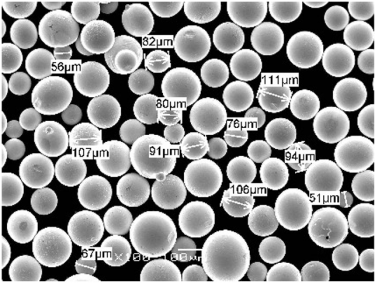
التعليمات
| سؤال | الإجابة |
|---|---|
| فيمَ تُستخدم LENS؟ | تُستخدم LENS لتصنيع قطع معدنية عالية الأداء، وإصلاح المكونات البالية، وإنشاء نماذج أولية. |
| كيف تختلف LENS عن التصنيع التقليدي؟ | تقوم LENS ببناء الأجزاء طبقة تلو الأخرى من المسحوق المعدني، مما يوفر دقة وكفاءة مادية أكبر مقارنة بالطرق التقليدية. |
| ما هي المواد التي يمكن استخدامها في LENS؟ | يمكن استخدام مجموعة واسعة من المساحيق المعدنية، بما في ذلك سبائك التيتانيوم والفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ والألومنيوم والسبائك الفائقة القائمة على النيكل. |
| هل عدسة LENS فعالة من حيث التكلفة؟ | يمكن أن تكون LENS فعالة من حيث التكلفة بالنسبة للأجزاء المعقدة عالية القيمة، ولكنها قد تكون مكلفة بالنسبة للإنتاج البسيط واسع النطاق. |
| ما هي الصناعات الأكثر استفادة من LENS؟ | تستفيد صناعات الطيران والفضاء والطب والسيارات والدفاع بشكل كبير من الدقة والتخصيص اللذين توفرهما LENS. |
| هل هناك أي قيود على الحجم مع LENS؟ | نعم، عادةً ما تكون LENS أكثر ملاءمة للأجزاء الأصغر حجمًا، على الرغم من أن التقدم في التكنولوجيا يوسع من قدراتها. |
| كيف يمكن مقارنة LENS بطرق التصنيع المضافة الأخرى؟ | توفر LENS خصائص مواد فائقة وتخصيصًا فائقًا ولكنها قد تكون أبطأ وأكثر تكلفة من طرق مثل DMLS أو SLM. |
| ما هي التحديات الرئيسية مع LENS؟ | يعد ارتفاع تكاليف الإعداد الأولي والتعقيد التقني والحاجة إلى مشغلين مهرة من التحديات الشائعة. |
| هل يمكن استخدام LENS للإنتاج بكميات كبيرة؟ | على الرغم من أن LENS مثالية للقطع المتخصصة عالية القيمة، إلا أنها لا تُستخدم عمومًا للإنتاج بكميات كبيرة نظرًا لسرعتها البطيئة وتكلفتها العالية. |
| ما هي المعالجة اللاحقة المطلوبة لأجزاء LENS؟ | تتطلب أجزاء LENS عادةً الحد الأدنى من المعالجة اللاحقة، على الرغم من أنه قد تكون هناك حاجة إلى تشطيب السطح حسب الاستخدام. |

